Tiempos Gramaticales Ingles
Cargado por
Miriam C. F. TapiaTiempos Gramaticales Ingles
Cargado por
Miriam C. F. TapiaESTRUCTURA
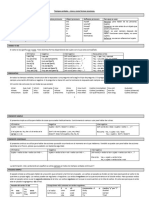
TIEMPO USOS
AFFIRMATIVE NEGATIVE INTERROGATIVE
Se usa para hablar de cosas
Sujeto + Verbo Sujeto + Do + Not + Verbo Do + Sujeto + Verbo? que suceden habitualmente,
de generalidades, eventos del
I talk I dont talk Do you talk? futuro próximo, instrucciones.
He eats He doesnt eat Does he eat? Se pueden usar adverbios de
They learn They don´t learn Do they learn? tiempo:
-Always, every day, usually,
SIMPLE PRESENT
often, sometimes, rarely,
never.
-I always talk to my mother on
Sunday.
-He never eats vegetables.
-They usually learn something
new in class.
Se usa para hablar de algo
Sujeto + Verbo to be + Verbo ing Sujeto + Verbo to be + not + Verbo to be + Sujeto + que esta pasando en este
Verbo ing Verbo ing? momento, algo que ya está
I´m talking decidido se hará en un futuro
He is eating I´m not talking Are you talking? próximo, algo que sucede en
They are learning He isn’t eating Is he eating? la actualidad pero no en el
PRESENT
They aren´t learning Are they learning? momento exacto cuando
CONTINUOUS
hablamos.
Se pueden usar expresiones
de tiempo:
-Currently, lately, these days.
-They are learning english.
-Are you working much lately?
Se usa para hablar de una
Sujeto + Verbo pasado Sujeto + Vebo do + not + Verbo do + sujeto + verbo acción que comenzó y terminó
verbo infinitivo infinitivo? en el pasado.
She was a doctor Se pueden usar adverbios de
The keys where in the drawer I didn’t want to dance Did you want to dance? tiempo:
I wanted to dance I didin´t buy a blue car Did you buy a blue car? -Last year, yesterday, last
I bought a blue car night.
SIMPLE PAST
Sujeto + Verbo to be + not Verbo to be + sujeto?
She wasn´t a doctor Was she a doctor?
The keys weren´t in the Were the keys in the drawer?
drawer
Se usa para una acción del
Sujeto + Verbo to be + Verbo ing Sujeto + Verbo to be + not + Verbo to be + sujeto + pasado pero que la
verbo ing verbo ing? interrumpe otra acción. Para
I was talking esto se usa when (y se usa
He was eating I wasn’t talking Were you talking? después el simple past) y
They were learning He wasn´t eating Was he eating? while (se usa después el past
They weren’t learning Were they learning? continuous).
-He was walking to work when
he fell.
-Jose called while I was
PAST CONTINUOUS
watching the news.
Se usa para hablar de
acciones del pasado en un
tiempo especifico ( hora
especifica o año).
Se usa para hablar de dos
acciones que estaban
ocurriendo al mismo tiempo.
-My son was Reading while I
was cooking.
Se usa will y going to para
Sujeto + Will + verbo Sujeto + Will + Not + Verbo Will + Sujeto + Verbo acciones que pasaran en el
Sujeto + verbo to be + going to + Sujeto + verbo to be + not + principal? futuro o hacer predicciones.
verbo going to + verbo Verbo to be + sujeto + Se usa Will para acciones
going to + verbo? voluntarias o hacer una
I will call you tonight I will not call you tonight promesa.
-I´ll call you tonight -I´ll not call you tonight Will you call me tonight? Se usa going to para hacer
SIMPLE FUTURE She will arrive late She will not arrive late Will she arrive late? planes.
They will be happy to see you They will not be happy to see Will they be hapyy to see
I am going to call you tonight you you?
She is going to arrive late I am not going to call you Are you going to call me
They are going to be happy to see tonight tonight?
you She is not going to arrive late Is she going to arrive late?
They are not going to be Are they going to be happy to
happy to see you see you?
Se usa para hablar sobre
Sujeto + will be + verbo ing Sujeto + will + not + be + Will + sujeto + be + verbo acciones del futuro en un
Sujeto + auxiliar to be + going to verbo ing ing? tiempo especifico (hora, año):
be + verbo ing Sujeto + auxiliar to be + not Auxiliar to be + sujeto + -Paula will be/ is going to be
FUTURE + going to be + verbo ing going to be + verbo ing? living in Spain next April.
CONTINUOUS I will be talking / I am going to be
talking I will not be talking / I am not Will you be talking? / Are you
He will be eating / He is going to be going to be talking going to be talking?
eating He will not be eating / He is Will he be talking? / Is he
not going to be eating going to be talking?
Se usa para acciones que
Sujeto + have/has + pasado Sujeto + have/has + not + Have + sujeto + pasado ocurrieron en un tiempo no
participio pasado participio participio? concreto antes de ahora.
Para describir una
I have talked to Peter I have not talek to Peter Have you talked to Peter? experiencia, logros,
She has gone to work She has not gone to work Has she gone to work? Se pueden usar adverbios yet
They have learned english They haven´t learned english Have they learned English? o still
Se pueden usar expresiones
PRESENT PERFECT
como never, ever, many
times, for, since, already.
-The plane hasn´t arrived yet.
-Our team still hasn´t won a
championship.
-I have never flown in a plane.
-He has worked in many
different museums.
Se usa cuando queremos
Sujeto + have + been + verbo ing Sujeto + have + not + verbo Have + sujeto + been + expresar el sentido de
ing verbo ing? continuidad de una acción que
They have been talking for three ha comenzado en el pasado y
hours They haven´t been talking for Have they been talking for a que dura todavía en el
She has been studying English since more than a few minutes long time? presente o que acabade
PRESENT PERFECT she was 16 She hasn´t been studying Have you been wainting terminar.
CONTINUOUS I have been waiting for you for over English for very long long? Si nos referimos a una acción
an hour Don´t worry. I haven´t been que se ha hecho en un
waiting long periodo de tiempo usamos for
o since.
Si no nos referimos a un
periodo de tiempo usamos
lately o recently
Se usa para referirnos a una
Sujeto + had + pasado participio Sujeto + had + not + pasado Had + sujeto + pasado acción que comenzó en el
participio participio? pasado y que es anterior a
I had visited the Louvre before, so I otra acción también en el
knew where the Mona Lisa was I had not visited the Louvre How did you know where the pasado.
They had studied English before before so I didn’t know where Mona Lisa was? Had you Se usa para acciones del
they went to London the Mona Lisa was visited the Louvre before? pasado que ocurrieron en un
PAST PERFECT Henry changed careers because he They had not studied English Had they studied English tiempo específico
had worked as an accountant for before they went to London before they went to London?
many years and was bored Henry changed careers even Had Henry worked as an
though he had not worked as accountant for long before he
an accountant for long. changed careers?(
Se usa para referirnos a algo
Sujeto + had + been + verbo ing Sujeto + had + not + been + Had + sujeto + been + que habíamos estado
verbo ing verbo ing? haciendo cuando otra acción
I had been studying English for 2 lo interrumpió.
years when I went to London I had not been studying Had you been studying El pasado perfecto continuo
Lindsay had been working at the English long when I went to English for a long time before se utiliza para la acción en
PAST PERFECT
store since 2005 when it closed London you went to London? proceso y el pasado simple
CONTINUOUS
They were surprised when the airline Lindsay had not been working Had Lindsay been working at para la acción que interrumpe.
lost their baggage as they had been at the store for long when it the store for a long time when
traveling for weeks without a closed it closed?
problem They had not been traveling Had they been traveling for a
long before they had their first long time when the airline lost
problem their luggage?
Se usa para acciones que ya
Sujeto + will have + pasado Sujeto + will + not + have+ Will + sujeto + have + se habrá terminado antes de
participio pasado participio pasado participio? otra acción en el futuro.
Sujeto + verbo to be + going to Sujeto + verbo to be + not + Verbo to be + sujeto + También, se puede usar para
have + pasado participio going to have + pasado going to have + pasado expresar que algo va a
participio participio suceder antes de un momento
FUTURE PERFECT
The party will /is going to have específico en el futuro.
ended by the time you finish work The party won’t /isn’t going to Will /Is the party /going to Se usa para mostrar que algo
I’ll /I’m going to have eaten before have ended by the time you have ended before you finish va a continuar hasta otra
we meet finish work work? acción en el futuro.
I won’t /I’m not going to have Will /Are you /going to have
eaten before we meet eaten before we meet?
Se usa para mostrar que algo
Sujeto + will have been + verbo Sujeto + will + not + have Will + sujeto + have been + va a continuar hasta otra
ing been + verbo ing verbo ing? acción o tiempo en el futuro.
Sujeto + verbo to be + going to Sujeto + verbo to be + not + Verbo to be + sujeto + Es una manera de mostrar
have been + verbo ing going to have been + verbo going to have been + verbo causa y efecto en el futuro.
ing ing?
FUTURE PERFECT
Francis will have been living in Italy
CONTINUOS
for 4 years by the time he finishes Francis won’t have been Will Francis have been living
his studies living in Italy for long when he in Italy for long by the time he
We’re going to have been working finishes his studies finishes his studies?
for 24 hours by the time we finish We’re not going to have been Are you going to have been
this project working too long by the time working for a long time when
we finish this project you finish this project?
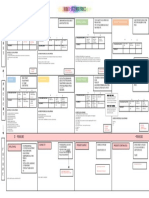
PRESENT
Infinitivo + s al final en la 3a persona del I play football twice a week.
Present simple
singular (Juego a fútbol una vez por semana.)
I’m buying make-up all the time.
Present continuous Verbo to be + verbo con –ing
(Compro maquillaje todo el tiempo.)
She has written five books and she’s
Present perfect Have/has + Participio pasado only 22!
(Ha escrito 5 libros y solo tiene 22 años!)
I have been waiting for you for 2 hours.
Present perfect
Have/has + been + verbo con -ing (Te he estado esperando durante 2
continuous
horas.)
PAST
Verbo + ed My sister helped me with my homework yesterday.
Past simple
(excepción verbos irregulares) (Mi hermana me ayudó con los deberes ayer)
She was terrified by that horror movie.
Past continuous Was / Were + Participio pasado
(Ella estaba horrorizada con esa película de terror)
I had already stopped playing when they came.
Past perfect Had + Participio pasado
(Ya había dejado de jugar cuando llegaron)
I had been looking forward to this!
Past perfect continuous Had/has + been + verbo con -ing
(Esperaba esto con ganas!)
FUTURE
I will meet you tomorrow.
Future simple Will / shall + Infinitivo
(Quedaré contigo mañana.)
Verbo to be + Going to + I’m going to cut my hair this summer.
Future continuous
Infinitivo (Me cortaré el pelo este verano.)
I will have saved a lot of money by summer!
Future perfect Will have + Participio pasado
(Para verano, habré ahorrado mucho dinero)
I’ll have been playing football for 10 years this
Future perfect Will have been + verbo con -
december.
continuous ing
(Habré jugado 10 años a fútbol para este diciembre.)
También podría gustarte
- Guía Completa de Tiempos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesGuía Completa de Tiempos Verbales en Inglés18 páginas
- Guía de Tiempos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesGuía de Tiempos Verbales en Inglés8 páginas
- Uso y Estructura del Futuro Perfecto en InglésAún no hay calificacionesUso y Estructura del Futuro Perfecto en Inglés14 páginas
- Resumen Gramática Inglesa (Para Bachillerato)81% (32)Resumen Gramática Inglesa (Para Bachillerato)20 páginas
- Estructura y Uso de Tiempos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesEstructura y Uso de Tiempos Verbales en Inglés8 páginas
- (+99) Aprende Los Tiempos Verbales en Ingles (Recomendado) - Taringa!Aún no hay calificaciones(+99) Aprende Los Tiempos Verbales en Ingles (Recomendado) - Taringa!10 páginas
- Guía de Tiempos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesGuía de Tiempos Verbales en Inglés7 páginas
- Tiempos Verbales y Pronombres en InglésAún no hay calificacionesTiempos Verbales y Pronombres en Inglés22 páginas
- Tiempos Verbales y Pronombres en InglésAún no hay calificacionesTiempos Verbales y Pronombres en Inglés22 páginas
- Gramática de Tiempos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesGramática de Tiempos Verbales en Inglés23 páginas
- Gramática General 2º Bachillerato Ingles para Bachillerato y Evau100% (3)Gramática General 2º Bachillerato Ingles para Bachillerato y Evau24 páginas
- Guía Completa de Tiempos VerbalesAún no hay calificacionesGuía Completa de Tiempos Verbales13 páginas
- Material 5to - Quinto Año - InglésAún no hay calificacionesMaterial 5to - Quinto Año - Inglés173 páginas
- Presente Simple vs. Continuo en InglésAún no hay calificacionesPresente Simple vs. Continuo en Inglés12 páginas
- Resumen de Tiempos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesResumen de Tiempos Verbales en Inglés5 páginas
- Gramática Inglesa: Tiempos Verbales IIAún no hay calificacionesGramática Inglesa: Tiempos Verbales II40 páginas
- Gramática del inglés: Tiempos verbalesAún no hay calificacionesGramática del inglés: Tiempos verbales10 páginas
- Guía de Tiempos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesGuía de Tiempos Verbales en Inglés9 páginas
- Guía del Estudiante: Gramática Nivel 7Aún no hay calificacionesGuía del Estudiante: Gramática Nivel 719 páginas
- Tiempos y Aspectos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesTiempos y Aspectos Verbales en Inglés9 páginas
- Uso de Tiempos Verbales en InglésAún no hay calificacionesUso de Tiempos Verbales en Inglés5 páginas
- Gramática inglesa para BachilleratoAún no hay calificacionesGramática inglesa para Bachillerato23 páginas
- Tiempos Verbales en Inglés: Guía CompletaAún no hay calificacionesTiempos Verbales en Inglés: Guía Completa9 páginas
- Reglas del Pasado Simple en InglésAún no hay calificacionesReglas del Pasado Simple en Inglés6 páginas