Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Presentacion Diagnostico Financiero
Cargado por
GERARSDO0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
45 vistas11 páginasdiagnostico financiero
Título original
PRESENTACION DIAGNOSTICO FINANCIERO
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentodiagnostico financiero
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PPTX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
45 vistas11 páginasPresentacion Diagnostico Financiero
Cargado por
GERARSDOdiagnostico financiero
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PPTX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 11
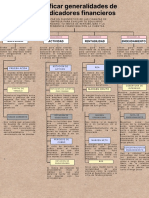
DIAGNOSTICO FINANCIERO
DEFINICIONES Y FORMULAS
MARIO ALEXANDER GAVIRIA GONZALEZ
2022
PLANEACION FINANCIERA
ANALISIS VERTICAL-DEFINICION
• El análisis vertical pretende determinar si la distribución de los activos y
pasivos de la empresa es la más idónea de cara a sus necesidades tanto
operativas como financieras.
• El análisis vertical pretende expresar la participación de cada una de las
cuentas de los estados financieros (balance y pérdidas y ganancias) como un
porcentaje.
• De cara al Balance nos permitirá medir cómo está compuesto el activo, el
pasivo y el patrimonio neto de la sociedad. La referencia por tanto será el
total del activo ó el total que forman el pasivo y patrimonio neto.
• De cara a la cuenta de cuenta de pérdidas y ganancias nos ayudará a
conocer, por ejemplo, que porcentaje de los ingresos representa el coste de
las ventas y los demás gastos a fin de poder ajustarlos y conseguir una
mayor rentabilidad. La referencia que se toma en este caso es el total de
ingresos por ventas.
FORMULA ANALISIS VERTICAL
• La fórmula es la siguiente: Partida del
activo/Activo total x 100. En consecuencia, lo
que se hace es determinar qué porcentaje del
total del activo representa cada rubro del
activo, dividiendo el valor de cada rubro por el
total del activo.
ANALISIS HORIZONTAL
• El análisis horizontal de los estados financieros
permite identificar las variaciones absolutas y
relativas que ha sufrido la estructura financiera de la
empresa en un año o periodo respecto al anterior.
• El análisis horizontal determina cuál fue el
crecimiento o decrecimiento de una cuenta en un
periodo determinado. Es el análisis que permite
determinar si el comportamiento de la empresa en
un periodo fue bueno, regular o malo.
FORMULA ANALISIS HORIZONTAL
LIQUIDITY INDICATORS
• The liquidity of an organization is judged by
the ability to settle obligations in the short
term. term that have been acquired as they
expire. They refer not only to finances
company totals, but rather its ability to
convert certain assets and liabilities into cash.
currents.
INDICATOR FORMULA INTERPRETATION
CURRENT REASON Current active Indicates the ability of the company to
meet its financial obligations, debts or
Current Liabilities liabilities to short term. By dividing
current assets by current liabilities, we
will know how many current assets
will we have to cover or support those
liabilities required in the short term.
ACID TEST Current Assets – Reveals the ability of the company to
Inventories cancel its current obligations, but
without counting on the sale of their
Current Liabilities inventories, that is, basically with the
cash balances, the produced from
your accounts receivable, your
temporary investments and some
another easily liquidated asset that
there may be, other than inventories.
NET WORKING CAPITAL Current Assets – Shows the value that would remain in
Inventories the company, after having paid its
short-term liabilities, allowing
Current Liabilities Management to make decisions on
temporary investment.
EFFICIENCY INDICATORS
• They establish the relationship between the
costs of inputs and the products of the
process; determine the productivity with
which resources are managed, to obtain the
results of the process and the fulfillment of
the objectives. Efficiency indicators measure
the level of execution of the process, focus on
how things were done, and measure the
performance of the resources used. for a
process. They have to do with productivity.
INDICATOR FORMULA INTERPRETATION
INVENTORY TURNOVER COST OF MERCHANDISE SOLD shows the times that the
costs in inventories are
AVERAGE INVENTORY converted to cash or placed
on credit.
INVENTORIES IN STOCK Average inventory x 365
Measures the number of
Cost of Goods Sold days of inventories
available for sale. to minor
number of days, greater
efficiency in inventory
management.
PURSE ROTATION Credit sales Measure the number of
times the Accounts
Average Accounts Receivable receivable rotate on
average, over a period of
time.
Financial diagnostic indicators
• The financial diagnosis is a set of indicators which,
unlike the financial analysis indicators, are built not
only from the Balance Sheet accounts but also of
accounts of the Income Statement, Cash Flow and
other external sources of valuation of market. This
leads to their conclusions and analysis measuring
in more dynamic terms, and not static, the
behavior of an organization in terms of profitability
and effectiveness in the use of your resources.
INDICATOR FORMULA INTERPRETATION
EVA It can be said that a company creates value
Profit before taxes only when the return on its capital is greater
than its opportunity cost or rate of return
(Assets x Cost of that shareholders could win in another
Capital) business of similar risk. Otherwise, a
company has EVA or generates value if it
covers the production or sales costs,
expenses operating costs and cost of capital
and there is something left
MARGINAL CONTRIBUTION Operating income – It is also considered as the excess of income
Costs and with respect to the
Variable expends variable costs, excess that must
cover fixed costs and profit or
gain.
CONTRIBUTION MARGIN marginal It determines for each peso that is made in
contribution Sales sales, that of it is left
to cover fixed costs and expenses
BALANCE Fixed costs It represents the level of activity that allows,
Contribution margin thanks to the margin made (difference
between the level of sales and the variable
expenses that derive implicitly from this
volume of businesses) to be able to pay all
other charges for the year, that is, the fixed
costs.
También podría gustarte
- Material Indicadores Financieros II - AsolnalpracDocumento4 páginasMaterial Indicadores Financieros II - AsolnalpracJulio Suarez100% (2)
- Indicadores FinancierosDocumento5 páginasIndicadores FinancierosCamila CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Optimización FinancieraDocumento9 páginasOptimización FinancieraJose Antonio Nicasio LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores FinancierosDocumento5 páginasIndicadores FinancierosOscar Augusto ALVAREZ PORRASAún no hay calificaciones
- 7-If Indicadores FinancierosDocumento12 páginas7-If Indicadores FinancierosnorlenAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Final de Presupuestos y Analisis FinancieroDocumento15 páginasTrabajo Final de Presupuestos y Analisis FinancieroAlvaro Alexis Lenis DominguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Act 7 Indicadores FinancierosDocumento8 páginasAct 7 Indicadores FinancierosKIMBERLY CHARRY TAVERAAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadro Comparativo Indicies Financieros Sena UnoDocumento8 páginasCuadro Comparativo Indicies Financieros Sena UnoAlfonso Lidoro Rosero DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Balance General Los Frasquitos FinalDocumento5 páginasBalance General Los Frasquitos Finalcarlijipin1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Principales Indicadores Financiero y GestionDocumento17 páginasPrincipales Indicadores Financiero y GestionHuarniz YandyAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores Financieros Equipo 1. 6DDocumento41 páginasIndicadores Financieros Equipo 1. 6DJuan Oscar DuranAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Final Capital de TrabajoDocumento6 páginasTrabajo Final Capital de Trabajodiana maria albis mendezAún no hay calificaciones
- Razones de LiquidezDocumento3 páginasRazones de LiquidezRoberto BarrerasAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores de Gestión (KPI's) FinancierosDocumento17 páginasIndicadores de Gestión (KPI's) FinancierosJohan SebastianAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores Financieros CuadroDocumento3 páginasIndicadores Financieros CuadroLIZETH GIRALDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores financieros liquidez, eficiencia y rentabilidad empresaDocumento9 páginasIndicadores financieros liquidez, eficiencia y rentabilidad empresaliliana sernaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 1.1 (Sena) Ind. Fin.Documento4 páginasActividad 1.1 (Sena) Ind. Fin.Jose Daniel MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Todos los temas 2Documento120 páginasTodos los temas 2lore gonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Conceptos de Contabilidad y FinanzasDocumento2 páginasConceptos de Contabilidad y Finanzasmarcela arangoAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 1 Razones de Rentabilidad y LiquidezDocumento4 páginasActividad 1 Razones de Rentabilidad y LiquidezRoberto BarrerasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ratios FinancierosDocumento18 páginasRatios Financieroskaren turpoAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadro Comparativo Indicadores FinancierosDocumento3 páginasCuadro Comparativo Indicadores FinancieroslilibehtAún no hay calificaciones
- Ratios - El SilencioDocumento11 páginasRatios - El SilencioZulemita VelasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores FinancierosDocumento4 páginasIndicadores FinancierosZULAY DANIELA RODRIGUEZ FLORIANAún no hay calificaciones
- RATIOS FinacierosDocumento6 páginasRATIOS FinacierosRenato saenzAún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis ratios financierosDocumento24 páginasAnálisis ratios financierosYanpol Aguirre YanquiAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores FinancierosDocumento2 páginasIndicadores FinancierosJessica PetroAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores Financieros, Un ResumenDocumento22 páginasIndicadores Financieros, Un ResumenAlejandro Tibana100% (1)
- Razones FinancierasDocumento4 páginasRazones FinancierasYosef CGAún no hay calificaciones
- Contabilidad y Finanzas Orientados A La Gestión y Análisis FinancieroDocumento3 páginasContabilidad y Finanzas Orientados A La Gestión y Análisis Financieroinvierte en tu serAún no hay calificaciones
- 3.4 Actividades de Transferencia Del ConocimientoDocumento2 páginas3.4 Actividades de Transferencia Del Conocimientocris137956Aún no hay calificaciones
- CuadroDocumento3 páginasCuadrojuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Mapa ConceptualDocumento2 páginasMapa ConceptualNathaly NoriegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Evidencia Mapa ConceptualDocumento4 páginasEvidencia Mapa Conceptualluisa Fernanda Cardenas BermudezAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 7. Presupuesto de Ingresos, Costos y GastosDocumento12 páginasTaller 7. Presupuesto de Ingresos, Costos y GastosJulián OlayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentacion de IndicadoresDocumento30 páginasPresentacion de IndicadoresbeyaniraAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores Financieros FORMULASDocumento1 páginaIndicadores Financieros FORMULASjulian cortes100% (1)
- Wa0001Documento27 páginasWa0001jessiAún no hay calificaciones
- CuadroDocumento2 páginasCuadroYesglys RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 3Documento4 páginasActividad 3Analida VargasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 11Documento14 páginasTema 11Abigail Jara VelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores FinancierosDocumento2 páginasIndicadores Financierosmaria ardilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Amortización y depreciación en el estado de resultadosDocumento2 páginasAmortización y depreciación en el estado de resultadosMARIA GUADALUPE GRACIA REYESAún no hay calificaciones
- Ratios Financieros Escuela NegociosDocumento14 páginasRatios Financieros Escuela NegociosAnthony Pinedo GalloAún no hay calificaciones
- Incubacion de Empresas 3.2Documento6 páginasIncubacion de Empresas 3.2Andrea PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadro DescriptivoDocumento3 páginasCuadro Descriptivoalgeidys tapia acostaAún no hay calificaciones
- S12.s1 Materiales Ratios FinancierosDocumento24 páginasS12.s1 Materiales Ratios FinancierosgilmerAún no hay calificaciones
- Principales Indicadores FinancierosDocumento4 páginasPrincipales Indicadores FinancierosEdith VR50% (2)
- Cuadro Razones Finacieras PFDocumento7 páginasCuadro Razones Finacieras PFBa ah.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 9 Indicadores FinancierosDocumento6 páginasTarea 9 Indicadores FinancierosBrayan MaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis e interpretación de índices financierosDocumento4 páginasAnálisis e interpretación de índices financierosDianaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadro ComparativoDocumento3 páginasCuadro Comparativolauro alberto hernadez cincoAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores Liquidez, Actividad, EndeudamientoDocumento19 páginasIndicadores Liquidez, Actividad, EndeudamientoHEIDI NATALIA CALIXTO INFANTEAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores Liquidez, Actividad, EndeudamientoDocumento19 páginasIndicadores Liquidez, Actividad, EndeudamientoHEIDI NATALIA CALIXTO INFANTEAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de Aprendizaje 1 - Sena - Guía 2Documento2 páginasActividad de Aprendizaje 1 - Sena - Guía 2VALENTINA MORENO HOLGUINAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase N°14-RATIOS FINANCIEROSDocumento22 páginasClase N°14-RATIOS FINANCIEROSAnonymous 0vpTHwMk100% (1)
- Evidencia de AprendizajeDocumento20 páginasEvidencia de AprendizajeElvia MagañaAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicadores Financieros 2023Documento2 páginasIndicadores Financieros 2023johnnyAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen de Ratios clave para la dirección de empresas de Ciaran WalshDe EverandResumen de Ratios clave para la dirección de empresas de Ciaran WalshAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen de Financial Intelligence de Karen Berman y Joe KnightDe EverandResumen de Financial Intelligence de Karen Berman y Joe KnightCalificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (1)
- Sinop TicoDocumento4 páginasSinop TicoGERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Times New Roman 12 Sin Negrita Ni Subrayado Ni Cursiva.: VioletaDocumento2 páginasTimes New Roman 12 Sin Negrita Ni Subrayado Ni Cursiva.: VioletaBëkérzz Ãbîî JhîömêrAún no hay calificaciones
- Conta Bili DadDocumento2 páginasConta Bili DadGERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Fase 2 Organizacion ComunitariaDocumento9 páginasFase 2 Organizacion ComunitariaGERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Final LegislacionDocumento5 páginasTrabajo Final LegislacionGERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo Diferencial Estudiante 4Documento8 páginasCalculo Diferencial Estudiante 4GERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Sistemas Integrados Fase 3Documento11 páginasSistemas Integrados Fase 3GERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Mapa ConceptualDocumento3 páginasMapa ConceptualGERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- LiderazgoDocumento9 páginasLiderazgoGERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Servicio AlclienteDocumento4 páginasServicio AlclienteGERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Fase 4-Kevin David Castillo Martínez-ACDocumento5 páginasFase 4-Kevin David Castillo Martínez-ACGERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Regulación contable: Flujo de efectivo y estados financierosDocumento4 páginasRegulación contable: Flujo de efectivo y estados financierospuccapressAún no hay calificaciones
- Eeff 2018 - Conecta Retail S.A.Documento3 páginasEeff 2018 - Conecta Retail S.A.DANIELA LIZETH LOPE ESPINOZAAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculo del interés compuesto: fórmulas, ejemplos y tasa efectivaDocumento16 páginasCálculo del interés compuesto: fórmulas, ejemplos y tasa efectivaVicmali Papeleria CiberAún no hay calificaciones
- Flujo Caja Neto (Htas Fin)Documento16 páginasFlujo Caja Neto (Htas Fin)Jenny SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Renta 2021 Claudia DelgadoDocumento1 páginaRenta 2021 Claudia DelgadoHernando Diaz OsunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Presupuesto de ventas y producción de bloques de concretoDocumento33 páginasPresupuesto de ventas y producción de bloques de concretoXIAOQI CHENAún no hay calificaciones
- Ganancias BrutasDocumento7 páginasGanancias BrutasCarlos Adonis Orbe IntriagoAún no hay calificaciones
- Caso VenusDocumento18 páginasCaso VenusJoel CuadrosAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuentas de ContabilidadDocumento13 páginasCuentas de ContabilidadEdgarAún no hay calificaciones
- 03 - Estudio de La CufinDocumento14 páginas03 - Estudio de La CufinJuan Carlos Reyes SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- 02 Análisis FinancieroDocumento52 páginas02 Análisis FinancieroRicardo RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Cap 5 y 10Documento10 páginasCap 5 y 10Karla MelendezAún no hay calificaciones
- FIN2Unidad 3BDocumento43 páginasFIN2Unidad 3BAna Paola Castro FernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 2 Unidad 2 Inversiones. Uni2 - Act2 - Cas - Emp - Cas - Pra - InvDocumento5 páginasActividad 2 Unidad 2 Inversiones. Uni2 - Act2 - Cas - Emp - Cas - Pra - InvDayana OrtizAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea No. 66 y 67Documento1 páginaTarea No. 66 y 67Luis Mazariegos0% (3)
- Enunciado Comercial FernandezDocumento3 páginasEnunciado Comercial FernandezJessica MaqueraAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucion Ejercicio 4-Ee FF ProyectadosDocumento5 páginasSolucion Ejercicio 4-Ee FF ProyectadosSantiago GómezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actualización registro web Régimen Tributario Especial 2020Documento2 páginasActualización registro web Régimen Tributario Especial 2020sara uribeAún no hay calificaciones
- 20 Minutes Manager Finance Basic Spanish PDFDocumento10 páginas20 Minutes Manager Finance Basic Spanish PDFJamesAún no hay calificaciones
- Dgrrhh02 t2 CasoDocumento4 páginasDgrrhh02 t2 Casomarllory100% (1)
- Modelo CAPMDocumento86 páginasModelo CAPMOriel Mesa GonzálezAún no hay calificaciones
- Conservadurismo en La Contabilidad R.L. Watts FinalDocumento36 páginasConservadurismo en La Contabilidad R.L. Watts FinalTeddy Fres100% (1)
- Trabajo Final Contabilidad 4 WordDocumento12 páginasTrabajo Final Contabilidad 4 WordMiriana Gonzalez SantanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ga2 Ata8 Taller2Documento9 páginasGa2 Ata8 Taller2lizeth0% (1)
- DPF - FAF Jaime Orellana Julio 2019Documento100 páginasDPF - FAF Jaime Orellana Julio 2019syxtynsAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 8 Costos y CosteoDocumento9 páginasTaller 8 Costos y CosteoJuanEstebanMartinVAún no hay calificaciones
- Precio de acciones con crecimiento de dividendosDocumento6 páginasPrecio de acciones con crecimiento de dividendosPatricio GalavizAún no hay calificaciones
- Pronóstico de ventas de celulares usando mínimos cuadradosDocumento4 páginasPronóstico de ventas de celulares usando mínimos cuadradosSamuel SotoAún no hay calificaciones
- Interés CompuestoDocumento8 páginasInterés CompuestoCésar David Marroni Serrano100% (1)
- Formulario 210 2019Documento1 páginaFormulario 210 2019Lady Marcela TIMANA BENAVIDESAún no hay calificaciones