Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Ejercicios de Funciones
Cargado por
ERIKA LUCERO ZAVALETATítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Ejercicios de Funciones
Cargado por
ERIKA LUCERO ZAVALETACopyright:
Formatos disponibles
INSTITUTO POLITECNICO NACIONAL
ESCUELA SUPERIOR DE INGENIERIA Y ARQUITECTURA
UNIDAD TICOMAN CIENCIAS DE LA TIERRA
CÁLCULO DIFERENCIAL E INTEGRAL
FUNCIONES
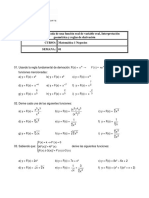
EN LOS SIGUIENTES EJERCICIOS HALLE EL DOMINIO DE f
3. f ( x ) x 9
2
1. f ( x) 3 x 5 2. f ( x) 7 2 x
x 1 4x 7 x 1
f ( x) f ( x) 2 f ( x) 3
4. x 9x
3
5. 6 x 13 x 5 6. x 9x
x 1 1
f ( x) f ( x) f ( x)
7. 16 x 2 8. x5 7 x 9. ( x 2) x
1
f (x )=
Sea √ x +1 . Encuentre lo siguiente.
(a) f (1) , (b) f (3) , (c) f (0) , (d) f ( 2 – 1) , (e) f (-x) , (g) f (x2) , (h) (f (x))2
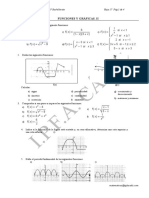
En los siguientes ejercicios trace la gráfica de f.
1. f (x )=1−4 x 2
2
2. f (x )=−1/( x +1) 4.
f (x )=¿{x si x<0 ¿ {3x si 0≤x<2¿¿¿
3. f (x )=|x+5|
Determine si f es par, impar, o no es par ni impar
3 3
a) f (x )=√ x3 +4 x c) f (x )=√ x 4 +3 x 2 +5
3
f (x )=√ 3 x 2 −x 3 d) f (x )=0
b)
Trace la gráfica de las siguientes ecuaciones usando desplazamientos horizontal y vertical
para c elegidas por ustedes.
2
a) y=√ x+4 b) y=x −2 x
10. Demuestre que f (x) = 5 – 7x es una función biunívoca.
En los siguientes ejercicios, determine:
(f +g )( x ), (f −g)( x ), ( fg)( x ), ( f /g )( x ), ( f ∘ g )( x ) y (g ∘ f )( x )
1. f (x )=x 2 +3 x+1, g( x )=2 x−1
2. f (x )=x 2 +4 , g ( x )=√ 2 x +5
3. f (x )=5 x−2 , g( x )=1/ x2
También podría gustarte
- Taller3 20171Documento7 páginasTaller3 20171Sebastián PabuenaAún no hay calificaciones
- EJERCICIOS de La Practica #2 - Calculo Diferencial-Nivelación-2021-0-DerivadasDocumento6 páginasEJERCICIOS de La Practica #2 - Calculo Diferencial-Nivelación-2021-0-DerivadasRichar Sevillano BejaranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 1Documento6 páginasPractica 1Cris LomasAún no hay calificaciones
- Limites PracticaDocumento3 páginasLimites PracticaCarlos SantistebanAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 01 DerivadasDocumento10 páginasGuia 01 DerivadascfloresahumadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 8 Evaluación de Funciones y Gráficos Con SoluciónDocumento4 páginasGuia 8 Evaluación de Funciones y Gráficos Con SoluciónpazAún no hay calificaciones
- Introducción A La Matemática - EjercitaciónDocumento22 páginasIntroducción A La Matemática - EjercitaciónLucas SosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea Semana 3Documento2 páginasTarea Semana 3Esteban ZelayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica 6 - 6ABC (Derivadas e Integrales)Documento5 páginasPráctica 6 - 6ABC (Derivadas e Integrales)Im BlueeAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento2 páginasUntitledAnibalGTXAún no hay calificaciones
- Guian 6 DerivadasDocumento3 páginasGuian 6 DerivadasPaulaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía - Derivadas 2Documento8 páginasGuía - Derivadas 2MaximilianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas 21-22Documento2 páginasDerivadas 21-22Fernando QuinteroAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Derivadas BásicasDocumento2 páginasEjercicios de Derivadas BásicasBrayan andrésAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia DerivadasDocumento9 páginasGuia DerivadasRolando EspinzaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Composicion e InversaDocumento3 páginasGuia Composicion e InversaeddioAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia No. 2 Mate II Ing. (02-2018)Documento6 páginasGuia No. 2 Mate II Ing. (02-2018)Moy DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Derivadas #1Documento3 páginasGuía Derivadas #1Max MaxmaxAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Derivada 2Documento13 páginasEjercicios de Derivada 2vicentecarlosmrAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía 6 Derivada NuevaDocumento2 páginasGuía 6 Derivada NuevaLuki TassAún no hay calificaciones
- DerivadaDocumento5 páginasDerivadagasty45Aún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones 2Documento4 páginasFunciones 2eddioAún no hay calificaciones
- Regla Del Producto y Cociente - Regla de La PotenciaDocumento5 páginasRegla Del Producto y Cociente - Regla de La Potenciawendy jaimesAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de DerivadasDocumento3 páginasEjercicios de DerivadasDANIELA VANESSA HERMOZA SAAZAún no hay calificaciones
- Cur 2 001 CD Ejercicios Funciones 002Documento2 páginasCur 2 001 CD Ejercicios Funciones 002Emmanuel JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento4 páginasUntitledAnibalGTXAún no hay calificaciones
- Lista 1 de Cálculo 1Documento3 páginasLista 1 de Cálculo 1Gabriel PortelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica 2Documento5 páginasPráctica 2Andre QuijanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Aplicativos Cáalculo DiferencialDocumento5 páginasEjercicios Aplicativos Cáalculo DiferencialMarden Puerta ChoctalinAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Derivadas OKDocumento6 páginasEjercicios Derivadas OKDeiner Yobit Riveros GeronimoAún no hay calificaciones
- T11. E. Recta Tangente PDFDocumento2 páginasT11. E. Recta Tangente PDFRodeo CrabAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo de Aula. Derivada de Una FunciónDocumento4 páginasTrabajo de Aula. Derivada de Una FunciónXiomara AlessandraAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivada de Una FunciónDocumento4 páginasDerivada de Una Funcióntelly tonAún no hay calificaciones
- Prac DerivadasDocumento10 páginasPrac Derivadasvladimir RiverosAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 Cálculo DiferencialDocumento6 páginasTaller 1 Cálculo DiferencialMauricio Ordoñez OrdoñezAún no hay calificaciones
- Lista 3 CalculoDocumento7 páginasLista 3 CalculoMaria Amelia Melo RualesAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía # 3. Funciones Inversas, Logarítmicas y ExponencialesDocumento9 páginasGuía # 3. Funciones Inversas, Logarítmicas y ExponencialesMoon PieAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 7Documento8 páginasPractica 7vegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia de Ejercicios Propuestos DerivadasDocumento8 páginasGuia de Ejercicios Propuestos DerivadasCarlos Rivera YanezAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller #4 Derivadas Calculo I Semestre 2017 02 EFRAIN - HECTOR PDFDocumento4 páginasTaller #4 Derivadas Calculo I Semestre 2017 02 EFRAIN - HECTOR PDFCristhian CadenaAún no hay calificaciones
- GUIA 6. DerivadasDocumento2 páginasGUIA 6. DerivadasSandra RedaelliAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica de DerivacionDocumento1 páginaPractica de DerivacionElias IsminioAún no hay calificaciones
- Miscelanea de Ejercicios Preparatorios Al Tercer ParcialDocumento2 páginasMiscelanea de Ejercicios Preparatorios Al Tercer ParcialJohn MorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica 3 M1A 2020Documento10 páginasPráctica 3 M1A 2020ana paula carosioAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratorio 11 - Tipos de Funciones, Función Compuesta.Documento2 páginasLaboratorio 11 - Tipos de Funciones, Función Compuesta.Romy DanaisAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo de Derivada de Una FunciónDocumento3 páginasTrabajo de Derivada de Una Funciónluis castilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia DerivadasDocumento3 páginasGuia DerivadasEmely Sabando VeraAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1 CálculoDocumento2 páginasTarea 1 CálculoMiguel VG ViteAún no hay calificaciones
- Pract. de DerivadasDocumento4 páginasPract. de Derivadasjose andrade vargasAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Material Complementario 1 - 2021-1Documento8 páginas1 Material Complementario 1 - 2021-1AleAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Derivadas y Sus AplicacionesDocumento20 páginasGuia Derivadas y Sus AplicacionesAndrea CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Derivada 1Documento7 páginasGuia Derivada 1SebastiánAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo de Aula. Derivada Aplicada A Los Negocios - Máximos y MínimosDocumento4 páginasTrabajo de Aula. Derivada Aplicada A Los Negocios - Máximos y MínimosJean CordovaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía-Derivadas 01 2016Documento20 páginasGuía-Derivadas 01 2016KatyaHernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso de Cálculo IDocumento6 páginasCurso de Cálculo IVALLEZLIAún no hay calificaciones
- HT01 - Derivadas de FuncionesDocumento2 páginasHT01 - Derivadas de FuncionesAnt AldAún no hay calificaciones
- 08 Máximo y Mínimo Absolutos, Relativos, Fórmula de TaylorDocumento4 páginas08 Máximo y Mínimo Absolutos, Relativos, Fórmula de TaylorHernán L. ZangaAún no hay calificaciones
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDe EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones Logarítmicas e HiperbólicasDocumento2 páginasFunciones Logarítmicas e HiperbólicasERIKA LUCERO ZAVALETAAún no hay calificaciones
- 1er Caso PracticoDocumento1 página1er Caso PracticoERIKA LUCERO ZAVALETAAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.-Introduccion A La Iii UnidadDocumento2 páginas2.-Introduccion A La Iii UnidadERIKA LUCERO ZAVALETAAún no hay calificaciones
- Tabla de Amortización de Capital y Calculo de InteresesDocumento3 páginasTabla de Amortización de Capital y Calculo de InteresesERIKA LUCERO ZAVALETAAún no hay calificaciones
- Ley de Hess (Termodinamica)Documento12 páginasLey de Hess (Termodinamica)Arnold José Aguas ZuñigaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Notacion CientificaDocumento2 páginasEjercicios Notacion CientificaCorsary MarrugoAún no hay calificaciones
- Propuesta Formal de Monografía. Karem Viviana Pérez ÁlvarezDocumento12 páginasPropuesta Formal de Monografía. Karem Viviana Pérez ÁlvarezJorge Alejandro CastañoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha Sistema Hidraulico SKDocumento3 páginasFicha Sistema Hidraulico SKAlejandro GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual de Usuario AlisstaDocumento279 páginasManual de Usuario AlisstaMar BolivarAún no hay calificaciones
- Anexo #2Documento3 páginasAnexo #2YonWil M. VilcaAún no hay calificaciones
- InglesDocumento142 páginasInglesMary H AlvaradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Diap. Tema 5.4 Estrangulador de FondoDocumento15 páginasDiap. Tema 5.4 Estrangulador de FondoZulmy yumara Lopez perezAún no hay calificaciones
- Discusión Sobre La Evaluación FormativaDocumento1 páginaDiscusión Sobre La Evaluación FormativaAlex Comun GallegosAún no hay calificaciones
- MC1 EmocionesDocumento4 páginasMC1 EmocionesEunice Lugo100% (1)
- Capitulo III Marco Metodologico - Red LanDocumento9 páginasCapitulo III Marco Metodologico - Red Lanjeslow24-8Aún no hay calificaciones
- Proyecto Cafe Terminado EnmarcadoDocumento7 páginasProyecto Cafe Terminado EnmarcadoGaby OrdoñezAún no hay calificaciones
- IN-CL-04 - Instructivo Tintas PenetrantesDocumento3 páginasIN-CL-04 - Instructivo Tintas PenetrantesLorena Grijalba LeónAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen EjecutivoDocumento6 páginasResumen EjecutivoWILFREDO PARI TAIPEAún no hay calificaciones
- Refrigeración o Sistema de EnfriamientoDocumento5 páginasRefrigeración o Sistema de EnfriamientoGutierrez EfrainAún no hay calificaciones
- Concepto de Proceso AdministrativoDocumento8 páginasConcepto de Proceso AdministrativoFernando Bautista100% (3)
- Latifundio y MinifundioDocumento9 páginasLatifundio y MinifundioFredy Miranda0% (1)
- P2.sistemas de Proyeccion GisDocumento9 páginasP2.sistemas de Proyeccion GiscuauhuAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo de Bomba y Tanques Vivienda MultifamiliarDocumento17 páginasCalculo de Bomba y Tanques Vivienda MultifamiliarPaoloTaboadaOreAún no hay calificaciones
- Primeraentrega PDFDocumento38 páginasPrimeraentrega PDFgilber pimentelAún no hay calificaciones
- Compendio INEI ArequipaDocumento482 páginasCompendio INEI ArequipaAguilar JoséAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodos y Tecnicas de EvaluacionDocumento7 páginasMetodos y Tecnicas de EvaluacionMary FuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- Folleto Tipo Acordeón Tríptico Itinerario Vacaciones Scrapbook Beige y VerdeDocumento2 páginasFolleto Tipo Acordeón Tríptico Itinerario Vacaciones Scrapbook Beige y VerdeGiancarlo Salazar AguilarAún no hay calificaciones
- Fase 2 - Segmentación de Mercado - 102054 - 2Documento20 páginasFase 2 - Segmentación de Mercado - 102054 - 2Zahira GarnicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplos Del Diptongo para Tercer Grado de PrimariaDocumento72 páginasEjemplos Del Diptongo para Tercer Grado de PrimariaL Martín M ChacónAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Miniterminos y Maxiterminos U 2Documento1 páginaEjercicios Miniterminos y Maxiterminos U 2Chuchuy ChocochuyAún no hay calificaciones
- Malla Curricular Comunicación Oral y Escrita 4ºDocumento8 páginasMalla Curricular Comunicación Oral y Escrita 4ºSulmy Vásquez100% (1)
- Aa4 IoDocumento10 páginasAa4 IoRonald SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica Cálculo IIDocumento5 páginasPráctica Cálculo IIErika GalvezAún no hay calificaciones
- Reporte de ConsolidaciónDocumento7 páginasReporte de ConsolidaciónAngel FloresAún no hay calificaciones