Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
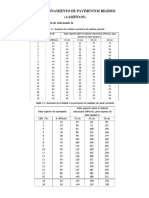
Ábacos 2 - A4 - Pavimento Flexible
Cargado por
Erick0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
71 vistas2 páginasabaco para pav flexible
Título original
0. ÁBACOS 2_A4_PAVIMENTO FLEXIBLE
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoabaco para pav flexible
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
71 vistas2 páginasÁbacos 2 - A4 - Pavimento Flexible
Cargado por
Erickabaco para pav flexible
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 2
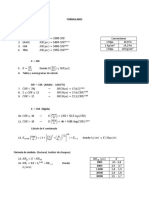
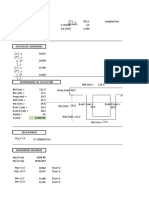
ECUACIONES DE MÓDULO RESILIENTE
a) 𝑪𝑩𝑹 ≤ 𝟕, 𝟐
𝑀𝑅 = 1500 × 𝐶𝐵𝑅
b) 𝟕, 𝟐 < 𝑪𝑩𝑹 ≤ 𝟐𝟎
𝑀𝑅 = 3000 × 𝐶𝐵𝑅0,65
c) 𝟐𝟎 < 𝑪𝑩𝑹 ≤ 𝟔𝟎
𝑀𝑅 = (4326 × ln 𝐶𝐵𝑅) + 241
d) 𝑪𝑩𝑹 ≥ 𝟔𝟎
𝑀𝑅 = [(4326 × ln 𝐶𝐵𝑅) + 241] × 1,55
ECUACIONES DE COEFICIENTE ESTRUCTURAL
1) Coeficiente estructural de la capa de rodadura. (Pulg.).
𝑎1 = 0,0052 × 𝐸 0,555 → 𝑬 = 𝑴𝑷𝒂
2) Coeficiente estructural de la base granular. (Pulg.).
𝑎2 = 0,032 × 𝐶𝐵𝑅 0,32
3) Coeficiente estructural de la sub- base granular. (Pulg.).
𝑎3 = 0,058 × 𝐶𝐵𝑅 0,19
4) Coeficiente estructural del mejoramiento. (Pulg.).
𝑎4 = (0,227 × 𝑙𝑜𝑔𝑀𝑅 ) − 0,839 → 𝑴𝑹 = 𝒑𝒔𝒊
ESPESORES MÍNIMOS SEGÚN EJES EQUIVALENTES
CONFIABILIDAD
DESVIACIÓN ESTÁNDAR
NIVELES DE SERVICIABILIDAD
Serviciabilidad inicial
po= 4,5 para pavimentos rígidos
po= 4,2 para pavimentos flexibles
Serviciabilidad final
pt= 2,0 para caminos de menor tránsito
pt= 2,5 o más para caminos muy importantes
pt= 3,0 para autopistas
También podría gustarte
- Analisis y Diseño Estructural Comparativo Entre Sistema de Muros de Ductilidad Limitada y Alabañileria Confinada para Edificaciones Con Plateas de CimentacionDocumento50 páginasAnalisis y Diseño Estructural Comparativo Entre Sistema de Muros de Ductilidad Limitada y Alabañileria Confinada para Edificaciones Con Plateas de Cimentacionmga2402Aún no hay calificaciones
- Parcial Final, Diseño Pavimentos FlexiblesDocumento11 páginasParcial Final, Diseño Pavimentos FlexiblesSantiago HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Universidad Industrial de Santander Escuela de Ingenería CivilDocumento13 páginasUniversidad Industrial de Santander Escuela de Ingenería CivilMiguel FernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Articulo de Opinion MartesDocumento34 páginasArticulo de Opinion MartesJoe Marco Fiestas Amaya100% (1)
- Analisis de Un Engrane PracticoDocumento22 páginasAnalisis de Un Engrane PracticoRafa NegritoAún no hay calificaciones
- Estructuración de Muros de Concreto CiclopeoDocumento10 páginasEstructuración de Muros de Concreto CiclopeoAbrahan Soto SamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio de Diseño de PavimentoDocumento8 páginasEjercicio de Diseño de PavimentoErick EucedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Vigas A FLEXION - EjemploDocumento10 páginasDiseño de Vigas A FLEXION - Ejemplorafael leoanrdo beltran jimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Correccion 1er Exámen Análisis EstructuralDocumento11 páginasCorreccion 1er Exámen Análisis EstructuralAnyela GalvisAún no hay calificaciones
- Proyecto Pavimentos Via - Pasto CebadalDocumento19 páginasProyecto Pavimentos Via - Pasto CebadalEsthefanny Gonzales SAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis y Diseño Estruct. Comp. Entre MDL Y AC Edif. Con Plateas CimentaciónDocumento42 páginasAnalisis y Diseño Estruct. Comp. Entre MDL Y AC Edif. Con Plateas CimentaciónJose David Loyaga MusayonAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 2 RicardoAdame 167258Documento14 páginasTarea 2 RicardoAdame 167258Ricardo AdameAún no hay calificaciones
- Diagrama de Interacción de Una Columna CorrDocumento20 páginasDiagrama de Interacción de Una Columna CorrAndreina ArciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplos de Permeabilidad de Los Suelos - Semana 2Documento8 páginasEjemplos de Permeabilidad de Los Suelos - Semana 2Roberto CarranzaAún no hay calificaciones
- Hoja de Calculo de Diseño de Muro EstructuralDocumento7 páginasHoja de Calculo de Diseño de Muro EstructuralEddy Santiago Vasquez MolinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grupo N°5 Informe FinalDocumento17 páginasGrupo N°5 Informe FinalBernhard RiemannAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 4Documento4 páginasClase 4Yandry JalcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios en Clase ASHTO FlexibleDocumento31 páginasEjercicios en Clase ASHTO FlexibleAlejandro Patiño100% (1)
- Guia TP 27 Tabiques - Dimensionado - 2016 - CDocumento15 páginasGuia TP 27 Tabiques - Dimensionado - 2016 - CFlorencia RomanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplo de Diseno de Puente Viga TDocumento12 páginasEjemplo de Diseno de Puente Viga TCristhian Quispe ManriqueAún no hay calificaciones
- SESION15Documento36 páginasSESION15CARLA BASTO HOSPINAAún no hay calificaciones
- Zapata Con Carga AxialDocumento7 páginasZapata Con Carga AxialLuifer VargasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplo Sol Portico MaderaDocumento28 páginasEjemplo Sol Portico MaderaSilver RomeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Prácticos 3 HinojosaDocumento24 páginasPrácticos 3 HinojosaSantiago HinojosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Pavimentos Flexibles Método de AASHTO 1993Documento6 páginasDiseño de Pavimentos Flexibles Método de AASHTO 1993Kevin ArteagaAún no hay calificaciones
- Escaleras OrtopoligonalesDocumento31 páginasEscaleras OrtopoligonalesGeorgeTamayDiaz100% (1)
- Ayudantía3 HAI ConPautaDocumento16 páginasAyudantía3 HAI ConPautaMarce NuñezAún no hay calificaciones
- Malla A TierraDocumento11 páginasMalla A TierraSiul VegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio de Aliviadero de DemasiasDocumento6 páginasEjercicio de Aliviadero de DemasiasEduardo Gastelo CayotopaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplo de Diseño de Puente Viga TDocumento12 páginasEjemplo de Diseño de Puente Viga TAlex Angel Taipe ZegarraAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño Geométrico de Una Fundación SuperficialDocumento8 páginasDiseño Geométrico de Una Fundación SuperficialCarlos Eduardo Raya MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Puentes PuentesDocumento12 páginasPuentes PuentesLuis Z100% (1)
- Aashto y Ii UnamDocumento10 páginasAashto y Ii UnamguadalupesampayoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2da Parte ZapatasDocumento12 páginas2da Parte Zapatasjesus martinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño A Torsion de Elementos No Preesforzados - Trabajo Final ExpDocumento6 páginasDiseño A Torsion de Elementos No Preesforzados - Trabajo Final ExpduvanAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Los Apoyos ElastomericosDocumento7 páginasDiseño de Los Apoyos Elastomericoskarina yoselin guerrero rosalesAún no hay calificaciones
- ExamenDocumento10 páginasExamenHenry MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio Columna EsbeltaDocumento23 páginasEjercicio Columna EsbeltaJoyCito PareDesAún no hay calificaciones
- Portico CerradoDocumento6 páginasPortico CerradoPierre NievesAún no hay calificaciones
- EJ7 (Resuelto) Madera MacizaDocumento12 páginasEJ7 (Resuelto) Madera MacizaFranco Vasquez100% (1)
- Trabajo Final Diseño Losa PuenteDocumento64 páginasTrabajo Final Diseño Losa PuenteFabian GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 1 AuxiDocumento8 páginasClase 1 AuxiSantos Tomas Dante AdailAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodo AasthoDocumento30 páginasMetodo AasthoDgsuspe BenAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis Sismico Estático y Dinámico de Estructuras Por El Metodo Matricial !Documento24 páginasAnalisis Sismico Estático y Dinámico de Estructuras Por El Metodo Matricial !Kevin Harold SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Parte 2Documento15 páginasParte 2HAILY BEATRIZ BLANCO ROSARIOAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Resistencia FlavioDocumento7 páginasExamen Resistencia FlavioJose MariaAún no hay calificaciones
- FORMULARIO PavimentosDocumento5 páginasFORMULARIO PavimentosShakira Castellano MelendezAún no hay calificaciones
- Norma BolivianaDocumento29 páginasNorma BolivianajuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo EstacionamientoDocumento60 páginasCalculo EstacionamientomartinbagoAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Pavimentos Flexibles Informe - Grupo 1Documento15 páginasDiseño de Pavimentos Flexibles Informe - Grupo 1Jo'el Vi'arAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Tuberias SimplesDocumento7 páginasTaller Tuberias SimplesDavid Andrés Pérez GalindoAún no hay calificaciones
- Problema 01Documento15 páginasProblema 01Anny leonela Zaña llanos100% (1)
- Seccion OptimaDocumento2 páginasSeccion OptimaAlexander PeresAún no hay calificaciones
- DIMENSIONAMIENTO DE PAVIMENTOS AashtoDocumento11 páginasDIMENSIONAMIENTO DE PAVIMENTOS AashtoJose RomanAún no hay calificaciones
- Ábacos 2 - A4 - Pavimento FlexibleDocumento2 páginasÁbacos 2 - A4 - Pavimento FlexibleErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño Pavimento para Trafico 20 Años DaularDocumento10 páginasDiseño Pavimento para Trafico 20 Años DaularErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Del Primer Parcial Grado 250Documento148 páginasExamen Del Primer Parcial Grado 250ErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Print CiiDocumento4 páginasPrint CiiErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen 1°parcialDocumento29 páginasResumen 1°parcialErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño Pavimento para Trafico 20 Años DaularDocumento10 páginasDiseño Pavimento para Trafico 20 Años DaularErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Sol L#1Documento4 páginasSol L#1ErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Ensayo FormalDocumento8 páginasGuia Ensayo FormalErickAún no hay calificaciones
- IPP-Monleón - Diseño Estructural de PuentesDocumento42 páginasIPP-Monleón - Diseño Estructural de PuentesChemo Grmr0% (1)
- Sol L#1Documento4 páginasSol L#1ErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea #1 Puentes 2019 CIIDocumento1 páginaTarea #1 Puentes 2019 CIIErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Topografia 2 ExposicionDocumento10 páginasTopografia 2 ExposicionErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Inf de Nivelacion y Faja Practica 2Documento3 páginasInf de Nivelacion y Faja Practica 2ErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Protocolo de Aforo VehicularDocumento3 páginasProtocolo de Aforo VehicularLuis Manuel SifontesAún no hay calificaciones
- Hormigon 2Documento3 páginasHormigon 2ErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 3 Elementos A TensionDocumento45 páginasCapitulo 3 Elementos A TensionKerly Od100% (1)
- Nervios y Cajonetas 1Documento1 páginaNervios y Cajonetas 1ErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe de ViviendasDocumento3 páginasInforme de ViviendasErickAún no hay calificaciones
- NodosDocumento1 páginaNodosErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe de Estudio de Tráfico Loja Zamora 25-09-2015Documento95 páginasInforme de Estudio de Tráfico Loja Zamora 25-09-2015ErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Expo de AceroDocumento3 páginasExpo de AceroErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Estabilidad de TaludesDocumento7 páginasEstabilidad de TaludesErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Criterio de FALLADocumento4 páginasCriterio de FALLAErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Determinación de Los Parámetros c y фDocumento3 páginasDeterminación de Los Parámetros c y фErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuentas Por PagarDocumento2 páginasCuentas Por PagarErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Curva de SaturacionDocumento7 páginasCurva de SaturacionErickAún no hay calificaciones
- Estabilidad de TaludesDocumento7 páginasEstabilidad de TaludesErickAún no hay calificaciones