Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Writing Informative or Explanatory Texts English Infographic in Colorful Pastel Doodle Style
Cargado por
Valentina Duarte GamboaDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Writing Informative or Explanatory Texts English Infographic in Colorful Pastel Doodle Style
Cargado por
Valentina Duarte GamboaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
ÉTICA EN LA
INVESTIGACIÓN
DEFINICIÓN:
La ética nos brinda un marco de referencia para examinar críticamente
nuestras decisiones y comportamientos, ayudándonos a reflexionar y
cuestionar las razones que tenemos para hacer algo.
TRES MOMENTOS CLAVES:
Finalidad de la investigación:
1. Debe ser clara y sin
ambigüedades
Medios y metodos de la
investigación:
2. -Coherencia entre métodos
-Medios legitimos
En la comunicación:
-Comunicación clara de resultados
3. de investigación
-Respeto a la confidencialidad de la
información.
-Solidaridad -Autonomia -Parcialidad en la
-Libertad -Beneficio evaluación
-Respeto -Justicia -Manipulación de datos
-Dialogo -No maleficiencia -Corrupción
-Igualdad -plagio
ETICA EN LA INVESTIGACION CON HUMANOS
INVESTIGACIÓN INVESTIGACIÓN
BIOMÉDICA PSICOLÓGICA Y SOCIAL
PRINCIPIOS DE LA PRINCIPIOS
BIOÉTICA PSICOSOCIALES
1.Autonomia 1.Autonomia
2. Beneficencia 2. Consentimiento
3.No maleficencia informado
4.Justicia 3.Privacidad y
confidencialidad
4.Riesgo- Beneficio
PROBLEMAS ÉTICOS EN LA TRANSFERENCIA DE CONOCIMIENTO
Dilemas y cuestiones relacionadas con la
Conflicto de intereses
manera en que se comparte, utiliza y aplica el
Fuentes y medios de financiación
conocimiento entre diferentes entidades, ya
Propiedad de los resultados de
sean individuos, organizaciones o sociedades
investigación y copyright
en general.
Writing
INFORMATIVE or
EXPLANATORY
Texts
definition
Informative or explanatory writing seeks to accurately
convey information to a reader with a primary purpose to
increase knowledge, help them better understand a
procedure or process, or to enhance their comprehension of
a concept.
types
The informative or explanatory genre covers a range of text
types such as such as autobiography and biography, literary
analysis, explanatory essays, summaries, scientific or
historical reports, scholarly articles and many more.
accuracy specificity clarity
As you are sharing Vague, broad or As a writer, you
knowledge, you general statements won’t always know
need to ensure the suggest that you exactly who is
information given haven't put in the reading your piece
is correct, factual, time or effort to so assume your
well-researched research properly. audience are
and referenced. As It's fine to start educated
a writer you should with general nonspecialists who
appear questions such as are new to the
trustworthy and who, what, where topic. The clearer
well-informed by and when but you are, the more
establishing a ensure you delve likely it is you will
sense of authority into the why and achieve your
and expertise over how and look for purpose of passing
your topic. interesting details. on knowledge to
the reader.
style, tone & formality
You should aim to write formally and objectively using
impersonal and precise language and delivering information in
a straightforward manner without sharing personal opinions.
You should also use appropriate transition words to link ideas
or topics. Avoid things like slang and colloquial phrases, low
modality language, contractions and first person pronouns.
evidence
When researching you'll want to locate as many primary
sources as possible as they are more credible when used as
evidence but it's okay to combine them with secondary
sources as these draw on existing research allowing you
access to other authors' interpretations. The two types
complement each other to help you convey a well-rounded
and convincing text.
