100% encontró este documento útil (1 voto)
452 vistas6 páginasDominio de Funciones
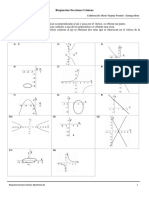
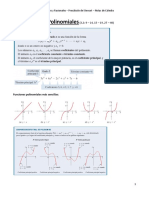
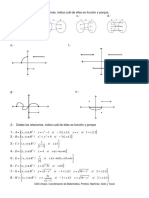
El documento presenta una serie de funciones y pide hallar el dominio de definición de cada una. Contiene funciones racionales, polinómicas, exponenciales y logarítmicas. El dominio de definición de cada función se define como el conjunto de todos los valores reales de la variable independiente para los cuales la función es bien definida.
Cargado por
Marco Antonio FloresDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd
100% encontró este documento útil (1 voto)
452 vistas6 páginasDominio de Funciones
El documento presenta una serie de funciones y pide hallar el dominio de definición de cada una. Contiene funciones racionales, polinómicas, exponenciales y logarítmicas. El dominio de definición de cada función se define como el conjunto de todos los valores reales de la variable independiente para los cuales la función es bien definida.
Cargado por
Marco Antonio FloresDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd