Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Importancia Nutrimental
Cargado por
Vera Garcia EmmanuelDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Importancia Nutrimental
Cargado por
Vera Garcia EmmanuelCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
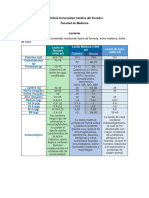
IMPACTO NUTRIMENTAL, ABSORCIÓN Y METABOLISMO
Leche y Salud
IMPORTANCIA NUTRIMENTAL
Es un alimento básico en la alimentación humana en
todas las etapas de la vida ya que proporciona un
elevado contenido de nutrientes en relación con su
contenido calórico.
PRESENTES
CONTENIDO GRASO
Combustible energético de reserva
70% ácidos grasos saturados
96-98%
triglicéridos Efectos cardioprotectores
30% ácidos grasos insaturados
Inmunomoduladores
Anticancerígenos
Ácido linoleico conjugado
Hipolipemiantes
PROTEINAS VITAMINAS Y MINERALES
Vitamina B12
Constituye al 3.5%
Vitamina B5
del valor total.
Ácido fólico
La caseína forma el 80%
de las pretinas totales. Calcio
α, β y K caseína Potasio
Magnesio
Nutrientes que favorecen en el desarrollo tanto a niños como a adultos.
AGUA
Es uno de los componentes
más abundantes de la leche.
Contribuye a mantener
los niveles de hidratación.
LACTOSA
Hidrato de carbono mayoritario de la leche.
Importante función energética.
5%
lactosa
Facilita la absorción de calcio.
INTOLERANCIA A LA LACTOSA ALERGIA A LA PROTEÍNA DE LA LECHE
Cuadro clínico caracterizado por:
Reacciones de hipersensibilidad iniciadas por un
dolor
náuseas flatulencias diarrea mecanismo inmunitario específico contra estas
abdominal
proteínas, manifestando síntomas:
Respiratorios
Cutáneos
Gastrointestinales
Ocasionados por la ingestión de lactosa, debido a
Sistémicos
la inexistencia parcial o total de la enzima lactasa
en la mucosa intestinal.
TRATAMIENTOS
No todos los productos lácteos son 100% libres de lactosa, las
empresas que se dedican a la producción y comercialización de
leche con la lactosa hidrolizada,comercialmente: leche deslactosada.
Los consumidores no presentan ninguna sintomatología
Fórmulas
variedad de alternativas según sus necesidades, bolsillos y
hidrolizadas
preferencias.
BIBLIOGRAFÍA
AGUDELO GÓMEZ, D. A., & Bedoya Mejía, O. Nutritional composition of milk from cattle. 2019. Lasallian Research, p. 38-42.
FERNANDEZ FERNANDEZ, Elena, et al. Consensus document: nutritional and metabolic importance of milk. Hospital Nutrition, 2015, vol. 31, not 1, p.
92-101.
GONZÁLES HERNANDEZ, Norma, et al. Part 1: Allergy to Cow's Milk Protein , 2016, Vol. 7, No. 1, p. 587-588.
ROSADO, Jorge L. Lactose intolerance. Gac. Med. Mex, 2016, vol. 152, p. 67-73.
USCANGA-DOMINGUEZ, L.F., et al. Technical position about milk and dairy derivatives in the health and disease of the adult of the Mexican
Association of Gastroenterology and the Mexican Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics. Journal of Gastroenterology of Mexico, 2019, vol.
84, no. 3, p. 357-371.
NUTRIMENTAL IMPACT, ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM
Milk and health
NUTRITIONAL IMPORTANCE
It is a staple food in human food at all stages of life as it
provides a high nutrient content in relation to its caloric
content.
PRESENT
FAT
Reserve energy fuel
70% saturated fatty acids
96-98%
Triglycerides Cardioprotective effects
30% unsaturated fatty acids
Immunomodulatory effects
Anticancer effects
conjugated linoleic acid
hypolipidizing effects
PROTEIN VITAMINS AND MINERALS
Vitamin B12
constitutes the 3.5%
Vitamin B5
the total value
Folic Acid
Casein forms 80% of the
total waistbands. Calcium
α, β y K casein Potassium
Magnesium
Nutrients that favor the development of both children and adults.
WATER
It is one of the most abundant
components of milk.
Contributes to maintaining
hydration levels.
LACTOSE
Majority carbohydrate from milk.
It has an important energy function.
5%
lactose
Lactose facilitates calcium absorption.
LACTOSE INTOLERANCE ALLERGY TO COW'S MILK PROTEIN
Condition characterized by:
Hypersensitivity reactions initiated by a specific
abdominal
nausea flatulence diarrhea immune mechanism against these proteins, manifesting
pain
the following types of symptoms:
Respiratory
Cutaneous
Gastrointestinal
Caused by ingestion of lactose, due to the partial
Systemic
or total absence of the enzyme lactase in the
intestinal mucosa.
TREATMENTS
Not all dairy products are 100% lactose-free,
companies engaged in the production and marketing
of milk with hydrolyzed lactose, commercially:
desctated milk.
Formulas
Consumers have no symptomatology variety of Formulas
alternatives according to your needs, pockets and Hydrolyzed
preferences.
REFERENCES
AGUDELO GÓMEZ, D. A., & Bedoya Mejía, O. Nutritional composition of milk from cattle. 2019. Lasallian Research, p. 38-42.
FERNANDEZ FERNANDEZ, Elena, et al. Consensus document: nutritional and metabolic importance of milk. Hospital Nutrition, 2015, vol. 31, not 1, p.
92-101.
GONZÁLES HERNANDEZ, Norma, et al. Part 1: Allergy to Cow's Milk Protein , 2016, Vol. 7, No. 1, p. 587-588.
ROSADO, Jorge L. Lactose intolerance. Gac. Med. Mex, 2016, vol. 152, p. 67-73.
USCANGA-DOMINGUEZ, L.F., et al. Technical position about milk and dairy derivatives in the health and disease of the adult of the Mexican
Association of Gastroenterology and the Mexican Association of Gerontology and Geriatrics. Journal of Gastroenterology of Mexico, 2019, vol. 84,
no. 3, p. 357-371.
También podría gustarte
- Tipos de DietaDocumento5 páginasTipos de DietaFer HrdzAún no hay calificaciones
- SUPLEMENTOS ALIMENTICIOS TurnoV PDFDocumento25 páginasSUPLEMENTOS ALIMENTICIOS TurnoV PDFMateo GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fórmulas InfantilesDocumento72 páginasFórmulas InfantilesMaría Manuela BarreiroAún no hay calificaciones
- Libro de ReforzamientoDocumento233 páginasLibro de ReforzamientoProfesora Gabriela ZepedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Composicion de La Leche MaternaDocumento29 páginasComposicion de La Leche MaternaFátimaAún no hay calificaciones
- FORMULAS INFANTILES PWR 2020Documento84 páginasFORMULAS INFANTILES PWR 2020MarAún no hay calificaciones
- 188.forever B12 PlusDocumento1 página188.forever B12 PlusKt ValeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Helado CaseroDocumento3 páginasHelado CaseroAlvaro Pastrana LosadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Infografía Fórmulas LácteasDocumento7 páginasInfografía Fórmulas LácteasDoris Vilca ÑaupaAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Formulas PediatricasDocumento11 páginas2 Formulas Pediatricasnando.nic19Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ud 2 T1 PDFDocumento24 páginasUd 2 T1 PDFRomina VargasAún no hay calificaciones
- Leches y Productos LácteosDocumento13 páginasLeches y Productos Lácteosclaudia graichtAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarjeton Caseinato WEBDocumento1 páginaTarjeton Caseinato WEBmanyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Valor Nutitivo de Los Productos Lacteos Equipo 2Documento27 páginasValor Nutitivo de Los Productos Lacteos Equipo 2Brenda Deméneghi LópezAún no hay calificaciones
- Leche y Derivados LacteosDocumento14 páginasLeche y Derivados Lacteoslupita martinezAún no hay calificaciones
- LecheDocumento27 páginasLecheDennis LimaymantaAún no hay calificaciones
- Vademecum. Interactivopdf-ComprimidoDocumento54 páginasVademecum. Interactivopdf-ComprimidoSkarleth Torres BeltránAún no hay calificaciones
- Método RV. Los Secretos de La Programación. PowerliftingDocumento2 páginasMétodo RV. Los Secretos de La Programación. PowerliftingBaltta AlasaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lactancia MaternaDocumento40 páginasLactancia MaternaAriel VargasAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Biología # 3 Trabajo Investigación CientificaDocumento6 páginasTrabajo Biología # 3 Trabajo Investigación CientificamerlyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lactancia MaternaDocumento47 páginasLactancia MaternaKarina Marilú SarangoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 1.1 Lactancia HumanaDocumento7 páginasTema 1.1 Lactancia HumanaRobelizthAún no hay calificaciones
- Bioquímica Grupo 6Documento33 páginasBioquímica Grupo 6Carmen Ana Velez CedenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadro Comparativo - Fórmulas NutricionalesDocumento11 páginasCuadro Comparativo - Fórmulas Nutricionaleslalo rgAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadro Comparativo NutricionalDocumento3 páginasCuadro Comparativo NutricionalSophiAún no hay calificaciones
- Lactancia MaternaDocumento42 páginasLactancia MaternaGLORIA ESTEFANIA BECERRA DE DIOSAún no hay calificaciones
- Bioquimica Lacteos 2021Documento93 páginasBioquimica Lacteos 2021ROCIO MILENKA QUISPE PARICAGUAAún no hay calificaciones
- Aminovit-Plus SC ESDocumento2 páginasAminovit-Plus SC ESFran A.mAún no hay calificaciones
- Evidencia Cuadro ComparativoDocumento1 páginaEvidencia Cuadro ComparativoJose QuinteroAún no hay calificaciones
- Lactologia Jessica FDocumento3 páginasLactologia Jessica FJessica FuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- NutracéuticoDocumento16 páginasNutracéuticoKaren RomeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Componentes Leche MaternaDocumento28 páginasComponentes Leche MaternaLaura BonillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminario Alimentacion Al Seno Materno 2Documento49 páginasSeminario Alimentacion Al Seno Materno 2DannyMichelle100% (1)
- Las Propiedades de La LecheDocumento4 páginasLas Propiedades de La LechepetuniascakeredesAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion 8 Lactancia MaternaDocumento29 páginasSesion 8 Lactancia MaternaYANELI YOSALIN MERCADO VALENCIA100% (1)
- DairyPilot Saleshelper ESDocumento1 páginaDairyPilot Saleshelper EScesarAún no hay calificaciones
- Evidencia 2. Documento, Conceptualización y Clasificación de AlimentosDocumento5 páginasEvidencia 2. Documento, Conceptualización y Clasificación de AlimentosjimenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual Dietas Veterinarias Disugual - Icono PetDocumento35 páginasManual Dietas Veterinarias Disugual - Icono PetPAULA MILENA LESMES BUSTOSAún no hay calificaciones
- #1 Guia de Ciencias Naturales Segundo PeriodoDocumento4 páginas#1 Guia de Ciencias Naturales Segundo PeriodoMaría Cecilia Montes TuiranAún no hay calificaciones
- Componentes Quimicos de La LecheDocumento2 páginasComponentes Quimicos de La LecheLuis WalterAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutricion Enteral en El Paciente QuemadoDocumento7 páginasNutricion Enteral en El Paciente QuemadoGiordan SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Qué Es La Caseína MicelarDocumento2 páginasQué Es La Caseína MicelarLuis Castro XtrmAún no hay calificaciones
- Proceso Digestivo Según El Plato Del Buen ComerDocumento5 páginasProceso Digestivo Según El Plato Del Buen ComerNOVELO CHULIM CRISTIAN ANTONIOAún no hay calificaciones
- DIETA HIPOCALÓRICA Fin TotalDocumento8 páginasDIETA HIPOCALÓRICA Fin TotalDuende ArrechoAún no hay calificaciones
- Lactancia Materna y AblactanciaDocumento5 páginasLactancia Materna y AblactanciajessicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Top One Brochure 2022Documento22 páginasTop One Brochure 2022Abner Estiven Vargas DukeAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutrina - FTDocumento20 páginasNutrina - FTYaretzi MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Leche y DerivadosDocumento50 páginasLeche y Derivadoskatherine.jimenez5276Aún no hay calificaciones
- Acidos Grados Omega 3 & 6 en El Embarazo y LactanciaDocumento14 páginasAcidos Grados Omega 3 & 6 en El Embarazo y LactanciaLAURA NATALIA TORRES IGUAAún no hay calificaciones
- Bromatologia en LecheDocumento14 páginasBromatologia en LecheMicaela Di BernardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion 8 Lactancia MaternaDocumento28 páginasSesion 8 Lactancia MaternaKARLITA YERELI RODRIGUEZ GOMEZAún no hay calificaciones
- Valor Nutricional de La LecheDocumento8 páginasValor Nutricional de La LecheOscar Samuel Bendezu CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Lactancia MaternaDocumento2 páginasLactancia MaternaSara Lucía MartínezAún no hay calificaciones
- Lácteos y Derivos 2Documento37 páginasLácteos y Derivos 2alejatefa70Aún no hay calificaciones
- DietaDocumento3 páginasDietaSuheila JaidarAún no hay calificaciones
- Al163a PDFDocumento3 páginasAl163a PDFAlba De la rosaAún no hay calificaciones
- 9 LácteosDocumento41 páginas9 Lácteoslucia mejiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tipos de Leche Por El Sistema de HigienizaciónDocumento7 páginasTipos de Leche Por El Sistema de HigienizaciónCristhian Tasayco100% (1)
- Resumen de Unidad Didáctica N02Documento4 páginasResumen de Unidad Didáctica N02Rocio tavara cumpaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grasas Sobrepasantes en RumiantesDocumento12 páginasGrasas Sobrepasantes en RumiantesCatalina GarzonAún no hay calificaciones
- Ensayo BiologiaDocumento4 páginasEnsayo BiologiaBenjamin ÁlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cotización Moly-Cop Adesur S.A.Documento1 páginaCotización Moly-Cop Adesur S.A.Giancarlo Tapia RondonAún no hay calificaciones
- Dieta para Vivir Mas de 100 AñosDocumento2 páginasDieta para Vivir Mas de 100 AñosAdministración LecvenAún no hay calificaciones
- Conocemos Las Vocales OoDocumento20 páginasConocemos Las Vocales OokatherinccAún no hay calificaciones
- Historia de CumanáDocumento7 páginasHistoria de CumanáLewis BermudezAún no hay calificaciones
- Nutrilac Del OrienteDocumento12 páginasNutrilac Del Orienterina pinoAún no hay calificaciones
- PseudorumiantesDocumento1 páginaPseudorumiantesLola MentoAún no hay calificaciones
- TomaTratamiento 20BDocumento73 páginasTomaTratamiento 20BAriana Rivera ZavalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aciclovir - Búsqueda de GoogleDocumento1 páginaAciclovir - Búsqueda de GoogleAlejandro CorzoAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminario Bachillerato - 230610 - 200744Documento49 páginasSeminario Bachillerato - 230610 - 200744Anner MaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- PDF Elaboracion Artesanal de Vino de Frutas CompressDocumento84 páginasPDF Elaboracion Artesanal de Vino de Frutas Compressyaoa1995Aún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis Microbiológico de AlimentosDocumento16 páginasAnálisis Microbiológico de AlimentosSophia AlvarengaAún no hay calificaciones
- Conta Vi-2022 Un Centro Un Producto Mundial IndonesiaDocumento2 páginasConta Vi-2022 Un Centro Un Producto Mundial IndonesiasaraAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 - Calculo de Pérdidas o Mermas Proceso de SecadoDocumento19 páginas2 - Calculo de Pérdidas o Mermas Proceso de SecadoPablo Alejandro Diaz SotoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 2 de Plan de Alimentaciòn Pollos de EngordeDocumento5 páginasTaller 2 de Plan de Alimentaciòn Pollos de EngordeAlex PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Dietas DisfagiaDocumento16 páginasDietas DisfagiaMiguel Ángel González BlázquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tres Niveles de Un ProductoDocumento11 páginasTres Niveles de Un ProductoDanielaAún no hay calificaciones
- Menu ToddlerDocumento9 páginasMenu Toddlerj luis duarteAún no hay calificaciones
- Maiz AmilaceoDocumento27 páginasMaiz AmilaceoSergio AntonyAún no hay calificaciones
- Oleatos de Hierbas o FloresDocumento5 páginasOleatos de Hierbas o FloresAnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bitacora Del Estudiante Paralelo IDocumento2 páginasBitacora Del Estudiante Paralelo ICalos Antonio Valero Cano0% (1)
- Etiqueta de Aji Pa Tu CaldoDocumento3 páginasEtiqueta de Aji Pa Tu CaldoCristofer EspinozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Instructivo de Proceso Filete N°2 2023Documento8 páginasInstructivo de Proceso Filete N°2 2023Joselyn MolinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Gomitas Cabello Piel Uñas Nature's Bounty Biotina 80ct Envío GratisDocumento1 páginaGomitas Cabello Piel Uñas Nature's Bounty Biotina 80ct Envío Gratisesmeralda mendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Enteral Clasificación-ComplicacionesDocumento27 páginasEnteral Clasificación-Complicacioneskatherine palma catalanAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.viticultura SueloDocumento4 páginas2.viticultura SueloLuis Oscar GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Néctar Mango Proteinizado ConservaciónDocumento17 páginasNéctar Mango Proteinizado ConservaciónYamileysis Cordero ConcepciónAún no hay calificaciones
- Precios Mayor Lista 28082021Documento10 páginasPrecios Mayor Lista 28082021Carla Diaz MontoyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 4 Espumantes y Otros VinosDocumento33 páginasUnidad 4 Espumantes y Otros VinosmarcosnemeAún no hay calificaciones