También podría gustarte
- La Intención de Los Textos OralesDocumento14 páginasLa Intención de Los Textos OralesDavid Ravelo FiscalAún no hay calificaciones
- Persuasión IIsemDocumento1 páginaPersuasión IIsemAlanís Nazareth Álvarez GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- TG2 - Busqueda de EvidenciaDocumento20 páginasTG2 - Busqueda de EvidenciaDavid SaltosAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 2 MetodoDocumento14 páginasCapitulo 2 Metodopaty781Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cuál Es La Finalidad de La InvestigaciónDocumento9 páginasCuál Es La Finalidad de La InvestigaciónJoseph228Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadro Comparativo (Mark Castillo)Documento3 páginasCuadro Comparativo (Mark Castillo)Mark CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- CANVA Proof II-AYusNnftPN5oDocumento2 páginasCANVA Proof II-AYusNnftPN5oEaduardo AcostaAún no hay calificaciones
- Revisión BibliograficaDocumento4 páginasRevisión BibliograficaclauAún no hay calificaciones
- La InformacionDocumento8 páginasLa InformacionDavid 8Aún no hay calificaciones
- Presentación Diapositiva Hasta Diap 51Documento51 páginasPresentación Diapositiva Hasta Diap 51Andrea LozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Juan Quispe Huamani MetodologiaDocumento5 páginasJuan Quispe Huamani Metodologia03-DE-LI-MARIA CLEDY CORDOVA GUERREROAún no hay calificaciones
- CLASE 1 - Clase Etica en InvestigacionDocumento32 páginasCLASE 1 - Clase Etica en InvestigacionKenny TurpoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller de Aprendizaje MetodologiaDocumento2 páginasTaller de Aprendizaje MetodologiaWilliam Camilo Angulo JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 3 Tecnicas de InvestigaciónDocumento6 páginasUnidad 3 Tecnicas de Investigaciónelio jose marquez tomeAún no hay calificaciones
- Entrevista EstructuradaDocumento7 páginasEntrevista EstructuradaAdriana BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Not FinalesDocumento4 páginasNot FinalesAnna Paola Cervantes RicoAún no hay calificaciones
- Técnicas y Herramientas de InvestigaciónDocumento7 páginasTécnicas y Herramientas de InvestigaciónWillerth ArancibiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 3Documento7 páginasSemana 3FRANS JOSEP TUANAMA CHAVEZAún no hay calificaciones
- Técnica de Grupos Focales. Fernando Hernandez HernandezDocumento2 páginasTécnica de Grupos Focales. Fernando Hernandez HernandezFeer HdezAún no hay calificaciones
- Carol Vera Ti m3 Analisis Cuantitativo y Cualitativos (8) - 1Documento6 páginasCarol Vera Ti m3 Analisis Cuantitativo y Cualitativos (8) - 1Carol Vera FuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía 1. Habilidades Investigativas y ComunicativasDocumento13 páginasGuía 1. Habilidades Investigativas y ComunicativasCamilo EstebanAún no hay calificaciones
- Apunte Criterios para Analizar Fuentes de InformaciónDocumento4 páginasApunte Criterios para Analizar Fuentes de InformaciónKarollAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 2 Lengua y Literatura 4°Documento10 páginasGuia 2 Lengua y Literatura 4°Carolina Andrea Sanhueza VasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- CastellanosDocumento4 páginasCastellanosjosyilAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller de Investigacion I PDFDocumento113 páginasTaller de Investigacion I PDFJaqueline BarraganAún no hay calificaciones
- Epistemologia Con Cuadro ComparativoDocumento8 páginasEpistemologia Con Cuadro ComparativoSara JamesAún no hay calificaciones
- Briana Ensayo TerminadoDocumento8 páginasBriana Ensayo TerminadoARMANDO CASASAún no hay calificaciones
- Perfil de Informante-Investigacion de Mercados. Nestor Betancourt PDFDocumento12 páginasPerfil de Informante-Investigacion de Mercados. Nestor Betancourt PDFNestorBetancourt100% (1)
- Información y Verificación en El Área de Investigación PeriodísticaDocumento10 páginasInformación y Verificación en El Área de Investigación PeriodísticaAlejandro AbacheAún no hay calificaciones
- Bioetica Grupo 7Documento11 páginasBioetica Grupo 7Noe SoriaAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodologia Del Estudio IDocumento37 páginasMetodologia Del Estudio IMaría Paola Chumbes SipánAún no hay calificaciones
- Modulo 1Documento5 páginasModulo 1Armando LucianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Copia de Copia de METODOLOGIA Y TECNICA DE LA INVESTIGACION 2Documento13 páginasCopia de Copia de METODOLOGIA Y TECNICA DE LA INVESTIGACION 2Steicy HidalgoAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen TextosDocumento4 páginasResumen TextosLola TAún no hay calificaciones
- Infografías PlegablesDocumento4 páginasInfografías PlegablesMelany CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- TABLA COMPARATIVA Grupo #3Documento6 páginasTABLA COMPARATIVA Grupo #3JORMAN SANTOS LOPEZ DIAZAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1 Investigacion e InnovacionDocumento3 páginasTarea 1 Investigacion e InnovacionElvis Chancayauri YlachoqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Los Grupos Focales.Documento12 páginasLos Grupos Focales.3102424531mariacespedesAún no hay calificaciones
- Contenido en Extenso Unidad 1 - Módulo 5 - Prepa en Línea - S.E.P.Documento67 páginasContenido en Extenso Unidad 1 - Módulo 5 - Prepa en Línea - S.E.P.Aldo Lazcano Francisco77% (13)
- Balotario de Fundamentos de InvestigaciónDocumento15 páginasBalotario de Fundamentos de InvestigaciónClases DE PortuguesAún no hay calificaciones
- La Técnica de Grupos Focales Resumen de Edu en SaludDocumento5 páginasLa Técnica de Grupos Focales Resumen de Edu en SaludNaty RojanoAún no hay calificaciones
- La Investigacion en La PublicidadDocumento19 páginasLa Investigacion en La Publicidadfideluzumaki2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo FinalizarDocumento6 páginasTrabajo FinalizarLorena SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamentos de InvestigaciónDocumento21 páginasFundamentos de InvestigaciónCARLOS ALBERTO CHI COCOMAún no hay calificaciones
- CuadernilloDocumento20 páginasCuadernilloOc gamesAún no hay calificaciones
- Método de Investigación DocumentalDocumento21 páginasMétodo de Investigación DocumentalRoger RangelAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 3 EL CONOCIMIENTODocumento2 páginasClase 3 EL CONOCIMIENTOSam Sel Hestra100% (1)
- Guía Unidad 1 Historia IIDocumento7 páginasGuía Unidad 1 Historia IISalome OttonelliAún no hay calificaciones
- Ética en La Investigación PsicológicaDocumento7 páginasÉtica en La Investigación PsicológicaMaría Fernanda Lucas de la LuzAún no hay calificaciones
- Caracteristicas Generales Del Discurso PDFDocumento4 páginasCaracteristicas Generales Del Discurso PDFHerber ZikicAún no hay calificaciones
- Sidney PinoDocumento4 páginasSidney Pinosidney pino rodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- A01 PDFDocumento13 páginasA01 PDFErick J. AriasAún no hay calificaciones
- T6 Colegio Alemán HumboldtDocumento7 páginasT6 Colegio Alemán HumboldtLEONARDO XDAún no hay calificaciones
- Inti Pontiggia - Actividad 6. Investigación Filosófica PersonalDocumento5 páginasInti Pontiggia - Actividad 6. Investigación Filosófica PersonalVALENTINA PAZ ESPINOZA RUIZAún no hay calificaciones
- Edwin Es Un MamaguevoDocumento6 páginasEdwin Es Un MamaguevoMiguel GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- CuestinarioDocumento2 páginasCuestinarioMaxim ArcosAún no hay calificaciones
- Cómo Se Originan Las InvestigacionesDocumento12 páginasCómo Se Originan Las InvestigacionesDalicet Cruz FelmarAún no hay calificaciones
- Compilacion 1.0Documento495 páginasCompilacion 1.0Jesus Arturo Tello LunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Video Clase 4 TEO 2023-ADocumento48 páginasVideo Clase 4 TEO 2023-ADAYSI DENISSE CAHUANA COAQUIRAAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Segundo CorteDocumento1 páginaTaller Segundo CorteValentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Roqueacr - Instrucciones IM CuantitativaDocumento3 páginasRoqueacr - Instrucciones IM CuantitativaValentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Estudio de Superficies Equipotenciales y Su Relacion Con El Campo ElectricoDocumento2 páginasEstudio de Superficies Equipotenciales y Su Relacion Con El Campo ElectricoValentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 B ElectromagnetismoDocumento3 páginasTaller 1 B ElectromagnetismoValentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis Estructural.Documento18 páginasAnalisis Estructural.Valentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Hellensi TallerDocumento1 páginaHellensi TallerValentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Jaidermu - RESUMEN TALLER PARCIAL 2Documento2 páginasJaidermu - RESUMEN TALLER PARCIAL 2Valentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Proceso Físico o QuímicoDocumento1 páginaTaller Proceso Físico o QuímicoValentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Modulo 2 - OndasDocumento3 páginasTaller Modulo 2 - OndasValentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 Ecuaciones A8Documento1 páginaTaller 1 Ecuaciones A8Valentina Duarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mata HariDocumento19 páginasMata HarikpiqaguiasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha - Incentivos Económicos - Economía AmbientalDocumento3 páginasFicha - Incentivos Económicos - Economía AmbientalLuis Chavarria PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Acta de Entrega de CargoDocumento2 páginasActa de Entrega de CargoAnac875Aún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Parcial Procesos Productivos PresencialDocumento2 páginas2 Parcial Procesos Productivos PresencialYannis Melo MeloAún no hay calificaciones
- EVALUACIÓN. Unidad 3Documento5 páginasEVALUACIÓN. Unidad 3Leito NikopolidisAún no hay calificaciones
- Aspectos Socioculturales de La AlimentaciónDocumento15 páginasAspectos Socioculturales de La Alimentaciónyazmin martinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Gimbersg - Improvisación en BeijingDocumento2 páginasGimbersg - Improvisación en BeijingnubboeAún no hay calificaciones
- Características de La Comunicación OrganizacionalDocumento9 páginasCaracterísticas de La Comunicación Organizacionalalexis43100% (1)
- Idea de CampañaDocumento11 páginasIdea de CampañamarzelajachoAún no hay calificaciones
- Inventario Millon de Estilos de PersonalidadDocumento3 páginasInventario Millon de Estilos de PersonalidadAle JoseAún no hay calificaciones
- Qué Dice La Biblia Acerca de Los Problemas FamiliaresDocumento11 páginasQué Dice La Biblia Acerca de Los Problemas FamiliaresArnold PosadasAún no hay calificaciones
- Juicio AgrarioDocumento19 páginasJuicio AgrarioFabiola Garcia TellesAún no hay calificaciones
- Ciclo Productivo y ProductoDocumento8 páginasCiclo Productivo y ProductoAngel CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Tratamiento Ybera Fashion Keratina MercadoLibreDocumento1 páginaTratamiento Ybera Fashion Keratina MercadoLibreamalohaAún no hay calificaciones
- San Juancito, Una Historia Minera para ConocerDocumento3 páginasSan Juancito, Una Historia Minera para ConocerPedro ParamoAún no hay calificaciones
- Respuestas Preguntas NietzscheDocumento2 páginasRespuestas Preguntas NietzscheRaül Soler0% (2)
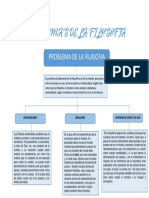
- Problemas de La FilosofiaDocumento1 páginaProblemas de La Filosofialuisa ramosAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo de Investigación de Prevención y Detección de FraudesDocumento60 páginasTrabajo de Investigación de Prevención y Detección de FraudesLuis Angel Quesada EnríquezAún no hay calificaciones
- (M1-E1) Evaluación (Prueba) - EMPRENDIMIENTO (OCT2019) PDFDocumento8 páginas(M1-E1) Evaluación (Prueba) - EMPRENDIMIENTO (OCT2019) PDFMarlene VillarroelAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía para La Elaboración de Un DictamenDocumento4 páginasGuía para La Elaboración de Un DictamennelsonAún no hay calificaciones
- O P VDocumento4 páginasO P VFernando HndzAún no hay calificaciones
- Formas de Pago de Una DeudaDocumento2 páginasFormas de Pago de Una DeudaMatias SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Pelea Por Tu FamiliaDocumento2 páginasPelea Por Tu FamiliaJhonfredy Alvarez100% (1)
- Síntomas Que Preceden Al AvivamientoDocumento12 páginasSíntomas Que Preceden Al Avivamientopalabra33Aún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica 8 Fase I 2023Documento6 páginasPráctica 8 Fase I 2023Elio Arias AlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Arte y Sociedad ParcialDocumento5 páginasArte y Sociedad ParcialManuel Torres NuñezAún no hay calificaciones
- lv2013 Obligaciones Empleador PDFDocumento394 páginaslv2013 Obligaciones Empleador PDFEnrique0% (1)
- Conferencias de La Haya de 1899 y 1907Documento4 páginasConferencias de La Haya de 1899 y 1907cieloAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase Medios ImpugnatoriosDocumento5 páginasClase Medios ImpugnatoriosJheyson Andy Jurado DE LA CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Fogg Phileas - El Libro de La NaturalezaDocumento2 páginasFogg Phileas - El Libro de La NaturalezamartionAún no hay calificaciones