Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Frobenius Method Derivadas
Cargado por
César AzumabitoDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Frobenius Method Derivadas
Cargado por
César AzumabitoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
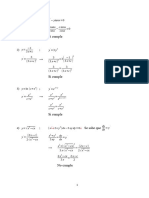
9/7/23, 11:12 frobenius method (d2)/(dx2)(y)=xy
2
series solution d y = xy
2
dx
Solución
(
y = c1 1 + x + x + … +
6 180
3 6
x
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) · 3n
3n
+ … + c2 )
( 4
x + x + x + … +
12 504
7
x
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
3n + 1
+… )
Pasos de solución
2
d y =
2 xy
dx
Sy
x
(
Solve using seriesmethod: y = c1 1 + +
6 180
3
x +… +
6
x
3n
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) · 3n
+… ) + c2
( 4 7
x + x + x + … +
12 504
x
3n+1
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
+… )
m
2
d y = xy
2
dx
bo
Ecuación diferencial lineal homogénea con coeficientes constantes
la
2
d y
Sustituir with y′′
2
dx
y′′ = xy
b
Reescribir como una EDO homogenea lineal con coeficientes constantes
y′′ − xy = 0
p ( x ) = 1, q ( x ) = 0, r ( x ) = −x
Check for singularity at x = 0: Ninguno
′′ ′
p ( x ) y + q ( x ) y + r ( x ) y = 0, if p ( x0 ) = 0 then x0 is a singular point.
Ingrese x = 0 en p ( x ) = 1
p( 0 ) = 1
p ( 0 ) ≠ 0, por lo tanto
Ninguno
https://es.symbolab.com/solver/frobenius-method-calculator/frobenius method %5Cfrac%7Bd2%7D%7Bdx2%7D%5Cleft(y%5Cright)%3Dxy?or=input 1/7
9/7/23, 11:12 frobenius method (d2)/(dx2)(y)=xy
For an equation p ( x ) y
′′ + q ( x ) y′ + r ( x ) y = 0 without singulatity point at x = 0, assume a solution of the form y = ∑∞ a xk
k= 0 k
∞ k− 1
y′ = ∑k= 1 akkx
∞ k
y = ∑ k = 0 akx
Diferenciar ambos lados
y′ = (∑k∞= 0 akxk ) ′
Reescribir como
( ∞
y′ = a 0 + ∑ k = 1 a k x
k
)′
Sy
Aplicar la regla de la suma/diferencia: ( f ± g ) ′ = f ′ ± g′
∞ k−1
y′ = ( a0 ) ′ + ∑k = 1 akkx
m
a 0′ = 0
bo
( a0 ) ′
d ( )
la
Derivada de una constante:
dx
a =0
=0
b
( akxk) ′ = akkxk− 1
( akxk ) ′
Sacar la constante: ( a · f ) ′ = a · f ′
= ak x ( k)′
Aplicar la regla de la potencia:
d a
dx
( )
x =a·x
a− 1
k−1
= akkx
∞ k−1
y′ = 0 + ∑k = 1 akkx
Simplificar
∞ k−1
y′ = ∑k = 1 akkx
∞ k− 2
y′′ = ∑k= 2 akk ( k − 1 ) x
https://es.symbolab.com/solver/frobenius-method-calculator/frobenius method %5Cfrac%7Bd2%7D%7Bdx2%7D%5Cleft(y%5Cright)%3Dxy?or=input 2/7
9/7/23, 11:12 frobenius method (d2)/(dx2)(y)=xy
∞ k−1
y′ = ∑k = 1 akkx
Diferenciar ambos lados
y′′ = (∑k∞= 1 akkxk − 1 ) ′
Sy
Reescribir como
(
y′′ = a1 + ∑k = 2 akkx
∞ k−1
)′
m
Aplicar la regla de la suma/diferencia: ( f ± g ) ′ = f ′ ± g′
∞ k−2
y′′ = ( a1 ) ′ + ∑k = 2 akkx (k − 1)
bo
a 1′ = 0
( a1 ) ′
la
d ( )
Derivada de una constante:
a =0
b
dx
=0
( akkxk− 1 )′ = akkxk− 2 ( k − 1 )
( akkxk − 1 ) ′
Sacar la constante: ( a · f ) ′ = a · f ′
= akk x ( k−1 )′
Aplicar la regla de la potencia: ( )
d a
dx
x =a·x
a− 1
k−1−1
= akk ( k − 1 ) x
Simplificar
k−2
= akkx (k − 1)
∞ k−2
y′′ = 0 + ∑k = 2 akk ( k − 1 ) x
Simplificar
∞ k−2
y′′ = ∑k = 2 akk ( k − 1 ) x
Plug into y′′ − xy = 0
∑k∞= 2 akk ( k − 1 ) xk − 2 − x · ∑k∞= 0 akxk = 0
https://es.symbolab.com/solver/frobenius-method-calculator/frobenius method %5Cfrac%7Bd2%7D%7Bdx2%7D%5Cleft(y%5Cright)%3Dxy?or=input 3/7
S
9/7/23, 11:12 frobenius method (d2)/(dx2)(y)=xy
∞ k
( )
Sy Combine into a single series: 2a2 + ∑k= 1 ak+ 2 ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 ) − ak− 1 x
∑k∞= 2 akk ( k − 1 ) xk − 2 − x · ∑k∞= 0 akxk
m Simplificar
∞
= ∑ k = 2 akk ( k − 1 ) x
k−2 ∞
− ∑ k = 0 akx
k+1
bo Shift series to get the same power of x
∞ k ∞
= ∑ k = 0 ak + 2 ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 ) x − ∑ k = 1 ak − 1x
k
Rewrite series starting at the same k = 1 la
∞ k
b ∞
= 2a2 + ∑k = 1 ak + 2 ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 ) x − ∑k = 1 ak − 1x
Simplificar
k
∞ k
(
= 2a2 + ∑k = 1 ak + 2 ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 ) − ak − 1 x )
∞ k
(
2a2 + ∑k = 1 ak + 2 ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 ) − ak − 1 x = 0 )
For a power series to be equal to 0 the coefficients must be equal to 0, therefore
2a2 = 0 : a2 = 0
2a2 = 0
Dividir ambos lados entre 2
a2 = 0
ak −1
ak+ 2 ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 ) − ak− 1 = 0 : ak+ 2 =
(k + 2 ) ( k + 1)
ak + 2 ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 ) − ak − 1 = 0
Mover ak− 1 al lado derecho
ak + 2 ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 ) = ak − 1
Dividir ambos lados entre ( k + 2 ) ( k + 1 )
ak−1
ak + 2 =
(k + 2) ( k + 1 )
ak−3
ak =
(k − 1 ) k
Sy
m
https://es.symbolab.com/solver/frobenius-method-calculator/frobenius method %5Cfrac%7Bd2%7D%7Bdx2%7D%5Cleft(y%5Cright)%3Dxy?or=input 4/7
ym
9/7/23, 11:12 frobenius method (d2)/(dx2)(y)=xy
Resolver para k = 3n: y1 = c1 1 + x + x + … +
6 180 ( 3 6
x
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) · 3n
+…
3n
)
bo
k = 3n
a3n−3
a3n =
( 3n − 1 ) · 3n
la
a0
a3 =
( 2) (3 )
b
a3 a0
a6 = =
( 5) (6 ) ( 2 ) (3) (5) ( 6 )
a0
a3n =
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) 3n
Por lo tanto, la solución es
(
y1 = a 0 1 + x
3
(2) (3 )
+ x
6
(2) (3) ( 5 ) ( 6 )
+… +
3n
x
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) · 3n
+… )
Simplificar
( 3
y1 = a0 1 + x + x + … +
6 180
6
x
3n
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) · 3n
+… )
Since a0 is a constant, replace a0 with c1
( 3
y1 = c1 1 + x + x + … +
6 180
6
x
3n
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) · 3n
+… )
Resolver para k = 3n + 1: y2 = c2 x + x + x + … +
12
504 ( 4
x
7
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
+…
3n+1
)
k = 3n + 1
a3n−2
a3n + 1 =
3n ( 3n + 1 )
a1
a4 =
( 3) (4 )
a4 a1
a7 = =
( 6) (7 ) ( 3 ) (4) (6) ( 7 )
⋮
Sy
a1
a3n+ 1 =
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
Por lo tanto, la solución es
m
(
y2 = a 1 x + x
4
(3) (4 )
+ x
7
(3) (4) ( 6 ) ( 7 )
+… +
3n+1
x
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
+… )
bo
Simplificar
la
https://es.symbolab.com/solver/frobenius-method-calculator/frobenius method %5Cfrac%7Bd2%7D%7Bdx2%7D%5Cleft(y%5Cright)%3Dxy?or=input 5/7
b
9/7/23, 11:12 frobenius method (d2)/(dx2)(y)=xy
ab
( 4
y2 = a1 x + x + x + … +
12 504
7
x
3n+1
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
+… )
Since a1 is a constant, replace a1 with c2
( 4
y2 = c2 x + x + x + … +
12 504
7
x
3n+1
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
+… )
Resolver para k = 3n + 2: Trivial Solution
k = 3n + 2
a3n−1
a3n + 2 =
( 3n + 1 ) ( 3n + 2 )
a2 = 0
a2
a5 = =0
( 4) (5 )
a5
a8 = =0
