Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Formulario Cónicas
Cargado por
colombamonaga19Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Formulario Cónicas
Cargado por
colombamonaga19Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
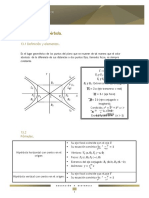
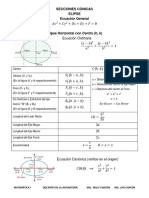
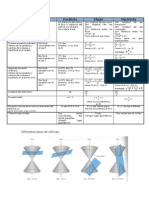
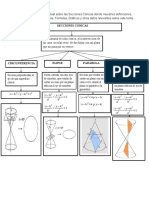
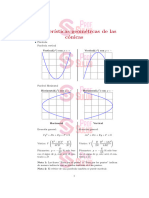
FORMULARIO DE CÓNICAS
Curva Parábola Elipse Hipérbola
Constantes 𝑝 = distancia del vértice al 2𝑎 = longitud del eje mayor 2𝑎 = longitud del eje real o transverso
foco y también distancia del 2𝑏 = longitud del eje menor 2𝑏 = longitud del eje imaginario o conjugado
vértice a la directriz. 2𝑐 = distancia entre los focos 2𝑐 = distancia entre los focos
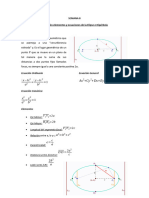
Foco sobre el eje 𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 − 𝑏 2 𝑐 2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2
Focos sobre el eje mayor Focos sobre el eje real o transverso
2 Asíntotas con 𝐶(ℎ, 𝑘) y eje
𝑦 = 4𝑝𝑥 x2 y 2 x2 y2
Ecuación Eje focal + =1 − =1 transverso paralelo al eje 𝑋
Directriz: 𝑥 = − 𝑝
Principal coincidente con Foco ( 𝑝 , 0 ) a 2 b2 a 2 b2 b
Vértices de la el eje 𝑋 Focos (𝑐, 0) ; (−𝑐, 0) Focos (𝑐, 0) ; (−𝑐, 0) y−k = ( x − h)
a
parábola y centro 𝑥 2 = 4𝑝𝑦 Asíntotas con 𝐶(ℎ, 𝑘) y eje
x2 y 2 y 2 x2
de la elipse e Eje focal Directriz: 𝑦 = − 𝑝 + =1 − =1 transverso paralelo al eje 𝑌
hipérbola en el coincidente con Foco ( 0 , 𝑝 ) b2 a 2 a 2 b2 a
origen el eje 𝑌 Focos (0, 𝑐) ; (0, −𝑐) Focos (0, 𝑐) ; (0, −𝑐) y−k = ( x − h)
b
(𝑦 – 𝑘)2 = 4𝑝(𝑥 – ℎ)
( x − h) (y −k) 𝑉 (ℎ + 𝑎 , 𝑘)
( x − h) (y −k)
2 2 2 2
𝑉 (ℎ + 𝑎 , 𝑘)
Ecuación Eje focal Directriz: 𝑥 = ℎ – 𝑝
2
+ 2
=1 𝑉 (ℎ – 𝑎 , 𝑘)
2
− 2
=1 𝑉 (ℎ – 𝑎 , 𝑘)
paralelo con Foco ( ℎ + 𝑝 , 𝑘 ) a b a b
Principal
el eje X Focos (ℎ + 𝑐, 𝑘) ; (ℎ – 𝑐, 𝑘) 𝐵 (ℎ, 𝑘 + 𝑏 ) Focos (ℎ + 𝑐, 𝑘) ; (ℎ – 𝑐, 𝑘) 𝐵 (ℎ, 𝑘 + 𝑏 )
Vértices de la 𝐵 (ℎ , 𝑘 – 𝑏 ) 𝐵 (ℎ, 𝑘 – 𝑏 )
parábola y centro (𝑥 – ℎ)2 = 4𝑝(𝑦 – 𝑘)
( x − h) (y −k) 𝑉 (ℎ , 𝑘 + 𝑎)
(y −k) ( x − h)
2 2 2 2
de la elipse e 𝑉 (ℎ , 𝑘 + 𝑎)
Eje focal Directriz: 𝑦 = 𝑘 – 𝑝 + =1 𝑉 (ℎ , 𝑘 – 𝑎 ) − =1 𝑉 (ℎ , 𝑘– 𝑎 )
hipérbola en el paralelo con Foco ( ℎ , 𝑘 + 𝑝 ) b 2
a 2
a 2
b 2
punto (ℎ, 𝑘) el eje Y Focos (ℎ, 𝑘 + 𝑐) ; (ℎ , 𝑘 – 𝑐) 𝐵 (ℎ + 𝑏 , 𝑘 ) Focos (ℎ, 𝑘 + 𝑐) ; (ℎ , 𝑘 – 𝑐) 𝐵 (ℎ + 𝑏, 𝑘 )
𝐵 (ℎ – 𝑏 , 𝑘) 𝐵 (ℎ– 𝑏 , 𝑘 )
2𝑏 2 2𝑏 2
Longitud del lado recto |4𝑝 |
𝑎 𝑎
c c
Excentricidad 𝑒=1 e= 1 e= 1
a a
Eje focal
coincidente con 𝑦 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0 𝐴𝑥 2 + 𝐶𝑦 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0; 𝐴 < C 𝐴𝑥 2 − 𝐶𝑦 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0
Ecuación general el eje 𝑋
de la cónica Eje focal
coincidente con 𝑥 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0 𝐴𝑥 2 + 𝐶𝑦 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0; A > C 𝐴𝑥 2 − 𝐶𝑦 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0
el eje 𝑌
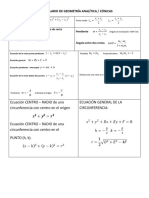
Circunferencia: Ecuación Canónica: 𝑥2 + 𝑦 2 = 𝑅 2 ; Ecuación Principal: (𝑥 − ℎ)2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑅 2 ; Ecuación General: 𝑥2 + 𝑦 2 + 𝐷𝑥 + 𝐸𝑦 + 𝐹 = 0
y2 − y1
( x1 − x2 )2 + ( y1 − y2 ) ; y − y1 = ( x − x1 ) ;
2
Recta : 𝑑(𝐴, 𝐵) = y2 − y1 ; x + x y + y2 ; y − y1 = m ( x − x1 ) ; y = mx + n ; Ax + By + C = 0
m= P1 = 1 2 , 1
x2 − x1 2 2 2 x2 − x1
También podría gustarte
- Resumen de CónicasDocumento1 páginaResumen de CónicasUciel nicolas MolaAún no hay calificaciones
