Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Comparativo y Superlativo en Ingles
Comparativo y Superlativo en Ingles
Cargado por
Ashley MirandaTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Comparativo y Superlativo en Ingles
Comparativo y Superlativo en Ingles
Cargado por
Ashley MirandaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
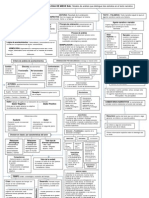
COMPARATIVO Y SUPERLATIVO EN INGLES
Al igual que en español, en inglés cuando queremos comparar dos cosas
utilizamos los adjetivos y sus distintos grados: positivo, comparativo y
superlativo.
- El grado positivo refiere la forma más simple:
A sunny day / Un día soleado
- El grado comparativo refiere una cualidad mayor de una cosa respecto de
otra.
A better day / Un día mejor
- El grado superlativo refiere la cualidad en su mayor expresión:
Today is the best day of the year / Hoy es el mejor día del año
CLASES DE COMPARACIÓN
Comparativo de igualdad
Se forma con el adjetivo intercalado entre la construcción "as...as"
(tan...como) para frases afirmativas e interrogativas y "not as...as" o
"not so...as" para las frases negativas.
I'm as young as you / soy tan joven como tú
am I as young as you? / ¿soy tan joven como tú?
I'm not so young as you / no soy tan joven como tú
Podemos emplear tras el segundo 'as' el pronombre en caso nominativo o
acusativo (He, his; She, her...)
He is as young as she; He is as young as her / Él es tan joven como ella
Si se trata de una comparación entre dos verbos, podemos usar la
expresión "as much as" (tanto como) también en forma negativa
She does not work as much as she should / Ella no trabaja tanto como
debería
Cuando la comparación se hace entre dos sustantivos se utiliza "as much
as" para el singular y "as many as" para el plural.
I have as much work as my boss / Tengo tanto trabajo como mi jefe
I have as many pencils as you / Tengo tantos lápices como tú
Si estamos comparando dos sustantivos contables (libros, coches, casas...)
utilizaremos "as many... as", pero si estamos comparando dos sustantivos
incontables (madera, tiempo, música...) usaremos la construcción "as
much...as".
We have as many books as them / Tenemos tantos libros como ellos
We have as much space as them / Tenemos tanto espacio como ellos
Comparativo de inferioridad
Se forma con el adjetivo intercalado entre la construcción "less...than"
(menos...que), aunque es más usual encontrar la comparación de igualdad en
forma negativa (que tiene el mismo significado).
He's less young than you / Él es menos joven que tú
He's not as young as you / Él no es tan joven como tú (más usual)
Normalmente se emplea less para incontables y fewer para contables
Comparativo de superioridad
Se forma de dos modos:
Añadiendo al adjetivo el sufijo -er para el comparativo de superioridad y -
est para el superlativo.
Big bigger biggest
Anteponiendo la palabra more (más) para el comparativo de superioridad y
"the most" para el superlativo
intelligent / inteligente
more intelligent / más inteligente
the most intelligent / el más inteligente
Los adjetivos de una sola sílaba forman el comparativo y el superlativo
con -er y -est
old, older, the oldest / viejo
new, newer, the newest / nuevo
dark, darker, the darkest / oscuro
Los de dos sílabas que terminan en er, y, le y ow y los que tienen el
acento (prosódico) en la última sílaba forman también el comparativo y el
superlativo con -er y -est
clever, cleverer, the cleverest / listo
idle, idler, the idlest / perezoso
happy, happier, the happiest / feliz
narrow, narrower, the narrowest / estrecho
El resto de adjetivos de dos sílabas y todos los de tres o más forman el
comparativo con more y el superlativo con most.
interesting, more interesting, the most interesting / interesante
COMPARATIVOS Y SUPERLATIVOS IRREGULARES
Algunos adjetivos forman el comparativo de manera irregular
good, better, the best / bueno, mejor, el mejor
bad, worse, the worst / malo, peor, el peor
far, further, the furthest / lejano, más lejano, el más lejano
CONSIDERACIONES
- Cuando un adjetivo termina en e solamente añade -r y -st para el
comparativo y superlativo.
large, larger, the largest / grande, más grande, el más grande
- Cuando terminan en consonante + y cambian la y por i
easy, easier, the easiest / fácil
- Si termina en una sola consonante prededida de una sola vocal, duplica la
consonante
big, bigger, the biggest / grande
- El segundo término de la comparación utiliza la forma than que
corresponde al que español.
He is taller than his brother / Él es más alto que su hermano
- Cuando la comparación se realiza entre dos adjetivos se usa more.
She is more funny than happy / Ella es más alegre que feliz
- La expresión española "cada vez más" equivale en inglés a los dos
comparativos del adjetivo.
The film is becoming more and more interesting / La película se vuelve
cada vez más interesante
CUÁNDO UTILIZAMOS FARTHER Y CUANDO FURTHER?
1. Utilizamos "farther" para referirnos a una distancia física. Por
ejemplo:
Paul's town is farther than Steve's town.
(La ciudad de Paul está más lejos que la ciudad de Steve).
2. Utilizamos "further" para referirnos a una distancia metafórica o
figurativa. Por ejemplo:
His madness has gone much further this year.
(Su locura ha ido mucho más lejos este año)
ELIGE LA RESPUESTA CORRECTA.
1. My mother is ____ than my father.
Old older the oldest the old
2. What is ____ movie you have ever seen?
Funny funnier the funniest the funny
3. That movie was bad, but it wasn't ____ I have ever seen.
Baddest worsest worse the worst
4. Rachel's hair is not as ____ as Sarah's.
Long longer the longest more long
5. Yesterday's exam was ____ than the one last month.
Difficult difficulter the difficultest more difficult
6. Peter is as ____ as Alex.
Fast faster the fastest the faster
7. I think Mary is ____ woman I have ever seen.
Beautiful the most beautiful the beautifulest
the beautifuler
8. Her room is only a little bit ____ than mine.
Bigger the bigger big he
biggest
9. He is ____ when he is playing football.
the happier happiest the happy happyest
10. Michael's house is ____ from the train than Betty's.
Far the furthest the farther further
𝐂𝐎𝐌𝐏𝐀𝐑𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐎 𝐃𝐄 𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐈𝐎𝐑𝐈𝐃𝐀𝐃 𝐄𝐍 𝐈𝐍𝐆𝐋𝐄́ 𝐒 ( 𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐈𝐎𝐑𝐈𝐓𝐘 𝐂𝐎𝐌𝐏𝐀𝐑𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐄)
𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐚 𝐥𝐚𝐬 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐮𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐞𝐬 𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐳𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐨 𝐞𝐥 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐨 𝐝𝐞 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐝𝐚𝐝 𝐞𝐧 𝐢𝐧𝐠𝐥𝐞́
𝐬.
(𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐬𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐬 𝐮𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐢𝐧 𝐄𝐧𝐠𝐥𝐢𝐬𝐡).
1. It's too noisy here. Can we go to a _________ (quiet) place?
2. The hotel was _________ (big) than that in which we stayed last year.
3. Your work is _______ (good) than mine.
4. The accident could have been __________ (bad) than it was.
5. I was __________ (nervous) in my exam yesterday than Mark.
6. I'd like to have a _________ (fast) car. The one I have now is really
old.
7. Last week it was really hot. Today is _________ (cold) than then.
𝐂𝐎𝐌𝐏𝐀𝐑𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐎 𝐃𝐄 𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐈𝐎𝐑𝐈𝐃𝐀𝐃 𝐄𝐍 𝐈𝐍𝐆𝐋𝐄́ 𝐒 (𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐈𝐎𝐑𝐈𝐓𝐘 𝐂𝐎𝐌𝐏𝐀𝐑𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐄)
𝗘𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗯𝗲 𝗹𝗮 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗽𝘂𝗲𝘀𝘁𝗮 𝗰𝗼𝗿𝗿𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗮 / 𝗖𝗵𝗼𝗼𝘀𝗲 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗰𝗼𝗿𝗿𝗲𝗰𝘁 𝗮𝗻𝘀𝘄𝗲𝗿:
1. I have an __________ (old) brother who lives in Miami.
2. Her illness is ___________ (serious) than what the doctors expected.
3. I like warm weather. If the weather is _________ (cold), I will get
sick.
4. This dress is __________ (beautiful) than that one.
5. He is _________ (rich) than Arthur.
6. This road is _________ (far) than the motorway.
7. Was the TV programme __________ (bad) than the film?
𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐎 𝐄𝐍 𝐈𝐍𝐆𝐋𝐄́ 𝐒 (𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐄 𝐈𝐍 𝐄𝐍𝐆𝐋𝐈𝐒𝐇)
𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐚 𝐥𝐚𝐬 𝐬𝐢𝐠𝐮𝐢𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐬 𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐞𝐬 𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐥𝐢𝐳𝐚𝐧𝐝𝐨 𝐥𝐚 𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐚 𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐛𝐚𝐥 𝐜𝐨𝐫𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐚 𝐝𝐞𝐥 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐨
𝐞𝐧 𝐢𝐧𝐠𝐥𝐞́
𝐬 / 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐬𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐬 𝐮𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐚𝐝𝐣𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐧
𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐤𝐞𝐭𝐬:
1. It's a very nice house. It's __________ (nice) house in the street.
2. This is a cheap restaurant. It's __________ (cheap) one I've ever seen.
3. It was a very valuable painting. I'm sure it was __________ (valuable)
painting in the gallery.
4. She is a very good tennis player. Her trainer says she is ________
(good).
5. He is a very dangerous criminal. The police says he is ___________
(dangerous) in the country.
6. We should buy him a beautiful present. Last year we gave him __________
(beautiful) gift of all in his birthday.
𝐂𝐎𝐌𝐏𝐀𝐑𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐎 𝐃𝐄 𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐈𝐎𝐑𝐈𝐃𝐀𝐃 𝐕𝐒 𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐎 (𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐈𝐎𝐑𝐈𝐓𝐘 𝐂𝐎𝐌𝐏𝐀𝐑𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐄 𝐕𝐒
𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐋𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐄)
𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐚 𝐥𝐚𝐬 𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐨𝐧𝐞𝐬 𝐜𝐨𝐧 𝐥𝐚 𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐚 𝐜𝐨𝐫𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐚 𝐝𝐞𝐥 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐨 𝐝𝐞 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐝𝐚𝐝 𝐨 𝐝𝐞𝐥
𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐨 𝐞𝐧 𝐢𝐧𝐠𝐥𝐞́
𝐬 / 𝐂𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐭𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐬𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐬 𝐮𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐜𝐨𝐫𝐫𝐞𝐜𝐭 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞
𝐨𝐫 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐚𝐝𝐣𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐬 𝐢𝐧 𝐛𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐤𝐞𝐭𝐬:
1. She was a very intelligent student. She was __________ (intelligent)
girl in her class.
2. It's a very old castle. Experts argued it is __________ (old) in
Britain.
3. I'm going to sleep on the sofa. The floor is ___________ (uncomfortable)
than it.
4. This new job is ___________ (important) for me than the last I had.
5. Living in the countryside is __________ (health) than living in town.
6. These instructions were ___________ (difficult) ones I have ever read.
𝐂𝐎𝐌𝐏𝐀𝐑𝐀𝐓𝐈𝐕𝐎 𝐃𝐄 𝐒𝐔𝐏𝐄𝐑𝐈𝐎𝐑𝐈𝐃𝐀𝐃
𝐖𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐞 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐜𝐨𝐦𝐩𝐚𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦 𝐨𝐟 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐥𝐥𝐨𝐰𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐚𝐝𝐣𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐬:
1. BEAUTIFUL - ____________ than
2. WIDE - ___________ than
3. HANDSOME - ___________ than
4. LAZY - ___________ than
5. UGLY - __________ than
6. SERIOUS - __________ than
7. CLEVER - __________ than
8. FUNNY - ____________ than
9. SOFT - ___________ than
10. GOOD - ___________ than
11. HARD - ___________ than
12. HEAVY - __________ than
13. LOUD - __________ than
14. NASTY - ___________ than
15. EXPENSIVE - ____________ than
16. DIRTY - __________ than
Complete the sentences using the superiority comparative form of the
adjectives in brackets:
1. Cindy's hat is________ (dark) than mine.
2. Snakes are__________ (dangerous) than rats.
3. My old trousers are_________ (long) than those black ones.
4. Mark is___________ (clever) than his brother.
5. German is___________ (difficult) than English.
6. I am_____________(strong) than my friend.
7. The teacher is_____________ (tall) than me.
8. My friend's eyes are____________ (big) than mine.
9. He sings____________ (good) than Betty.
10. Lucy's hair is_____________ (curly) than yours.
Cuáles son los adverbios de modo en inglés?
Puntos principales
La mayoría de los adverbios de modo se forman añadiendo -ly a un adjetivo,
aunque a veces es necesario hacer otros cambios en la escritura.
No se puede formar adverbios a partir de los adjetivos que terminan en -ly.
Hay adverbios que tienen la misma forma que los adjetivos.
Detrás de los verbos copulativos no se usan los adverbios, sino los
adjetivos.
Los adverbios de modo suelen ser sintagmas preposicionales o sintagmas
nominales.
1 Los adverbios de modo se suelen formar añadiendo -ly a un adjetivo.
Adjetiv bad beautifu carefu quick quiet soft
os: l l
Adverbi badl beautifu carefu quick quiet soft
os: y lly lly ly ly ly
2 Los adverbios que se forman de este modo suelen tener un significado
parecido al del adjetivo.
She is as clever as she is beautiful.He talked so politely and danced
so beautifully.‘We must not talk. We must be quiet,’ said Sita.She wanted
to sit quietly, to relax.
3 A veces, cuando se forma un adverbio a partir de un adjetivo, se
producen cambios en la escritura.
-le se cambia a -ly: gentle ➔ gently
-y se cambia a -ily: easy ➔ easily
-ic se cambia a -ically: automatic ➔ automatically
-ue se cambia a -uly: true ➔ truly
-ll se cambia a -lly: full ➔ fully
Obsérvese que public se cambia a publicly.No es posible formar adverbios a
partir de adjetivos que ya acaban en -ly. Por ejemplo no puede formarse un
adverbio a partir de los adjetivos friendly, lovely o likely. En su lugar,
a veces se usa un sintagma preposicional, por ejemplo in a friendly
way.4 Hay algunos adverbios de modo que tienen la misma forma que los
adjetivos y que tienen un significado parecido, por
ejemplo fast, hard y late.
I’ve always been interested in fast cars. (adjetivo)He was driving
too fast. (adverbio)
Obsérvese que hardly y lately no son adverbios de modo y tienen
significados diferentes a hard y a late.
It was a hard decision to make.I hardly had any time to talk to her.The
train was late as usual.Have you seen John lately?
5 El adverbio de modo que se corresponde con good es well.
He is a good dancer.He dances well.
Obsérvese que well a veces puede ser un adjetivo cuando se refiere a la
salud de una persona.
‘How are you?’ – ‘I am very well, thank you.’
6 Los adverbios no se usan detrás de verbos copulativos
como be, become, feel, get, look y seem. Detrás de estos verbos se usa un
adjetivo, por ejemplo, no se dice Sue felt happily, sino Sue felt
happy.7 Los sintagmas preposicionales o los sintagmas nominales no suelen
usarse como construcciones adverbiales de modo. Sin embargo, en ocasiones
es necesario utilizarlos, por ejemplo cuando no se dispone de una forma
adverbial. En el sintagma preposicional y en el sintagma nominal se suelen
incluir sustantivos como way, fashion o manner, o un sustantivo que se
refiera a la voz de alguien.
She asked me in such a nice manner that I couldn’t refuse.He did it the
right way.They spoke in angry tones.
Los sintagmas preposicionales que llevan like también se usan como
construcciones adverbiales de modo.
I slept like a baby.He drove like a madman.
Lista de adverbios de modo en inglés
Naturally → Naturalmente
A continuación te mostramos cuáles Neatly → Ordenadamente
son los adverbios de modo.
Only → Solamente
Patiently → Pacientemente
Alone → Solo/a
Professionally → Profesionalmente
Accidentally → Accidentalmente
Quickly → Rápidamente
Accurately → Acertadamente
Quietly → Silenciosamente
Actually → Realmente
Really → Realmente
Angrily → Furiosamente
Reluctantly → De mala gana
Anxiously → Ansiosamente
Roughly → Aproximadamente
Badly → Mal
Right → Correctamente
Beautifully → Hermosamente
Separately → Separadamente
Better → Mejor
Simply → Simplemente
Cautiously → Cautelosamente
Softly → Suavemente
Carefully → Cuidadosamente
Slowly → Lentamente
Carelessly → Descuidadamente
Straight → Derecho
Calmly → Calmadamente
Successfully → Exitosamente
Cleverly → Inteligentemente
Suddenly → Repentinamente
Dangerously → Peligrosamente
Together → Juntos
Easily → Fácilmente
Well → Correctamente
Elegantly → Elegantemente
Wrong → Incorrectamente
Expertly → Expertamente
Fast → Rápido
Fluently → Con fluidez
Gently → Suavemente
Greedily → Ávidamente
Happily → Felizmente
Hard → Difícil
Heavily → Pesadamente
Intentionally → Intencionalmente
Loudly → Ruidosamente
También podría gustarte
- Cómo Construir Oraciones en InglésDocumento9 páginasCómo Construir Oraciones en InglésEmilio CarbonellAún no hay calificaciones
- 001.5 - Yanked - Melanie HarlowDocumento111 páginas001.5 - Yanked - Melanie HarlowJuanpocortegon CAún no hay calificaciones
- Mapa Conceptual NarratologiaDocumento6 páginasMapa Conceptual NarratologiaJezzika Roa Muñoz100% (2)
- Psicologia de Erikson en La PNLDocumento23 páginasPsicologia de Erikson en La PNLalexxmejiarAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso de Lengua de Señas ManualdelmonitorDocumento70 páginasCurso de Lengua de Señas ManualdelmonitorValeria Gaete Donoso100% (1)
- El Comparativo y El Superlativo en InglésDocumento13 páginasEl Comparativo y El Superlativo en InglésJosé Solh100% (1)
- Resumen de Gramatical InglesDocumento17 páginasResumen de Gramatical InglesYazminAún no hay calificaciones
- Test Comprensión LectoraDocumento16 páginasTest Comprensión LectoraCarolinaMariman100% (2)
- Examen Lengua 2 EsoDocumento5 páginasExamen Lengua 2 EsoAlba AivAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 6Documento17 páginasUnidad 6Pedro Hernandez Santos100% (1)
- Examen de Historia T 1 A RégimenDocumento2 páginasExamen de Historia T 1 A RégimenJOSÉ LUIS TRUJILLO RODRÍGUEZ71% (7)
- Comparative and SuperlativeDocumento6 páginasComparative and SuperlativeAlejandraVasquezHoyosAún no hay calificaciones
- Liliana Suarez, Rosalva Aida (Eds.) - Descolonizando El FeminismoDocumento472 páginasLiliana Suarez, Rosalva Aida (Eds.) - Descolonizando El FeminismoJorge Andrés Jiménez Rodas100% (1)
- El Adjetivo Comparativo y El SuperlativoDocumento4 páginasEl Adjetivo Comparativo y El SuperlativoIsaac Ginoris OramasAún no hay calificaciones
- El Comparativo y El Superlativo en InglésDocumento2 páginasEl Comparativo y El Superlativo en InglésJ Fernando Audeves GambaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clases de ComparativosDocumento3 páginasClases de ComparativosGabriela GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos en InglésDocumento4 páginasComparativos en Ingléseducate10Aún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos y Superlativos.Documento4 páginasComparativos y Superlativos.FrankRamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Espe Apuntes Adjetivos Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento3 páginasEspe Apuntes Adjetivos Comparativos y SuperlativosAnnieAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe Adjetivos Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento7 páginasInforme Adjetivos Comparativos y SuperlativosGreyJosept Galindez Rojas100% (2)
- Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento3 páginasComparativos y SuperlativosEugenio HuertasAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjetivos en InglésDocumento22 páginasAdjetivos en InglésGio NaAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparative and SuperlativeDocumento3 páginasComparative and SuperlativeSaid StevensonAún no hay calificaciones
- En Inglés Cuando Comparamos Dos Cosas Usamos Los Adjetivos y Sus Tres GradosDocumento12 páginasEn Inglés Cuando Comparamos Dos Cosas Usamos Los Adjetivos y Sus Tres GradosDixie NahiAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento4 páginasComparativos y Superlativossoft241Aún no hay calificaciones
- EnglishDocumento9 páginasEnglishReMus GonAún no hay calificaciones
- 125 - Comparatives and SuperlativesDocumento9 páginas125 - Comparatives and SuperlativesMartaAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento6 páginasComparativos y SuperlativosulisesongsAún no hay calificaciones
- Adj Comparativos y Superlativos - Ingles - AloDocumento6 páginasAdj Comparativos y Superlativos - Ingles - AloGisela LuchiñskiAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento4 páginasComparativos y SuperlativosTito MutiAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocumento2 páginasComparatives and SuperlativesAna-Maria VladAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjetivos Comparativos y Superlativos en InglésDocumento18 páginasAdjetivos Comparativos y Superlativos en InglésMarisa MerloAún no hay calificaciones
- Parative Adejectives and PronounsDocumento7 páginasParative Adejectives and PronounsJordi MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos en InglésDocumento9 páginasComparativos en InglésbebecitoluisAún no hay calificaciones
- Grados de AdjetivosDocumento4 páginasGrados de AdjetivosMarisela SosaAún no hay calificaciones
- 3P Guia 3 Ingls 3 CentralDocumento4 páginas3P Guia 3 Ingls 3 CentralPaola Herrera PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Manuel Zapata OlivellaDocumento41 páginasManuel Zapata OlivellaSin NombreAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparatives SuperltivesDocumento6 páginasComparatives SuperltivesDaissy ChAún no hay calificaciones
- Los Grados Del AdjetivoDocumento6 páginasLos Grados Del AdjetivoPedro Hernandez SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparative and Superlative AdjetivesDocumento6 páginasComparative and Superlative AdjetivesJoadel TomasAún no hay calificaciones
- Superlative & Comparative Adjectives 7th GradeDocumento9 páginasSuperlative & Comparative Adjectives 7th GradeJohn ArredondoAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjetivos ComparativosDocumento20 páginasAdjetivos ComparativosRony Mamani NinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjetivos Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento8 páginasAdjetivos Comparativos y Superlativosbelen8jacquetAún no hay calificaciones
- 4thB. EPWN9. TheoryDocumento4 páginas4thB. EPWN9. TheoryPaz BrodskyAún no hay calificaciones
- El Comparativo Se Usa para Hacer Una Comparación Entre Dos PersonasDocumento3 páginasEl Comparativo Se Usa para Hacer Una Comparación Entre Dos PersonasEventosFormativosPerezFPAún no hay calificaciones
- DocumentoDocumento6 páginasDocumentoBelkis SolisAún no hay calificaciones
- Desinencias Del InglesDocumento11 páginasDesinencias Del InglesJosé Angel Sequera CamacaroAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparative and Superlative of AdjectivesDocumento2 páginasComparative and Superlative of AdjectivesTeresa PerlesAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos y Superlativos - InglesDocumento5 páginasComparativos y Superlativos - InglesEnny Irlette Menenez RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- AdjetivosDocumento8 páginasAdjetivosmelisa collinsAún no hay calificaciones
- ComparativoDocumento6 páginasComparativoVerônicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Muestra Al Grupo Diferentes Ilustraciones de Frutas y VerdurasDocumento13 páginasMuestra Al Grupo Diferentes Ilustraciones de Frutas y Verdurasapi-310063182Aún no hay calificaciones
- SuperlativosDocumento13 páginasSuperlativosMichael A. OcampoAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjetivos ComparativosDocumento17 páginasAdjetivos ComparativosVichy OttoAún no hay calificaciones
- 32° Clase. Martes 20 de Julio. U 17Documento11 páginas32° Clase. Martes 20 de Julio. U 17Juan SylvesterAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento22 páginasComparativos y Superlativosjuanmesa76381Aún no hay calificaciones
- El Comparativo y El SuperlativoDocumento2 páginasEl Comparativo y El SuperlativojoshuaAún no hay calificaciones
- Comparativos As... As PDFDocumento4 páginasComparativos As... As PDFMarcela PazAún no hay calificaciones
- Investigacion InglesDocumento4 páginasInvestigacion InglesRigoberto Labrador RamírezAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 ERO A Y B-Guia Tema #2 Grados de Loa Adjetivos C.Documento4 páginas3 ERO A Y B-Guia Tema #2 Grados de Loa Adjetivos C.Johann PachecoAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIDAD 3comparativo y SuperlativoDocumento4 páginasUNIDAD 3comparativo y SuperlativoAna BetancourtAún no hay calificaciones
- ADJETIVOS COMPARATIVOS y SUPERLATIVOSDocumento11 páginasADJETIVOS COMPARATIVOS y SUPERLATIVOSnelsa jimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Grados de ComparaciónDocumento7 páginasGrados de ComparaciónPilar Fernández Álvarez100% (1)
- Superlativos en InglésDocumento7 páginasSuperlativos en InglésMónica CuevasAún no hay calificaciones
- Compendio de Adjetivos Comparativos y SuperlativosDocumento14 páginasCompendio de Adjetivos Comparativos y SuperlativoscarAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía completa de adjetivos en inglés: Aprende categorías de la gramática en inglés, #4De EverandGuía completa de adjetivos en inglés: Aprende categorías de la gramática en inglés, #4Aún no hay calificaciones
- Recup Lengua FPBDocumento2 páginasRecup Lengua FPBAlba AivAún no hay calificaciones
- CIENCIAS SOCIALES RecupDocumento2 páginasCIENCIAS SOCIALES RecupAlba AivAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 8 ATENCIÓN A LA DIVERSIDAD MARCO LEGALDocumento23 páginasTema 8 ATENCIÓN A LA DIVERSIDAD MARCO LEGALAlba AivAún no hay calificaciones
- La Leyenda de Santa ClausDocumento1 páginaLa Leyenda de Santa ClausAlba AivAún no hay calificaciones
- Lengua Modelo 18Documento2 páginasLengua Modelo 18Alba AivAún no hay calificaciones
- Completar PalabrasDocumento3 páginasCompletar PalabrasAlba AivAún no hay calificaciones
- Encuesta A EstudiantesDocumento1 páginaEncuesta A EstudiantesAlba AivAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis Documental I TeoríaDocumento72 páginasAnalisis Documental I TeoríaDeprofesion BibliotecarioAún no hay calificaciones
- 1°artes Visuales EDDocumento11 páginas1°artes Visuales EDGisela Francisca Garrido LlanténAún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis Sintáctico No Te TemoDocumento16 páginasAnálisis Sintáctico No Te TemoNoris ContrerasAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta de Evaluacion Fonoaudiologica para Sujetos Sobre 12 AñosDocumento7 páginasPauta de Evaluacion Fonoaudiologica para Sujetos Sobre 12 AñosCristina Andrea Vidal Gatica0% (1)
- Yolanda Perez - Estoy Enamorada - ArbeitsblattDocumento6 páginasYolanda Perez - Estoy Enamorada - ArbeitsblattsusiinberlinAún no hay calificaciones
- Álgebra Repaso 5Documento11 páginasÁlgebra Repaso 5Cliffor Jerry Herrera CastrilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Articulo Embera ChamíDocumento18 páginasArticulo Embera ChamíSteven Caceres OrdoñezAún no hay calificaciones
- Oregairu Shin Vol. 1Documento92 páginasOregairu Shin Vol. 1Angel RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Nosilatiaj La Belleza Como Diálogo InterculturalDocumento3 páginasNosilatiaj La Belleza Como Diálogo Interculturalandrea_jimena_2Aún no hay calificaciones
- REPASO Poema 5° BÁSICODocumento3 páginasREPASO Poema 5° BÁSICOAnonymous j2jUylAún no hay calificaciones
- Flujograma InglesDocumento4 páginasFlujograma InglesJoudy3XAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Años CONCLUSIONES DESCRITIVAS 3 AÑOSDocumento8 páginas3 Años CONCLUSIONES DESCRITIVAS 3 AÑOSRoxana RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- El Uso de La Mayuscula 22Documento9 páginasEl Uso de La Mayuscula 22Sunmi Angela Alvarez VasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de IngenioDocumento19 páginasProblemas de IngenioIgnacio González-LlanosAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica SegundoDocumento1 páginaMatematica SegundoEdwiin HuertasAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 UNIT 8 ACTIVITY 1 Do You Have Long HairDocumento5 páginas1 UNIT 8 ACTIVITY 1 Do You Have Long HairdanyAún no hay calificaciones
- Deleuze y ComunicaciónDocumento8 páginasDeleuze y ComunicacióndoraAún no hay calificaciones
- Lengua y Literatura 1º ESODocumento16 páginasLengua y Literatura 1º ESOMaria GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- El Rigor Semántico de John LockeDocumento5 páginasEl Rigor Semántico de John LockeOscar VillafanAún no hay calificaciones
- Caso de Estudio LinuxDocumento8 páginasCaso de Estudio LinuxAnonymous kPuiPxWAún no hay calificaciones
- Competencias Matemáticas en El IEMSDocumento40 páginasCompetencias Matemáticas en El IEMSOsman Villanueva100% (1)
- Tertulias Dialógicas-Esther M-Carmen GDocumento2 páginasTertulias Dialógicas-Esther M-Carmen GToni de la TorreAún no hay calificaciones
- Nuestro Conocimiento Del Lenguaje HumanoDocumento17 páginasNuestro Conocimiento Del Lenguaje HumanoDaniel FrazónAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial SymbalooDocumento7 páginasTutorial Symbaloojosecajoseca7635100% (1)