Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Conjugación en present continuous (listen
Cargado por
León Olvera Emilio G0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
19 vistas3 páginasEste documento presenta las reglas para la conjugación del verbo "to listen" en presente continuo (present continuous) en inglés. Explica que la terminación dominante es "-ing", pero algunos verbos duplican la última letra o eliminan una "e" antes de agregar "-ing". También identifica verbos de estado que generalmente no se conjugan en presente continuo y casos especiales donde el significado determina si se usa o no la forma "-ing".
Descripción original:
Título original
Documento 35
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoEste documento presenta las reglas para la conjugación del verbo "to listen" en presente continuo (present continuous) en inglés. Explica que la terminación dominante es "-ing", pero algunos verbos duplican la última letra o eliminan una "e" antes de agregar "-ing". También identifica verbos de estado que generalmente no se conjugan en presente continuo y casos especiales donde el significado determina si se usa o no la forma "-ing".
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
19 vistas3 páginasConjugación en present continuous (listen
Cargado por
León Olvera Emilio GEste documento presenta las reglas para la conjugación del verbo "to listen" en presente continuo (present continuous) en inglés. Explica que la terminación dominante es "-ing", pero algunos verbos duplican la última letra o eliminan una "e" antes de agregar "-ing". También identifica verbos de estado que generalmente no se conjugan en presente continuo y casos especiales donde el significado determina si se usa o no la forma "-ing".
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 3
Conjugación en present continuous (listen)
Afirmativo Negativo Interrogativo
I am listening to I am not listening to Am I listening to
music music music?
You are listening to You are not listening Are you listening to
music to music music?
He is listening to He is not listening to Is he listening to
music music music?
She is listening to She is not listening Is she listening to
music to music music?
It is listening to It is not listening to Is it listening to
music music music?
We are listening to We are not listening Are we listening to
music to music music?
They are listening to They are not Are they listening to
music listening to music music?
Reglas
Como puedes ver, la terminación dominante en este tiempo verbal es –ing, sin
embargo, cabe subrayar las siguientes reglas para la formación de gerundios en
algunos verbos:
• Regla 1. Todos los verbos terminan en –ing.
No hay que darle muchas vueltas a esto. Todo verbo conjugado en present
continuous debe tener esta terminación.
Ejemplo: The elephant is playing in the water.
• Regla 2. Cuando un verbo termina en consonante, se debe duplicar la última
letra para agregar la terminación –ing.
Ejemplo: The jaguar is running.
• Regla 3. Si el verbo termina en e muda, se elimina esta letra y se coloca la
terminación –ing.
Ejemplo: They are dancing cumbias.
• Regla 4. Los verbos que terminan en doble e conservan esta terminación y
agregan al final –ing.
Ejemplo: I am seeing my lawyer next Monday.
• Regla 5. Verbos terminados en -–ie colocan en su lugar una y + -ing.
Ejemplo: He is lying to his boss.
Excepciones
La naturaleza de algunos verbos impide su conjugación en presente continuo en
inglés, por lo que no suelen tener terminación -ing. Estos verbos son conocidos
como “de estado” o stative verbs. ¿Qué señalan los stative verbs? Estados
emocionales o mentales, sensaciones, comunicación y otros. En este cuadro podrás
encontrar algunos ejemplos:
Stative verbs
Estados Sensaciones Comunicación Otros estados
emocionales
o mentales
Believe (creer) Appear Agree (estar Be (ser/estar)
Dislike (aparecer) de acuerdo) Belong
(disgustar) Hear (oír) Astonish (pertenecer)
Doubt (dudar) See (ver) (asombrar) Concern
Imagine Seem Deny (negar) (concernir)
(imaginar) (parecer) Disagree (no Consist
Know (saber) Smell (oler) estar de (consistir)
Like (gustar) Sound (sonar) acuerdo) Contain
Love (amar) Taste (saber, Impress (contener)
Hate (odiar) de sabor) (impresionar) Cost (costar)
Prefer (preferir) Mean Depend
Realize (notar / (significar) (depender)
darse cuenta) Please Deserve
Recognize (complacer) (merecer)
(reconocer) Promise Include (incluir)
Remember (prometer) Involve
(recordar) Satisfy (involucrar)
Suppose (satisfacer) Lack (faltar)
(suponer) Surprise Matter
Understand (sorprender) (importar)
(entender) Need
Want (querer) (necesitar)
Wish (desear) Owe (deber,
de deuda)
Own (tener)
Possess
(poseer)
Pero hay casos especiales cuya conjugación en presente continuo depende del
significado. En esta tabla puedes conocerlos:
Stative verbs: casos especiales
Verbo Significado Ejemplo Significado Ejemplo
sin con
terminación terminación
-ing -ing
Appear Parecer / It appears to Presentarse My band is
Asemejar be an UFO (en un appearing at
escenario) / his party
Actuar tonight
Feel Opinar I feel you Sentir She is feeling
deserve pain in her
more chest
Look Parecer It looks too Ver They are
weird to me looking at
the puppies
See Entender He can’t see Visitar He is seeing
your point his couch
again
Think Opinar She thinks Pensar I am thinking
you are her about your
best teacher offer
Sigue aprendiendo a usar los tiempos verbales en inglés
Para perfeccionar tu conocimiento del present continuous debes aprenderte las
estructuras y reglas mencionadas arriba y, sobre todo, practicar mucho, ya sea en
conversaciones escritas u orales con amigos o familiares, o inscribiéndote a cursos
donde puedes conocer este y todos los demás tiempos verbales.
También podría gustarte
- The Spanish Subjunctive Explained- Over 100 examplesDe EverandThe Spanish Subjunctive Explained- Over 100 examplesAún no hay calificaciones
- Present Continuous de InglesDocumento21 páginasPresent Continuous de InglesYunkli AristimuñoAún no hay calificaciones
- Simple Present, Simple Past, Continous PresentDocumento24 páginasSimple Present, Simple Past, Continous PresentEiber SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Presente Continuo - UsosDocumento5 páginasPresente Continuo - UsosOrosia FerrerAún no hay calificaciones
- I Would Like To Have A Conversation On English With YouDocumento8 páginasI Would Like To Have A Conversation On English With YouMonserrat GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- Present ProgressiveDocumento10 páginasPresent ProgressiveJAFET VERAAún no hay calificaciones
- Present ProgressiveDocumento6 páginasPresent ProgressiveAdrien O'dowdAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuál Es La Estructura Del Presente Simple en La Formación de Oraciones - Docx PRESENTE CONTINUODocumento4 páginasCuál Es La Estructura Del Presente Simple en La Formación de Oraciones - Docx PRESENTE CONTINUOAna Laura PañellaAún no hay calificaciones
- Present Continuous - Formación, Uso y Ejemplos - British CouncilDocumento3 páginasPresent Continuous - Formación, Uso y Ejemplos - British Councilpatricia 2006Aún no hay calificaciones
- 4 Present ContinuousDocumento8 páginas4 Present ContinuousKeyla Celina Nuñez LunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Present Continuous en inglésDocumento7 páginasPresent Continuous en inglésMichel CavazosAún no hay calificaciones
- Presente ContinuoDocumento7 páginasPresente ContinuoGermania GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Present Continuo y Present SimpleDocumento16 páginasPresent Continuo y Present SimpleMonte BelloAún no hay calificaciones
- Present Continuous - Ejemplos y Estructura en InglésDocumento4 páginasPresent Continuous - Ejemplos y Estructura en InglésJesus Alexis martinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía 4 Ciclo 5 InglésDocumento10 páginasGuía 4 Ciclo 5 InglésFernando Villafañe ArredondoAún no hay calificaciones
- Verbos de Estado y de Acción en InglésDocumento8 páginasVerbos de Estado y de Acción en InglésFernando Cruz50% (2)
- Presente Irregular - Irregular Verbs in SpanishDocumento9 páginasPresente Irregular - Irregular Verbs in SpanishKember SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Stative VerbsDocumento6 páginasStative VerbsFelix Junior Vilchez CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- State VerbsDocumento6 páginasState VerbsJamy SmithAún no hay calificaciones
- ExPOSICION JUEVESDocumento2 páginasExPOSICION JUEVESIker MuguerzaAún no hay calificaciones
- Present ProgressiveDocumento9 páginasPresent ProgressivezafrarodriguezmercyAún no hay calificaciones
- SubjunctivesDocumento3 páginasSubjunctivesMadhav AgarwalAún no hay calificaciones
- El SubjuntivoDocumento6 páginasEl SubjuntivoJandorfAún no hay calificaciones
- Separata InglesDocumento1 páginaSeparata Inglesmirssea nananaAún no hay calificaciones
- presente regular e irregular españolDocumento10 páginaspresente regular e irregular españoldmh56cbz2qAún no hay calificaciones
- Verbos Irregulares en PresenteDocumento9 páginasVerbos Irregulares en PresenteConstantin ScutariAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso (Tuportugues) PDFDocumento150 páginasCurso (Tuportugues) PDFDiego Eme100% (1)
- Segundo Material.Documento15 páginasSegundo Material.Wilkerman LópezAún no hay calificaciones
- SubjuntivoDocumento3 páginasSubjuntivoClaudia CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- VerbosIrregularesDocumento14 páginasVerbosIrregularesGeno ExpositoAún no hay calificaciones
- Verbos EspañolDocumento4 páginasVerbos EspañolAugustoAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.8 Tiempos Verbales. PRESENTEDocumento7 páginas1.8 Tiempos Verbales. PRESENTENereaAún no hay calificaciones
- Categorías Framaticales Clase 2Documento22 páginasCategorías Framaticales Clase 2Daniela LagunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia N.5 2020 Verbos Regulares e Irregulares EsapDocumento5 páginasGuia N.5 2020 Verbos Regulares e Irregulares EsapLina Marcela Perez AriasAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuándo Se Usa El Presente de SubjuntivoDocumento6 páginasCuándo Se Usa El Presente de SubjuntivoAngie AlalAún no hay calificaciones
- Francés Unidad 3 ContenidosDocumento14 páginasFrancés Unidad 3 Contenidosseurkone1988Aún no hay calificaciones
- Antologia ItalianoDocumento19 páginasAntologia ItalianoVíctor Hugo Cueto RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Antologia Ing 2Documento26 páginasAntologia Ing 2Lorena MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Simple PastDocumento9 páginasSimple PastBelen Del Carmen MartínezAún no hay calificaciones
- Irregular Present-2Documento3 páginasIrregular Present-2Oliver SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ingles No Entiendo Na Peo BuenoDocumento15 páginasIngles No Entiendo Na Peo BuenoKaren Mendoza AparicioAún no hay calificaciones
- Esquema de Los VerbosDocumento27 páginasEsquema de Los VerbosInge Dirk Verbeeck MaesAún no hay calificaciones
- Presente Indicativo - Ficha de EspanholDocumento3 páginasPresente Indicativo - Ficha de EspanholCindy DafflonAún no hay calificaciones
- Verbos-Modelos ConjugaciónDocumento2 páginasVerbos-Modelos ConjugaciónMaríaAún no hay calificaciones
- Verbos IrregularesDocumento8 páginasVerbos IrregularesBemegoAún no hay calificaciones
- Secuencia A2 Simple Past Irregular VerbsDocumento11 páginasSecuencia A2 Simple Past Irregular VerbsCamilo MangonesAún no hay calificaciones
- EspanholDocumento13 páginasEspanholJéssica CassianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Presente Simple de Los Verbos Irregulares: 1. Verbos Con Alteraciones VocálicasDocumento6 páginasPresente Simple de Los Verbos Irregulares: 1. Verbos Con Alteraciones VocálicasAlinaAdrianaAún no hay calificaciones
- NulsDocumento18 páginasNulsmouhamedbalde292003Aún no hay calificaciones
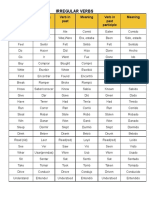
- Lista de verbos irregulares en inglésDocumento19 páginasLista de verbos irregulares en inglésAlvaroAún no hay calificaciones
- VerbosDocumento4 páginasVerbosJanette LomeliAún no hay calificaciones
- Passe ComposeDocumento5 páginasPasse ComposeValeria TradottiAún no hay calificaciones
- Lección 6Documento15 páginasLección 6Arden JamaesAún no hay calificaciones
- Presente de Indicativo-Irregular PDFDocumento4 páginasPresente de Indicativo-Irregular PDFEXP_PDP_IRLAún no hay calificaciones
- PresenteDocumento1 páginaPresenteAlejandra RomeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Presente de IndicativoDocumento2 páginasPresente de IndicativoVictisto ElioverAún no hay calificaciones
- Regular VerbsDocumento5 páginasRegular VerbsEdith Sanchez HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Глаголы Presente de IndicativoDocumento1 páginaГлаголы Presente de Indicativo12345kolia1966Aún no hay calificaciones
- Condicionales italianos y conjugación del imperativoDocumento8 páginasCondicionales italianos y conjugación del imperativoPERDHRO DIEGOAún no hay calificaciones
- Instructivo Unidad 5 Inglés 1Documento7 páginasInstructivo Unidad 5 Inglés 1juan.sarmientoAún no hay calificaciones
- EVALUACIÓN DE PUESTO DE GERENCIA (4) (1)_removed (2)Documento2 páginasEVALUACIÓN DE PUESTO DE GERENCIA (4) (1)_removed (2)León Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentación de Plan Turístico para ViajesDocumento16 páginasPresentación de Plan Turístico para ViajesLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- TRABAJO RETRIBUCIONDocumento3 páginasTRABAJO RETRIBUCIONLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentación de Plan Turístico para ViajesDocumento16 páginasPresentación de Plan Turístico para ViajesLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de Capaciotacion (1) 2 (2) - 1Documento1 páginaActividad de Capaciotacion (1) 2 (2) - 1León Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Contrato Tiempo DeterminadoDocumento4 páginasContrato Tiempo DeterminadoLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 4s-3-55Documento53 páginasUnidad 4s-3-55León Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- KevinAxelLeonOlvera (2) - CompressedDocumento1 páginaKevinAxelLeonOlvera (2) - CompressedLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- A.2.1. Investigación Documental - LeonOlveraEmilioGeovanyDocumento13 páginasA.2.1. Investigación Documental - LeonOlveraEmilioGeovanyLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Cabañas YelaagDocumento4 páginasCabañas YelaagLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Caso Practico 3Documento5 páginasCaso Practico 3León Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Importancia Del Comercio ElectronicoDocumento2 páginasImportancia Del Comercio ElectronicoLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Estudio Sobre El CaosDocumento1 páginaEstudio Sobre El CaosLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
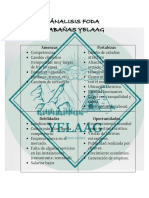
- Ánalisis FodaDocumento1 páginaÁnalisis FodaLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodo experimental en la búsqueda de un libro extraviadoDocumento2 páginasMetodo experimental en la búsqueda de un libro extraviadoLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Func AdtivaDocumento1 páginaFunc AdtivaLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuarocomparativodisolucinecsisinytransformacin 12Documento3 páginasCuarocomparativodisolucinecsisinytransformacin 12León Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de apuntesDocumento3 páginasDiseño de apuntesLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- El Dilema de Las Redes SocialesDocumento2 páginasEl Dilema de Las Redes SocialesLeón Olvera Emilio GAún no hay calificaciones
- Formato STSGDocumento1 páginaFormato STSGMaría Gabriela JeriaAún no hay calificaciones
- ES Presentaciones Multimedia Unidad 4Documento10 páginasES Presentaciones Multimedia Unidad 4Mar Ortiz GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tabla de Verbos de GriegoDocumento6 páginasTabla de Verbos de GriegoPtr Hugo Flores ChiriAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 5 The Gerund and InfinitiveDocumento4 páginasUnidad 5 The Gerund and InfinitiveAgustin RavenaAún no hay calificaciones
- 5eplc SV Es Ud09 RF PDFDocumento3 páginas5eplc SV Es Ud09 RF PDFMayte Avariento RogláAún no hay calificaciones
- Esquema Oración CompuestaDocumento1 páginaEsquema Oración CompuestaCarlos DarkAún no hay calificaciones
- English GrammarDocumento59 páginasEnglish GrammarSebastia Corbella Garrido100% (5)
- Ortografia P S ADocumento13 páginasOrtografia P S ALuis Alberto Mayorga JacobiAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Final Ingles III UnadDocumento17 páginasExamen Final Ingles III UnadJason Jones100% (2)
- Guia311 3BDocumento3 páginasGuia311 3BOscar Pardo PardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Aprendiendo TenekDocumento25 páginasAprendiendo TenekLorenzo Hernández GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lenguaje5 Promobre Articulo PreposicionDocumento13 páginasLenguaje5 Promobre Articulo PreposicionElvis Omar Atalaya Rafael0% (1)
- La Oración SimpleDocumento4 páginasLa Oración Simplea srAún no hay calificaciones
- Datos de La SilabaDocumento2 páginasDatos de La SilabaFrancisco SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Signos de PuntuaciónDocumento12 páginasSignos de PuntuaciónCesar ZuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Passive VoiceDocumento4 páginasPassive VoicemarcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Verbos, tiempos y funcionesDocumento7 páginasVerbos, tiempos y funcionespaula castilloAún no hay calificaciones
- SintDocumento34 páginasSintalvaronairaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecciones de ConversacionDocumento27 páginasLecciones de Conversacioncamiloco88Aún no hay calificaciones
- Futuro PerfectoDocumento2 páginasFuturo Perfectoaris42Aún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis sintagmático y reglas de reescrituraDocumento40 páginasAnálisis sintagmático y reglas de reescrituraCarlosAndrésMorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- MORFOLOGIADocumento27 páginasMORFOLOGIAlucasAún no hay calificaciones
- El Verbo UdepDocumento7 páginasEl Verbo UdepYdelsi San JuAún no hay calificaciones
- CyberTeachers - Program 3 PDFDocumento3 páginasCyberTeachers - Program 3 PDFJury UmeresAún no hay calificaciones
- Formativa Sustantivos AdjetivosDocumento6 páginasFormativa Sustantivos AdjetivosCarolina Vargas100% (1)
- 2 Bachillerato. Cuadro Usos de Se y Pronombres AtonosDocumento1 página2 Bachillerato. Cuadro Usos de Se y Pronombres AtonosRicardo BABARRO ANTOLINAún no hay calificaciones
- Español FinalDocumento10 páginasEspañol FinalTORRES MOLINA LEIDY SOFIAAún no hay calificaciones
- Concepto de Enunciado Caso y Declinacion FMM 2012 2013 (Unidad 2 4)Documento11 páginasConcepto de Enunciado Caso y Declinacion FMM 2012 2013 (Unidad 2 4)federicomezme0% (1)
- Guia 5 Oración y Sus ElementosDocumento5 páginasGuia 5 Oración y Sus ElementosGissell Pantoja MercadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Skin structure 40Documento2 páginasSkin structure 40Erica RajoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Yo Pude, ¡Tú Puedes!: Cómo tomar el control de tu bienestar emocional y convertirte en una persona imparable (edición revisada y expandida)De EverandYo Pude, ¡Tú Puedes!: Cómo tomar el control de tu bienestar emocional y convertirte en una persona imparable (edición revisada y expandida)Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (7)
- Recupera tu mente, reconquista tu vidaDe EverandRecupera tu mente, reconquista tu vidaCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (5)
- Influencia. La psicología de la persuasiónDe EverandInfluencia. La psicología de la persuasiónCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (14)
- ¿Por qué mis padres no me aman?: Empezando a sanarDe Everand¿Por qué mis padres no me aman?: Empezando a sanarCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (33)
- Psicología Oscura: Aprende técnicas de control mental y cómo analizar a las personas para influir en el comportamiento humano con manipulación encubierta, lenguaje corporal, PNL y persuasión subliminal.De EverandPsicología Oscura: Aprende técnicas de control mental y cómo analizar a las personas para influir en el comportamiento humano con manipulación encubierta, lenguaje corporal, PNL y persuasión subliminal.Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (56)
- Terapia cognitivo-conductual (TCC) y terapia dialéctico-conductual (TDC): Cómo la TCC, la TDC y la ACT pueden ayudarle a superar la ansiedad, la depresión, y los TOCSDe EverandTerapia cognitivo-conductual (TCC) y terapia dialéctico-conductual (TDC): Cómo la TCC, la TDC y la ACT pueden ayudarle a superar la ansiedad, la depresión, y los TOCSCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Ansiosos por nada: Menos preocupación, más pazDe EverandAnsiosos por nada: Menos preocupación, más pazCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (582)
- No desperdicies tus emociones: Cómo lo que sientes te acerca a Dios y le da gloriaDe EverandNo desperdicies tus emociones: Cómo lo que sientes te acerca a Dios y le da gloriaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (11)
- Resetea tu mente. Descubre de lo que eres capazDe EverandResetea tu mente. Descubre de lo que eres capazCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (196)
- El poder del optimismo: Herramientas para vivir de forma más positivaDe EverandEl poder del optimismo: Herramientas para vivir de forma más positivaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (15)
- Hazte amigo del miedo: Cómo superar la ansiedad social y avanzar hacia la vida que deseasDe EverandHazte amigo del miedo: Cómo superar la ansiedad social y avanzar hacia la vida que deseasCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (159)
- Tu cerebro emocional: Saca partido de lo que sientes y transforma tu vidaDe EverandTu cerebro emocional: Saca partido de lo que sientes y transforma tu vidaCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (2)
- Autolesiones: Cortarse como un modo de canalizar el dolor emocionalDe EverandAutolesiones: Cortarse como un modo de canalizar el dolor emocionalCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (2)
- Teoría polivagal práctica y terapiaDe EverandTeoría polivagal práctica y terapiaCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (4)
- Superar experiencias traumáticas: Una propuesta de intervención desde la Terapia Sistémica BreveDe EverandSuperar experiencias traumáticas: Una propuesta de intervención desde la Terapia Sistémica BreveCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (7)
- Disciplina con amor para adolescentes (Discipline With Love for Adolescents): Guía para llevarte bien con tu adolescente (A Guide for Getting Along Well With Your Adolescent)De EverandDisciplina con amor para adolescentes (Discipline With Love for Adolescents): Guía para llevarte bien con tu adolescente (A Guide for Getting Along Well With Your Adolescent)Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (10)
- Contra la ansiedad: Una guía completa para manejar emociones difícilesDe EverandContra la ansiedad: Una guía completa para manejar emociones difícilesCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (58)
- Cómo terminar lo que empiezas: El arte de perseverar, pasar a la acción, ejecutar los planes y tener disciplinaDe EverandCómo terminar lo que empiezas: El arte de perseverar, pasar a la acción, ejecutar los planes y tener disciplinaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (6)
- Cómo Conversar Con Cualquier Persona: Mejora tus habilidades sociales, desarrolla tu carisma, domina las conversaciones triviales y conviértete en una persona sociable para hacer verdaderos amigos y construir relaciones significativas.De EverandCómo Conversar Con Cualquier Persona: Mejora tus habilidades sociales, desarrolla tu carisma, domina las conversaciones triviales y conviértete en una persona sociable para hacer verdaderos amigos y construir relaciones significativas.Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (54)
- Terapia cognitiva: Conceptos básicos y profundizaciónDe EverandTerapia cognitiva: Conceptos básicos y profundizaciónCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Libro de Trabajo DE LA TERAPIA DE ACEPTACIÓN Y COMPROMISO (ACT). UNA GUÍA COMPLETA PARA CAMBIAR EL MINDFULNESS Y RECUPERARSE DE LA ANSIEDAD, LA DEPRESIÓN, LOS ATAQUES DE PÁNICO Y LA IRADe EverandLibro de Trabajo DE LA TERAPIA DE ACEPTACIÓN Y COMPROMISO (ACT). UNA GUÍA COMPLETA PARA CAMBIAR EL MINDFULNESS Y RECUPERARSE DE LA ANSIEDAD, LA DEPRESIÓN, LOS ATAQUES DE PÁNICO Y LA IRACalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (26)
- Disciplina Mental: Técnicas infalibles para lograr todo lo que te propones y eliminar la pereza y la procrastinación de tu vida para siempreDe EverandDisciplina Mental: Técnicas infalibles para lograr todo lo que te propones y eliminar la pereza y la procrastinación de tu vida para siempreCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (3)
- Psicología y trastornos de los niños en la edad evolutiva: Qué son y cómo funcionanDe EverandPsicología y trastornos de los niños en la edad evolutiva: Qué son y cómo funcionanCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Maneja tus emociones: Curso intensivo de mindfulness y regulación emocionalDe EverandManeja tus emociones: Curso intensivo de mindfulness y regulación emocionalCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (140)
- Clics contra la humanidad: Libertad y resistencia en la era de la distracción tecnológicaDe EverandClics contra la humanidad: Libertad y resistencia en la era de la distracción tecnológicaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (117)
- Una mente en calma: Técnicas para manejar los pensamientos intrusivosDe EverandUna mente en calma: Técnicas para manejar los pensamientos intrusivosCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (141)