- Resumen Secciones Cónicas PDFDocumento1 páginaResumen Secciones Cónicas PDFMaría Isabel Martínez OrtizAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 13 HiperbolaDocumento5 páginasUnidad 13 HiperbolaREQUELMER BENAVIDES NUÑEZ - FA - ESTUDIANTEAún no hay calificaciones
- Secciones Cónicas - ElipseDocumento2 páginasSecciones Cónicas - Elipsestefany sierraAún no hay calificaciones
- Complemento Matemàtico para Ingenieros: SESIÓN 6: Ecuación de La HipérbolaDocumento28 páginasComplemento Matemàtico para Ingenieros: SESIÓN 6: Ecuación de La HipérbolajahairaAún no hay calificaciones
- La HiperbolaDocumento10 páginasLa HiperbolaIvan TelloAún no hay calificaciones
- Teorema de Steiner o de Ejes ParalelosDocumento59 páginasTeorema de Steiner o de Ejes ParalelosROSALIA VICTORIA TAPIA CHAVEZAún no hay calificaciones
- Tablas ElipseDocumento1 páginaTablas ElipseSamuelAún no hay calificaciones
- Conicas PDFDocumento9 páginasConicas PDFGiovanni Ignacio Simoni StoccoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Geo 9 25 - 04 - 2022Documento22 páginasTaller Geo 9 25 - 04 - 2022jamileth cardenasAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario de Geometria AnaliticaDocumento2 páginasFormulario de Geometria AnaliticaAndré LujánAún no hay calificaciones
- ElipseDocumento6 páginasElipseVictor CalvoAún no hay calificaciones
- FormularioDocumento2 páginasFormulariojaqueline rodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Elipse Parábola HiperbolaDocumento5 páginasGuía Elipse Parábola Hiperbolaluispdzp100% (31)
- 2 - CAP 6 La Elipse Parte 2 AD 22Documento4 páginas2 - CAP 6 La Elipse Parte 2 AD 22IsabellaAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoría Sobre La HipérbolaDocumento3 páginasTeoría Sobre La Hipérbolamariaalejandrarodriguez2107Aún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica Undecimo Nuredine GaviriaDocumento23 páginasMatematica Undecimo Nuredine GaviriaJulian PadillaAún no hay calificaciones
- S10MRMDocumento28 páginasS10MRMMilan Alessandro Lavado JaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Parabola Circ Elipse HiperbDocumento1 páginaParabola Circ Elipse HiperbobnergupiocAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 5 - HiperbolaDocumento7 páginasSemana 5 - HiperbolaSonia CasaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 6 HiperbolaDocumento9 páginasUnidad 6 HiperbolaXim GBAún no hay calificaciones
- Conicas Formula PDFDocumento1 páginaConicas Formula PDFCata PeronaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion 3 ElipseDocumento7 páginasSesion 3 ElipseNIURKA BELEN RAMIREZ SILVAAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario Etapa 4 FyRDocumento2 páginasFormulario Etapa 4 FyRsytelbanregioAún no hay calificaciones
- CónicasDocumento3 páginasCónicasJOHANA GOMEZ ZENTENOAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia#8-Matematicas-Secciones Conicas-10°cDocumento3 páginasGuia#8-Matematicas-Secciones Conicas-10°cYamelys Isabel Mercado De Los Reyes100% (2)
- Secciones ConicasDocumento6 páginasSecciones ConicasGio Josué FernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Parabola Elipse e HiperboleDocumento10 páginasParabola Elipse e Hiperboledilan avilaAún no hay calificaciones
- HIPERBOLADocumento5 páginasHIPERBOLAramonramon5265Aún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario Geometria Analitica 385178 Downloable 2053608Documento3 páginasFormulario Geometria Analitica 385178 Downloable 2053608Moni NuñezAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Geo 5 11 - 04 - 2022Documento22 páginasTaller Geo 5 11 - 04 - 2022jamileth cardenasAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 8Documento5 páginasSemana 8p41573354Aún no hay calificaciones
- La HipérbolaDocumento6 páginasLa HipérbolaEdwin GanazhapaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fórmulas VRP, Cónicas y CuádricasDocumento3 páginasFórmulas VRP, Cónicas y CuádricasMelina GabarruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Elipse e HiperbolaDocumento12 páginasElipse e HiperbolaLore CasaAún no hay calificaciones
- Conicas IPNDocumento3 páginasConicas IPNAna HOAún no hay calificaciones
- La Hiperbola y TallerDocumento17 páginasLa Hiperbola y TallerMaria Jose Valencia GaviriaAún no hay calificaciones
- Parabola Elipse e HiperboleDocumento7 páginasParabola Elipse e HiperboleDilan AvilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Parabola, Elipse e HiperbolaDocumento5 páginasParabola, Elipse e HiperbolaJorge Edgar C SAún no hay calificaciones
- Subtemas 6.1 - 6.2.-La HiperbolaDocumento19 páginasSubtemas 6.1 - 6.2.-La HiperbolaPablo AndresAún no hay calificaciones
- S14.s1 - IMI SECCIONES CONICAS LA HIPERBOLADocumento5 páginasS14.s1 - IMI SECCIONES CONICAS LA HIPERBOLASupellex AqpAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuacion de La Parabola 2022Documento3 páginasEcuacion de La Parabola 2022César Hilton Aguilar RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Material 003Documento9 páginasMaterial 003Victoria TarapaquiAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulas Geometria AnaliticaDocumento1 páginaFormulas Geometria AnaliticaDaniel M. MoreiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Elipse - Parábola - HipérbolaDocumento4 páginasGuía Elipse - Parábola - Hipérbolacarolina bombigAún no hay calificaciones
- CónicasDocumento23 páginasCónicasantonela nogueiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadro Comparativo AlgebraDocumento2 páginasCuadro Comparativo Algebragustavogiagnorio04Aún no hay calificaciones
- AnalisisDocumento6 páginasAnalisisJoel ManriqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Ing Civil ConicasDocumento8 páginasIng Civil ConicasDylan VelateguiAún no hay calificaciones
- ElipseDocumento10 páginasElipseLIDIA YANAAún no hay calificaciones
- Conic AsDocumento12 páginasConic AsurielAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Geo 13 09 - 05 - 2022Documento19 páginasTaller Geo 13 09 - 05 - 2022Jamileth Cardenas VegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoria de HiperbolasDocumento3 páginasTeoria de HiperbolasELIEZER ROJAS83% (18)
- HiperbolaDocumento8 páginasHiperbolaalex altamiranoAún no hay calificaciones
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDe EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas resueltos de electromagnetismo. Volumen I: ElectrostáticaDe EverandProblemas resueltos de electromagnetismo. Volumen I: ElectrostáticaAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 8Documento23 páginasCapitulo 8Austin Carter O'NealAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.2 Revision de Algebra MatricialDocumento6 páginas1.2 Revision de Algebra MatricialNathaly Soledad NazarenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Modulo 3 - Mezcla CrudaDocumento49 páginasModulo 3 - Mezcla CrudaSantiago MadridAún no hay calificaciones
- Elementos de Mecanismos - PDFDocumento172 páginasElementos de Mecanismos - PDFRafael GutiérrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion 3-4 EjerciciosDocumento9 páginasSesion 3-4 EjerciciosPercyAún no hay calificaciones
- Segundo Taller de Introduccion - Mate. Ing. Ii-2018-IiDocumento4 páginasSegundo Taller de Introduccion - Mate. Ing. Ii-2018-IiRenzo CcopaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Propiedades de La Roca Porosidad MaterialDocumento41 páginas1 Propiedades de La Roca Porosidad MaterialManuel Azancot100% (1)
- Discusion Practica 1Documento2 páginasDiscusion Practica 1ariAún no hay calificaciones
- Memoria de CalculoDocumento14 páginasMemoria de CalculoJorge Veramendi SilvaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuaderno de Informe MantenimientoDocumento11 páginasCuaderno de Informe MantenimientoBeto RffoBalTAún no hay calificaciones
- Teorema de Pitagoras y Euclides - Paulo Mu Oz LozanoDocumento9 páginasTeorema de Pitagoras y Euclides - Paulo Mu Oz LozanoPaulo Muñoz LozanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sistema de Base de Datos II Tarea 2.1Documento2 páginasSistema de Base de Datos II Tarea 2.1EmmanuelBeltreAún no hay calificaciones
- CONSECUENCIAS DE LA FRAGMENTACIÓN Vial - Efecto de BordeDocumento45 páginasCONSECUENCIAS DE LA FRAGMENTACIÓN Vial - Efecto de BordeAna RamírezAún no hay calificaciones
- Características Fotografía EstenopeicaDocumento5 páginasCaracterísticas Fotografía EstenopeicaDouglas Segovia P.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Final de Doctrina PolicíalDocumento4 páginasExamen Final de Doctrina PolicíalPaulina Mamani VargasAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía #2 Matematicas 3° Periodo Grado 3Documento7 páginasGuía #2 Matematicas 3° Periodo Grado 3ANGELA MILENA MORENO ESTUPIÑANAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de Puntos Evaluables - Escenario 6 - Primer Bloque-Ciencias Basicas - Virtual - Cálculo 2 - (GrupoDocumento7 páginasActividad de Puntos Evaluables - Escenario 6 - Primer Bloque-Ciencias Basicas - Virtual - Cálculo 2 - (GrupoYHEISONAún no hay calificaciones
- Unsch: Capitulo 5 Mínimos Cuadrados RestringidosDocumento8 páginasUnsch: Capitulo 5 Mínimos Cuadrados RestringidosJUAN ALBERTO HUARIPUMA VARGASAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesión 2Documento45 páginasSesión 2Joan EspinozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Glosario de Las Matemáticas en InglésDocumento7 páginasGlosario de Las Matemáticas en Inglésmariyons-1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ley de HessDocumento7 páginasLey de HessAndres Camilo Moreno GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica Matlab 2Documento11 páginasPráctica Matlab 2Diego VillasmilAún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis Del Pib de EE - UU A Través Del Modelo KeynesianoDocumento39 páginasAnálisis Del Pib de EE - UU A Través Del Modelo Keynesianosofia avendañoAún no hay calificaciones
- S - Matematica - II 11 1Documento13 páginasS - Matematica - II 11 1Tristan ParkerAún no hay calificaciones
- Enterprise Java Beans, Session Beans, Transacciones y ExcepcionesDocumento161 páginasEnterprise Java Beans, Session Beans, Transacciones y ExcepcionesHugo Ernesto EspinosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Formato Del Número de Serie de 17 Dígitos para Productos de Construcción de CNHDocumento3 páginasFormato Del Número de Serie de 17 Dígitos para Productos de Construcción de CNHKrumaq Refacciones AcapulcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Texto Descartes Selectividad PDFDocumento7 páginasTexto Descartes Selectividad PDFVictorianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen U1 Sdlle 2021 83v Final BDocumento1 páginaExamen U1 Sdlle 2021 83v Final BEduardo TorresAún no hay calificaciones
- Control Naturales LA MATERIADocumento2 páginasControl Naturales LA MATERIACristian Ba EnAún no hay calificaciones
- Introducción A La Agrimensura Tarea 7Documento5 páginasIntroducción A La Agrimensura Tarea 7Ramón Leandro Ozoria De la CruzAún no hay calificaciones