Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Multiplicación y División de Monomios 4º
Cargado por
HERNAN LIZARVE ROMERO0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
2 vistas2 páginasalgebra 4°
Título original
MULTIPLICACIÓN Y DIVISIÓN DE MONOMIOS 4º
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoalgebra 4°
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
2 vistas2 páginasMultiplicación y División de Monomios 4º
Cargado por
HERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROalgebra 4°
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como DOCX, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 2
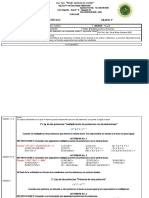
INSTITUCIÓN EDUCATIVA PARTICULAR INSTITUCIÓN EDUCATIVA PARTICULAR
“IZAGUIRRE DE ARIEL” “IZAGUIRRE DE ARIEL”
MULTIPLICACIÓN Y DIVISIÓN DE MONOMIOS 4º
1. ¿Cómo se multiplican MONOMIOS? EJERCICIOS DE APLICACIÓN 4º
Primero: Se multiplican las partes numéricas, signos y números 1. Resuelve las multiplicaciones de monomios:
(coeficientes). a. (4 a3mx7) . (5amx3)
Segundo: Se multiplican las partes literales, si tienen variables
diferentes, solo se juntan. b. (3 a2m4 x2) . (2 a4 mx3)
Si tienen variables iguales, se pone la misma variable y se c. (3 a4m2x9) . (2 amx4)
suman los exponentes.
Es decir: b n . b m = b n + m d. (− 4 a3b4x2) . (3 a2bx2)
Ejemplo:
e. (5 x4yz2) . (− 3 x4y4z2)
(3 a x9) (2 a x4)
2. Resuelve las divisiones de monomios:
= ( 3 . 2) a1 + 1 x 9 + 4
a) ( 27 m4 n5 ) : ( 3 m2 n2 )
= 6 a2 x13
b) (− 36 m4 n5 x 8) ÷ ( 6 m3 n4 x 8)
2. ¿Cómo se dividen MONOMIOS? c) (−30 m7 n3 y) : (− 6 m5 n3y)
Primero: Se dividen las partes numéricas, signos y números.
7 8 6
Segundo: Se dividen las partes literales, si tienen variables iguales, se 64 x y z
d) 7 5 4
pone la misma variable y se restan los exponentes. 8x y z
Si tienen variables diferentes, se deja el cociente indicado. 12
−18 x y z
4 8
Se divide coeficiente entre coeficiente y variables iguales e) 10 4 8
−6 x y n
respectivamente.
sigamos practicando:
m
b
Es decir: n
=b
m−n
a. (−4 ab3x7) . (−2 a3by5)
b
Ejemplo: b. (−10 x3y4) . (− 3 x4y3)
5 4 5
10 a m n
3 5 c. (7 ax2y4) . (3 ax2y) =
5am n
c. (− 20 m4 n5 x 8) ÷ ( 5 m3 n4 x 8)
= (10 :5) a 5−1 m4 −3 n5−5 d. (− 63 m8 n3 y) : (− 7 m5 n3y)
= 2 a 4 m1 n0
10 4 7
= 2 a4 m −27 x y z
e. 10 4 5
3x y n
Profesor: Hernán Lizarve Romero
INSTITUCIÓN EDUCATIVA PARTICULAR INSTITUCIÓN EDUCATIVA PARTICULAR
“IZAGUIRRE DE ARIEL” “IZAGUIRRE DE ARIEL”
Profesor: Hernán Lizarve Romero
También podría gustarte
- Multiplicación y División de Monomios 6ºDocumento2 páginasMultiplicación y División de Monomios 6ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- ALGEBRA (Agosto-Set) 4Documento18 páginasALGEBRA (Agosto-Set) 4Rolando PozoAún no hay calificaciones
- ALGEBRA (Agosto-Set) 4Documento18 páginasALGEBRA (Agosto-Set) 4LeDiazAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.2guia Division de PolinomiosDocumento5 páginas2.2guia Division de PolinomiosCLAUDIA RODRIGUEZAún no hay calificaciones
- Expresiones Algebraicas para Segundo de SecundariaDocumento5 páginasExpresiones Algebraicas para Segundo de SecundariaCleover Duan Acho RengifoAún no hay calificaciones
- División de Monomios Y Polinomios: (X) (X) X XDocumento4 páginasDivisión de Monomios Y Polinomios: (X) (X) X Xapi-250398026Aún no hay calificaciones
- 2do Grado - Expresiones Algebraicas I (Z)Documento2 páginas2do Grado - Expresiones Algebraicas I (Z)katsumi 1324Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Sec Ga Mat Semana 2 - SiewebDocumento10 páginas1 Sec Ga Mat Semana 2 - SiewebMathias ZFAún no hay calificaciones
- Intermedio AlgebraDocumento17 páginasIntermedio AlgebraAli Ala Sufa TerrenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Asignacion IDocumento16 páginasAsignacion IYUREYNIS MUJICAAún no hay calificaciones
- Término AlgebraicoDocumento4 páginasTérmino AlgebraicoJuan SalasAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion Nº1 - Expresiones Algebraicas IDocumento5 páginasSesion Nº1 - Expresiones Algebraicas Ialberto condemarin miroAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía de Álgebra Auxiliar Administrativo Semana 2024 - 1Documento4 páginasGuía de Álgebra Auxiliar Administrativo Semana 2024 - 1mariajosebetancurromanAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Algebra para RepasoDocumento4 páginasEjercicios de Algebra para Repasomartin gutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- A L G e B R ADocumento4 páginasA L G e B R ASeijuro Enishi ShishioAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Bimestral Álgebra 3er AñoDocumento2 páginasExamen Bimestral Álgebra 3er AñoEnrique Nuñez del ArcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia de Sesión 1Documento6 páginasGuia de Sesión 1José Castro AntonioAún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha - Actividad 04-Eda 03Documento5 páginasFicha - Actividad 04-Eda 03Yaritza LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Notación Algebraica - Presentación en Clase - Matemáticas Psicología G102Documento9 páginasNotación Algebraica - Presentación en Clase - Matemáticas Psicología G102Nata GonzálezAún no hay calificaciones
- Expresiones Algebraicas I (Z)Documento5 páginasExpresiones Algebraicas I (Z)Evert valencia sebastianAún no hay calificaciones
- Expresiones Algebraicas Carolina Tovar PDFDocumento4 páginasExpresiones Algebraicas Carolina Tovar PDFEdgar Ernesto Villamizar DelgadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 6 Operaciones Con Reales - Expresiones Algebraicas - PolinomiosDocumento8 páginasTaller 6 Operaciones Con Reales - Expresiones Algebraicas - Polinomiospaola zuluagaAún no hay calificaciones
- Matemática Básica Sem-01 Sesión-02 2023-2 Leyes de ExponentesDocumento23 páginasMatemática Básica Sem-01 Sesión-02 2023-2 Leyes de ExponentesWilliam MedinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía - N°1 - Unidad N°0 - NM3Documento2 páginasGuía - N°1 - Unidad N°0 - NM3María José Salas PereiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Expresiones AlgebraicasDocumento5 páginasExpresiones AlgebraicasLuis SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- AlgebraDocumento73 páginasAlgebraEL ProletaAún no hay calificaciones
- Modulo Repaso División Algebraica.Documento6 páginasModulo Repaso División Algebraica.Cindi MorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Expresiones Algebraicas ModuloDocumento12 páginasExpresiones Algebraicas ModuloXimenaRoldanCruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller+de+diagnóstico+matematicas 9°Documento7 páginasTaller+de+diagnóstico+matematicas 9°Becquer PozoAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia de Conceptos AlgebraDocumento4 páginasGuia de Conceptos AlgebraMatematica LIMID100% (1)
- Expresiones Algebraicas IDocumento6 páginasExpresiones Algebraicas IJosé PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Adición y Sustracción de Monomios 6ºDocumento2 páginasAdición y Sustracción de Monomios 6ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones EponencialesDocumento4 páginasEcuaciones Eponencialesurjc4alumnoAún no hay calificaciones
- Octavo JulioDocumento8 páginasOctavo JulioShirley GalvánAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 1-Algebra-2doDocumento5 páginasTema 1-Algebra-2doYoshiy CarhuallanquiAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 1 PDFDocumento13 páginasSemana 1 PDFGerson Enriquez100% (1)
- Multiplicacion de Expresiones AlgebraicasDocumento5 páginasMultiplicacion de Expresiones AlgebraicasElva MalagonAún no hay calificaciones
- Valor Expresiones Algebraicas C3Documento4 páginasValor Expresiones Algebraicas C3Jose QuijanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Monomios 4 y 5 SecDocumento7 páginasMonomios 4 y 5 SecJuan Miguel Aquije IncaAún no hay calificaciones
- Planiacion 24 - 28 Oct Mat8Documento3 páginasPlaniacion 24 - 28 Oct Mat8Miguel Angel Montejano CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Libro de Texto: Segunda EdiciónDocumento21 páginasLibro de Texto: Segunda EdiciónEstefany GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- A L G e B R ADocumento4 páginasA L G e B R Agerardo lealAún no hay calificaciones
- Apuntes Antiguos 4Documento9 páginasApuntes Antiguos 4Jorge Andres Olivares FunesAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia2 Jueves 1agostoDocumento4 páginasGuia2 Jueves 1agostoCarolina Vicencio FernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Modulo Grado 8° Tercer PeriodoDocumento98 páginasModulo Grado 8° Tercer PeriodoKarol MuñozAún no hay calificaciones
- Expresiones AlgebraicasDocumento6 páginasExpresiones AlgebraicasMelissaAyalaAllpajaAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematicas Hoy Final Cap 3Documento41 páginasMatematicas Hoy Final Cap 3Carolina Almanzar0% (1)
- Álgebra - 1° - BIM IDocumento14 páginasÁlgebra - 1° - BIM IAstrid Chacon RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía de Recuperación de Matemáticas Del Grado NovenoDocumento4 páginasGuía de Recuperación de Matemáticas Del Grado NovenoManuel Molano50% (2)
- Ecuaciones Exponenciales 1 4° SecDocumento1 páginaEcuaciones Exponenciales 1 4° SecJorge Santiago Bejarano GoicocheaAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra - 1 - 1 BimDocumento47 páginasAlgebra - 1 - 1 BimWilliam Mora OrtegaAún no hay calificaciones
- AlgebraDocumento5 páginasAlgebraCesar Huayhua CondoriAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad IX POTENCIACIÓN ALGEBRAICADocumento8 páginasUnidad IX POTENCIACIÓN ALGEBRAICARobertAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra ResumenDocumento5 páginasAlgebra ResumenFran PinedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sobre Nilálgebras Conmutativas de Potencias AsociativasDe EverandSobre Nilálgebras Conmutativas de Potencias AsociativasAún no hay calificaciones
- Operaciones Combinadas Con Decimales 5ºDocumento1 páginaOperaciones Combinadas Con Decimales 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Sobre Cortes 4ºDocumento2 páginasProblemas Sobre Cortes 4ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Division Con Números Decimales 5ºDocumento2 páginasDivision Con Números Decimales 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Los Números Decimales 5ºDocumento3 páginasLos Números Decimales 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Ley de Exponentes de La Potenciación 6ºDocumento3 páginasLey de Exponentes de La Potenciación 6ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Clasificación de Los Números Decimales 5ºDocumento3 páginasClasificación de Los Números Decimales 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Suma y Resta Con Números Enteros II 5ºDocumento1 páginaSuma y Resta Con Números Enteros II 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Operaciones Combinadas Con Fracciones 5 ºDocumento2 páginasOperaciones Combinadas Con Fracciones 5 ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Monomios - Gardos 6ºDocumento3 páginasMonomios - Gardos 6ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Leyes de Los Radicales 6ºDocumento3 páginasLeyes de Los Radicales 6ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- LAS FRACCIONES Clases 5ºDocumento3 páginasLAS FRACCIONES Clases 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- REPASO PARA EL EXAMEN Matemática 5° (Setiembre)Documento3 páginasREPASO PARA EL EXAMEN Matemática 5° (Setiembre)HERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Adición y Sustracción de Monomios 6ºDocumento2 páginasAdición y Sustracción de Monomios 6ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiplicación y División de Fracciones 5ºDocumento3 páginasMultiplicación y División de Fracciones 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Repaso Examen Del Iii Bimestre de Álgebra 4°Documento2 páginasRepaso Examen Del Iii Bimestre de Álgebra 4°HERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Repaso Examen Del Iii Bimestre Geometría 6°Documento3 páginasRepaso Examen Del Iii Bimestre Geometría 6°HERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Numeros Primos y Compuesto 5ºDocumento2 páginasNumeros Primos y Compuesto 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Potencia y Radicación de Fracciones 5ºDocumento3 páginasPotencia y Radicación de Fracciones 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Repaso Examen Del Iii Bimestre RM 4°Documento3 páginasRepaso Examen Del Iii Bimestre RM 4°HERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Mínimo Común Múltiplo y Máximo Común Divisor 5ºDocumento3 páginasMínimo Común Múltiplo y Máximo Común Divisor 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Operaciones Combinadas 5ºDocumento2 páginasOperaciones Combinadas 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Múltiplos y Divisores de Un Número 5ºDocumento3 páginasMúltiplos y Divisores de Un Número 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Criterios de Divisibilidad 5ºDocumento2 páginasCriterios de Divisibilidad 5ºHERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Los Triángulos - Clases 5° (Alum)Documento4 páginasLos Triángulos - Clases 5° (Alum)HERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Los Angulos I - Clasificación 5°Documento3 páginasLos Angulos I - Clasificación 5°HERNAN LIZARVE ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones