Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Laboratorio 3 VRF - Servicios Por Internet
Cargado por
Luis CandiaTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Laboratorio 3 VRF - Servicios Por Internet
Cargado por
Luis CandiaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
CURSO: SERVICIOS POR INTERNET
PROFESOR: VILCHEZ SANDOVAL JESUS ALBERTO
TEMA: LABORATORIO VRF
ESCUELA: INGENIERIA DE TELECOMUNICACIONES
ALUMNOS:
- Berrú Huamán, Sebastián Alonso – 16190251
- Candia Gonzalez, Luis Samuel - 12190267
SERVICIOS POR INTERNET
INTRODUCCIÓN
Entrando al mundo del routing, es factible realizar la segmentación del tráfico cuando
tenemos diferentes clientes o cuando necesitamos por ejemplo el tráfico de
management quede aislado del resto. Esto es posible a lo llamado VRF (Virtual Routing
and Forwarding).
Las VRFs son principalmente utilizadas en la MPLS para aislar el tráfico de cada cliente,
pero no se encuentra limitada a dicha tecnología. Cuando las VRFs son usadas en una
red que no trabaja con MPLS, son llamadas VRF-Lite.
La importancia de usar VRFs es que se crean contextos de routing (routers virtuales
dentro del router físico), donde cada uno de estos posee una tabla de enrutamiento
completamente aislada de las demás, permitiendo configurar protocolos de
enrutamiento en cada contexto.
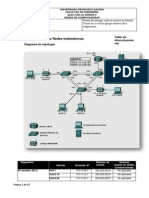
Tabla de direccionamiento:
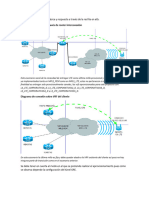
IMPLEMENT VRF LITE
SERVICIOS POR INTERNET
Parte 1: configurar y verificar VRF y direccionamiento de interfaz
En lo que concierne a la parte 2, se configurará y verificará VRF-Lite en R1. Los otros
dispositivos, R2, R3, D1, D2 y A1 no requieren configuración adicional. Una vez más, la
configuración que se utiliza aquí no pretende representar las mejores prácticas, la
finalidad es evaluar su capacidad para completar las configuraciones requeridas.
Paso 1: en el R1, cree los VRF requeridos.
1° Creación de los Customer_A y Customer_B VRF e inicialícelos tanto para IPv4 como
para IPv6. Los nombres VRF distinguen entre mayúsculas y minúsculas.
Open configuration window
R1(config)# vrf definition Customer_A
R1(config-vrf)# address-family ipv4
R1(config-vrf-af)# address-family ipv6
R1(config-vrf-af)# exit
R1(config-vrf)# vrf definition Customer_B
R1(config-vrf)# address-family ipv4
R1(config-vrf-af)# address-family ipv6
R1(config-vrf-af)# exit
IMPLEMENT VRF LITE
SERVICIOS POR INTERNET
2° Configure las interfaces G0/0/0 y S0/1/0 para la red Customer A.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/0
R1(config-if)# vrf forwarding Customer_A
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1:1 link-local
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1012::1/64
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# exit
R1(config)# interface s0/1/0
R1(config-if)# vrf forwarding Customer_A
R1(config-if)# ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address fe80::1:4 link-local
R1(config-if)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1013::1/64
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# exit
3° Configure la interfaz R1 G0/0/1 para admitir las redes Customer_B. G0/0/1 realizará
enrutamiento entre VLAN entre VLAN 5 y 8.
R1(config)# interface g0/0/1
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
R1(config-if)# exit
R1(config)# interface g0/0/1.5
R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 5
R1(config-subif)# vrf forwarding Customer_B
R1(config-subif)# ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-subif)# ipv6 address fe80::1:2 link-local
R1(config-subif)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1012::1/64
R1(config-subif)# exit
R1(config)# interface g0/0/1.8
R1(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 8
R1(config-subif)# vrf forwarding Customer_B
R1(config-subif)# ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-subif)# ipv6 address fe80::1:3 link-local
R1(config-subif)# ipv6 address 2001:db8:acad:1013::1/64
R1(config-subif)# end
IMPLEMENT VRF LITE
SERVICIOS POR INTERNET
Paso 2: Verifique la configuración de VRF-Lite.
1° Compruebe las asignaciones de interfaz mediante el comando show ip vrf
interfaces.
R1# show ip vrf interfaces
Interface IP-Address VRF Protocol
Gi0/0/0 10.1.2.1 Customer_A up
Se0/1/0 10.1.3.1 Customer_A up
Gi0/0/1.5 10.1.2.1 Customer_B up
Gi0/0/1.8 10.1.3.1 Customer_B
IMPLEMENT VRF LITE
SERVICIOS POR INTERNET
2° Verifique las tablas de enrutamiento VRF con el comando show ip route vrf vrf_name
y show ipv6 route vrf vrf_name.
R1# show ip route vrf Customer_A | begin Gateway
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 4 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.1.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
L 10.1.2.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
C 10.1.3.0/24 is directly connected, Serial0/1/0
L 10.1.3.1/32 is directly connected, Serial0/1/0
R1# show ipv6 route vrf Customer_B
IPv6 Routing Table - Customer_B - 5 entries
Codes: C - Connected, L - Local, S - Static, U - Per-user Static route
<output omitted>
a - Application
C 2001:DB8:ACAD:1012::/64 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0/1.5, directly connected
L 2001:DB8:ACAD:1012::1/128 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0/1.5, receive
C 2001:DB8:ACAD:1013::/64 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0/1.8, directly connected
L 2001:DB8:ACAD:1013::1/128 [0/0]
via GigabitEthernet0/0/1.8, receive
IMPLEMENT VRF LITE
SERVICIOS POR INTERNET
Configure static routing at R1 for each VRF.
En este paso, configurará R1 para que pueda llegar a redes distantes en cada VRF. Los
sistemas vecinos (D1, D2, R2 y R3) ya tienen rutas estáticas configuradas, por lo que tan
pronto como instale correctamente estas rutas estáticas, habrá una accesibilidad total
dentro de cada VRF.
3° En R1, cree rutas estáticas para las redes distantes en el Customer_A VRF utilizando
el comando ip route vrf vrf_name destination_network next-hop .
R1(config)# ip route vrf Customer_A 192.168.2.0 255.255.255.0 g0/0/0 10.1.2.2
R1(config)# ip route vrf Customer_A 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 s0/1/0 10.1.3.2
R1(config)# ipv6 route vrf Customer_A 2001:db8:acad:2000::/64 g0/0/0 2001:db8:acad:1012::2
R1(config)# ipv6 route vrf Customer_A 2001:db8:acad:3000::/64 s0/1/0 2001:db8:acad:1013::2
IMPLEMENT VRF LITE
También podría gustarte
- UF1879 - Equipos de interconexión y servicios de redDe EverandUF1879 - Equipos de interconexión y servicios de redAún no hay calificaciones
- Equipos de interconexión y servicios de red. IFCT0410De EverandEquipos de interconexión y servicios de red. IFCT0410Aún no hay calificaciones
- Configurar VRFDocumento9 páginasConfigurar VRFJairo Alfonso AvilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guion PracticasDocumento16 páginasGuion PracticasMarta MoratillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Virtual Routing and ForwardingDocumento12 páginasVirtual Routing and ForwardingChristian ContrerasAún no hay calificaciones
- VRFDocumento12 páginasVRFChristian ContrerasAún no hay calificaciones
- Implement VRF-Lite Network with IPv4 and IPv6Documento13 páginasImplement VRF-Lite Network with IPv4 and IPv6Omar RomeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Enrutamiento VRFDocumento6 páginasEnrutamiento VRFMigue HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Introducción A VRF Lite - PacketLifeDocumento12 páginasIntroducción A VRF Lite - PacketLifeJesus RosalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Mejor práctica Cisco para puertos switch sin usarDocumento20 páginasMejor práctica Cisco para puertos switch sin usareliasAún no hay calificaciones
- CCNA 2 Final TestDocumento22 páginasCCNA 2 Final TestTerryBonsAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller VoIP con VLANs para Voz y DatosDocumento3 páginasTaller VoIP con VLANs para Voz y Datoswilliam100% (1)
- Guia 1 Unidad 2Documento27 páginasGuia 1 Unidad 2Justin MillerAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionarios CiscoDocumento48 páginasSolucionarios CiscoJuan Sanchez100% (1)
- 8.1.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 On A SwitchDocumento10 páginas8.1.2.5 Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 On A SwitchMAURICIO CHAVEZ DIAZAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe Caso de Estudio MPLS VPNDocumento17 páginasInforme Caso de Estudio MPLS VPNDavid GuevaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Grupo19 Tarea1Documento269 páginasGrupo19 Tarea1kevinAún no hay calificaciones
- VRF router tablaDocumento3 páginasVRF router tablaFASTDROIDGENAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Final Respuestas Ccna2Documento22 páginasExamen Final Respuestas Ccna2DouglasAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Telecomunicaciones Prueba ResueltaDocumento5 páginasExamen Telecomunicaciones Prueba ResueltaYair MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuestionario Configuración CME y QoSDocumento3 páginasCuestionario Configuración CME y QoSGhino ArandaAún no hay calificaciones
- BSCIInter VRFRoutingDocumento21 páginasBSCIInter VRFRoutingrichardbernalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Final Respuestas Ccn2 6Documento52 páginasExamen Final Respuestas Ccn2 6Enrique SandovalAún no hay calificaciones
- Examin Final Modulo 4Documento31 páginasExamin Final Modulo 4andres_sg07Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de OSPF PDFDocumento10 páginasEjercicios de OSPF PDFMairim LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Ospf 2022Documento19 páginasOspf 2022DavidFer DuraznoAún no hay calificaciones
- MRADocumento2 páginasMRAJohn QuerolAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio OSPFDocumento9 páginasEjercicio OSPFGerman Arteaga RiosAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 04 - Configuración de VTP y Enrutamiento Entre VLANDocumento10 páginasLab 04 - Configuración de VTP y Enrutamiento Entre VLANRicardo AndrésAún no hay calificaciones
- Part 1Documento11 páginasPart 1Donaldo BejeranoAún no hay calificaciones
- 10.2.4.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv2Documento4 páginas10.2.4.3 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv2Denilson MolinaAún no hay calificaciones
- guia cisco 819_LTEDocumento7 páginasguia cisco 819_LTELuis FernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Facilidad VRF LiteDocumento15 páginasFacilidad VRF LiteOmar Garcia FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- !!!prueba de Habilidades CCNA!!!Documento9 páginas!!!prueba de Habilidades CCNA!!!paraestudiounadAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.2.2 LAB EspañolDocumento11 páginas1.2.2 LAB EspañolJhan Pablo Forero SalasAún no hay calificaciones
- Monografia Proyecto de InvestigacionDocumento26 páginasMonografia Proyecto de InvestigacionDiegoJaraEsquivelAún no hay calificaciones
- Red MPLS - Metroethernet Une V2Documento57 páginasRed MPLS - Metroethernet Une V2José Guillermo Silva AcevedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Red tres sucursales RIPng V.35 interfaces pasivasDocumento17 páginasRed tres sucursales RIPng V.35 interfaces pasivasCamilo Andrés Peña QuintanaAún no hay calificaciones
- CCNA 2 Exámen Final Modelo2Documento20 páginasCCNA 2 Exámen Final Modelo2gerenas34Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lab3 ProtocolosDocumento14 páginasLab3 ProtocolosRenato Tomas Davila MayorgaAún no hay calificaciones
- ISP Failover With Default Routes Using IDocumento5 páginasISP Failover With Default Routes Using INelson MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.1.2 Lab - Implement Inter-VLAN RoutingDocumento11 páginas1.1.2 Lab - Implement Inter-VLAN RoutingOmar RomeroAún no hay calificaciones
- 10.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv3Documento4 páginas10.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv3juanvelusAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 1 Vo IPDocumento30 páginasEjercicio 1 Vo IPOswaldo AlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuaderno de InformesDocumento15 páginasCuaderno de InformesMiguel angel Canales preciadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Configuración OSPFDocumento34 páginasTaller Configuración OSPFJOHAN CASTELLANOS GALINDOAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 OSPF ExercisesDocumento10 páginas04 OSPF ExercisesHoracio Alejandro KAún no hay calificaciones
- Kadr U2 Ea LupmDocumento22 páginasKadr U2 Ea LupmJhorge TerrezpAún no hay calificaciones
- 7.3.2.4 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 and RIPngDocumento13 páginas7.3.2.4 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 and RIPngdiana paola puentes pachecoAún no hay calificaciones
- 10.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv3Documento5 páginas10.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv3Marcos Antonio de LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Configuración de DHCPv4 Básico en Un Swich Ejer4Documento13 páginasConfiguración de DHCPv4 Básico en Un Swich Ejer4Diego SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Enrrutamiento 5-Vlan - Ros - AclDocumento16 páginasEnrrutamiento 5-Vlan - Ros - AclHugoAtaucusiAltamiranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 6Documento11 páginasCapitulo 6c2franco23Aún no hay calificaciones
- CCNA 2 R & S Fundamentos Práctica Final v5.0 2.014 Respuestas de Exámenes - Examen CCNA5Documento12 páginasCCNA 2 R & S Fundamentos Práctica Final v5.0 2.014 Respuestas de Exámenes - Examen CCNA5Liliann Vidaurre TuñoqueAún no hay calificaciones
- 10.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv3Documento4 páginas10.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv3ameliaAún no hay calificaciones
- 7.3.2.4 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 and RIPngDocumento13 páginas7.3.2.4 Lab - Configuring Basic RIPv2 and RIPngAlex Enrique Arenas OviedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Configuración Rápida de Switches de Área de Campus de La Serie S PDFDocumento61 páginasConfiguración Rápida de Switches de Área de Campus de La Serie S PDFOscar Javier MonsalveAún no hay calificaciones
- Examennn-Final-Henry Raul Ccama CruzDocumento3 páginasExamennn-Final-Henry Raul Ccama CruzHenry Raul Ccama CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- 10.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv3 - ILMDocumento5 páginas10.2.4.4 Packet Tracer - Troubleshoot Multiarea OSPFv3 - ILMÁngel Rafael Ogando VenturaAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratorio # 2Documento7 páginasLaboratorio # 2Cesar Buitrago LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Encuesta Socioeconomica Saneamiento SC HumalsoDocumento3 páginasEncuesta Socioeconomica Saneamiento SC HumalsoGrisel Franci Calizaya FalcónAún no hay calificaciones
- Segundo BásicoDocumento5 páginasSegundo Básicocarolina castroAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario para revisión modalidad educativa virtualDocumento1 páginaFormulario para revisión modalidad educativa virtualAnonymous wpgPkYfkXAún no hay calificaciones
- Plan de Tutoria y Convivencia Escolar-17Documento36 páginasPlan de Tutoria y Convivencia Escolar-17Marco TiconaAún no hay calificaciones
- Matriz Herramientas Formato Sar 07-10-2019Documento2 páginasMatriz Herramientas Formato Sar 07-10-2019Lizeth Yadira Silva RondonAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis y Diseño de Sistemas de Informacion Unidad 2Documento2 páginasAnalisis y Diseño de Sistemas de Informacion Unidad 2Alex Ochoa FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- MÓDULO I CompetenciasDocumento25 páginasMÓDULO I CompetenciasRusell Iuit ManzaneroAún no hay calificaciones
- Secadores de TamborDocumento5 páginasSecadores de TamborFavio Andrés Chavez0% (1)
- Banco Total FPHDocumento151 páginasBanco Total FPHDaniela BañosAún no hay calificaciones
- Bombas HidraulicasDocumento2 páginasBombas HidraulicasJorge E ÁvilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cotizacion Gestion CorponariñoDocumento1 páginaCotizacion Gestion CorponariñoChristian David Tapia LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Materiales para La Fabricacion de TanqueDocumento15 páginasMateriales para La Fabricacion de TanqueKristal valera gonzalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño y AnálisisDocumento5 páginasDiseño y AnálisisJuan Garcia L.Aún no hay calificaciones
- The Execution TrapDocumento2 páginasThe Execution TrapIsmael Pérez Montes de OcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad No. 2 Modulo 3 LLENODocumento3 páginasActividad No. 2 Modulo 3 LLENODamarys Del rosarioAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario de Inscripción CampamentoDocumento2 páginasFormulario de Inscripción Campamentoanonimo anonimoAún no hay calificaciones
- Montaje de sistema electrohidráulico para prensa de construcción de tolvasDocumento78 páginasMontaje de sistema electrohidráulico para prensa de construcción de tolvasAlberto OrihuelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Schweblin Samanta Bibliografia 2019Documento5 páginasSchweblin Samanta Bibliografia 2019Fernando EspositoAún no hay calificaciones
- D1 A2 FICHA Elaboramos Los Diseños de Las Mantas.Documento4 páginasD1 A2 FICHA Elaboramos Los Diseños de Las Mantas.Lucia VillanuevaAún no hay calificaciones
- Administración de negocios: Antropología filosófica y teológicaDocumento3 páginasAdministración de negocios: Antropología filosófica y teológicaJulio Ernesto Montero BenavidesAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuestiones Éticas en Psicoterapia en LíneaDocumento72 páginasCuestiones Éticas en Psicoterapia en LíneaEva PardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Marco Disciplinar HeliconiaDocumento5 páginasMarco Disciplinar HeliconiaNatalia BravoAún no hay calificaciones
- CIMENTACIONESDocumento89 páginasCIMENTACIONESmilo_122_Aún no hay calificaciones
- El OrnitorrincoDocumento20 páginasEl OrnitorrincoSantocielo1Aún no hay calificaciones
- CONDUCCION Y TRASLADO Transporte Ext e Int Faena Puerto en Vehiculo Liviano - 31.08.20Documento25 páginasCONDUCCION Y TRASLADO Transporte Ext e Int Faena Puerto en Vehiculo Liviano - 31.08.20Ventas De Ocacion100% (1)
- Instrumentacion en EspectrosDocumento4 páginasInstrumentacion en EspectrosMigue EspinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Documento Tecnico #84 Planificacion Del Trabajo de Auditoria V0.2Documento87 páginasDocumento Tecnico #84 Planificacion Del Trabajo de Auditoria V0.2RobertoAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 Juegos Divertidos para Aprender A LeerDocumento4 páginas10 Juegos Divertidos para Aprender A LeerSonia RiveraAún no hay calificaciones
- 3.3 Civilizacion ChinaDocumento2 páginas3.3 Civilizacion ChinaGeraldine GutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Correo Propuesta Rebajas de ClasificadoresDocumento1 páginaCorreo Propuesta Rebajas de ClasificadoresJack Robert Meza SanchezAún no hay calificaciones