Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Las Oraciones Subordinadas Relativas TEORIA
Cargado por
Sylvia RodríguezDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Las Oraciones Subordinadas Relativas TEORIA
Cargado por
Sylvia RodríguezCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Las oraciones subordinadas relativas en ingls
Las subordinadas relativas (relative clauses) tienen como funcin aportar informacin suplementaria sobre una persona, un objeto, un sitio, o una situacin. Estas oraciones dependen siempre de un sustantivo o de un pronombre y estn introducidas por pronombres relativos (who, which, whose, that) u otras conjunciones como when o where. Particularidades de estas subordinadas. A. Tipos de conectores relativos Los pronombres relativos 1. who se utiliza para personas: The man who lives on the second floor is a doctor. 2. which se utiliza para objetos / animales: The book which you gave me is interesting. 3. that puede sustituir tanto a who como a which en un registro ms informal: The man that lives //The book that you gave me is Los pronombres relativos tienen una doble funcin: por un lado sustituyen al nombre que les precede (en los ejemplos anteriores, man y book) y por otro lado, tienen una funcin en la frase relativa: The man who lives . (who = sujeto de la frase relativa) // The book which you gave me (which = complemento de objeto directo de la frase relativa) Importante: Who, which y that se pueden omitir cuando tienen funcin de complemento en la frase relativa. Cuando el pronombre relativo es el sujeto de la frase relativa, tiene que ser expresado. Por lo tanto, podemos decir: The book you gave me is interesting. Pero no podemos decir: *The man lives on the second floor is a doctor. 4. whom puede sustituir a who cuando este cumple una funcin de complemento en la frase relativa. Tambin puede ser omitido: The man (who / whom) you saw is my brother Importante: whom es la nica opcin cuando el pronombre va precedido por una preposicin. The man to whom you spoke is my brother. (Y no: The man to who you spoke )
5. whose es un pronombre relativo posesivo que se utiliza siempre en conjunto con un segundo nombre ( el objeto de la posesin). Whose no se puede ometer. I saw the boy whose father is a doctor. (cuyo padre.) 6. which puede tambin tener como referente a toda una frase: He got married again a year later, which surprised everybody. Importante: what no es un pronombre relativo, por lo tanto no tiene un sustantivo como antecedente: This is what she told me. (what = the thing which) Asi qu frases como *The only thing what keeps me awake is coffee no son correctas. Las conjunciones relativas 1. where tiene como antecedente a un sustantivo que hace referencia a un sitio: Its the place where I was born. 2. when tiene como antecedente a un sustantivo que hace referencia a una nocin temporal: The year when I was born was very cold. 3. why tiene como antecedente el sustantivo reason: The reason why I am here is to convince you to come to the party. Where, when y why pueden ser sustituidos por la construccin preposition + which: Its the place in which I was born. // The year in which I was born//The reason for which I am here B Tipos de subordinadas relativas Existen dos grandes tipos de frases relativas:
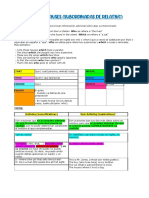
Defining relative clauses la informacin que aportan es esencial:
People who do exercise live longer.
Non-defining relative clauses la informacin que aportan no es esencial. Este tipo de relativas estan siempre marcadas por comas. Recordad tambin que en las relativas non-defining los pronombres relativos no se pueden omitir, aunque tengan una funcin de complemento en la subordinada, y tampoco se pueden intercambiar con that:
I gave him a glass of water, which he drank very quickly. (Y no: *I gave him a glass of water, he drank very quickly.) Nota final: Cuando el verbo de la frase relativa tiene una preposicin obligatoria, esta preposicin puede acompaar el pronombre relativo en posicin inicial de la frase relativa, o bien acompaar el verbo, en posicin final de la frase relativa: 1. The book in which you are interested is on the shelf. 2. The book which you are interested in is on the shelf. La primera construccin es habitual en un registro ms formal, mientras que las construcciones con la preposicin en posicin final son ms coloquiales.
También podría gustarte
- Aprende los pronombres en inglés: Aprende categorías de la gramática en inglés, #3De EverandAprende los pronombres en inglés: Aprende categorías de la gramática en inglés, #3Aún no hay calificaciones
- Relative ClausesDocumento4 páginasRelative Clausescorreoparaelcol7862Aún no hay calificaciones
- Los Adverbios en Inglés: ¿Dónde se colocan?De EverandLos Adverbios en Inglés: ¿Dónde se colocan?Calificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Defining Relative Clauses1Documento29 páginasDefining Relative Clauses1Le DracAún no hay calificaciones
- Gramática Inglesa A2-B1: Domina la gramática de inglés, #3De EverandGramática Inglesa A2-B1: Domina la gramática de inglés, #3Aún no hay calificaciones
- Relative ClausesDocumento8 páginasRelative ClausesLuiAún no hay calificaciones
- Gramática Inglesa B1: Domina la gramática de inglés, #4De EverandGramática Inglesa B1: Domina la gramática de inglés, #4Aún no hay calificaciones
- Defining Relative Clauses1 PDFDocumento29 páginasDefining Relative Clauses1 PDFshdfibbdsiAún no hay calificaciones
- UNIDAD 17 InglesDocumento15 páginasUNIDAD 17 InglesRafael Ruiz Diaz SaggiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Uso Del Relativo QueDocumento3 páginasUso Del Relativo Quefr9595Aún no hay calificaciones
- Relative Clauses TheoryDocumento7 páginasRelative Clauses TheoryLalyFernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Uso de Es en AlemanDocumento13 páginasUso de Es en AlemanAnonymous 0oQHdzb7pv100% (1)
- Relative Clauses - 2 PDFDocumento7 páginasRelative Clauses - 2 PDFtrejanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sistemas Temas V Expresiones de Causa y Tema Vi Clausulas Relativas ContractadasDocumento7 páginasSistemas Temas V Expresiones de Causa y Tema Vi Clausulas Relativas Contractadasgeomar cedeñoAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia de Ingles 3era EvaluacionDocumento5 páginasGuia de Ingles 3era EvaluacionOriana LópezAún no hay calificaciones
- Oraciones SubordinadasDocumento4 páginasOraciones SubordinadasFátima CaroAún no hay calificaciones
- RelativesDocumento3 páginasRelativesbpxamzAún no hay calificaciones
- 15 M.Seco (Cap. 9, 13)Documento12 páginas15 M.Seco (Cap. 9, 13)Florencia SouzaAún no hay calificaciones
- PronombresDocumento5 páginasPronombresYeremy BussinesAún no hay calificaciones
- Relatives Theory.Documento3 páginasRelatives Theory.Carla Carvajal muñizAún no hay calificaciones
- 16 - Subordinadas de Relativo - IIDocumento9 páginas16 - Subordinadas de Relativo - IImartin rrAún no hay calificaciones
- Clausulas RelativasDocumento9 páginasClausulas RelativasARÓM CHINCHAYAún no hay calificaciones
- Oración SubordinadaDocumento6 páginasOración SubordinadaÁngel MancillaAún no hay calificaciones
- AB. Sujeto. T y Práctica CON SOLUCIONESDocumento12 páginasAB. Sujeto. T y Práctica CON SOLUCIONESantoniolopez_32Aún no hay calificaciones
- Oraciones de RelativoDocumento5 páginasOraciones de Relativosara carmonaAún no hay calificaciones
- AA. Sujeto. T y Práctica SIN SOLUCIONESDocumento13 páginasAA. Sujeto. T y Práctica SIN SOLUCIONESantoniolopez_32Aún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 5 - La Oración Simple - FuncionalidadDocumento10 páginasUnidad 5 - La Oración Simple - FuncionalidadRosaBonilloNavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Partes de La OracionDocumento6 páginasPartes de La Oracionraul.marca1812Aún no hay calificaciones
- Relative ClausesDocumento2 páginasRelative Clausesnuria02650vrAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso Gratis Ingles Euroresidentes Com PDFDocumento5 páginasCurso Gratis Ingles Euroresidentes Com PDFRaúl SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Oraciones Subordinadas AdjetivasDocumento9 páginasOraciones Subordinadas Adjetivasalfredo luisAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 18 - Las Oraciones Del Relativo (Relative Clauses)Documento22 páginasTema 18 - Las Oraciones Del Relativo (Relative Clauses)Alejandro JiménezAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjetivos Pronombres Blanco y NegroDocumento6 páginasAdjetivos Pronombres Blanco y NegroOscar PachecoAún no hay calificaciones
- Oraciones de Relativo EspecificativasDocumento8 páginasOraciones de Relativo EspecificativasAnna Karen MojicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Pronombres InglesDocumento6 páginasPronombres InglesIvàn Carbonell FausAún no hay calificaciones
- Las Funciones Del SustantivoDocumento5 páginasLas Funciones Del Sustantivomafaldo100% (2)
- Tipos de Oraciones Simples Según El PredicadoDocumento4 páginasTipos de Oraciones Simples Según El PredicadoEliana AriasAún no hay calificaciones
- Usos de SEDocumento3 páginasUsos de SEJuan Párraga MarsillaAún no hay calificaciones
- InglesDocumento8 páginasInglesAlee'x D' MxDeroAún no hay calificaciones
- ES-relative ClausesDocumento4 páginasES-relative ClausesMario LucasAún no hay calificaciones
- Inglés Relative ClausesDocumento5 páginasInglés Relative ClausesGabriela GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sujeto y PredicadoDocumento3 páginasSujeto y PredicadoAbg María Solis de Pérez100% (1)
- Las Oraciones SubordinadasDocumento11 páginasLas Oraciones Subordinadasandoni_losada3501Aún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones Del RelativoDocumento2 páginasFunciones Del Relativopeque07Aún no hay calificaciones
- Guìa de Estudio de La Oración CompuestaDocumento6 páginasGuìa de Estudio de La Oración Compuestawilyanny franjulAún no hay calificaciones
- Gramatica Open EnglishDocumento60 páginasGramatica Open EnglishFranklyn ParadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guias de Lectura - Hasta Teorico 3Documento9 páginasGuias de Lectura - Hasta Teorico 3Lautaro ParedesAún no hay calificaciones
- Cap2 InglesDocumento65 páginasCap2 InglesbeatrizAún no hay calificaciones
- Gramatica EnglishDocumento74 páginasGramatica EnglishJulián FdzAún no hay calificaciones
- Let 113 Unidad VII Material de LecturaDocumento7 páginasLet 113 Unidad VII Material de Lecturayeyfry de la rosaAún no hay calificaciones
- 9 - AdjetivosDocumento10 páginas9 - Adjetivosmartin rrAún no hay calificaciones
- Evirtual Taller No 6 Grado 8Documento2 páginasEvirtual Taller No 6 Grado 8Vivy CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Acordeón de Forma SeDocumento3 páginasAcordeón de Forma SeOasis 141Aún no hay calificaciones
- Los AdjetivosDocumento12 páginasLos Adjetivossasany culmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoría Completa de Oraciones ComplejasDocumento4 páginasTeoría Completa de Oraciones ComplejasLaura SantiagoAún no hay calificaciones
- Oraciones Segun Naturaleza PredicadoDocumento2 páginasOraciones Segun Naturaleza PredicadomariaAún no hay calificaciones
- Relative ClausesDocumento19 páginasRelative ClausesCoriangela Mercedes Cumarin SolorzanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Pronombres RelativosDocumento4 páginasPronombres RelativosGustavo Edenilson Ramos JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- InglesDocumento10 páginasInglesVictor TikisaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Las Oraciones Subordinadas y Sus TiposDocumento5 páginasLas Oraciones Subordinadas y Sus TiposMaría DimasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ingles 4Documento24 páginasIngles 4Sylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Main Uses of The Verbs DO and MakeDocumento8 páginasMain Uses of The Verbs DO and MakeSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- The Earth Has Got Three Main PartsDocumento1 páginaThe Earth Has Got Three Main PartsSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplo de Entrevista de TrabajoDocumento10 páginasEjemplo de Entrevista de TrabajoSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Las Diferencias Entre Do y MakeDocumento3 páginasLas Diferencias Entre Do y MakeSylvia Rodríguez100% (1)
- Traducción 1º BTO Top Marks (1-3) 09Documento1 páginaTraducción 1º BTO Top Marks (1-3) 09Sylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Anexo Boda PDFDocumento2 páginasAnexo Boda PDFSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Bares de Intercambio LingüisticoDocumento1 páginaBares de Intercambio LingüisticoSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Describe Que Están Haciendo Usando El Verbo DadoDocumento5 páginasDescribe Que Están Haciendo Usando El Verbo DadoEnglish StationAún no hay calificaciones
- Presente Simple o Continuo - TheORY and EXERCISESDocumento4 páginasPresente Simple o Continuo - TheORY and EXERCISESSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Pasado Simple y Continuo - TheORY and EXERCISESDocumento4 páginasPasado Simple y Continuo - TheORY and EXERCISESSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Futuro Simple, Progresivo, PerfectoDocumento6 páginasFuturo Simple, Progresivo, PerfectoSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Futuro Simple, Progresivo, PerfectoDocumento6 páginasFuturo Simple, Progresivo, PerfectoSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Futuro Simple, Progresivo, PerfectoDocumento6 páginasFuturo Simple, Progresivo, PerfectoSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Question TagsDocumento7 páginasQuestion TagsSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Pre Posicion EsDocumento3 páginasPre Posicion EsSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- The Earth Has Got Three Main PartsDocumento1 páginaThe Earth Has Got Three Main PartsSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Have ToDocumento2 páginasHave ToSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Futuro Simple, Progresivo, PerfectoDocumento6 páginasFuturo Simple, Progresivo, PerfectoSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Describe Que Están Haciendo Usando El Verbo DadoDocumento5 páginasDescribe Que Están Haciendo Usando El Verbo DadoEnglish StationAún no hay calificaciones
- Tipos de TextosDocumento2 páginasTipos de TextosSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- La Fecha en InglésDocumento1 páginaLa Fecha en InglésSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Programacion Sciences Thirdcycle AndaluciaDocumento158 páginasProgramacion Sciences Thirdcycle AndaluciaSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 3AA - Evaluación Del AprendizajeDocumento4 páginasActividad 3AA - Evaluación Del AprendizajeSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- MacarioDocumento7 páginasMacarioSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Destrezas Receptivas y Destrezas Productivas Pablo Dominguez. Campus VirtualDocumento201 páginasDestrezas Receptivas y Destrezas Productivas Pablo Dominguez. Campus VirtualAlexandra-Ioana ȘvețAún no hay calificaciones
- Cómo Contestar El Teléfono en InglésDocumento5 páginasCómo Contestar El Teléfono en InglésSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Conversaciones Telefónicas en Inglés Entre Amigos 2Documento4 páginasConversaciones Telefónicas en Inglés Entre Amigos 2Sylvia Rodríguez100% (1)
- Programacià n+EIM2 2edition Revisiã n+FINAL+22june10Documento97 páginasProgramacià n+EIM2 2edition Revisiã n+FINAL+22june10Sylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- El Aprendizaje de Lenguas Asistido Por OrdenadorDocumento7 páginasEl Aprendizaje de Lenguas Asistido Por OrdenadorSylvia RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones