0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
138 vistas70 páginasInducción Polipastos STHAL Esp
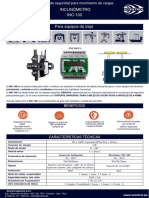
The motor management protects the hoist motor from overheating by limiting the operating time and number of starts per hour based on the motor size and duty cycle. It ensures safe operation by preventing rapid changes in direction and enforcing cooling periods between operations.
Cargado por
kamuixxxDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd
0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
138 vistas70 páginasInducción Polipastos STHAL Esp
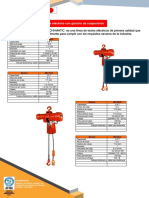
The motor management protects the hoist motor from overheating by limiting the operating time and number of starts per hour based on the motor size and duty cycle. It ensures safe operation by preventing rapid changes in direction and enforcing cooling periods between operations.
Cargado por
kamuixxxDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd