0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
144 vistas7 páginasIntroducción a Profesiones en Español
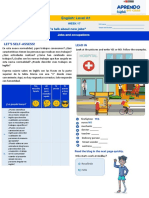
Este documento presenta información sobre profesiones en español. Incluye vocabulario de profesiones masculinas y femeninas y sus lugares de trabajo respectivos, así como notas gramaticales sobre cómo preguntar y hablar de profesiones en presente.
Cargado por
manar ahmedDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd
0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
144 vistas7 páginasIntroducción a Profesiones en Español
Este documento presenta información sobre profesiones en español. Incluye vocabulario de profesiones masculinas y femeninas y sus lugares de trabajo respectivos, así como notas gramaticales sobre cómo preguntar y hablar de profesiones en presente.
Cargado por
manar ahmedDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd