Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Examen
Cargado por
Jenny AariasTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Examen
Cargado por
Jenny AariasCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Se utiliza el comparativo para comparar dos cosas entre s. Hay varios tipos : 1.De superioridad.
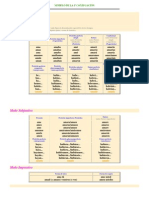
Por ejemplo : Tom is taller than Mary ( Tom es ms alto que Mary ) -Cuando el adjetivo solo tiene una slaba ,en el comparativo se le aade la terminacin -er. taller , shorter ... -Cuando un adjetivo de dos slabas termina en -y (happy) se sustituye por una -i latina (happier) - Cuando el adjetivo tiene dos o ms slabas se aade more antes del adjetivo. Ejemplo : Mary is more beautiful than Rachel ( Mary es ms guapa que Rachel ) 2. De igualdad. Su estructura es AS+ADJETIVO+AS. Tom is AS TALL AS Mary (Tom es tan alto como Mary ) 3.De inferioridad. Primer tipo--> Su estructura : (not)+AS o SO + adjetivo + AS Tom isn't as tall as Mary (Tom no es tan alto como Mary ) Tom isn't so tall as Mary ( Tom no es tan alto como Mary) Segundo tipo --> Su estructura : LESS+adjetivo+ THAN. Tom is less tall than Mary ( Tom es MENOS alto que Mary). Superlativo. 1.De superioridad.Se usa para referirnos al mejor de todos , al ms superior por as decirlo. 1 slaba --> se aade THE + la terminacin -EST al adjetivo. Tom is THE tallEST in his class (Tom es el ms alto de su clase). 1 o 2 slabas que terminan en -y --> se sustituye la y por una -i y se le sigue aadiendo THE + la terminacin -EST al adjetivo. Tom is the happiest in his class. (Tom es el ms feliz de su clase). 2 o ms slabas--> se aade THE MOST + el adjetivo sin variaciones. Tom is the most intelligent in his class (Tom es el ms inteligente de su clase). 2. De inferioridad. Se aade THE LEAST + el adjetivo sin variaciones. Tom is the least tall in his class. (Tom es el MENOS alto en su clase ). la forma comparativa y superlativa: aadiendo: -ER para el comparativo -EST para el superlativo ejemplo: una slaba de adejetivo: forma comparativa forma superlativa
tall............ taller.................... tallest old........... older................... oldest long........... longer............. longest comparative: mary is TALLER THAN max superlative: mary is THE TALLEST of all student comparative: max is OLDER THAN jhon superlative: og the three student, max is YHE OLDEST -COMPARATIVE: (comparas dos cosas) "The parents are angrier than the principal" utilizas THAN despues de el adjetivo Reglas: -cuando el adjetivo termina en "e" le agregas r ejm: fine finer -cuando es corto y termina en consonante vocal consonante duplicas la ultima consonante y agregas "er" ejm: big bigger -cuando termina en "y" la cambias por "i" y agregas "er" ejm: happy happier -cuando es muy larga agregas antes de la palabra "MORE" i el adjetivo queda igual ejm: expensive MORE EXPENSIVE .las demas que son cortas les agregas "er" ejm: cheap cheaper -SUPERLATIVE: (para elegir el mejor entre varios) "Wartress is the most atractive in the restaurant" Sustantivo is/are THE adjetivo complemento utilizas THE antes del adjetivo Reglas: son las mismas pero el "er" ahora es "est" y el MORE para adjetivos largos lo cambias por MOST hay adjetivos irregulares: adjetivo comparative superlative good better the best bad worse the worst much/many more the most little less the leaste
far farther the farthest little less the least Adjetivos de una sola slaba (cortos) que forman el comparativo aadiendo er, y el superlativo -est strong stronger - strongest tall taller - tallest late later - latest nice nicer - nicest short shorter shortest great greater greatest En estos tres, se dobla la consonante porque est precedida por una vocal corta: sad sadder - saddest fat fatter fattest big - bigger - biggest thin thinner - thinnest cheap cheaper cheapest large larger - largest dirty dirtier dirtiest (cuando hay una consonante antes de la y se cambia por i) ugly uglier ugliest (la misma regla anterior) stos tambin son de una sola slaba, pero son irregulares, no siguen la regla anterior: good better - best bad worse - worst late latter - last little smaller smallest (tamao) old older eldest (slo para personas) far further - furthest (lugar y tiempo) far farther - farthest (lugar) Adjetivos de ms de una slaba (largos): beautiful - more beautiful - most beautiful handsome more handsome most handsome difficult - more difficult - most difficult important - more important - most important expensive - more expensive - most expensive comfortable more comfortable most comfortable
uncomfartable more uncomfortable most uncomfortable careful more careful most careful interesting more interesting- most interesting ridiculous more ridiculous most ridiculous elegant more elegant most elegant generous more generous most generous sensitive more sensitive most sensitive sensible more sensible most sensible humble more humble most humble pretentious more pretentious most pretentious oraciones con superlartive They chose the darkest brown they could find. The dancer moved the most gracefully of all the performers. France is beautiful, but Chile is the most beautiful country in the world. Tokyo is one of the largest country in the world Mary's car is larger than Max's car. Mary's house is the tallest of all the houses on the block. Max is the wisest person I know. My dog is the biggest of all the dogs in the neighborhood. Mary is the fattest person I've ever seen. Forming Comparative and Superlative Adjectives One-syllable adjectives. Form the comparative and superlative forms of a one-syllable adjective by adding er for the comparative form and est for the superlative. One-Syllable Adjective Comparative Form Superlative Form tall taller tallest old older oldest long longer longest Mary is taller than Max. Mary is the tallest of all the students. Max is older than John. Of the three students, Max is the oldest. My hair is longer than your hair. Max's story is the longest story I've ever heard. If the one-syllable adjective ends with an e, just add r for the comparative form and st for the superlative form. One-Syllable Adjective with Final -e Comparative Form Superlative Form
large larger largest wise wiser wisest Mary's car is larger than Max's car. Mary's house is the tallest of all the houses on the block. Max is wiser than his brother. Max is the wisest person I know. If the one-syllable adjective ends with a single consonant with a vowel before it, double the consonant and add er for the comparative form; and double the consonant and add est for the superlative form. One-Syllable Adjective Ending with a Single Consonant with a Single Vowel before It Comparative Form Superlative Form big bigger biggest thin thinner thinnest fat fatter fattest My dog is bigger than your dog. My dog is the biggest of all the dogs in the neighborhood. Max is thinner than John. Of all the students in the class, Max is the thinnest. My mother is fatter than your mother. Mary is the fattest person I've ever seen. Two-syllable adjectives. With most two-syllable adjectives, you form the comparative with more and the superlative with most. Two-Syllable Adjective Comparative Form Superlative Form peaceful more peaceful most peaceful pleasant more pleasant most pleasant careful more careful most careful thoughtful more thoughtful most thoughtful This morning is more peaceful than yesterday morning. Max's house in the mountains is the most peaceful in the world. Max is more careful than Mike. Of all the taxi drivers, Jack is the most careful. Jill is more thoughtful than your sister. Mary is the most thoughtful person I've ever met.
If the two-syllable adjectives ends with y, change the y to i and add er for the comparative form. For the superlative form change the y to i and add est. Two-Syllable Adjective Ending with -y Comparative Form Superlative Form happy happier happiest angry angrier angriest busy busier busiest John is happier today than he was yesterday. John is the happiest boy in the world. Max is angrier than Mary. Of all of John's victims, Max is the angriest. Mary is busier than Max. Mary is the busiest person I've ever met. Two-syllable adjectives ending in er, -le, or ow take er and est to form the comparative and superlative forms. Two-Syllable Adjective Ending with -er, -le, or -ow Comparative Form Superlative Form narrow narrower narrowest gentle gentler gentlest The roads in this town are narrower than the roads in the city. This road is the narrowest of all the roads in California. Big dogs are gentler than small dogs. Of all the dogs in the world, English Mastiffs are the gentlest. Which: usado para cosas Who: usado para personas That: puede ser usado para ambos what = que wich = cual who= quien why: por que El will y el won't son parte del futuro simple: Afirmativo: Sujeto + will + verbo en presente simple + complemento Negativo: Sujeto + won't + verbo en presente simple + complemento Interrogativo: Will + sujeto + verbo en presente simple + complemento + ? Ambos going to y will se usan para hablar del futuro. 1. GOING TO: A. PLANES, COSAS ARREGLADAS DE ANTEMANO.
I am going to start university in September. VERB TO BE + GOING TO + VERBO INFINITIVO. B. PREDICCIONES CON EVIDENCIA. It is going to rain because the sky is dark. Negativo, se hace el negativo del verb to be. am not, is not, are not + going to + verbo infinitivo. He is not going to study. Interrogar: Verbo to be + persona + going to + verbo infinitivo. Are you going to come tomorrow? 2. WILL: A. PROMESAS. I will always love you. will + verbo en infinitivo sin TO. will + love B. DECISIONES EN EL MOMENTO EN QUE SE HABLA. - It's my birthday today. - Really? I'll buy you a present now. C. PREDICCIONES SIN EVIDENCIA. I think she will be here in an hour or two. Yo pienso, nada me lo indica. La prediccin est basada en lo que yo creo, no en evidencias. D. OFRECIMIENTOS. - I can't carry this bag, it's too heavy. - Don't worry, I'll carry it for you. Cuando dice 'll, es la contraccin de will. Para formar el negativo, se usa won't en lugar de will. They won't come. Para interrogar, primero Will, luego la persona, luego el verbo en infinitivo. Will they come?
También podría gustarte
- ExamenDocumento7 páginasExamenJenny AariasAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase Sartas de PerforaciondosDocumento42 páginasClase Sartas de PerforaciondosRobinson Romero TiqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Plane Ac I On ProducDocumento125 páginasPlane Ac I On ProducfralnovaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tipos de Terminacion de PozosDocumento50 páginasTipos de Terminacion de PozosGaabrieLla C-tAún no hay calificaciones
- Expo InstrumentacionDocumento14 páginasExpo InstrumentacionJenny AariasAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 5. Elementos Finales de ControlDocumento0 páginasCapitulo 5. Elementos Finales de ControlHeller AriasAún no hay calificaciones
- Estructrura ProtocoloDocumento3 páginasEstructrura ProtocoloLuis Antonio Martinez BlasAún no hay calificaciones
- Estructrura ProtocoloDocumento3 páginasEstructrura ProtocoloLuis Antonio Martinez BlasAún no hay calificaciones
- Estructrura ProtocoloDocumento3 páginasEstructrura ProtocoloLuis Antonio Martinez BlasAún no hay calificaciones
- Estructrura ProtocoloDocumento3 páginasEstructrura ProtocoloLuis Antonio Martinez BlasAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Valvulas AisladorasDocumento5 páginas2 Valvulas AisladorasJenny AariasAún no hay calificaciones
- Estructrura ProtocoloDocumento3 páginasEstructrura ProtocoloLuis Antonio Martinez BlasAún no hay calificaciones
- IntroducciónDocumento4 páginasIntroducciónJenny AariasAún no hay calificaciones
- Era Mesozoica Presentacion 2003Documento40 páginasEra Mesozoica Presentacion 2003Pedro Rodriguez MazaAún no hay calificaciones
- Era Cenozoica ExpoDocumento5 páginasEra Cenozoica ExpoJenny AariasAún no hay calificaciones
- Actuadores HidráulicosDocumento16 páginasActuadores Hidráulicostio_louisAún no hay calificaciones
- Valvulas de ControlDocumento8 páginasValvulas de ControlJulitza MierezAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo Iii - Separación de Los Fluidos ProducidosDocumento108 páginasCapitulo Iii - Separación de Los Fluidos ProducidosLucas LunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taxonomia VerbosDocumento7 páginasTaxonomia Verbosheankimaga100% (1)
- Sintaxis QuechuaDocumento26 páginasSintaxis QuechuaYessy GM0% (1)
- La GramáticaDocumento26 páginasLa GramáticaMarta FonsecaAún no hay calificaciones
- Categorías Gramaticales VariablesDocumento15 páginasCategorías Gramaticales VariablesRafaAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 9 LatinDocumento5 páginasUnidad 9 LatinCecilia Garcia0% (1)
- 3ESO TEMA6 Sin CelestinaDocumento12 páginas3ESO TEMA6 Sin CelestinaRaúl RubioAún no hay calificaciones
- Apretar ColarDocumento2 páginasApretar ColarRocío EgeaAún no hay calificaciones
- II - El Uso Adecuado de Las LetrasDocumento7 páginasII - El Uso Adecuado de Las LetrasCarlos Enrique Vilca CarreñoAún no hay calificaciones
- T.3 CASTellano Anaya. SolucionarioDocumento8 páginasT.3 CASTellano Anaya. Solucionariodayana100% (2)
- Pages From El Habla de Mi Tierra-1Documento670 páginasPages From El Habla de Mi Tierra-1kinjatt33% (12)
- CUESTIONARIODocumento6 páginasCUESTIONARIOFrancisco Javier Galera FernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ser y EstarDocumento10 páginasSer y EstarJoe RicksAún no hay calificaciones
- Formas Del DiscursoDocumento16 páginasFormas Del DiscursoIreri FiguritasAún no hay calificaciones
- Iii Bim - Leng - Guia Nº7 - Complemento Predicado Sub-ObjDocumento3 páginasIii Bim - Leng - Guia Nº7 - Complemento Predicado Sub-ObjRicardo Rodríguez0% (1)
- Conditional Sentences ChartDocumento2 páginasConditional Sentences ChartGabriela GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- EnglishDocumento9 páginasEnglishReMus GonAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen de Verbos y Sus FormasDocumento4 páginasResumen de Verbos y Sus FormasJuan de BiasiAún no hay calificaciones
- Gramática Del Chino MandarínDocumento6 páginasGramática Del Chino MandarínGilberto ManhattanAún no hay calificaciones
- SolecismoDocumento16 páginasSolecismoDomingoMontero100% (2)
- Uso de La C, S y ZDocumento8 páginasUso de La C, S y ZMaria Agustina Galan FiestasAún no hay calificaciones
- Identifica El Tipo de Arrador Presente en Los Siguientes FragmentosDocumento5 páginasIdentifica El Tipo de Arrador Presente en Los Siguientes FragmentosAnonymous T9kpBSXodVAún no hay calificaciones
- Enunciado y Oración en La Nueva GramáticaDocumento2 páginasEnunciado y Oración en La Nueva GramáticaFederico Lepre67% (3)
- Spanish IGCSE VocabDocumento18 páginasSpanish IGCSE VocabJason LeeAún no hay calificaciones
- Diccionario de LingüísticaDocumento21 páginasDiccionario de LingüísticaEduard Antonio Caballero100% (1)
- 11-Derivación de Verbos en GuajiroDocumento13 páginas11-Derivación de Verbos en GuajiroLuis Alfredo Diaz OrtegaAún no hay calificaciones
- ¿Cómo Empezar A Redactar La Tesina, Tesis o CasoDocumento25 páginas¿Cómo Empezar A Redactar La Tesina, Tesis o CasoJuan Carlos RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Dosificación Comunicación y LenguajeDocumento15 páginasDosificación Comunicación y LenguajeAnonymous NmpTZlvgMAún no hay calificaciones
- Rubrica Dictado SignosDocumento1 páginaRubrica Dictado SignosPauln Pareja100% (9)
- Mi Guia Taller de Redaccion3Documento165 páginasMi Guia Taller de Redaccion3David Rodriguez100% (1)
- Acciones Estados y ProcesosDocumento16 páginasAcciones Estados y ProcesosOctavio AlonsoAún no hay calificaciones