Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
EJERCICIOS de La Practica #2 - Calculo Diferencial-Nivelación-2021-0-Derivadas
Cargado por
Richar Sevillano BejaranoTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
EJERCICIOS de La Practica #2 - Calculo Diferencial-Nivelación-2021-0-Derivadas
Cargado por
Richar Sevillano BejaranoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
FACULTAD DE LA FIZAB
ESCUELA PROFESIONAL DE AGRONEGOCIOS
DERIVADAS Y APLICACIONES DE LA DERIVADA
2021-0
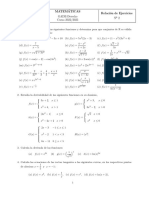
I. Calcular las siguientes derivadas, usando la definición.
2x + 3 k) f (x ) = cos x
f (x ) =
a) 3x −2 3 + 2x
f (x )=
1 l) 3 − 2x
f (x ) =
b) √x + 2 1
f (x ) =
c) f (x ) =x √ x + 1 m) √ 6x +3
n) f ( x )=(2 x−5)(2 x +3)
d) f (x ) = √4 − x 2
3 o) f ( x )=tan 2 x
e) f (x ) = √2 x + 3
x
p) f ( x )=
f) f (x )= √3 − 2 x 7 x−1
2
x −1 q) f ( x )=e2 x−5
f (x ) = 2
g) x +1 r) f ( x )=Sen2 x
1
f (x ) = s) f ( x )=x 3−5 x
h) √ 3x
t) f ( x )=x Sen 3 x
x3 + 1
f (x ) = x 2−9
i) x u) f ( x )=
a x−2
f (x ) = √ax +
j) √ ax v) f ( x )=x 2 e 4 x
II. f ( x )=(x 2+ 3 x )Calcular la derivada en el punto indicado usando la definición
a) f (x )= √ 1 + 9x , a = 7 d) f (x ) = √ x 2 − 4 , a = 5
1 2
f (x ) = , a= 3 f (x ) = −1 , a=4
b) √ 2x + 3 e) √x
f (x ) = ( x2 + x)2 , a = 2 x +3
c) f (x ) = , a=2
f) 2x −5
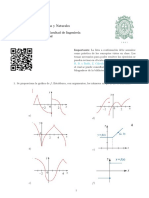
III. Determinar, cuáles de las funciones siguientes son derivables en los números dados
por a
Lic. MsC OSCAR ESTEBAN GARCIA GRADOS
a) d)
f (x)=¿ { √ x , x ≤ 4 ¿ ¿¿ f (x)=¿ { x2 −4 , x < 2 ¿ ¿¿
b)
e)
f (x)=¿ { √ 1−x , x <1 ¿ ¿¿ f (x)=¿ { x2 , x <−1 ¿ ¿¿
c) 2 x−1 , si x <3
f) f ( x )={ 8 – x , si 3 ≤ x
a=3
f (x)=¿ { √ |x| , x < 1 ¿ ¿¿
IV. Usando las reglas de derivación calcular la derivada de las siguientes
funciones:
4
1. f (x )=x −3 x 2. f (t )=√ t+5
r3+ 4 r
f (r )= 5
3. r +2 4. f (x )=( x −8 x )(2 x−1)
sen r
3 4 f (r )=
5. f (t )=√ t −3t (5 t+2 ) 6. 2 r3
5 2
7. f (x )=( x −8 x )tg( x ) 8. f (t )=sen t
2 5 5 3 6
9. f (s)=cos (7 s +4 s ) 10. f (x )=( x + 9 x )
5 3 1/6
11. f (x )=( x −2 x ) 12.
3
f (x )=ln( x +9 x )
5
5 3
13. f (t )=sen (t )ln(t −t ) 14. f ( y)=e ( y −8 y)
7 f (s )=
√ s−5 s6
15. f (x )=e( x +6 x ) sen ( x2 ) 16. s 7 −9 s
17. f (x )=x ( x5 −2 x 3 ) 18. f (x )=ln( x +9 x 3 )2 x−3
5
19. f (t )=cos(t )ln (t 5 −t 3 ) 20. f ( y )=xe( y −8 y )
Lic. MsC OSCAR ESTEBAN GARCIA GRADOS
7
21. f (x )=e( x +6 x )
sec(x 2 ) 22.
4 s−3 √ s−5 s6
f (s )=
s7 −9 s
V. Usando las reglas de derivación calcular la derivada de las siguientes
funciones:
2
1) y= √ x 2 + √ x 2 + √ x 2x
17) y=e
x
y= (2 x + 1)
3
2) √ a2 − x2 18) y=e
3 2 x3
y=
√ x 3 + 3x 2 19) y=3
3) x 2
20) y = (2x 3 )3 x
4) y = (3 x 2 + 4 x + 8) √ x − 1
21)
2
x
y= − 8x+ 7 5
5) 4 y = ( 3 x 4 − x 2 )3 x
6) y = ( 3 x 4 − 4 x 2 )3 22)
y = 3 x 2 (−2 x3 + 2 x −3) y = 4 x3 + 7 x2 + 3 x − 1
7)
23)
2
8) y = Sen 2 x
y = 2x 5 − 6 x 4 + 7 x 3 − 2 x 2 + 9x − 4
3
9) y = Cos 3 x
24)
2
10) y = Tg ( x +1) y = 5x 20 − 3 x10 + 2 x 5 − 7 x 3
11) y = Ctg 3 x2 25)
12) y = Sec (2 x − 3)3 y =|(x2 + 3x) (x 2 −3x + 5)|
13) 7x
y=
26) Senx
3
y = Ctg ( 2 x −1)
1− x
y = Csc ( 4 x + 1) y=
14) 1 + x2
27)
4
15) y = Ln 3 x y = √1 + 7x
28)
16) y = Ln (2x 2 −3)
Lic. MsC OSCAR ESTEBAN GARCIA GRADOS
1 45)
y=
29) √ 2 x +3 y = arc.sen ( Ln x )
2
30) y = Sen (2x + 1) 46)
31) y = √ x 2 − 11 y = arc.tg √ 3 x 2 − 2
cos x
47) y= x
32)
y = Ln ( 1+1−xx ) 48)
x +3
y= 2 3
33) 2x − 9 y = Sen ( 3 x2 ) − Sen (5 x2 )
3 4
34) y = Ln ( x 2 + x) y=
sen x + cos x
49) sen x − cos x
2
x +5
y= 2 50)
35) x −1
36) y = Ln (sen x ) 1 − sen x
37) y = Cos 5 x 4
y = Ln
√ 1 + sen x
51)
38) 3 4
x
f (t )=√ t −3t (5 t+2 )
y = Sen ( 2 x 3 + e )
52)
39) 5 3
f (t )=sen(t )ln(t −t )
y = Tg (cos x + sen x)
53)
40)
( x7 +6 x ) 2
3 f (x )=e sen ( x )
y = Cos (sen x + x )
54)
41)
2x
e s−5 s6
f (s )= √ 7
y = Ctg ( + Ln x )
x2 + 2 x s −9 s
42) y=e
sen r
f (r )=
3 2
2 r3
43) y = 7x − x 55)
x
44) y=
56) √ a − x2
2
y = Ln ( a + x + √ x2 + 2ax) y= √
2 x2 −2 x + 1
57) x
Lic. MsC OSCAR ESTEBAN GARCIA GRADOS
3 3 2
y = √x + 3x 68)
58) x
x
y = Sen ( e + Ln x )
59)
69)
2
y = (3 x + 4 x +8) √ x − 1
y = Cos ( log 5 x + √ x )
4x+6
y=
60) √x2 + 3x + 4 70)
61) y = Ln ( 3 x2 + √ 9 x 4 + 1 ) }
y = Arctg √√11−+ Cos
Cosx
x x+1
y = Tan ( Sen x )
71)
1 + Tan x
62)
y = Ln √ 1 − Tan x
72)
63) y = Sec (2 x 2 − Log3 x )
4 3
73) y = 7x − x
x2 + 1
y = Ctg ( e + Ln ( √ x + 1))
74)
64)
y = Cosec ( √ x + Ln x )
y = Ln ( √2 Sen x + 1 + √2 Sen x − 1 ) 75)
65)
y = Arc.tg √ 5x 2 − 2
y = Ln ( b + x + √ x 2 + 3bx ) 76)
66) y = Arc . Sen ( Ln x + e x )
77)
y = Arc. sen e x + arc. sen √1 − e 3x
67) y = Arc ..cot g √ 5x 2 − 2
4
x3 − senx
y = Ln2 x − Ln ( Ln x) y=
( 2x + Tanx )
3
78)
VI. Problemas de diferenciabilidad.
a) Calcular los valores de a y b de la función f para que sea derivable en x=2
2
f ( x )= −3 x , Si x ≤ 2
{ ax +b , Si x>2
b) Calcular los valores de a y b de la función f para que sea derivable en x=2
Lic. MsC OSCAR ESTEBAN GARCIA GRADOS
f ( x )= ax2+b , Si x <2
{ 2 x −1, Si x ≥ 2
c) Hallar los valores de a y b de manera que exista f ´ (2) sí:
f ( x )=
{axx −3+b ,, SiSi xx ≤>22
2
x2 , Si x<1 Encontrar los valores de a y b tal que f ´ (1) exista.
d) Si f ( x )= {
ax +b , Si x ≥ 1
2
x +mx+3 , Si x ←1
e) Hallar las constantes m y n de tal manera que la función f ( x )= {−4 mx+ n , Si x >−1
dy
VII. Derivación Implícita. Hallar Sí:
dx
a) e y =x + y g) x 4 + y 4 =x 2 y 2
x h) x 2−a √ xy + y 2=a
b) ln y + =k
y
i) 2 x 4 y2 −4 x 2 y 4 + x 2 y 2=6
3 x− y
c) y = j) y 5−2 x 2 y 3 +3 x 4 y−x 5=5
x+ y
d) xseny −cosy +cos 2 y=0 k) x 3+ 2 x 2 y−x y 2 +2 y 3=2
e) y senx- cos(x - y)=0 l) x 3−3 axy + y 3=a3
f) x 3+ a x 2 y +bx y 2+ y 3 =0 m) x 3+ x y 2=x 2 y
VIII. Derivadas de las funciones y=( f ( x ) )g (x)
senx
1) y=( x2 +1 ) 6) y=x lnx
7) y=(lnx)x
x
x
2) y=e x
3) y=( 1+ x2 )
arc tgx 8) y=(senx)cosx
4) y=2 x √ x 9) y=(cosx )x
5) y=x senx 10) x y = y x
2
11) y=x x
1
12) y=x x
Lic. MsC OSCAR ESTEBAN GARCIA GRADOS
También podría gustarte
- Limites PracticaDocumento3 páginasLimites PracticaCarlos SantistebanAún no hay calificaciones
- Pract - Derivadas UnivalleDocumento1 páginaPract - Derivadas UnivalleMisael MaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- HT01 - Derivadas de FuncionesDocumento2 páginasHT01 - Derivadas de FuncionesAnt AldAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 01 DerivadasDocumento10 páginasGuia 01 DerivadascfloresahumadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 4 Limite de FuncionesDocumento6 páginasPractica 4 Limite de FuncionesAylen MazzagliaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 3 Calculo Parte 2 PDFDocumento11 páginasTaller 3 Calculo Parte 2 PDFVALENTINA RESTREPO CARDONAAún no hay calificaciones
- MATE1109 G07 - Definición de Derivada y Sus PropiedadesDocumento2 páginasMATE1109 G07 - Definición de Derivada y Sus PropiedadesBenito antonio martinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Lista 1 de Cálculo 1Documento3 páginasLista 1 de Cálculo 1Gabriel PortelaAún no hay calificaciones
- DerivadaDocumento5 páginasDerivadagasty45Aún no hay calificaciones
- Matemáticas Básicas (303-118) Taller #3Documento7 páginasMatemáticas Básicas (303-118) Taller #3Sebastián PabuenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 Cálculo diferencialDocumento6 páginasTaller 1 Cálculo diferencialMauricio Ordoñez OrdoñezAún no hay calificaciones
- 6.taller DerivadasDocumento4 páginas6.taller DerivadasANTONI avilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 Calculo DiferencialDocumento4 páginasTaller 1 Calculo DiferencialFelicity GuerreroAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 Calculo DiferencialDocumento4 páginasTaller 1 Calculo DiferencialangieAún no hay calificaciones
- Limites EjerciciosDocumento6 páginasLimites EjerciciosbeagarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctico III Funciones y Gráficas I-2023Documento3 páginasPráctico III Funciones y Gráficas I-2023MALDONADO ARRAYASA JOHN JOSIASAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica 6 - 6ABC (Derivadas e Integrales)Documento5 páginasPráctica 6 - 6ABC (Derivadas e Integrales)Im BlueeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios - Derivadas IDocumento5 páginasEjercicios - Derivadas Imillaray loyolaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introducción A La Matemática - EjercitaciónDocumento22 páginasIntroducción A La Matemática - EjercitaciónLucas SosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas - Ejercicios resueltos de cálculo de derivadas de funcionesDocumento3 páginasDerivadas - Ejercicios resueltos de cálculo de derivadas de funcionesKristian Saavedra (DJKristianS)Aún no hay calificaciones
- Relacion 2Documento2 páginasRelacion 2Paola FdezAún no hay calificaciones
- PR Viejo AntiderivadaDocumento3 páginasPR Viejo AntiderivadaArmando AransagAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones 2Documento4 páginasFunciones 2eddioAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea General de La Tercera Unidad DidácticaDocumento5 páginasTarea General de La Tercera Unidad DidácticaJunior HenostrozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller # 3Documento6 páginasTaller # 3Juan Camilo Sierra PerdomoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 1Documento6 páginasPractica 1Cris LomasAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía para El Segundo Parcial de Matemáticas I Verano 2021Documento11 páginasGuía para El Segundo Parcial de Matemáticas I Verano 2021Emmanuel ArmentaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1Documento4 páginasTaller 1Anthony TrianaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Derivadas #1Documento3 páginasGuía Derivadas #1Max MaxmaxAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 2Documento3 páginasTarea 2DAVID ANDRES PALMA CORDOVAAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo. Practico 3-3Documento7 páginasCalculo. Practico 3-3Jaime Hugo Chura QuispeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Derivadas OKDocumento6 páginasEjercicios Derivadas OKDeiner Yobit Riveros GeronimoAún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis funcional y derivabilidadDocumento5 páginasAnálisis funcional y derivabilidaddavidAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica de DerivacionDocumento1 páginaPractica de DerivacionElias IsminioAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica VDocumento2 páginasPractica VJerson NeyraAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 5Documento3 páginasTaller 5David martinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 7Documento8 páginasPractica 7vegaAún no hay calificaciones
- 09-24-2019 111848 Am Practica de Clase 03Documento1 página09-24-2019 111848 Am Practica de Clase 03Torres RosaAún no hay calificaciones
- 5-Derivadas-Guia Cálculo I - FIng Práctica 08Documento3 páginas5-Derivadas-Guia Cálculo I - FIng Práctica 08Nerak ZilramAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia DerivadasDocumento9 páginasGuia DerivadasRolando EspinzaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia6 (Mat12020) PDFDocumento6 páginasGuia6 (Mat12020) PDFWill RodríguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones matemáticas IDocumento9 páginasFunciones matemáticas IAna CuentalAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas y aplicaciones económicasDocumento3 páginasDerivadas y aplicaciones económicasLic Ronal BardalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía # 3. Funciones Inversas, Logarítmicas y ExponencialesDocumento9 páginasGuía # 3. Funciones Inversas, Logarítmicas y ExponencialesMoon PieAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas-Análisis-MatemáticoDocumento2 páginasDerivadas-Análisis-MatemáticoGonziAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo de Aula. Derivada de Una FunciónDocumento4 páginasTrabajo de Aula. Derivada de Una FunciónXiomara AlessandraAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía de Ejercicios de Matemática II con aplicaciones de la derivadaDocumento21 páginasGuía de Ejercicios de Matemática II con aplicaciones de la derivadaVIANKA CELESTE AVENDAÑO RIOSAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía 6 DerivadasDocumento8 páginasGuía 6 DerivadasCatalina JorqueraAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1Documento3 páginasTaller 1Edgar ReyAún no hay calificaciones
- PD3 Mef1 2024-0Documento4 páginasPD3 Mef1 2024-0The milfs fuckerAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 PCIIDocumento4 páginasTaller 1 PCIIKaren Daniela Sepulveda Carrero0% (2)
- Práctica 2Documento5 páginasPráctica 2Andre QuijanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Funciones Nº 4 PDFDocumento6 páginasEjercicios Funciones Nº 4 PDFJuan Manuel AlbarracinAún no hay calificaciones
- Prac DerivadasDocumento10 páginasPrac Derivadasvladimir RiverosAún no hay calificaciones
- FuncionesDocumento2 páginasFuncionesAlvaro EspinozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Derivada 1Documento7 páginasGuia Derivada 1SebastiánAún no hay calificaciones
- Reglas de derivación y ejercicios resueltosDocumento1 páginaReglas de derivación y ejercicios resueltosIsabel CárcamoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1Documento4 páginasTaller 1natalia ruedaAún no hay calificaciones
- ENSAYO - La antropología filosófica y su relación con la educación y la pedagogía.Documento10 páginasENSAYO - La antropología filosófica y su relación con la educación y la pedagogía.Richar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- El-Vanguardismo PeruanoDocumento6 páginasEl-Vanguardismo PeruanoRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Zonas de VidaDocumento271 páginasZonas de Vidamaria juradoAún no hay calificaciones
- ENSAYO - La antropología filosófica y su relación con la educación y la pedagogía.Documento10 páginasENSAYO - La antropología filosófica y su relación con la educación y la pedagogía.Richar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ensayo - de Grecia Sevillano NuñezDocumento19 páginasEnsayo - de Grecia Sevillano NuñezRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivada de Una Función Paramétrica - CalculadoraDocumento5 páginasDerivada de Una Función Paramétrica - CalculadoraRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Documentos y Fichas de InvestigacionDocumento15 páginasDocumentos y Fichas de InvestigacionRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha de Pre y Post Test AplicaciónDocumento2 páginasFicha de Pre y Post Test AplicaciónRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Material de Laboratorio BásicoDocumento3 páginasMaterial de Laboratorio BásicoRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Modelo de ContextualizacionDocumento2 páginasModelo de ContextualizacionRichar Sevillano Bejarano100% (1)
- Guia de Observacion de La Capacidad AprehensiónDocumento2 páginasGuia de Observacion de La Capacidad AprehensiónRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Aplicaciones de Los Límites Matematicos en La Ingenieria ZootecnistaDocumento7 páginasAplicaciones de Los Límites Matematicos en La Ingenieria ZootecnistaRichar Sevillano Bejarano0% (1)
- Apreciacion y ExpresionDocumento18 páginasApreciacion y ExpresionRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe de investigación educativa en arte de BaguaDocumento4 páginasInforme de investigación educativa en arte de BaguaRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Estudio Del Rostro de Semiperfil Mirando Hacia AbajoDocumento10 páginasEstudio Del Rostro de Semiperfil Mirando Hacia AbajoRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Material de Laboratorio BásicoDocumento3 páginasMaterial de Laboratorio BásicoRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Operacionalización de Variables 4.0Documento2 páginasOperacionalización de Variables 4.0Richar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Apreciacion y ExpresionDocumento18 páginasApreciacion y ExpresionRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Apreciacion y ExpresionDocumento18 páginasApreciacion y ExpresionRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Apreciacion y ExpresionDocumento18 páginasApreciacion y ExpresionRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Instrumento de EvaluacionDocumento7 páginasInstrumento de EvaluacionRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Arte y Tecnologia en El Siglo XXDocumento41 páginasArte y Tecnologia en El Siglo XXjosemiguelcc100% (1)
- Instrumento de EvaluacionDocumento7 páginasInstrumento de EvaluacionRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Peces - Nombres CientificosDocumento58 páginasPeces - Nombres CientificosMarlon AngelesAún no hay calificaciones
- La Enseñanza ArtisticaDocumento3 páginasLa Enseñanza ArtisticaRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicos de EscalasDocumento2 páginasEjercicos de EscalasRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Brown PazIncierta LibroEnteroDocumento280 páginasBrown PazIncierta LibroEnteroAlmendraAguilarAguirreAún no hay calificaciones
- EscalaDocumento15 páginasEscalaRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Peces - Nombres CientificosDocumento58 páginasPeces - Nombres CientificosMarlon AngelesAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluación y reflexión de las actividades implementadas en la IEDocumento12 páginasEvaluación y reflexión de las actividades implementadas en la IETeresa Sanchez SolanoAún no hay calificaciones
- HistoriaspsDocumento1 páginaHistoriaspsFanny ValAún no hay calificaciones
- Bol Valores Sociales Juventud 2018 PDFDocumento125 páginasBol Valores Sociales Juventud 2018 PDFVania Vanessa CopaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fichero Area SocioafectivaDocumento10 páginasFichero Area SocioafectivajocelynAún no hay calificaciones
- ObrasHidráulicasDocumento6 páginasObrasHidráulicasJulietaAún no hay calificaciones
- Las 10 LeyesDocumento5 páginasLas 10 LeyesJhon UtxjAún no hay calificaciones
- Gestión Del Mantenimiento: Sesión: 11 Profesor: David VargasDocumento33 páginasGestión Del Mantenimiento: Sesión: 11 Profesor: David VargasJorge EspinozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia GitbotDocumento31 páginasGuia GitbotGabriel GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Perfil PuestosDocumento46 páginasPerfil Puestoschris bernabel100% (1)
- Ficha de Trabajo 2017 Semana26Documento4 páginasFicha de Trabajo 2017 Semana26Montserrat CaviedesAún no hay calificaciones
- Annotated-Laboratorio 4 - Mecanica de FluidosDocumento15 páginasAnnotated-Laboratorio 4 - Mecanica de Fluidoshayfa.yalleAún no hay calificaciones
- Principales RequisitosDocumento5 páginasPrincipales RequisitosfrancojanAún no hay calificaciones
- Administración de Base de Datos Ii PDFDocumento8 páginasAdministración de Base de Datos Ii PDFroy saavedraAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual de Operación 4807 Rev1.4 Español InclinometroDocumento17 páginasManual de Operación 4807 Rev1.4 Español InclinometroRamonAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculo de valor futuro de anualidades anticipadasDocumento4 páginasCálculo de valor futuro de anualidades anticipadasSamuelHernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Planeación y OrganizaciónDocumento24 páginasPlaneación y OrganizaciónTANIA VILLATORO CRUZAún no hay calificaciones
- P1. Dos Partículas: P3. Cuando Se Incluye El Efecto de La Resistencia Aerodinámica, LaDocumento2 páginasP1. Dos Partículas: P3. Cuando Se Incluye El Efecto de La Resistencia Aerodinámica, LaFFFFAún no hay calificaciones
- MANUAL Lengua y Literatura ELISALDEDocumento175 páginasMANUAL Lengua y Literatura ELISALDENacho ChasquiAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 Hábitos para Deshacerte de La Ansiedad y El Exceso de PensamientoDocumento2 páginas5 Hábitos para Deshacerte de La Ansiedad y El Exceso de PensamientoAgustina AlarcónAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 3 PREPARACION GENERAL DE UNA MINA PDFDocumento43 páginasTema 3 PREPARACION GENERAL DE UNA MINA PDFKaren ContrerasAún no hay calificaciones
- Demanda Prescripcion Nov - 2022 - Sra Diana Chanatosig AvilaDocumento6 páginasDemanda Prescripcion Nov - 2022 - Sra Diana Chanatosig AvilaJohn GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Modelo de Fiedler 1Documento17 páginasModelo de Fiedler 1CHILCON MEGO ANJHELA DEL PILARAún no hay calificaciones
- Métodos en economía, positiva vs normativa, discrepancias y enseñanzaDocumento12 páginasMétodos en economía, positiva vs normativa, discrepancias y enseñanzaRiding&MoreAún no hay calificaciones
- Hds-Jabón Neutro QNDocumento3 páginasHds-Jabón Neutro QNvikthorolivesAún no hay calificaciones
- Investigacion de ExpocisionDocumento3 páginasInvestigacion de ExpocisionKirstie GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.1 Concepto de Administración EstratégicaDocumento7 páginas1.1 Concepto de Administración EstratégicaDiego Alejandro González ZavalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 Matemáticas Tercer Periodo SergioDocumento17 páginasTaller 1 Matemáticas Tercer Periodo Sergiokokito riosAún no hay calificaciones
- Control de Calidad en Farmacia QFDocumento8 páginasControl de Calidad en Farmacia QFMaria Huaman NovilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Material de Apoyo Revisado para Realizar Un Trabajo MonográficoDocumento4 páginasMaterial de Apoyo Revisado para Realizar Un Trabajo MonográficoJose Ricardo PachecoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tesis Trasvase de Agua Unac 2018Documento76 páginasTesis Trasvase de Agua Unac 2018Carlos MonsalveAún no hay calificaciones