0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
51 vistas4 páginasCircuitos Neurales en el Cerebro Humano
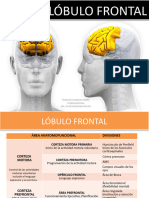
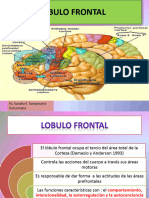
Este documento resume tres circuitos de los ganglios basales: el circuito esquelomotor, el circuito oculomotor y el circuito prefrontal. Cada circuito describe la ruta de las neuronas corticales desde las áreas motoras y asociativas de la corteza a través de los núcleos grises centrales y el talamo de regreso a la corteza. Los circuitos se relacionan con la ejecución de movimientos, la fijación ocular y las funciones mentales superiores respectivamente.
Cargado por
Yesenia Elizabeth Jiménez ZamoranoDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd
0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
51 vistas4 páginasCircuitos Neurales en el Cerebro Humano
Este documento resume tres circuitos de los ganglios basales: el circuito esquelomotor, el circuito oculomotor y el circuito prefrontal. Cada circuito describe la ruta de las neuronas corticales desde las áreas motoras y asociativas de la corteza a través de los núcleos grises centrales y el talamo de regreso a la corteza. Los circuitos se relacionan con la ejecución de movimientos, la fijación ocular y las funciones mentales superiores respectivamente.
Cargado por
Yesenia Elizabeth Jiménez ZamoranoDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd