Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
08.tiempos Verbales
Cargado por
Mario Edgardo GonzalezTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
08.tiempos Verbales
Cargado por
Mario Edgardo GonzalezCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Introduccin a la Lectura Comprensiva de Ingls Acadmico para Medicina Veterinaria
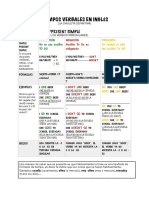
FICHA #8: TIEMPOS VERBALES (formacin)
En un curso de lectura comprensiva, la idea de presentar la formacin de los tiempos verbales es slo para reconocimiento de los mismos en los textos. El siguiente cuadro muestra, de manera muy sinttica y a travs de ejemplos, cmo se forman los tiempos verbales llamados simple en ingls, en sus formas afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa. SIMPLE PRESENT
I (You, We, They) need some more tests. (Yo) necesito algunos tests ms. She (He, It) works perfectly in this environment. (Ella) trabaja perfectamente en este ambiente. How do you (I, we, they) prepare the samples? Cmo prepars (vos) las muestras? DO+I, WE, THEY+INFINITIVO What does she (he, it) measure? Qu mide (ella)? DOES+SHE, HE, IT+INFINITIVO (NO S) They do not (dont) understand the reason. (Ellos) no comprenden la razn. DO + NOT + INFINITIVO He does not (doesnt) consider that variable at all. (l) no considera para nada esa variable. DOES + NOT + INFINITIVO (NO s)
SIMPLE PAST
I worked all night yesterday. (Yo) trabaj toda la noche ayer. VERBOS REGULARES (desinencia ed) They took it to the laboratory. (Ellos) lo llevaron al laboratorio. VERBOS IRREGULARES (2 columna, ver siguiente tema de este manual) What did you bring to the field last week? Qu trajiste al campo (vos) la semana pasada? DID+SUJETO+INFINITIVO We did not (didnt) believe it. (Nosotros) no lo cremos. DID+ NOT+VERBO INFINITIVO
SIMPLE FUTURE (will)
She will decide soon. (Ella) decidir pronto. SUJETO+WILL+INFINITIVO What will you write in the abstract? Qu escribirs (vos) en el abstract? WILL+SUJETO+ INFINITIVO They will not (wont) come until tomorrow. (Ellos) no vendrn hasta maana. SUJETO+WILL+NOT+INFINITIVO SIMPLE CONDITIONAL (WOULD) She would come if she could. (Ella) vendra si pudiera. SUJETO+WOULD+VERBO INF. What would you do if you were very rich? Qu haras si tuvieras mucho dinero? WOULD+SUJETO+VERBO INF. They would not live here if it were not for you. (Ellos) no viviran aqu si no fuera por vos. SUJ.+WOULD+NOT+VERBO INF.
1. Encerr con Prctica Opcional:
los verbos en tiempos simple de los siguientes enunciados excepto to be-
2. Expreslas en espaol. 3. Transformlas al negativo y al interrogativo, para lo cual identific correctamente el actor del enunciado. 4. Record consultar la lista de verbos irregulares para familiarizarte con los infinitivos. Ej: Zoby and Holmes (1983) reported that with extreme differences in animal size (mature cows vs stockers vs
calves), bite size values calculated indirectly from estimated herbage intake and total daily bites were different. Zoby y Holmes informaron que, con extremas diferencias en tamao del animal, (vacas maduras vs vacas en engorde vs terneros) los valores del tamao del mordisco, calculados indirectamente a partir de la ingesta de hierba y los mordiscos diarios, eran diferentes. Zoby and Holmes did not report that . Did Zoby and Holmes report that ?
1. Vaccines do not always prevent infection.
Tiempos Verbales
2. Apocrine edenomas resemble the secretory region of the apocrine glands.
3. Dry-cow therapy will cure some infections that exist at the time of drying off.
4. Basosquamous cell carcinomas do not have a tendency to develop on the head.
5. Equine Infectious Anemia tends to become an inapparent infection but occasionally results in death.
6. This observation indicates that the relationship of bite size to animal size needs further consideration.
7. Estrogen, by itself, does not contribute to the development of cystic endometrial hyperplasia or pyometra.
8. A neoplasm of intermediate malignancy is locally infiltrative and difficult to excise but does not metastasize.
9. Canine demodicosis is a common disease in dogs and occurs when large numbers of Demodeex canis mites inhabit hair follicles, sebaceous glands, or apocrine sweat glands.
10. Prevention of new cases of mastitis depends on reducing exposure of uninfected cows to infected cows during milking.
Introduccin a la Lectura Comprensiva de Ingls Acadmico para Medicina Veterinaria
El siguiente cuadro muestra, por su parte, de manera muy sinttica y a travs de ejemplos tambin, cmo se forman los tiempos verbales llamados progressive en ingls, en sus formas afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa. PRESENT PROGRESSIVE
I am analyzing the data now. (Yo) estoy analizando los datos ahora. She (He, It) is testing the equipment right now. (Ella) est probando el equipo en este momento. We (They, You) are controlling the plague. (Nosotros) estamos controlando la plaga.
PAST PROGRESSIVE
She (He, It) was working when they arrived. (Ella) estaba trabajando cuando (ellos) llegaron. I, HE, SHE, IT+WAS+ ING You, (We, They) were talking when the class started. (Vos) estabas conversando cuando la clase comenz. YOU, WE, THEY+WERE+VERBO+ -ING He was not (wasnt) reading when the phone rang. (l) no estaba leyendo cuando el telfono son. I, HE, SHE, IT+WAS+NOT+ING They were not (werent) watching the students when the accident happened. (Ellos) no estaban observando a los estudiantes cuando ocurri el accidente. YOU, WE, THEY+WERE+NOT+ ING
FUTURE PROGRESSIVE
I will be travelling by the time they arrive. SUJETO+ WILL BE+ ING Will you be waiting for us? WILL+SUJETO+BE+ ING? They will not (wont) be listening to you by the time you finish the class. SUJETO+WILL+NOT+BE+ ING CONDITIONAL PROGRESSIVE She would be studying here if she could. SUJETO+WOULD BE+ING What would you be doing if you were in the Caribbean now? WOULD+SUJETO+BE+ING He would not (wouldnt) be complaining if he knew the reason. SUJ.+WOULD NOT BE+ING
SUJETO+AM, IS, ARE+ING What is he (she, it) preparing? Qu est preparando (l) What are you (we, they) doing there? Qu ests haciendo (vos) ah? What am I doing? Qu estoy haciendo (yo)? AM, IS, ARE+SUBJECT+ING?
I am not (m not) saying that. (Yo) no estoy diciendo eso. Why was she analyzing the samples, He is not (isnt) looking at that instead of you, when I arrived? sample. Por qu estaba ella analizando las muestras, (l) no est mirando esa muestra. y no vos, cuando (yo) llegu? They are not (arent) recording it. WAS+I, HE, SHE, IT+ING? (Ellos) no estn registrndolo. SUJETO+ AM, IS, What were you doing when they arrived? ARE+NOT+ING Qu estabas haciendo cuando (ellos) llegaron? WERE+ YOU, WE THEY+ ING?
1. Encerr con Prctica Opcional:
las frases verbales de los siguientes enunciados en tiempos progressive o continuos.
2. Expreslas en espaol. 3. Transformlas al negativo y al interrogativo, para lo cual identific correctamente el actor del enunciado. 4. Escrib el infinitivo del verbo principal. Record consultar la lista de verbos irregulares para familiarizarte con los infinitivos. 1. The cow is calving in the pen right now.
2. They are measuring the feed intake.
3. He was isolating the piglets when they arrived.
4. We were weighing the steers when the bull attacked us.
5. He will be examining the fecal samples tomorrow morning in the lab.
Tiempos Verbales
El siguiente y ltimo cuadro muestra, de manera muy sinttica y a travs de ejemplos, al igual que los anteriores, cmo se forman los tiempos verbales llamados perfect en ingls, en sus formas afirmativa, negativa e interrogativa. PRESENT PERFECT
I (You, We They) have already finished. (Yo) ya termin. He (She, It) has already started. (l) ya comenz. VERBOS REGULARES: SUJETO+HAVE/HAS+ED I (You, We, They) have taken a decision. He tomado / Tom una decisin. She (He, It) has brought this new idea for us to analyze. (Ella) ha trado / trajo esta nueva idea para que nosotros la analicemos. VERBOS IRREGULARES: SUJETO+HAVE/HAS+P ARTICIPIO: -ED O 3 COLUMNA) She has not (hasnt) finished yet. (Ella) no They have not (havent) met. HAD+SUJETO+PARTICIPIO SUJETO+HAVE/HAS+NOT+PARTICIPIO What have you used here? Where has she failed? PARTICIPIO: VERBOS REGULARES: DESINENCIA ED VERBOS IRREGULARES: 3 COLUMNA
PAST PERFECT
They had collected the samples when it started to rain. (Ellos) haban juntado las muestras cuando comenz a llover. She had taken everything out before the building collapsed. (Ella) haba sacado todo antes de que el edificio se viniera abajo. SUJETO+HAD+PARTICIPIO We had not (hadnt) finished when they arrived. (Nosotros) no habamos terminado cuando ellos llegaron. SUJETO+HAD+NOT+PARTICIPIO How many samples had you taken before we changed the method? Cuntas muestras habas tomado antes de que (nosotros) cambiramos el mtodo?
FUTURE PERFECT
I will have finished by the time they arrive. (Yo) habr terminado para cuando (ellos) lleguen. SUJETO+WILL HAVE+PARTICIPIO They will not (wont) have finished the career by the time they get married. (Ellos) no habrn terminado la carrera para cuando se casen. SUJETO+WILL NOT+PARTICIPIO Will you have practiced enough when the date of the exam finally arrives? Habrs practicado lo suficiente para cuando llegue la fecha del examen? WILL+SUJETO+HAVE+PARTICIPIO
CONDITIONAL PERFECT
We would have understood if you had explained. SUJ.+WOULD HAVE+ PARTICIPIO The researcher would not (wouldnt) have told you that if he had known the conditions. SUJ.+WOULD NOT HAVE+PART. How would you have reacted if you have been in the same situation? WOULD+SUJ.+HAVE+PARTICIPIO
HAVE/ HAS+SUJETO+PARTICIPIO
1. Encerr con Prctica Opcional:
las frases verbales de los siguientes enunciados en tiempos perfect.
2. Expreslas en espaol. 3. Transformlas al negativo y al interrogativo, para lo cual identific correctamente el actor del enunciado. 4. Escrib el infinitivo del verbo principal. Record consultar la lista de verbos irregulares para familiarizarte con los infinitivos. 1. The infected calves will have died by next Friday.
2. No scientist has established the origin of canine parvovirus.
3. Use of penicillin in mastitis therapy has led to problems of human health.
4. Variants of the parvovirus have appeared since the disease was first recognized.
Introduccin a la Lectura Comprensiva de Ingls Acadmico para Medicina Veterinaria
5. Before the experiment, these animals had received the regular herd concentrate.
6. Consumer confidence in the safety of food has become a priority issue for all the people involved in the food supply chain.
7. Advances in analytical techniques have contributed to awareness and concern about toxic residues.
8. Dry cow therapy has been part of mastitis control since the 1970s and has been one point of the five point control plan.
9. Public concern over the presence of drug residues in edible products of food-producing animals has reached unprecedented heights.
10. Immunoassay technology has gained rapid acceptance in veterinary and human medicine owing to its high performance capabilities and versatility in applications.
11. Efforts to induce dairy farmers to make greater use of high-quality pastures and reduce their dependency on imported concentrates have met with little success.
12. Certain countries have banned the use of specific compounds, whereas other countries on the base of scientific criteria have permitted the continued the use of similar products (e.g., growth promoters are banned in the European Community and permitted in the United States).
Tiempos Verbales
LISTA DE VERBOS IRREGULARES
Cmo utilizarla? La columna INFINITIVE nos da el nombre del verbo, es decir el verbo sin conjugar en ningn tiempo verbal; de esta columna formamos el simple present agregndole s o es para las terceras personas del singular (he, she, it). La columna SIMPLE PAST nos informa acerca de los verbos irregulares en simple past (pretritos perfecto e indefinido del espaol), y la forma que se presenta es la misma para todos los pronombres. No figuran aqu los verbos regulares, porque su simple past se forma agregando ed al infinitivo. La columna PAST PARTICIPLE nos informa acerca del pasado participio (terminacin ado -ido del espaol) de los verbos irregulares; una vez ms, no figuran aqu los verbos regulares porque su pasado participio se forma agregando ed al infinitivo. Comnmente se llama primera columna a la INFINITIVE, segunda columna a la SIMPLE PAST, y tercera columna a la PAST PARTICIPLE.
TRADUCCIN
ser/estar: golpear: convertirse, volverse: comenzar: soplar, explotar: romper, estallar: traer: construir: quemar: comprar: atrapar, tomar: elegir, seleccionar: venir, llegar: cortar: hacer, realizar: dibujar, deslizar, atraer: beber: conducir, manejar: comer: caer: sentir: encontrar, hallar: volar: olvidar: conseguir, comprar, llegar: dar, otorgar: ir, dirijirse: crecer: tener, haber: oir: esconder, ocultar: golpear: sostener, mantener, llevarse a cabo herir, lastimar: mantener, guardar, seguir: saber, conocer: poner, colocar, recostar: llevar, conducir, liderar: aprender, enterarse: partir, dejar, abandonar: prestar:
INFINITIVE
be (am, is, are) beat become begin blow break bring build burn buy catch choose come cut do draw drink drive eat fall feel find fly forget get give go grow have hear hide hit hold hurt keep know lay lead learn leave lend
SIMPLE PAST
was/were beat became began blew broke brought built burnt bought caught chose came cut did drew drank drove ate fell felt found flew forgot got gave went grew had heard hid hit held hurt kept knew laid led learnt left lent
PAST PARTICIPLE
been beaten become begun blown broken brought built burnt bought caught chosen come cut done drawn drunk driven eaten fallen felt found flown forgotten gotten given gone grown had heard hidden hit held hurt kept known laid led learnt left lent
Introduccin a la Lectura Comprensiva de Ingls Acadmico para Medicina Veterinaria
dejar, permitir: yacer, recostarse: alumbrar, encender: perder, extraviar: hacer, realizar: significar, querer decir: encontrarse con, conocerse: equivocarse, errar: pagar, prestar (atencin): poner: leer: llamar, sonar: elevarse, levantarse: correr, administrar: decir: ver: vender: enviar: sacudir: brillar: disparar: mostrar: cerrar: hundir: sentarse: dormir: oler: gastar: untar, esparcir: levantar: robar: golpear: nadar: tomar, llevar: ensear: rasgar, romper: narrar, decir, contar: pensar, opinar: arrojar: entender, comprender: despertar: usar (ropa): ganar: escribir:
let lie light lose make mean meet mistake pay put read ring rise run say see sell send shake shine shoot show shut sink sit sleep smell spend spread stand steal strike swim take teach tear tell think throw understand wake wear win write
let lay lit lost made meant met mistook paid put read rang rose ran said saw sold sent shook shone shot showed shut sank sat slept smelt spent spread stood stole stroke swam took taught tore told thought threw understood woke wore won wrote
let lain lit lost made meant met mistaken paid put read rung risen run said seen sold sent shaken shone shot shown shut sunk sit slept smelt spent spread stood stolen stricken swum taken taught torn told thought thrown understood waken worn won written
Tiempos Verbales
Otros tiempos verbales:
PERFECT PROGRESSIVE:
SUJETO + TO HAVE (PRESENTE PASADO FUTURO) + BEEN + VERBO + -ING The cat has been vomiting for the last three days. Hace tres das que el gato vomita. El gato ha estado vomitando por tres das. TO HAVE (PRESENTE PASADO FUTURO) + SUJETO + BEEN + VERBO + -ING How long have you been studying this subject? Cunto hace que ests estudiando este tema?
SUJETO + TO HAVE (PRESENTE PASADO FUTURO) + NOT + BEEN + VERBO + -ING I havent been following the progress of this project work, to tell you the truth. A decir verdad, no he estado siguiendo el progreso de este trabajo de campo.
BE + GOING TO + VERBO INFINITIVO = futuro para expresar planes e intencin
They are going to build a new research hall over there. Van a construir un nuevo pabelln de investigacin all. Are you going to start the test next month? Vas a comenzar la prueba el mes prximo? We are not going to write a new paper on this subject. No vamos a escribir un nuevo paper sobre este tema. Cuadro resumen Tiempos Verbales:
PRESENT
PAST
I worked all night yesterday. VERBOS REGULARES (terminacin ed) They took it to the laboratory. VERBOS IRREGULARES (2 columna) What did you bring to the field last week? DID + SUJETO + VERBO INFINITIVO They will not (wont) come until tomorrow. SUJETO + WILL + NOT + VERBO INFINITIVO What will you write in the abstract? WILL + SUJETO + VERBO INFINITIVO She will decide soon. SUJETO + WILL + VERBO INFINITIVO How would you carry this out? WOULD + SUJETO + VERBO INFINITIVO I would not (wouldnt) measure here. SUJETO + WOULD + NOT + VERBO INFINITIVO She would be doing research here if she could. SUJETO + WOULD + BE + VERBO + -ING I would like to test the place. SUJETO + WOULD + VERBO INFINITIVO
FUTURE (will)
CONDITIONAL (would)
I (You, We, They) need some more tests. She (He, It) works perfectly in this environment.
How do you (I, we, they) prepare the samples? DO + I, WE, THEY + INFINITIVE VERB. What does she (he, it) measure? DOES + SHE, HE, IT + INFINITIVE VERB (NO S)
SIMPLE
They do not (dont) understand the reason. We did not (didnt) believe it. DO + NOT + INFINITIVE VERB DID + NOT + VERBO INFINITIVO He does not (doesnt) consider that variable at all. DOES + NOT + INFINITIVE VERB (NO s) She (He, It) was working when they arrived. I, HE, SHE, IT + WAS + VERBO + -ING You, (We, They) were talking when the class started. YOU, WE, THEY + WERE + VERBO + -ING He was not (wasnt) reading when the phone rang. They were not (werent) watching the students when the accident happened. I will be traveling by the time they arrive. SUJETO + WILL BE + VERBO +-ING Will you be waiting for us? WILL + SUJETO + BE + VERBO + ING
I am analyzing the data now. She (He, It) is testing the equipment right now. We (They, You) are controlling the plague. SUBJECT + AM, IS, ARE, + VERBO + -ING
What is he (she, it) preparing? What are you (we, they) doing there? What am I doing? AM, IS, ARE + SUBJECT + VERBO + -ING
PROGRESSIVE (-ing: -ando, -endo)
What would they be studying now if they had come? WOULD + SUJETO + BE + VERBO + -ING He would not (wouldnt) be complaining if he knew the reason. SUJETO + WOULD + NOT + BE + VERBO + -ING
I am not (m not) saying that. He is not (isnt) looking at that sample. They are not (arent) recording it. SUBJECT + AM, IS, ARE + NOT + VERBO + -ING What were you doing when they arrived? They had collected the samples when it started to rain. She had taken everything out before the building collapsed. SUJETO + HAD + VERBO (PAS. PART.) We had not (hadnt) finished when they arrived. SUJETO + HAD + NOT + VERBO (PAS. PART.)
They will not (wont) be listening to you by the time you finish the class. Why was she analyzing the samples, instead of you, when SUJETO + WILL + NOT + BE + I arrived? VERBO + -ING
Introduccin a la Lectura Comprensiva de Ingls Acadmico para Medicina Veterinaria
I (You, We They) have already finished. He (She, It) has already started. VERBOS REGULARES: SUJETO + HAVE / HAS + VERBO + -ED
I will have finished by the time they arrive. SUJETO + WILL HAVE + VERBO (PAS. PART.)
We would have understood if you had explained. SUJETO + WOULD HAVE + VERBO (PAS. PART.) The researcher would not (wouldnt) have told you that if he had known the conditions. SUJETO + WOULD NOT HAVE + VERBO (PAS. PART.)
PERFECT
I (You, We, They) have taken a decision. She (He, It) has brought this new idea for us to analyze. VERBOS IRREGULARES: SUJETO + HAVE / HAS + VERBO (PASADO PARTICIPIO: -ED O 3 COLUMNA)
She has not (hasnt) finished yet. They have not (havent) met. SUJETO + HAVE / HAS + NOT + VERBO (PAS. PART.)
They will not (wont) have finished the career by the time they get married. SUJETO + WILL NOT + VERBO (PAS. How many samples had you taken before we changed the PART.) method? HAD + SUJETO + VERBO (PAS. PART.) Will you have practiced enough when the date of the exam finally arrives? PASADO PARTICIPIO: WILL + SUJETO + HAVE + VERBO VERBOS REGULARES: TERMINACIN ED (PAS. PART.) VERBOS IRREGULARES: 3 COLUMNA
How would you have reacted if you have been in the same situation? WOULD + SUJETO + HAVE + VERBO (PAS. PART.)
También podría gustarte
- Los Tiempos en InglésDocumento21 páginasLos Tiempos en InglésKaritza Keny90% (10)
- Resumen de Los Tiempos Verbales Del InglésDocumento5 páginasResumen de Los Tiempos Verbales Del InglésErick Pereda100% (1)
- Frases y Modismos ExcelDocumento7 páginasFrases y Modismos ExcelManuel Emilio Gonzalez SantanaAún no hay calificaciones
- PreposicionesDocumento7 páginasPreposicionesjegalex100% (15)
- Muestra LOS LÍOS DEL INGLÉS PDFDocumento21 páginasMuestra LOS LÍOS DEL INGLÉS PDFvilma gAún no hay calificaciones
- Vocabulario y Expresiones Esenciales Free PDFDocumento44 páginasVocabulario y Expresiones Esenciales Free PDFEvanderVillarrealNavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Diferencia Entre Los Verbos DO y MAKE en Inglés PDFDocumento3 páginasDiferencia Entre Los Verbos DO y MAKE en Inglés PDFHectorDiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Tiempos Verbales Del InglesDocumento10 páginasTiempos Verbales Del InglesBrian GaleanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Cómo Conjugar Los Verbos en InglésDocumento107 páginasCómo Conjugar Los Verbos en InglésrosyAún no hay calificaciones
- Lista de Preposiciones SilaDocumento5 páginasLista de Preposiciones SilaHectorDiazAún no hay calificaciones
- El Circo de Los Verbos - MuestraDocumento9 páginasEl Circo de Los Verbos - Muestramarcela33% (3)
- Gramática Nivel b2 InglésDocumento3 páginasGramática Nivel b2 InglésPedro Jesús Flores LópezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tiempos Verbales en InglesDocumento3 páginasTiempos Verbales en Inglessixto_pqAún no hay calificaciones
- OM GRAMMAR-Gramática Inglesa Gratuita en EspanolDocumento4 páginasOM GRAMMAR-Gramática Inglesa Gratuita en EspanolAngel Estuardo Jimenez NajeraAún no hay calificaciones
- Gramatica InglesaDocumento27 páginasGramatica Inglesajesusjgl100% (3)
- Tiempos Verbales Presente InglésDocumento5 páginasTiempos Verbales Presente InglésnadiaAún no hay calificaciones
- NSNU - U1 - Nutricion de La InvestigaciónDocumento91 páginasNSNU - U1 - Nutricion de La InvestigaciónCarlos Sáenz100% (1)
- Los Verbos en Inglés Todo Lo Que Necesita Saber Sobre Las Formas Verbales en Inglés 1Documento22 páginasLos Verbos en Inglés Todo Lo Que Necesita Saber Sobre Las Formas Verbales en Inglés 1anita manriqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Reglas Pronunciación InglésDocumento6 páginasReglas Pronunciación InglésMiguel LazoAún no hay calificaciones
- Inglés Formal Vs InformalDocumento7 páginasInglés Formal Vs InformalCristina ParraAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso de Inglés Vaughan - El Mundo - Fichas 1 A 169 (Todas) PDFDocumento338 páginasCurso de Inglés Vaughan - El Mundo - Fichas 1 A 169 (Todas) PDFsachave80% (5)
- Inglés Nivel B2: Mejores Libros para Aprender Ingles Nivel B2Documento28 páginasInglés Nivel B2: Mejores Libros para Aprender Ingles Nivel B2Consuelo Benavent Gavidia100% (1)
- Decargar Tiempos Verbales InglesDocumento3 páginasDecargar Tiempos Verbales Inglesalukard_2010100% (1)
- English GrammarDocumento48 páginasEnglish GrammarpepeenytAún no hay calificaciones
- Grámatica Inglesa 1Documento41 páginasGrámatica Inglesa 1Lias CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Los Phrasal Verbs Más UsadosDocumento18 páginasLos Phrasal Verbs Más UsadosJean Max Henrich67% (3)
- Lista de Phrasal Verbs para Aprobar El B1 - Academia Puerta RealDocumento9 páginasLista de Phrasal Verbs para Aprobar El B1 - Academia Puerta RealMartha MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Todo Los Tiempos de InglesDocumento16 páginasTodo Los Tiempos de Inglesjosemeneses1993100% (1)
- Presente Simple en InglésDocumento3 páginasPresente Simple en Inglésanierbta100% (3)
- Menu de 11 Dias, Dieta SecretaDocumento15 páginasMenu de 11 Dias, Dieta SecretaBrenda Rodriguez de Morantes50% (2)
- Aplicaciones para Aprender InglésDocumento37 páginasAplicaciones para Aprender InglésmasmenachoAún no hay calificaciones
- Class 47.1 GrammarDocumento4 páginasClass 47.1 GrammarDiana Pena100% (1)
- English GrammarDocumento10 páginasEnglish GrammarMaria Cebrian Perruca100% (1)
- Temario b1 Frances GramáticaDocumento1 páginaTemario b1 Frances GramáticaLucía MorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Gramática Inglesa ResumidaDocumento25 páginasGramática Inglesa Resumidawarrior_bren6116100% (2)
- Resumen de Gramatical InglesDocumento17 páginasResumen de Gramatical InglesYazminAún no hay calificaciones
- Verb Tenses en Inglés COMO NO FALLARDocumento7 páginasVerb Tenses en Inglés COMO NO FALLARNatalia LozadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Using Gerunds and InfinitivesDocumento51 páginasUsing Gerunds and InfinitivesmercedesgutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Queso MozarrellaDocumento11 páginasQueso MozarrellaanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tension Sexual Entre Tu y Yo - Merenciano Navarro, CristinaDocumento121 páginasTension Sexual Entre Tu y Yo - Merenciano Navarro, CristinaChristopher RiceAún no hay calificaciones
- Prepocisiones en InglesDocumento50 páginasPrepocisiones en InglesJapananda Das AcbspAún no hay calificaciones
- Verbos Basicos Mas Confusos Del InglesDocumento19 páginasVerbos Basicos Mas Confusos Del InglesFelix Cuevas100% (1)
- Tabla de Equivalencias GastronomicasDocumento5 páginasTabla de Equivalencias Gastronomicaslugonavarro100% (1)
- Ingles Intermedio b1 Online 2014Documento11 páginasIngles Intermedio b1 Online 2014Carlota Almeida Garcia100% (1)
- Tiempos Verbales (Inglés)Documento7 páginasTiempos Verbales (Inglés)MiZuKiRuHm100% (2)
- Expo GranulacionDocumento38 páginasExpo Granulacionivan0% (1)
- Ingles para PrincipiantesDocumento17 páginasIngles para PrincipiantesLuis AntonioAún no hay calificaciones
- Planificacion 11 JesseniaDocumento10 páginasPlanificacion 11 JesseniaOrdoñez SaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Adjectives Ending Ing - EdDocumento2 páginasAdjectives Ending Ing - EdakneronAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso de Ingles Aula FácilDocumento2 páginasCurso de Ingles Aula FácilLola MentoAún no hay calificaciones
- Los Pronombres en FrancésDocumento3 páginasLos Pronombres en Francésguilleee14Aún no hay calificaciones
- English GrammarDocumento16 páginasEnglish GrammarHeriberto LuisAún no hay calificaciones
- In - On - AT - Aprende Cuándo Usar Las Preposiciones de Tiempo y Lugar - Aprobar El CAEDocumento12 páginasIn - On - AT - Aprende Cuándo Usar Las Preposiciones de Tiempo y Lugar - Aprobar El CAERomina CaceresAún no hay calificaciones
- Tabla Equivalencia de Tiempos Roberto ReboredoDocumento4 páginasTabla Equivalencia de Tiempos Roberto ReboredoeslebynAún no hay calificaciones
- Grammar PDFDocumento77 páginasGrammar PDFarblank100% (1)
- B2.2 Unit 2Documento26 páginasB2.2 Unit 2rgarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Past Perfect Simple and Past Perfect ContinuousDocumento4 páginasPast Perfect Simple and Past Perfect ContinuouscarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Student S Manual de Vaughan Richard AdamsDocumento1 páginaStudent S Manual de Vaughan Richard Adamsdarkan50% (2)
- Ingles AvanzadoDocumento3 páginasIngles AvanzadoHeinfieldrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Conditional Sentences TheoryDocumento4 páginasConditional Sentences TheoryLalyFernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Yes-Not Questions With Perfect Tense 10 A-B and 11th GradesDocumento5 páginasYes-Not Questions With Perfect Tense 10 A-B and 11th GradesGabriela FuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.8 Tiempos Verbales. PRESENTEDocumento7 páginas1.8 Tiempos Verbales. PRESENTENereaAún no hay calificaciones
- ProgresivoDocumento14 páginasProgresivoleonelAún no hay calificaciones
- Do You Live Near Here 8Documento18 páginasDo You Live Near Here 8Natalia PitacuarAún no hay calificaciones
- Módulo 1 IDIOMASDocumento42 páginasMódulo 1 IDIOMASjulyrocio1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pasado ContinuousDocumento5 páginasPasado ContinuousRamiro Alejandro Rodríguez GuzmánAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento51 páginasUntitledcarmencita30Aún no hay calificaciones
- EmbarazoDocumento1 páginaEmbarazocarmencita30Aún no hay calificaciones
- Padecimientos Agregados Al EmbarazoDocumento70 páginasPadecimientos Agregados Al EmbarazoLic Ervin GpeAún no hay calificaciones
- Chiguire Venezuela 9estudiosdetressectoresbiocomercioDocumento62 páginasChiguire Venezuela 9estudiosdetressectoresbiocomerciocarmencita30Aún no hay calificaciones
- BIO18 Web PesquisaNEONATALDocumento10 páginasBIO18 Web PesquisaNEONATALcarmencita30Aún no hay calificaciones
- BIO18 Web PesquisaNEONATALDocumento10 páginasBIO18 Web PesquisaNEONATALcarmencita30Aún no hay calificaciones
- Modulo Orientacion LaboralDocumento138 páginasModulo Orientacion LaboralOihel HuxAún no hay calificaciones
- Autismo Criterios Diagnosticos DiferencialDocumento8 páginasAutismo Criterios Diagnosticos DiferencialDaniela Collio Moya100% (1)
- ESTUDIO DE BIODIVERSIDAD EN EL CACAO - CONSERVACION & DESARROLLO, Make A Donation@ccd - Org.ec / Haga Una DonaciónDocumento92 páginasESTUDIO DE BIODIVERSIDAD EN EL CACAO - CONSERVACION & DESARROLLO, Make A Donation@ccd - Org.ec / Haga Una DonaciónCONSERVACION Y DESARROLLO SOSTENIBLEAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluación de Destrezas 1er Quimestre 4º B 2012-2013Documento8 páginasEvaluación de Destrezas 1er Quimestre 4º B 2012-2013Sixto GerardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Anu XP 1Documento722 páginasAnu XP 1Fatima Manzano OrtizAún no hay calificaciones
- Tipos de FideosDocumento10 páginasTipos de FideosMirco Suarez RodasAún no hay calificaciones
- Terapia Nutricional Hecho-1Documento17 páginasTerapia Nutricional Hecho-1Aniela Andrea Ordoñez RaveloAún no hay calificaciones
- Gastronomia Navideña de VenezuelaDocumento3 páginasGastronomia Navideña de Venezuelacoreliz33100% (1)
- Plan de Sesion Educativa OsteoporosisDocumento2 páginasPlan de Sesion Educativa Osteoporosis71004524Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ubuntu Huertas A DedoDocumento2 páginasUbuntu Huertas A DedoFernando ChacanaAún no hay calificaciones
- For MatosDocumento9 páginasFor MatosvenusAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual de Economía Popular para NiñesDocumento11 páginasManual de Economía Popular para NiñesMilway Tupayachi AbarcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Farmacognosia ProteinasDocumento25 páginasFarmacognosia ProteinasAnonymous GNiOkl3nslAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Inglés CIUDocumento155 páginasGuía Inglés CIUowenAún no hay calificaciones
- Homónimos Ejercicios para Sexto Grado de PrimariaDocumento6 páginasHomónimos Ejercicios para Sexto Grado de PrimariaEricka Diaz ChicahuariAún no hay calificaciones
- Espirulina MaximaDocumento11 páginasEspirulina MaximaEduardo Castañeda100% (1)
- DesintoxicacionDocumento14 páginasDesintoxicacionJose Antonio Alvarez CardielAún no hay calificaciones
- EJERCICIO.. Problemas MatemáticosDocumento92 páginasEJERCICIO.. Problemas MatemáticosCarmen Reyes NavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Calderón de Rzedowski, 2004 #1411Documento316 páginasCalderón de Rzedowski, 2004 #1411Paulina BravoAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Plantas Seminario 1Documento11 páginasDiseño de Plantas Seminario 1poolAún no hay calificaciones
- Carta Surista (Incluye Bebestible)Documento1 páginaCarta Surista (Incluye Bebestible)Catalina JaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 4Documento7 páginasTarea 4Leo NúñezAún no hay calificaciones
- Biologia 4to AñoDocumento2 páginasBiologia 4to AñoAntonio FigueraAún no hay calificaciones
- Fondos BásicosDocumento10 páginasFondos BásicosVogus VdjAún no hay calificaciones
- Plan de Exportación de Aceitunas RellenasDocumento32 páginasPlan de Exportación de Aceitunas RellenasVictor Raúl Quispe Mamani100% (1)