Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Si385 s3 Mad Ui Design p1
Cargado por
Natanael David Soto SalisTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Si385 s3 Mad Ui Design p1
Cargado por
Natanael David Soto SalisCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
UI DESIGN
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas
UPC, 2021.
UI DESIGN
CONTENIDO
Objetivo de aprendizaje 3
Introducción 3
UI design elements 4
Conclusiones 13
Referencias 13
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 2
UI DESIGN
1. Objetivo de aprendizaje
Al finalizar la unidad de aprendizaje, el estudiante identifica con propiedad las necesidades de los
usuarios evidenciando sensibilidad y empatía.
2. Introducción
Recuerda qué se debe tomar en Como has visto anteriormente, UX es un concepto más
cuenta al momento de elaborar amplio que UI. UI se enfoca en aspectos como la estructura,
propuestas de UX. el diseño y los prototipos de interfaz de usuario.
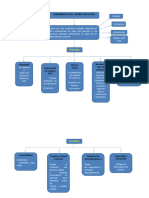
Understand the product
BUSINESS TECHNOLOGY
Marketing needs Available technology Understand the user
Financial needs
Research
UI/ UX Structure
UX Design UI
Prototype
USERS
User needs
User behaviors Testing and feedback
Recuerda que, se nutre de los resultados obtenidos de Information Architecture.
UX
Information architecture
Content inventory Content audit Navigation and mapping
UI
Wireframes
Low fidelity (sketches) High fidelity
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 3
UI DESIGN
3. UI design elements
El diseño está constituido por dos tipos de conceptos: design elements (elementos de diseño) y design
principles (principios de diseño).
The things that make up a design.
• Line • Size
Elements
• Shape • Texture
• Direction • Colour
Design
What we do to those elements.
Principles • Balance • Repetition
• Proximity • Contrast
• Alignment • Space
3.1. Elements of design
L o s e l e m e nto s d e l a
interfaz de usuario son
los componentes básicos
de todas las aplicaciones.
Son responsables de las
interacciones entre el usuario
y la aplicación. Son lo que
permiten una navegación de
usuario efectiva y datos de
entrada / salida, entre otras
funcionalidades.
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 4
UI DESIGN
ELEMENTS OF DESIGN
Quick reference sheet
LINE
A line is a mark between two pints. There are various types of lines, from straight to squiggly to curve
and more. Lines can be used for a wide range of purposes: stressing a word or phrase, connecting
content to one another, creating patterns and much more.
COLOR
Color is used to generate emotions, define importance, create visual interest and more. CMYK (cyan/
magenta/yellow/black) is subtractive; RBG (red/green/blue) is additive.
Some colors are warm and active (orange, red); some are cool and passive (blue, purple).
There are various color types (primary to analogous) and relationships (monochromatic to triad)
worth learning more about as well.
SIZE
Size is how small or large something is; is a small shirt vs. an extra large shirt, for example. Use size to
define importance, create visual interest in a design (via contrasting size), attract attention and more.
TEXTURE
Texture relates the to surface of an object; the look or feel of it. Concrete has a rough texture; drywall
has a smooth and subtle texture. Using texture in design is a great way to add depth and visual interest.
Printed material has actual, textile texture while screen material has implied texture.
SPACE
Space is the area around or between elements in a design. It can be used to separate or group
information. Use it effectively to: give the eye a rest; define importance; lead the eye through a
design and more.
VALUE
Value is how light or how dark an area looks. A gradient, shown above, is a great way to visualize value
– everything from dark to white, all the shades in-between, has a value. Use value to create depth
and light; to create a pattern; to lead the eye; or to emphasize.
SHAPE
Height + width = shape. We all learned basic shapes in grade school – triangles, squares, circles and
rectangles. Odd or lesser seen shapes can be used to attract attention.
There are three basic types of shape: geometric (triangles, squares, circles, etc.), natural (leaves,
animals, trees, peoples), and abstracted (icon, stylizations, graphic representations, etc.).
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 5
UI DESIGN
3.2. Principles of design
A menudo, puede
C.R.A.P. es un principio de
resultarte difícil idear
diseño desarrollado por
diseños que atraigan
Resulta de mucha Robin Patricia Williams,
de manera efectiva a tu
utilidad el conocer que significa contraste,
público objetivo y los
en detalle C.R.A.P. repetición, alineación y
impulsen a realizar la
proximidad.
acción deseada.
PRINCIPLES OF DESIGN
Quick reference poster
Constrast
Color Unique elements in a design should stand apart from one another. One way
to do this is to use contrast. Good contrast in a design – which can be achieved
Tone/Value using elements like color, tone, size, and more – allows the viewer’s eye to
Size/Shape flow naturally.
Direction To the left, you can see 4 ways to create contrast in your design.
Alignment
Proper alignment in a design means that every element in it is visually
connected to another element. Alignment allows for cohesiveness; nothing
feels out of place or disconnected when alignment has been handled well.
Repetition
Repetition breeds cohesiveness in a design. Once a design pattern has been
established- for example, a dotted border or a specific typographic styling
- repeat this pattern to establish consistency.
The short version?
Establish a style for each element in a design and use it on similar elements.
Proximity
Proximity allows for visual unity in a design. If two elements are related to
each other, they should be placed in close proximity to one another. Doing
so minimizes visual clutter, emphasizes organization, and increases viewer
comprehension.
Imagine how ridiculous it would be if the proximity icons on this graphic were
located on the other side of this document.
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 6
UI DESIGN
3.3. UI DESIGN ELEMENTS
Language (lenguaje)
Un conjunto de palabras puede
El nombre del product tiene aplicarse para establecer la
El lenguaje utilizado el poder de establecer el dirección del diseño. Los tonos
como herramienta estado anímico (mood) desde pueden variar según la intención
de diseño. el primer contacto en la y decisiones de la marca (estricto,
experiencia. científico, entretenido, divertido,
entre otros).
Clear Jargon-free, offers context
Concise Economical, frontloaded
Useful Direct next action
El ejemplo permite apreciar cómo las diferencias, en apariencia
sutiles, permiten lograr un efecto muy diferente.
Failure
“Wrong password.
Original An authentication error has ocurred. Try again. Recover
Ok password”.
OK
Sign-in error
Clear You entered an incorrect password.
Ok
C l e a r, Wrong password
concise Ok Decisiones adecuadas
sobre el lenguaje,
pensando en la claridad
C l e a r, y utilidad producen una
Wrong password experiencia mucho más
concise,
useful Try again Recover password satisfactoria.
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 7
UI DESIGN
Colour (color)
El color es un elemento El color puede ayudar a
El color también establece
de diseño poderoso, más mostrar estados como
el mood, dado que los
aún cuando se combina pasivo (inactive), activo
humanos responden de
con principios como el (touch / hover) o activado
forma emotiva y subjetiva.
contraste. (press / click).
Este gráfico resume los conceptos principales que constituyen la teoría del color.
COLOUR THEORY Analogous
CMYK Quick reference sheet Colours that are adjacent to each
other on the colour wheel.
Subtractive
Created with ink Red Red orange Yellow orange
Yellow Yellow green Green
When mix colours using
paint, or through the printing
process, we are using Complementary
subtractive colour method.
Colours opposite to each other
Subtractive colour mixing
on the colour wheel.
means that one begins with
white and ends with black; Blue green Red orange Yellow Violet
as one adds colour, the result Yellow
Blue Orange Red violet
gets darker and tends to black. green
Blue violet Yellow Green Red
orange
Triadic
Three colours spaced equally
apart on the colour wheel.
RGB Red Yellow Blue
Additive Blue violet Red orange Yellow green
Created with light Orange Green Violet
If we are working on a Yellow orange Blue green Red violet
computer, the colours we see
on the screen are created with
light using the additive colour Split complement
method. Additive colour
A colour and the two colours
mixing begins with black and next to its complement on the
ends with white; as more colour wheel.
colour is added, the result is
lighter and tends to white. Yellow Blue violet Red violet
Yellow green Violet Red
Green Red violet Red orange
Blue green Red Orange
Blue Red orange Yellow orange
Greyscale
Colour meanings Blue violet Orange Yellow
Intesity of black
Violet Yellow orange Yellow green
Red Intense, fire, blood, energy, love, passionate, strong.
Black Black Black
Red violet Royality, power, nobility, wealth, ambition, dignified, mysterious. Red violet Yellow Green
Blue Sky, sea, depth, stability, trust, masculine, tranquil. Monochromatic Red Yellow green Blue green
Green Nature, growth, fertility, freshness, healing, safety, money. Colours of a single hue Red orange Green Blue
Yellow Sunshine, joy, cheerfulness, intellect, energy, attention. Blue Blue Blue Orange Blue green Blue violet
Orange
Warm, stimulating, enthusiasm, happiness, success, creative,
Red Red Red Yellow orange Blue Violet
autumn.
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 8
UI DESIGN
El color puede producir emociones o establecer el mood o estado anímico que puede servir de
base al resto de componentes de la experiencia.
VISUAL IDENTITY
Deciding on key colors
Red Orange
Visceral, bold, courageous, energetic. Friendly, cheerful, confident, fun, vitality,
Stimulates apetite and the pituitary gland. lighter, shades appeal to upscale market.
Increases heart rate, creates urgency Signifies aggression. Creates call to action:
often seen in clearance, used for impulsive buy, sells, subscribe. Found in impulsive
shoppers. shoppers.
Yellow Black
Represents optimism, clarity, warmth, Prestige, serious, bold, classic, powerful.
positivity. Eyes see yellow first, great for Works well for expensive products.
POS display.
Green Blue
Balance, harmony, health, growth, Trustworthy, strong, dependable, secure,
freshness, deep greens are associated with preferred by men, popular in corporate
prestige. Used to relax in stores, associated because its productive and non-invasive.
with wealthy, has long been a symbol of
fertility.
Purple White
Wise, creative, imaginative, royalty, Suggets cleanliness and sterility, gives
lavender evoques nostalgia, sentimentality. a sense of refinement, indicates space
Used often in beauty, or anti-aging and openness, encourages the clearing
products, used to soothe or calm. of clutter, clarity, purity, simplicity,
sophistication, freshness.
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 9
UI DESIGN
Imagery (imágenes)
Las imágenes y el estilo
Pueden servir como Abarca formas,
de las mismas puede
contenido, mood y ilustraciones, fotografías,
colaborar en establecer
navegación en el contexto rendering en 3D, etc.
una línea de diseño o un
de UI design.
estilo.
Content marketing Marketing software
Advanced training in executing Marketing software training and
an effective inbound marketing certification for HupSpot Marketing
strategy. Platform users.
Buy for $15 Buy for $15
Sales software HubSpot design
HubSpot CRM and HubSpot Technical product training for
Sales software training and web designers using HubSpot
certification for HubSpot Sales COS, templates, and website
Platform users. pages.
Buy for $15 Buy for $15
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 10
UI DESIGN
Icons (íconos)
Icon vs Symbol:
Representación visual de algo Actúan como elementos de interfaz
relativamente realista (pictorial). representando ciertas acciones.
ICON
Pueden actuar como representación
No luce necesariamente como lo
instantánea de un producto, marca
que representa (non-pictorial).
SYMBOL o compañía.
Typography (tipografía)
La tipografía es un área que abarca varios conceptos y características que definen a la misma,
como baseline, x-height, etc.
La tipografía puede funcionar en muchas formas en el contexto de una app o website.
Parte del sistema
Contenido que Parte de la interfaz en de branding para
consumes. términos de botones o dar al producto una
etiquetas. identidad.
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 11
UI DESIGN
Recuerda que cada elemento tiene diversas características que pueden aportar
mucho para definir el diseño.
Los principios aplicados adecuadamente sobre los elementos, pueden producir diseños que
resulten en experiencias de usuario satisfactorias, útiles, fáciles para interactuar. Es importante
entender estos elementos y principios.
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 12
UI DESIGN
4. conclusiones
• En el UI design, los elementos y principios de
diseño son conceptos que aportan a definir
el diseño (los elementos) y pueden producir
experiencias satisfactorias, útiles y fáciles al
usuario en la interacción con la aplicación (los
principios).
Referencias
Para profundizar
• https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/topics/color-theory
Material producido por la Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas. UPC, 2021. 13
©️ UPC. Todos los derechos reservados
Autor: Ángel Velásquez Núñez
También podría gustarte
- Diseño de experiencias de usuario: Introducción prácticaDe EverandDiseño de experiencias de usuario: Introducción prácticaCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- DISEÑO ELECTRICO DE UN EDIFICIO RESIDENCIAL (Licdo. Nelson Gregorio Leal) I.U.T.C.Documento118 páginasDISEÑO ELECTRICO DE UN EDIFICIO RESIDENCIAL (Licdo. Nelson Gregorio Leal) I.U.T.C.NELSON GREGORIO LEAL100% (15)
- Análisis de RiesgosDocumento3 páginasAnálisis de RiesgosGabriel VazquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseno HumanoDocumento42 páginasDiseno HumanoRobert Rincon0% (1)
- Introducción Al Diseño UX/UI - DCUDocumento340 páginasIntroducción Al Diseño UX/UI - DCULiliana GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad IV - Analisis de Las Tecnicas para El Diseño de Procedimientos.Documento36 páginasUnidad IV - Analisis de Las Tecnicas para El Diseño de Procedimientos.camus126100% (1)
- Diseño UI Interfaz Del UsuarioDocumento21 páginasDiseño UI Interfaz Del UsuarioDiego CifuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- Planificación de Educación Artística 4to GradoDocumento3 páginasPlanificación de Educación Artística 4to GradoDaianaIbarrolaAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe 1.2 Areas de Aplicacion de La GraficacionDocumento10 páginasInforme 1.2 Areas de Aplicacion de La GraficacionLUIS DE LOS SANTOSAún no hay calificaciones
- Jesus Ruiz DurandDocumento6 páginasJesus Ruiz Durandrebeca73Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ux Ui PDFDocumento24 páginasUx Ui PDFAndres Camilo Lazaro RoaAún no hay calificaciones
- Capítulo Ii. Marco Teórico: Ii.1 El Diseño MecánicoDocumento11 páginasCapítulo Ii. Marco Teórico: Ii.1 El Diseño MecánicoOmar MéndezAún no hay calificaciones
- Dibujo Electrico y de RedesDocumento24 páginasDibujo Electrico y de RedesRenato Xavier Pusma SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Industria Del Vestido 2Documento21 páginasIndustria Del Vestido 2Hugo German Perez PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño InteractivoDocumento14 páginasDiseño Interactivoaprendiz alumnoAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 1 Interfaces y MultimediaDocumento90 páginasUnidad 1 Interfaces y MultimediaReny AlfonzoAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño Centrado en El UsuarioDocumento44 páginasDiseño Centrado en El UsuarioMaría Isabel KaliptsianAún no hay calificaciones
- Si385 s3 Mad Usability v1Documento16 páginasSi385 s3 Mad Usability v1Natanael David Soto SalisAún no hay calificaciones
- Si385 - S6 - Mad - Mobile Design and PatternsDocumento15 páginasSi385 - S6 - Mad - Mobile Design and PatternsAndre BernaolaAún no hay calificaciones
- EBSCO FullText 2023 09 30.en - EsDocumento8 páginasEBSCO FullText 2023 09 30.en - EsErick DWAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso Especializacion UX UIDocumento5 páginasCurso Especializacion UX UIiria gomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 1. Introducción Al Diseño UX - UI - DCUDocumento31 páginasClase 1. Introducción Al Diseño UX - UI - DCUCamila GilburtAún no hay calificaciones
- Todo JuntoDocumento1692 páginasTodo JuntoRocio AcuñaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 1Documento14 páginasClase 1Fernanda Villagrán EspinozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 1. Introducción Al Diseño UX - UI - DCUDocumento31 páginasClase 1. Introducción Al Diseño UX - UI - DCURomii MoránAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía UXDocumento24 páginasGuía UXAlma JiménezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 2.1Documento4 páginasActividad 2.1Isay SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 05-2021Documento38 páginasClase 05-202101-IS-HU-ERICK JEFRI CHAVEZ CANCHANYAAún no hay calificaciones
- Archivologocompendio 20211026121538Documento16 páginasArchivologocompendio 20211026121538Steven TusabesAún no hay calificaciones
- Contenidos TeóricosDocumento17 páginasContenidos TeóricosnatrodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 15 - Como en El Mundo Físico, Pero en La Pantalla PDFDocumento85 páginasClase 15 - Como en El Mundo Físico, Pero en La Pantalla PDFAlduAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 2.1Documento4 páginasActividad 2.1Isay SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- OpenClass DPUIWeb v3Documento24 páginasOpenClass DPUIWeb v3Elia NallelyAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuaderno de Trabajo - Fundamentos de UXDocumento54 páginasCuaderno de Trabajo - Fundamentos de UXLourdes ArbaizaAún no hay calificaciones
- Perfil UX:UI Designer IDMDocumento3 páginasPerfil UX:UI Designer IDMOscar SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen de Documentos de Diseño de Interfaces Web ISODocumento11 páginasResumen de Documentos de Diseño de Interfaces Web ISOMichael MejiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Saber U2 UXDocumento9 páginasSaber U2 UXFabian IbarraAún no hay calificaciones
- Cortes-Flores-Jonatan - Ejercicio 04Documento4 páginasCortes-Flores-Jonatan - Ejercicio 04JonatanAún no hay calificaciones
- Introducción de Diseños de Interfaces e Interacciones (En GRUPO)Documento11 páginasIntroducción de Diseños de Interfaces e Interacciones (En GRUPO)Nicolle RipamonteAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 1 - Fundamentos Del Diseño EducativoDocumento4 páginasActividad 1 - Fundamentos Del Diseño EducativoLizett DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño Digital Clase 03Documento19 páginasDiseño Digital Clase 03LindaMRaveloAún no hay calificaciones
- Int2 s3 ImprimibleDocumento17 páginasInt2 s3 Imprimiblegabriel garciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Interfaces de UsuarioDocumento8 páginasDiseño de Interfaces de UsuarioJorge Uriel Gorgonio CobaxinAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIDAD 4 UxDocumento16 páginasUNIDAD 4 UxAvid UrrAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 2.3Documento7 páginasActividad 2.3fernandofapsquashAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 1Documento156 páginasUnidad 1Anonymous ehKkEmVAún no hay calificaciones
- Que Es Experiencia de Usuario y Como La Construimos - ComprimidoDocumento49 páginasQue Es Experiencia de Usuario y Como La Construimos - ComprimidoCarlos Enrique Vilchez MedinaAún no hay calificaciones
- PDF Unidad 1Documento16 páginasPDF Unidad 1Keren MontasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 2. Elementos Del Diseño de La InteracciónDocumento42 páginasTema 2. Elementos Del Diseño de La InteracciónChriso AndressAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Interfaces Web Stefania TrisottiDocumento337 páginas3 Interfaces Web Stefania TrisottiMaria Carolina Urrego MontoyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño Ux/Ui Clase 32: Portfolio y Reporte UXDocumento53 páginasDiseño Ux/Ui Clase 32: Portfolio y Reporte UXLiliana GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Programación UX IUDocumento9 páginasProgramación UX IUOctavio Mamando AlanocaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia y Principios de AplicacionesDocumento19 páginasGuia y Principios de AplicacionesMario VegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Conceptual Diseño Interfaces PintoDocumento8 páginasGuia Conceptual Diseño Interfaces PintoGuilebaldo LópezAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana02 - S003Documento3 páginasSemana02 - S003BEYBI JOEL ESTEBAN VARGASAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana02 - S003Documento3 páginasSemana02 - S003BEYBI JOEL ESTEBAN VARGASAún no hay calificaciones
- Diesño de InterfazDocumento21 páginasDiesño de InterfazSuhaAún no hay calificaciones
- AP04 OA IntGraUsu PDFDocumento19 páginasAP04 OA IntGraUsu PDFYudy Johana Patiño RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 1Documento26 páginasUnidad 1marti muratoreAún no hay calificaciones
- InfografíaDocumento4 páginasInfografíaLisney GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 1 2023Documento26 páginasUnidad 1 2023micaelalopezsantAún no hay calificaciones
- Principios Del Diseño UIDocumento7 páginasPrincipios Del Diseño UIFabyAún no hay calificaciones
- Modelo de Diseño para Aplicaciones Web - Equipo 2 - Unidad I - Tema 1.3-1.4Documento21 páginasModelo de Diseño para Aplicaciones Web - Equipo 2 - Unidad I - Tema 1.3-1.4ArYaoi Cruz RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- FORMATO Experiencia de UsuarioDocumento2 páginasFORMATO Experiencia de UsuarioNicoAlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Isc - Interaccion - Humano - Computador - 2016-1 PDFDocumento2 páginasIsc - Interaccion - Humano - Computador - 2016-1 PDFJAIMEAún no hay calificaciones