( 7) (8 )
a3n+ 2 = 0
Por lo tanto, la solución es
Trivial Solution
(
6 180
3
y = c1 1 + x + x + … +
6
x
3n
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) · 3n ) ( 4
+ … + c2 x + x + x + … +
12 504
7
x
3n+1
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
+… )
( 6 180
3
y = c1 1 + x + x + … +
6
x
3n
( 2 ) ( 3 ) ( 5 ) ( 6 ) … ( 3n − 1 ) · 3n
) ( 4 7
+ … + c2 x + x + x + … +
12 504
x
3n+1
( 3 ) ( 4 ) ( 6 ) ( 7 ) … 3n ( 3n + 1 )
+… )
https://es.symbolab.com/solver/frobenius-method-calculator/frobenius method %5Cfrac%7Bd2%7D%7Bdx2%7D%5Cleft(y%5Cright)%3Dxy?or=input 6/7
9/7/23, 11:12 frobenius method (d2)/(dx2)(y)=xy
Sy
m
bo
la
b
https://es.symbolab.com/solver/frobenius-method-calculator/frobenius method %5Cfrac%7Bd2%7D%7Bdx2%7D%5Cleft(y%5Cright)%3Dxy?or=input 7/7
También podría gustarte
- Caso Final Pagina 115Documento2 páginasCaso Final Pagina 115Reyes Rivas Barón67% (3)
- La Tactica en Las Batallas de La Historia Tomo IDocumento242 páginasLa Tactica en Las Batallas de La Historia Tomo IRodrigo Cruz0% (2)
- Ecuaciones EjercicioDocumento3 páginasEcuaciones EjerciciocarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Ec. DiferencialesDocumento4 páginasEc. Diferencialesfelix.fiee2018Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sol PS 4Documento4 páginasSol PS 4Gabriel GuilcapiAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 4 DerivadasDocumento11 páginasTarea 4 DerivadasCamila cardozoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1 Concepto IntegralDocumento26 páginasTarea 1 Concepto IntegralOscar RoaAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo Integral - Tarea 1Documento8 páginasCalculo Integral - Tarea 1Melissa Naranjo GuzmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 8 IntegralesDocumento48 páginasTema 8 IntegralesLeilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Anexo 2 - Ejercicios Tarea 1 (Letra B) CompletaDocumento15 páginasAnexo 2 - Ejercicios Tarea 1 (Letra B) CompletaAutocad TutorialesAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos Semana 4Documento4 páginasEjercicios Resueltos Semana 4MAXIMILIANO ORTUZAR MARDONESAún no hay calificaciones
- Esta (Xy+1+ (2x) - (E (Xy) ) ) DX+ (X 2) Dy 0 - Ecuaciones Diferenciales Exactas - SymbolabDocumento3 páginasEsta (Xy+1+ (2x) - (E (Xy) ) ) DX+ (X 2) Dy 0 - Ecuaciones Diferenciales Exactas - Symbolabjacobo galicinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica Semana 6Documento5 páginasPráctica Semana 6Juan JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta Taller 7 Bloque 5-6Documento6 páginasPauta Taller 7 Bloque 5-6Matias McGregorAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucion EjerciciosDocumento6 páginasSolucion EjerciciossandraAún no hay calificaciones
- Listado 3 AT 2023 1Documento2 páginasListado 3 AT 2023 1shinyloabsterAún no hay calificaciones
- DocmatDocumento3 páginasDocmatLeonel Andres AlfonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Tipo para Preparacio - N de EtsDocumento6 páginasProblemas Tipo para Preparacio - N de EtsCasimiro Aviles Eliot AmauryAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta Primera Prueba CalculoDocumento3 páginasPauta Primera Prueba CalculovicentecarlosmrAún no hay calificaciones
- MetodosNumericos Foro 2Documento9 páginasMetodosNumericos Foro 2Joshua CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe Semana 2-1Documento8 páginasInforme Semana 2-1LADY JUDYT JAKELYN PEREZ VILLALOBOSAún no hay calificaciones
- MAT1502-4 Guia de Diferenciabilidad (Derivada y Sus Aplicaciones) (Fernando Arenas Daza) (UC)Documento9 páginasMAT1502-4 Guia de Diferenciabilidad (Derivada y Sus Aplicaciones) (Fernando Arenas Daza) (UC)Meztli 3kAún no hay calificaciones
- El Conpseto de IntegralDocumento8 páginasEl Conpseto de IntegralCesar GuzmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Variables Separables (2 (X+y) Sec 2x+tanx) Dx+tanx Dy 0 - SymbolabDocumento4 páginasVariables Separables (2 (X+y) Sec 2x+tanx) Dx+tanx Dy 0 - SymbolabSamuel Roman VelizAún no hay calificaciones
- Integral Indefinida Cálculo Integral 2023Documento2 páginasIntegral Indefinida Cálculo Integral 2023jonatan.carespenrrosAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas PDFDocumento9 páginasDerivadas PDFJancAún no hay calificaciones
- Week 3,1Documento2 páginasWeek 3,1Gabi OtakuAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 8Documento7 páginasPractica 8Vladimir Omar Lobo AchoAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 25 Más Ejemplos de Coeficientes Indeterminados 27-10-21Documento3 páginasClase 25 Más Ejemplos de Coeficientes Indeterminados 27-10-21JORDI NOEL CORTES GUILLENAún no hay calificaciones
- Integración de Fracciones ParcialesDocumento2 páginasIntegración de Fracciones Parcialeskevin Huayama VAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrales ParcialesDocumento3 páginasIntegrales Parcialesdeysy sucasaca parilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen PC1 de Calculo IntegralDocumento4 páginasResumen PC1 de Calculo Integrallaurencehr100% (2)
- Solucion Tarea 4 Calculo Diferencial Anayivi DiazDocumento11 páginasSolucion Tarea 4 Calculo Diferencial Anayivi DiazJohn Jairo Aristizabal MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica #0 Integrales PDFDocumento2 páginasPráctica #0 Integrales PDFfedecoroliAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica A.M II - UNLPDocumento2 páginasPractica A.M II - UNLPmargotAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller de EcuacionesDocumento6 páginasTaller de Ecuacionesluis mesaAún no hay calificaciones
- 16 - Integración DefinidaDocumento2 páginas16 - Integración DefinidaMelina Beatriz Hermosilla BenitezAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo I Tarea 1Documento8 páginasCalculo I Tarea 1Lisette Johana Silva ManosalvaAún no hay calificaciones
- ACFrOgC-j4Owj nls7 WsZp3ghq BcvvNQZqNFgi6pbb8KGbhATqhsceUUVMVK6OtbZRMxJDx0jxgPg1hET06ldn8E7OdRIPXzjVZNXYP3vKKWKqg8TuPMvG6M7kjNJngMfrEdBH-yNcZbGD5C9Documento2 páginasACFrOgC-j4Owj nls7 WsZp3ghq BcvvNQZqNFgi6pbb8KGbhATqhsceUUVMVK6OtbZRMxJDx0jxgPg1hET06ldn8E7OdRIPXzjVZNXYP3vKKWKqg8TuPMvG6M7kjNJngMfrEdBH-yNcZbGD5C9Cynthia EsquiembreAún no hay calificaciones
- Módulo Mes de Abril - Algebra 1° AñoDocumento9 páginasMódulo Mes de Abril - Algebra 1° AñoDominguez EsmeraldaAún no hay calificaciones
- G17 - 2021-02 - CVV-ADM - Ecuaciones Diferenciales - ED LinealDocumento2 páginasG17 - 2021-02 - CVV-ADM - Ecuaciones Diferenciales - ED LinealJime Vargas ObandoAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrales MúltiplesDocumento70 páginasIntegrales MúltiplesRodil Huillca AnccoAún no hay calificaciones
- Reglas de Derivación1Documento2 páginasReglas de Derivación1WAYNE FFAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Variables Aleatoria y ConjuntaDocumento8 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de Variables Aleatoria y ConjuntaMarjorie RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Literal D 1-2Documento4 páginasLiteral D 1-2Andres EstradaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía 6 - InducciónDocumento2 páginasGuía 6 - InducciónRubén Adolfo Quijón MoyanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 3 DerivadasDocumento3 páginasTarea 3 DerivadasAlessandra Magaly Martinez RuizAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos para Aprender A Integrar - Julián Moreno MestreDocumento30 páginasEjercicios Resueltos para Aprender A Integrar - Julián Moreno MestreLuis Arita0% (1)
- Unidad Ii - Arturo CarrascoDocumento3 páginasUnidad Ii - Arturo CarrascoMariana BastidasAún no hay calificaciones
- T10DDocumento3 páginasT10DRuy PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Parcial 1 - Guia - Prof - Ga2Documento1 páginaParcial 1 - Guia - Prof - Ga2Vicente ChavezAún no hay calificaciones
- Anexo 2 - Tarea 1 Natalia - Paez CalculoDocumento14 páginasAnexo 2 - Tarea 1 Natalia - Paez CalculoSelena GaliciaAún no hay calificaciones
- (Xy+1+ (2x) - (E (Xy) ) ) DX+ (X 2) Dy 0 - Calculadora de Ecuaciones Diferenciales de Segundo Orden - SymbolabDocumento2 páginas(Xy+1+ (2x) - (E (Xy) ) ) DX+ (X 2) Dy 0 - Calculadora de Ecuaciones Diferenciales de Segundo Orden - SymbolabFerney GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mate 3roDocumento94 páginasMate 3roCarlos CheroAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrales Indefinidas Resueltas 046 PDFDocumento3 páginasIntegrales Indefinidas Resueltas 046 PDFmendobeceAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 3 Integración Método HermiteDocumento3 páginasEjercicio 3 Integración Método Hermitere-natoAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Calculo (Volumen de Solidos Metodo Discos)Documento5 páginasTrabajo Calculo (Volumen de Solidos Metodo Discos)Miguel Antonio Bula Picón0% (1)
- Integrales Hoy 1Documento6 páginasIntegrales Hoy 1paula ordoñezAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucion 3 Parcial-I2018Documento5 páginasSolucion 3 Parcial-I2018Kira SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Unad CalculoDocumento5 páginasUnad CalculoMonica MoralesAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.1 Introducción Ergonomia PDFDocumento12 páginas1.1 Introducción Ergonomia PDFRoger Adrian Montes RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Marcadores TextualesDocumento15 páginasMarcadores TextualesMaría Alejandra Méndez100% (1)
- Aplicaciones para Lubricantes para MotocicletasDocumento20 páginasAplicaciones para Lubricantes para Motocicletasluismanuel.g10Aún no hay calificaciones
- Valor PicoDocumento2 páginasValor PicoDouglas Israel Casa50% (4)
- Sistemas de Representación 10Documento3 páginasSistemas de Representación 10Alexander BelandriaAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta Certamen2 In1002c 2011 1Documento4 páginasPauta Certamen2 In1002c 2011 1Mauricio DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- CorneaDocumento6 páginasCorneaJoel BurgosAún no hay calificaciones
- Progpedamusi 03Documento4 páginasProgpedamusi 03Berny Le CuontAún no hay calificaciones
- PEMC Ciclo 2020 2021Documento3 páginasPEMC Ciclo 2020 2021Michelle Arramvide ZapataAún no hay calificaciones
- Filosofia Oxford Cap 1Documento23 páginasFilosofia Oxford Cap 1Nicol FigueroaAún no hay calificaciones
- Qué Hemos Heredado de La Antigüedad ClásicaDocumento5 páginasQué Hemos Heredado de La Antigüedad ClásicaFernando de los ÁngelesAún no hay calificaciones
- Cfdi de Ingreso Front MXN: Inmobiliaria Hotelera Cancun Urban Inmobiliaria Hotelera Cancun UrbanDocumento1 páginaCfdi de Ingreso Front MXN: Inmobiliaria Hotelera Cancun Urban Inmobiliaria Hotelera Cancun UrbanJORGE ALBERTO QUEZADA SANTIBAÑEZAún no hay calificaciones
- Ensayo DPL ExposicionDocumento23 páginasEnsayo DPL ExposicionEfrain Trujillo ChambiAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuestionario de Diagnóstico EstudiantesDocumento4 páginasCuestionario de Diagnóstico EstudiantesVictor Campos0% (1)
- Sesión de Aprendizaje N05 Ciencia y Ambiente SentidosDocumento15 páginasSesión de Aprendizaje N05 Ciencia y Ambiente SentidosCarlos Cornejo LlontopAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen Capitulo 4Documento14 páginasResumen Capitulo 4nandouriasAún no hay calificaciones
- Especificaciones Tecnicas - Construccion de Vivienda Estudiantil - Unsaac 2 FinalDocumento52 páginasEspecificaciones Tecnicas - Construccion de Vivienda Estudiantil - Unsaac 2 FinalJhonCcoaQAún no hay calificaciones
- LA Función de La Filosofía en América Latina - Eduardo MurilloDocumento20 páginasLA Función de La Filosofía en América Latina - Eduardo MurilloInquinaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 5064626590789403309Documento124 páginas1 5064626590789403309Fabiana Kippes Medrano100% (1)
- Evidence Forum My Ideal HomeDocumento2 páginasEvidence Forum My Ideal Homepcdatos120% (1)
- A 70 Genetica y Politica CriminalDocumento41 páginasA 70 Genetica y Politica CriminalLaura Elizabeth AbadAún no hay calificaciones
- Criterios de Noticiabilidad en La Construcción de Las Noticias PolicialesDocumento89 páginasCriterios de Noticiabilidad en La Construcción de Las Noticias PolicialesPostítulo Periodismo UnrAún no hay calificaciones
- Lenguaje Ii: Cohesión Y CoherenciaDocumento28 páginasLenguaje Ii: Cohesión Y CoherenciaJuan Moscoso CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 4 Matematica Discreta TeoriaDocumento10 páginasUnidad 4 Matematica Discreta TeoriaSebastian CenturionAún no hay calificaciones
- Un Poco de Consenso - Freud y FrommDocumento4 páginasUn Poco de Consenso - Freud y FrommSaulin13Aún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones Esenciales de La FamiliaDocumento3 páginasFunciones Esenciales de La FamiliaCarmen TipianAún no hay calificaciones
- Prohibiciones de Los Aprendicez Sena: Capitulo IVDocumento27 páginasProhibiciones de Los Aprendicez Sena: Capitulo IVAlex AvilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Huaripampa ModelDocumento1 páginaHuaripampa ModelYulia Tabraj FloresAún no hay calificaciones