Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Práctica Semana 1 Producto Cartesiano
Cargado por
Alfredotavi CantosuasnabarDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Práctica Semana 1 Producto Cartesiano
Cargado por
Alfredotavi CantosuasnabarCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Complementos de Matemática
Guía de práctica N°01: Producto Cartesiano- Relaciones Binarias
Apellidos y Nombres:
Sección:
Fecha : / /
Docente: Mg. Lucía Joyce Taipe Quispe
Tipo de práctica: Individual
Instrucciones: Resolver las siguientes peguntas de forma personal.
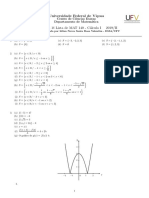
Producto Cartesiano
1. Halle el valor de x e y, en cada caso:
a. (4, 2𝑥 — 10) = (𝑥— 1, 𝑦 + 2)
b. (𝑦— 2 , 2 𝑥 + 1 ) = (𝑥 — 1 , 𝑦 + 2 )
c. (𝑥 + 4, 6) = (10, 𝑦 — 𝑥)
d. (𝑥 + 𝑦, 3) = (5, 𝑦 − 𝑥)
e. (4 ,2𝑥 — 10) = (𝑥 — 1, 𝑦 + 2)
f. (5𝑥 + 2𝑦, −4) = (−1,2𝑥 — 𝑦)
g. (𝑥 + 5 , 3 − 𝑦 ) = (7,2)
h. (𝑥 — 7𝑦 , 2𝑥 — 6𝑦) = (15, −10)
i. (3𝑥 — 8𝑦 , 4𝑥 + 3𝑦) = ( 4 − 2 𝑥 − 10𝑦 , 2𝑥 + 4𝑦 + 7)
j. (2𝑥 — 𝑦 , 𝑥 + 𝑦 + 3) = (𝑥 + 𝑦 + 1 , 2𝑥 + 𝑦)
2. Dados los conjuntos
𝐴 = {𝑥 ∈ 𝑍/ − 𝑙 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 }
𝐵 = {𝑥 ∈ 𝑍/1 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4}
𝐶 = {𝑥 ∈ 𝑍 / 1 < 𝑥 ≤ 4}
Halla los siguientes conjuntos: 𝐴𝑥𝐵, 𝐵𝑥𝐶, (𝐴 − 𝐶)𝑥𝐵
3. Sea 𝐴 = {𝑥 ∈ 𝑅 /1 < 𝑥 < 3} y 𝐵 = {𝑦 ∈ 𝑅 / 2 < 𝑦 < 4}. Hallar 𝐴 𝑥 𝐵
4. Dados los conjuntos: 𝐴 = {𝑥 ∈ 𝑁/𝑥 < 3}, 𝐵 = {𝑥 𝑒𝑁 / 𝑥 𝑒𝑠 𝑝𝑎𝑟 𝑦 𝑥 < 5}, 𝐶 = {𝑥 ∈
𝑁 /𝑥 𝑒𝑠 𝑖𝑚𝑝𝑎𝑟 𝑦 𝑥 ≤ 4}. Hallar el conjunto (𝐴 ∩ 𝐵)𝑥(𝐶 − 𝐴)
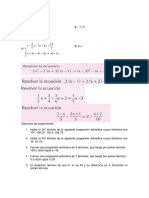
Producto Cartesiano
Representa cada relación, como un conjunto de pares ordenados, y halla su dominio y su rango
1. A = 3x+4/ - 6 x 1; x Z R4 = (x,y) G x IN / y = 4 – 2x
x−2
B= / − 6 x 3; x Z 5. H = 10 - x2 / -6 x 2; x Z
2
x+5 R5 = (x,y) H x Z / y = 30 – 3x
R1 = (x,y) AxB/ y=
2
x −1
2. C = 3 - 2x/ -5 x 7; x Z 6. B= / − 3 x 3; x Z
4
1 − 3x
D= / − 7 x 3; x Z R6 = (x,y) B x Z / y = 4x – 1
3
x+7
R2 = (x,y) C x D / y =
3 2x − 1
7. H= / − 5 x 3; x Z
2
3. E = x2 –7/ -5 x 3; x Z R7 = (x,y) H x Z / y = 6 – 2x
F = 2x + 7/ - 5 x 4; x Z
R3 = (x,y) E x F / y = -2x + 1
8. J = 5 - 3x / -6 x 5; x Z
R8 = (x,y) J2 / y = 3x -10
4. G = 2x2 –10/ -3 x 4; x Z
También podría gustarte
- SEMANA 1 Resuelta CalculoDocumento43 páginasSEMANA 1 Resuelta CalculoALDAIR ERICK MORA CUEVA100% (1)
- Guía 2 Ecuaciones Lineales, Aplicaciones y Despeje de VariablesDocumento4 páginasGuía 2 Ecuaciones Lineales, Aplicaciones y Despeje de VariablesYeissonAlexisAcevedoAgudeloAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Ecuaciones e InecuacionesDocumento4 páginasGuía Ecuaciones e InecuacionesJonathan SalasAún no hay calificaciones
- 05 Operaciones Con Polinomios RevisadaDocumento5 páginas05 Operaciones Con Polinomios RevisadaAdriana AvelarAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Calculo D.BDocumento4 páginasEjercicios Calculo D.BDaniela BermudezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios CalculoDocumento4 páginasEjercicios CalculoDaniela BermudezAún no hay calificaciones
- Gabarito 1 CorrigidoDocumento4 páginasGabarito 1 CorrigidoIsabela FidelisAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Matemática I-InECUACIONESDocumento2 páginasEjercicios de Matemática I-InECUACIONESAdrián Hector Reyes CalderónAún no hay calificaciones
- Uni2 Act7 Tal Exp AlgDocumento3 páginasUni2 Act7 Tal Exp Algdiana maria salcedo pelaezAún no hay calificaciones
- Despeje Ecu2xc2Documento1 páginaDespeje Ecu2xc2profe2000Aún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Superior - Ecuaciones y DesigualdadesDocumento5 páginasAlgebra Superior - Ecuaciones y DesigualdadesOscar Garate0% (1)
- Taller 5 Cálculo IIIDocumento8 páginasTaller 5 Cálculo IIIMaria CeliaAún no hay calificaciones
- Par Ordenado JesusDocumento6 páginasPar Ordenado JesusjesusalvaradojassoAún no hay calificaciones
- 3.TP Sistemas de Ecuaciones No LinealesDocumento17 páginas3.TP Sistemas de Ecuaciones No Linealesnoelia CufreAún no hay calificaciones
- Facultad de Ciencias de La Salud Programa de Odontología: Informe AcadémicoDocumento7 páginasFacultad de Ciencias de La Salud Programa de Odontología: Informe AcadémicoAlexandra Mori TorresAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Matemáticas 25 de MayoDocumento13 páginasEjercicios de Matemáticas 25 de MayoShirly MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad N°8-Practica-Relaciones Binarias y Funciones-Matematica y LogicaDocumento8 páginasActividad N°8-Practica-Relaciones Binarias y Funciones-Matematica y LogicaCristianHerbasPillacaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea de Mate #4Documento3 páginasTarea de Mate #4dcrispinpradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Relaciones RMDocumento1 páginaRelaciones RMjaimeduH.Aún no hay calificaciones
- La RectaDocumento9 páginasLa RectaOne lef YaquiAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Grupal 4 AlgDocumento14 páginasTrabajo Grupal 4 AlgTernurita Valentina VeraAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea Agronomía Relaciones y FuncionesDocumento3 páginasTarea Agronomía Relaciones y FuncionesIsraelís 950% (1)
- Ejercicios Relaciones y Funciones-DPLMDocumento4 páginasEjercicios Relaciones y Funciones-DPLMJohan PCAún no hay calificaciones
- TALLER No 2. DERIVADASDocumento17 páginasTALLER No 2. DERIVADASYeims Anthony FLOREZ CASTELLANOSAún no hay calificaciones
- Rodrigo Antonio Mota Martínez Ecuaciones y DesigualdadesDocumento6 páginasRodrigo Antonio Mota Martínez Ecuaciones y DesigualdadesRodrigo Antonio Mota MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Del Portafolio de Matemáticas Del IDEADocumento2 páginasProblemas Del Portafolio de Matemáticas Del IDEACarlos RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Practica n0 12 Espero AyudarlosDocumento9 páginasGuia Practica n0 12 Espero AyudarlosRosita Geraldine Raymundo ParedesAún no hay calificaciones
- VECTORESDocumento12 páginasVECTORESAxsel LunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad Calculo 1 PDFDocumento15 páginasActividad Calculo 1 PDFAndrea RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Resolvemos Problemas - SEMANA 15Documento3 páginasResolvemos Problemas - SEMANA 15Kate LilithAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica de Matemática #08 - 3° - Relaciones BinariasDocumento3 páginasPráctica de Matemática #08 - 3° - Relaciones BinariasjustofloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 11 APDocumento8 páginasActividad 11 APDiana Marcela QUESADA GILAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller N 2 Concepto de Derivada PDFDocumento2 páginasTaller N 2 Concepto de Derivada PDFPURIFICADORA SICARU SASAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratorio 3Documento5 páginasLaboratorio 3Carlos Vicente Quiche ChiyalAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 11 MatematicasDocumento8 páginasActividad 11 Matematicasdiana maria salcedo pelaezAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia PDFDocumento2 páginasGuia PDFAlexy BordonesAún no hay calificaciones
- Resultados Ejercicios Gabriel La Cruz - C.I 28.532.730 - AdministraciónDocumento2 páginasResultados Ejercicios Gabriel La Cruz - C.I 28.532.730 - AdministraciónGabriel LacruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Practica #11 ResueltoDocumento14 páginasGuia Practica #11 ResueltoRosita NamucheAún no hay calificaciones
- TALLER SEMANA 6 RIESGOS LABORALES Jefferson CuelloDocumento6 páginasTALLER SEMANA 6 RIESGOS LABORALES Jefferson CuelloAndrea ChavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Retroalimentacion Matemática 1Documento9 páginasRetroalimentacion Matemática 1Macarena VillagraAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller de Ecuaciones Lineales DCDocumento7 páginasTaller de Ecuaciones Lineales DCDiego CuadradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas de Funciones Logaritmicas y ExponencialesDocumento7 páginasDerivadas de Funciones Logaritmicas y ExponencialesMARITZA DE LA PAZ ORTIZAún no hay calificaciones
- Rodolfo Rojas s4 Calculo 1Documento6 páginasRodolfo Rojas s4 Calculo 1max aalejandro tapia escobarAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad Dos 1algebraDocumento2 páginasUnidad Dos 1algebraFranklin Coronel RafaelAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad Dos 1algebraDocumento2 páginasUnidad Dos 1algebraFranklin Coronel RafaelAún no hay calificaciones
- Grupo - 301301-436-Tarea 3Documento19 páginasGrupo - 301301-436-Tarea 3Christian PinedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios #1Documento6 páginasEjercicios #1Ruby Del Carmen Berna VelasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario 01 de Básica 1Documento11 páginasSolucionario 01 de Básica 1juliusoneAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 5 TallerDocumento7 páginasActividad 5 TallerAndrés CaicedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 3 FuncionesDocumento8 páginasActividad 3 FuncionesJose Angel GodoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones LinealesDocumento9 páginasEcuaciones LinealesElvis ArreguiAún no hay calificaciones
- Relaciones Binarias y FuncionesDocumento12 páginasRelaciones Binarias y FuncionesAldakithoChavezLozanoAún no hay calificaciones
- 348 Tarea3Documento15 páginas348 Tarea3Kevin MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiplicación de Polinomios para Sexto de PrimariaDocumento5 páginasMultiplicación de Polinomios para Sexto de PrimariaGladysAún no hay calificaciones
- Suma de PolinomiosDocumento10 páginasSuma de Polinomiosbrayanrenezambranodiaz89Aún no hay calificaciones
- Grupo 4 - Taller # 2 DerivadasDocumento26 páginasGrupo 4 - Taller # 2 DerivadasYeims Anthony FLOREZ CASTELLANOSAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra IV BimDocumento22 páginasAlgebra IV BimJuan Carlos Sanchez DamianAún no hay calificaciones
- Alumna: Zamarith Pérez Moreno CI:31310535 3 "D"Documento16 páginasAlumna: Zamarith Pérez Moreno CI:31310535 3 "D"Marino MorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- To General de La DGETIDocumento19 páginasTo General de La DGETIapi-3730132100% (5)
- Dxsanred - La Didáctica de La Literatura Una Cuestión de ContagioDocumento7 páginasDxsanred - La Didáctica de La Literatura Una Cuestión de ContagioFundamentos InvestigaciónAún no hay calificaciones
- Caso Raquel - Marina BeneitoDocumento3 páginasCaso Raquel - Marina BeneitoMarina BeneitoAún no hay calificaciones
- Aristóteles - Poética (Ed. Alianza)Documento62 páginasAristóteles - Poética (Ed. Alianza)hurracapepe92% (36)
- La Empleabilidad Del Criminólogo/a: Propuestas para El Ámbito Público y PrivadoDocumento9 páginasLa Empleabilidad Del Criminólogo/a: Propuestas para El Ámbito Público y PrivadoArchivos de Criminología, Seguridad Privada y CriminalísticaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mapa Mental VientosDocumento2 páginasMapa Mental VientosAndres AlarconAún no hay calificaciones
- ReflexionDocumento2 páginasReflexionlichielbambino100% (1)
- Parálisis FacialDocumento4 páginasParálisis FacialEzeBorjesAún no hay calificaciones
- Fisiopatologia de PierreDocumento12 páginasFisiopatologia de PierrenoguesseAún no hay calificaciones
- Modulo de Danza Folklorica EcuatorianaDocumento99 páginasModulo de Danza Folklorica EcuatorianaMariella Centeno JaureguiAún no hay calificaciones
- Mi Credo PersonalDocumento4 páginasMi Credo PersonalSagrario Martinez RuizAún no hay calificaciones
- Aeropuerto Del Dorado EspecificacionesDocumento14 páginasAeropuerto Del Dorado EspecificacionesrolorieraAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe Técnico Ampliatorio Alca - MontegrandeDocumento7 páginasInforme Técnico Ampliatorio Alca - MontegrandeJulio Mazza CallirgosAún no hay calificaciones
- La Influencia de La Cultura y Las Identidades en Las Relaciones InterculturalesDocumento4 páginasLa Influencia de La Cultura y Las Identidades en Las Relaciones InterculturalesYulibeth Paternina GonzálezAún no hay calificaciones
- PDF Higado y Vias Biliares - CompressDocumento70 páginasPDF Higado y Vias Biliares - CompressEduardo VerdugoAún no hay calificaciones
- Biología 4Documento62 páginasBiología 4angel2 beltranAún no hay calificaciones
- Contrato Adopción de MascotaDocumento7 páginasContrato Adopción de MascotaDavid JaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedad Del Ganado y La Reforma Del Codigo Civil Por MAIZTEGUI MARTINEZ EN CONGR - DE SALTADocumento11 páginasPropiedad Del Ganado y La Reforma Del Codigo Civil Por MAIZTEGUI MARTINEZ EN CONGR - DE SALTAGiuliana PachecoAún no hay calificaciones
- Grupo Aspg Sac Constancia Pension (3) La PositivaDocumento2 páginasGrupo Aspg Sac Constancia Pension (3) La PositivaCondesu FCAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe de Modelado. FINDocumento27 páginasInforme de Modelado. FINJaner Urango AnayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 2 Condiciones Previas de La EntrevistaDocumento7 páginasTarea 2 Condiciones Previas de La Entrevistayisus CisCAAún no hay calificaciones
- Carpio Capitulo III Esquema CompressDocumento4 páginasCarpio Capitulo III Esquema Compressrocy grimesdixonAún no hay calificaciones
- Aeropuertos PresentacionDocumento46 páginasAeropuertos PresentacionRaymundo Rodriguez LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Los Números NaturalesDocumento2 páginasLos Números Naturalesnachota largaAún no hay calificaciones
- Poetas ClásicosDocumento9 páginasPoetas ClásicosJesús Eduardo Serdán SantiagoAún no hay calificaciones
- U3 VetoDocumento35 páginasU3 VetoLeandro StagnoAún no hay calificaciones
- Documento - 1992611 RESERVA 10Documento1 páginaDocumento - 1992611 RESERVA 10Luis Fernando GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Colpaso en Edificio de MiamiDocumento3 páginasColpaso en Edificio de MiamiPablo castroAún no hay calificaciones
- Relacion de EquivalenciaDocumento1 páginaRelacion de EquivalenciaJavier Alberto Baron ArangurenAún no hay calificaciones
- 1º y 2º ESO Encuesta de La Amabilidad CastillaDocumento3 páginas1º y 2º ESO Encuesta de La Amabilidad CastillasemanamjAún no hay calificaciones