- UXUIDocumento7 páginasUXUIRomina CostaAún no hay calificaciones
- T5.2. Principios de ComposiciónDocumento76 páginasT5.2. Principios de ComposiciónManuel Gértrudix Barrio100% (5)
- Material 9 - Unidad 3 PROGRAMACIÓN DE APLICACIONES WEBDocumento28 páginasMaterial 9 - Unidad 3 PROGRAMACIÓN DE APLICACIONES WEBvote fortyAún no hay calificaciones
- Si385 LMM Mod3 HTML Foundations v1Documento22 páginasSi385 LMM Mod3 HTML Foundations v1Natanael David Soto SalisAún no hay calificaciones
- Si385 LMM Desc Css Foundation v1Documento24 páginasSi385 LMM Desc Css Foundation v1Natanael David Soto SalisAún no hay calificaciones
- SI385 - S13 - MAD - Visualización de DatosDocumento20 páginasSI385 - S13 - MAD - Visualización de DatosNatanael David Soto SalisAún no hay calificaciones
- Si385 s03 LMM Inclusive Design v1Documento25 páginasSi385 s03 LMM Inclusive Design v1Natanael David Soto SalisAún no hay calificaciones
- Si385 s3 Mad Ia Foundation v1Documento19 páginasSi385 s3 Mad Ia Foundation v1Natanael David Soto SalisAún no hay calificaciones
- Norma COPC-2000 VMO 2.4 PDFDocumento100 páginasNorma COPC-2000 VMO 2.4 PDFedgarinho753642Aún no hay calificaciones
- "Dar El Tono" en El Diseño Corporativo - Norberto ChavesDocumento4 páginas"Dar El Tono" en El Diseño Corporativo - Norberto ChavesSol MilagrosAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Final - Caminos IDocumento52 páginasTrabajo Final - Caminos ILucessitha Tenazoa UriarteAún no hay calificaciones
- Viento Robot StructuralDocumento27 páginasViento Robot StructuralLuis Fernando RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- LCI Barcelona - Master Concept ArtDocumento3 páginasLCI Barcelona - Master Concept ArtLaia DmAún no hay calificaciones
- AE025 Estadística Inferencial II EQDocumento12 páginasAE025 Estadística Inferencial II EQPacoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sistema Metálico Tubest TPMS PDFDocumento107 páginasSistema Metálico Tubest TPMS PDFmario ulices rivera diazAún no hay calificaciones
- Principios Básicos en La Distribución en PlantaDocumento3 páginasPrincipios Básicos en La Distribución en PlantaAlex ARAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 1 IntroductoriaDocumento44 páginasClase 1 IntroductoriayersonAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen de Metrados Alan CariDocumento7 páginasResumen de Metrados Alan CariDW Walter McjAún no hay calificaciones
- Estudios Críticos Sobre Diseño de Información - Interactivo - 0Documento325 páginasEstudios Críticos Sobre Diseño de Información - Interactivo - 0Mateo Nielsen ObietaAún no hay calificaciones
- Equipamiento Urbano, Solucion de Instalaciones y Ambientes Escolares en Un Contexto RibereñoDocumento10 páginasEquipamiento Urbano, Solucion de Instalaciones y Ambientes Escolares en Un Contexto RibereñoJhonatan LoteroAún no hay calificaciones
- Abp-Colapso de Estructuras en ColombiaDocumento11 páginasAbp-Colapso de Estructuras en ColombiaVieris JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- B - 06 - Sistemas Digitales y Ep PDFDocumento2 páginasB - 06 - Sistemas Digitales y Ep PDFCastamereAún no hay calificaciones
- Diferencias Entre Cobit e ItilDocumento8 páginasDiferencias Entre Cobit e ItilLuis BeltranAún no hay calificaciones
- 5.diseño Conceptual - Generacion de Alternativas - 182Documento30 páginas5.diseño Conceptual - Generacion de Alternativas - 182Juan David Reyes GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lista de Utiles Primer GradoDocumento2 páginasLista de Utiles Primer GradoYover Amado AliagaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mejoramiento de La Via Carlos IzaguirreDocumento54 páginasMejoramiento de La Via Carlos IzaguirreCarlos Escobar100% (1)
- PMO (Oficina de Proyectos y Programas)Documento18 páginasPMO (Oficina de Proyectos y Programas)José Carlos Gamero LeónAún no hay calificaciones
- Componentes de La ComputadoraDocumento1 páginaComponentes de La ComputadoraYIMY JUAN FERNANDEZ CONTRERASAún no hay calificaciones
- Lucas Uno de Los Estudiantes Del Tercer Grado Está Utilizando La Metodología Design Thinking, enDocumento12 páginasLucas Uno de Los Estudiantes Del Tercer Grado Está Utilizando La Metodología Design Thinking, enMRAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia DMA DGrafico Dibujo Artistico 2016-17Documento12 páginasGuia DMA DGrafico Dibujo Artistico 2016-17Ariel Rios EscobedoAún no hay calificaciones