Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
D-Ficha 1 - Teoría de Exponentes
Cargado por
rylexsTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
D-Ficha 1 - Teoría de Exponentes
Cargado por
rylexsCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
BANCO DE PREGUNTAS
PREGUNTAS DE DE ÁLGEBRA
ÁLGEBRA
ÁLGEBRA: FICHA 1
BANCO DE PREGUNTASBANCO DE
DE ÁLGEBRA
SOLUCIONARIO DE ÁLGEBRA
Alumno: _________________________________________________________________________________
Solucionario DE ÁlGEBra
9. Sabiendo que
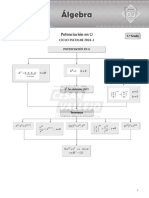
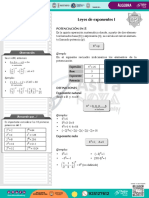
TEORíA DE EXPONENTES
P(x - 2) = 3x - 5 7. f(k(x)) = k(x) + 2 = x - 2
Teoría =de27x
P[Q(x)] exponentes
+4 & k(x) = x - 4
1.1. Reduce: Resolución:
Calcula: Q(-2) & k[f(4)] = f(4) - 4
BANCO 3n +DE
3
− 3nPREGUNTAS
+1
BANCO
BANCO DE PREGUNTAS
DE PREGUNTAS DE
DE ÁLGEBRA DE ÁLGEBRA
ÁLGEBRA
3 n - 1 _3 4 - 3 2 i =4+2-4=2
S= 1. S =A) -16 n - 1 B) -17 C) -18
3 3 n −1
( ) D) -19 3 _3 i E) -20 Clave B
SOLUCIONARIO
4 2
DE ÁLGEBRA
S = 3 - 3 = 33 - 3 = 24 8. Hacemos x2 + 1 = a & a - 1 = x :
n
A) 3 - 1
n
B) 3 + - 1
1
C) 24 10.
9. Calcula
3
Sabiendoel valor
que del coeficiente Solucionario
del monomio: DE2
ÁlGEBra
n m 3m + 2n 5m - 3 & P(a) = 2 _ a - 1 i - 5 _ a - 1 i + 8
D) 1 - 3 E) 18 P(x - 2) = 3x M(x; - 5y) = 4n xClave Cy 2
si su GA
P[Q(x)] = 27x + 4 = 19 y GR(y) = 7. 7. P(xf(k(x))
- 3) == 2k(x)_ x+-24=i x--52_ x - 4 i + 8
1.
2. Reduce: Teoría x de x exponentes &-k(x)
Calcula: + Q(-2) P(x 3) == 2x_-x - 4 4i - 5 x - 4 + 8
3n + 3 − 3n +1 2. S =A)x 4 a b B) 36 C) 12
S= ax + bx
A)3n-16
1 1
- 1x_ +4 x 2 i -17
P(x - 3) = 2x - 5 4 x - 4
&
C) -18
k[f(4)] = f(4) -
( )
S= B) 48
x D) 26 E)
3 3n −1 a 3 -
b 3 =4+2-4=2
a− x + b− x 1. S =D) -19 E) -20 Clave C
n - 1xi
11. S =Calcula 3a 3+ab en el polinomio:
_x Clave B
x2 x a + 6 a - 2 9. P[Q(x)]
+ 5 a = 3(Q(x) + 2) - 5 = 27x + 4
A) 3
ab B) 3 ++ b- 1
B) a C)
C) 1/ab x3 4 -b 3 + a
n n 1 a-1 a+2 a 2
A) -1 24 10. S =Calcula P(x)el == valor
32x
3
- 3 del
= + 3x y del 8.
y 24coeficiente + 4xHacemos
monomio: y x + 1 = a & a - 1 = x:
2 2
3 a x-b xGR(x) m 3m 2n 5m 3 & 3(Q(x) + 2) = 27x + 2 9
D)
D) a/b E) 18 + b
E) a
n
1-3 Si: GA M(x; = y)8= 4n x + y - & P(a) = 2 _2 =a- 1+i 3- 5 _ a - 1 i + 8
Q(x) + 9x
S =six su a x bGA x = 19 y GR(y) = 7.
= ab Clave C 2
2.2. Reduce: Resolución:
A) 9 B) 6 C) 8P(x - 3) =Q(x) 2_ = x -9x4+i 1- 5 _ x - 4 i + 8
Clave A & Q(-2)
ax + bx
D)
A) 4 7 x+ x
a b
E)
B) 5 36 P(x
C) 12 - 3) ==29(-2)_ x - 4+i -1= 5 -17
x-4 +8
S = x −x 2. S =D) 26 E) 48
x 1 + 1 P(x - 3) = 2x - 5 x - 4 Clave B
3. Si: P(x) = 3x + 1. a + b− x 12. Si: x
a Polinomios
bx
Halla: S = P(P(x)) - 3P(x) + x 11. P(x) =x 2xa +
Calcula en3 el polinomio:
x
10. GR(y) = 5m - 3 = 7 & m = 2 Clave C
A) ab B) a + b C) 1/ab a + b GA = y 3m 2n ++5m2)--35==8m
=+ 27x++2n4 - 3
a-1 a+2 a+6 a-2 a+5 a
S =Q(x - P(x)
x
3) =x x2x+ 1 y + 3x y + 4xP[Q(x)]
9. 3(Q(x)
D) a/b
2
a +
E) 2x
2 x
3. S =Calcula:
P(3x b +
1) a 3(3x 1) x
- b1 + -
P[Q(P(1))]
Si: GA x- xGR(x) = 8 + + 8m + 2n 2) 3==27x19 + 9
2
A) x - 1 B) C) x - x & 3(Q(x) +-
S = 3(3x +a 1)b + 1 - 9x - 3 + x
&
D) x + 1 E) -2 16Q(x)
+ 2n+-2 3==9x19+ 3
x 13
S= =A)9x a9+x b3 x+=1 ab - 9x - 3B) + x- 6 13 C) 21
8
Q(x)2n==9x6 + 1
S =D) x +-26
71 E) 395 n=3
4. Si: P(x) = 4x + 2 y P(3x - 2) = ax + b Clave A & Q(-2)
Clave D m = 9(-2) 2 + 1 = -17
Halla (a + b). & 4n = 4(3) = 36
3. Si: P(x) = 3x + 1. 12.
13. Si: a(x + b) + b(x + a) = x + 26
Si: Clave B
Clave B
A) 6 S = P(P(x)) B)
Halla: - 3P(x)
2 +x C) 3 4. 4(3x=-Polinomios
P(x)
Calcula: 2x
2)E+ +=23a= +axab + b+ b 10. GR(y) = 5m - 3 = 7 & m = 2
Q(x -- 3)8=+x2 += 1ax + b 11. GA = GA
D) 4 E) 16 12x
Calcula: 3m - + GR(x)
2n + 5m = 8- 3 = 8m + 2n - 3
A) x - 1 B) 2x - 1 C) x - x
2
A) 10 12xP[Q(P(1))]
- 6 = ax + B)b 14 C) 27
(2a + 5) - (a + 6) = 8
3. S =D) P(3x 25+ 1) - 3(3x + 1) E)+5x & 8m + 2n - 3= 198
5. Si
D) el
x +grado
1 del monomio-2 siguiente es 8:
oE)falso. a- 1=
3. Indica verdadero S
& =aA) +13
Resolución:
3(3x b= + 121) +- 16 -= 9x 6 -B)3 + - x13 C) 21 16 + 2n - 3 = 199
a=
I. aP(x) M+( x2. )a=
. a=-44x
.a 6 5 =4a3-2612 S I.=D)
a9x +. a3-4+. 1a-6 - 9x . a--8 3E)
. a+-10x39 Clave
(A 2n = 6
y .3x
a-10 x- 2)x = axxm
+ (b )
-2 -6 -8 -2-26
4. Si: P(3x = a-26 F)
II. 2x + 5 ' 2x - 3 = 256 ( ) SII.= 2xx++ 51' 2x - 3 = 256 n=3 Clave
Calcula (V)
Halla n el valor
+ 24 de m.
III. 3(8(a )= b).n
( ) 13.
5. M(x) Si:
III. 3(8 n 6 + 4/5
a(x b)
= 3x) =. x24 . x xn + 15b(x 12 + m
a) = x +
Clave( DF ) 12. P[Q(2(1)
26 m
& 4n =+4(3) 2
3)] = 36
2
A) VFV
6 6
B) B)
2 C) 9 = 3x6 . xS:
14. M(x)Calcula:
Calcula 4/5 12/15 m/30
E= . xa + ab .x +b P[Q(5)]
A) E) 16FFV C)3FVF = 3xS(6-= +2)4/5++212/15 m/30) Clave C
Clave B
D) 4
12
D) VVF E) FVV
4. M(x) 4(3x
& 6A)+12x
(
4/5-+812/15
10
8
)(
+ 2 =+ax
= ax+ +
)( b
+B)b=148
m/30
)( )( )
2 + 1 8 2 − 1 4 2 + 1 2 + 1 P[82+ 1] = P[9] = 21
C) 27 GA - GR(x) = 8
11.
Clave C
6.
5. Sabiendo
Si el gradoquedel monomio siguiente es 8: D) 25 12x - 624= ax m + E)b 5 (2a + 5) - (a + 6) = 8
A) 1 + B) =2 2 C) 2 2
f(x) + xg(x) = 4x + 5 & a+b= 12 - 615= 6 30 84 13. ax + ab +abx - 1+ =ab8 = x + 26
xf(x) + g(x)M=( 3xx ) 2=+3x 6 5 4 3 12
4x x x xm D) 2 E)
m = 12 (a + b)x +a2ab = 9= x + 26
Clave A & E = (a + b) + (ab) = 1 + 13 = Clave
14
Calcula el + g(2).
f(2)valor de m. Clave D
15. Resuelve: P = 4 + 15 . 4 − 15
4/5 15 12 Clave B
9
A) 2 4
B) 6 11
C) 9 = 3x6 . xS:
5.14. M(x)Calcula . x xm 12. P[Q(2(1) + 3)]
6. f(x)A)+ 1xg(x) 6 =4/54x +12/15 5 B) ...m/30
(i)
2 C) 3
M(x) = 3x . x 8 .2x .x P[Q(5)]
6
D) 12 7
E) 16 xf(x) + g(x) S= ( = 3x2 + )( +14x 8E)
M(x)D)= 43x(6 + 4/5 + 12/15 + m/30) )(
...
2 −(ii)
16 )( )( )
1 4 2 + 1 2 + 1 2 Productos notables
P[8 + 1] = P[9] = 21
Hacemos + 4/52i + x(ii): + m/30 = 8
- 12/15
6.
7. Sabiendo
Si: f(k(x)) =que x - 2 / f(x) = x + 2
4. Relaciona correctamente. 16. & 6Simplifica S:
A)-1x f(x) = 4x + 5 -B)3x2 - 4x 3 2 2 2
C) Usamos Clave C
f(x)
Resolución: 24 + m2 = 2 14. la diferencia de cuadrados:
f(x) + el
Halla xg(x) = 4x
valor de +k[f(4)].
5 2
f(x)(1 -2x2) = -3x 15x 3 -y30 E)2 + 84
4x 4x +
x 5 y 13. ax_ 4+ ab-+1ibx _ 4+2ab+= 1ix_ +226+ 1i_ 2 i
I. [(x+6)4]g(x)
' [(x=5)3x
] + 4x III. [(x5)3] ' [(x2)7] I-d,D)II-b, III-a, 3 + m2 =−12 − ; x,y ≠S0= (a2 + b)x
5 2
xf(x) S =IV-c
A) 3 y + x4x - 4x -y5 x
x + 2ab =_x + i26
II. 1[(x3)6]f(2)
Calcula ' [(x )5] B) 2 IV. [(x8)4] ' [(x
+4g(2). C)7)35] f(x) = S = _ 2 - 1i_ 2 + 1i 2
D) 4 E) 5 15. Resuelve:
A) 1 P= 4x 2B)
+- 2115 . Clave4Clave
− D15E C) 3& E = (a + b) + (ab) = 1 + 13 = 14
S = _2 - 1i_ 2 i = 2
a. x1
A) 9-2 2 B) 4
c. x-3
C) 11 D) 4 f(2) = 9 E) 5 Clave B
b. x 2 d. x-1 A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 Clave D
8. Si
D) P(x6 + 1) = 2x E) - 5x
7 + 8, halla P(x - 3). 6. 9++xg(x)
f(x)D)
& 2g(2)==4x4(2) + + 5 ... (i)
5
17. Halla 4 P: E) 16
xf(x) + g(x) 2g(2)= =3x42 + 4x ... (ii)
15. P = Productos
_ 4 + 15 i_ 4 notables
- 15 i
( )( )
2
A) I-a, II-b,
- 12x III-c, IV-d B) 2x - 16 + 5 x + 4
7. Si: 2x
f(k(x)) = x +- 82 / f(x) =x+2 16. Hacemos
Simplifica Pg(2)
i- =S:
= x(ii): 22 + 3 + 5 2 + 3 − 5 −2 6
B) I-b,
C) 2x el II-c, III-d,
- 5valor
x −de4 IV-a D) 2x - 16 - 5 x + 4 2
Halla k[f(4)]. f(2)
&f(x) 2
A)-0+x g(2) 9 +
f(x) = 4x 2 = 11
x+ 5y-B)
23x3 - 4x2
1 x y 2 14. P = 4 2 la
C) 2Usamos 15 = 16
- diferencia 15 = 1
de-cuadrados:
C) I-c, II-b, III-a, IV-d 2S = 3+ 2 − − ; x,y ≠ 0
E) 2x - 16 - 5 x − 4 f(x)(1
D) 2-6x ) = -3x - 4x 10 + 4x Clave
+5
D)
A) 1I-d, II-b, III-c, IV-a
B) 2 C) 3 y3 x E) y x C S = _ 4 2 - 1i_ 4 2 + 1i_ 2 + 1iClave
_ 2i
D) I-d,
4 II-b, III-a, IV-c E) 5 3 x + 4 x 2 - 4x - 5
E) A) 1 f(x) = B) 2 C) 3S = _ 2 - 1i_ 2 + 1i_ 2 i
D) 4 - Banco de x 2E)- 51
2 2
Solucionario f(2) = 9 preguntas de ÁlgeBra S =-_3.° i_ s2ecundaria
2 - 1de i= 2
B8.
ANCOSiDE
P(x + 1) = 2x DE
PREGUNTAS - 5x + 8, halla- P(x
ÁLGEBRA - 3).
3.° DE SECUNDARIA 1
17. & Halla P: = 4(2) + 5
9 + 2g(2) Clave D
( )( )
2 o
A) 2x - 12x + 8 B) 2x - 16 + 5 x + 4 2g(2)
P= Matemática
= 4
2+ 3+ 5 3. de secundaria
2 + 3 − 15. - Ediciones Lexicom
5 −P2= 6 _4 + 15 i_4 - 15 i
C) 2x - 5 x − 4 D) 2x - 16 - 5 x + 4 g(2) = 2
A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 2
E) 2x - 16 - 5 x − 4 & f(2) + g(2) = 9 + 2 = 11 P = 4 2 - 15 = 16 - 15 = 1
D) 2 6 E) 10
Clave C Clave
También podría gustarte
- Ficha 1 - Teoría de ExponentesDocumento1 páginaFicha 1 - Teoría de ExponentesrylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Exponentes 2022Documento4 páginasExponentes 2022Caleb QuisbertAún no hay calificaciones
- CRP Hora 1 Semana 2 2022.7Documento4 páginasCRP Hora 1 Semana 2 2022.7Ricardo Rosales GasteloAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller No.3 Exponentes RadicalesDocumento15 páginasTaller No.3 Exponentes RadicalesAntonio MolinaAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 Operac Con Polinom 9 Dic 2016Documento25 páginas4 Operac Con Polinom 9 Dic 2016MAPVArelyAún no hay calificaciones
- X AUNI Sem2 DomDocumento3 páginasX AUNI Sem2 DomAlexander Villanueva HuamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 01Documento6 páginasPractica 01rodrigo salinasAún no hay calificaciones
- Leyes de Exponentes y RadicalesDocumento3 páginasLeyes de Exponentes y RadicalesMelidy Eided Hinostroza MitaccAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 Trig 4 TM Sol SimulDocumento4 páginas4 Trig 4 TM Sol SimulTeka ProductionsAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 Trig 4 TM Sol SimulDocumento4 páginas4 Trig 4 TM Sol SimulmariajoseAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 3 - Algebra - Operaciones BasicasDocumento2 páginasPractica 3 - Algebra - Operaciones BasicasJose HerbertAún no hay calificaciones
- Potenciacion de Números RealesDocumento3 páginasPotenciacion de Números RealesErick Reyna100% (1)
- Alg Uni 1Documento5 páginasAlg Uni 1Giovanna TiconaAún no hay calificaciones
- Operaciones Algebraicas y EcuacionesDocumento33 páginasOperaciones Algebraicas y EcuacionesBryan NachoAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoria de ExponentesDocumento13 páginasTeoria de ExponentesJEISON HESNIL CAMIZÁN CUZQUE0% (1)
- Razonamiento PDFDocumento78 páginasRazonamiento PDFOlmer Jobaldo Jara ChihualaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ex Resuelto Final MatiiDocumento3 páginasEx Resuelto Final MatiiJorge CuderoAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 1-Superficie Cilindrica, Conica y de RevoluciónDocumento25 páginasSemana 1-Superficie Cilindrica, Conica y de RevoluciónantonioAún no hay calificaciones
- LGF2V0Documento9 páginasLGF2V0victoria huayamaveAún no hay calificaciones
- GHFKJHDocumento70 páginasGHFKJHpaco medinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen de MatematicaDocumento5 páginasExamen de Matematicadorac03Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1.2 Potencia de Un Número Real: Clase 02 - Matemática BásicaDocumento11 páginas1.2 Potencia de Un Número Real: Clase 02 - Matemática BásicaJeanmarco Straus Paxi floresAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario IIrep-176 2011-IVDocumento5 páginasSolucionario IIrep-176 2011-IVJnnr DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoria de ExponentesDocumento5 páginasTeoria de ExponentesItalo Jesus Cabrera CalderonAún no hay calificaciones
- 3b. PolinimiosDocumento2 páginas3b. Polinimiosvalerihuevo2021Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha Teoria de ExponentesDocumento10 páginasFicha Teoria de ExponentesDenny CárdenasAún no hay calificaciones
- X 1º Esc Diri Sem3Documento2 páginasX 1º Esc Diri Sem3Juan Alfredo Barrios PUCHOCAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario - UnjDocumento12 páginasFormulario - UnjVaranny Leiser Cueva PeralesAún no hay calificaciones
- División de PolinomiosDocumento28 páginasDivisión de PolinomiosAbraham Frederisck Salazar PumaAún no hay calificaciones
- S7 - PPT - Ecuaciones ExponencialesDocumento23 páginasS7 - PPT - Ecuaciones ExponencialesCesar DavidAún no hay calificaciones
- VAL-F08B-02 Binomio de NewtonDocumento3 páginasVAL-F08B-02 Binomio de NewtonAlfa VDAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra - Semana #01 - Alfa y TethaDocumento5 páginasAlgebra - Semana #01 - Alfa y TethaAugusto Rumiche AmayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Año de La Unidad, La Paz Y El Desarrollo: "Prestigiosa Universidad Nacional de Tumbes"Documento18 páginasAño de La Unidad, La Paz Y El Desarrollo: "Prestigiosa Universidad Nacional de Tumbes"José Clavijo BarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Anual San Marcos 2020 Pal LibroDocumento162 páginasAlgebra Anual San Marcos 2020 Pal LibroCarlos Velasquez VergaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra BásicaDocumento16 páginasAlgebra Básica1IM16González Avila Diego AlejandroAún no hay calificaciones
- Sol D 28 SeptDocumento3 páginasSol D 28 SeptJuan Jose VRAún no hay calificaciones
- Sem#1-Teoría de Exponentes-Alg-AstraNova - DADocumento5 páginasSem#1-Teoría de Exponentes-Alg-AstraNova - DANaidely Rosa Sofía OSCO MANRIQUEAún no hay calificaciones
- Ec Algebra 1 Repaso Integral - Aduni 2016Documento14 páginasEc Algebra 1 Repaso Integral - Aduni 2016Yerson RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- 4º 1Documento78 páginas4º 1Jesus Figueredo OneeglioAún no hay calificaciones
- Álgebra - Ciclo VeranoDocumento50 páginasÁlgebra - Ciclo VeranoAlexander Guerrero Rosales0% (1)
- Balotario de Preguntas de MatematicaDocumento4 páginasBalotario de Preguntas de MatematicaHernan Miranda RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoria de ExponentesDocumento14 páginasTeoria de Exponentesruben darioAún no hay calificaciones
- Ciclo Primera Oportunidad 2022: CepruDocumento58 páginasCiclo Primera Oportunidad 2022: CepruRoger Cano AsllaAún no hay calificaciones
- Grupo C Completo Primera OportunidadDocumento491 páginasGrupo C Completo Primera OportunidadRAUL EVARISTO CHCHAMA MACHACCAAún no hay calificaciones
- Preguntas para El Segundo SimuDocumento2 páginasPreguntas para El Segundo Simurafael jairo gomez chavezAún no hay calificaciones
- Anexo 1 - Ejercicios Tarea 2Documento8 páginasAnexo 1 - Ejercicios Tarea 2Nicol SuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Radicación en Q-Definición y PropiedadesDocumento4 páginasRadicación en Q-Definición y PropiedadesKentaroAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometría 1°-IV Bal-Bim - 18Documento7 páginasTrigonometría 1°-IV Bal-Bim - 18Giovanni SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Refor AlgebraDocumento2 páginasRefor AlgebraJhon Alarcon JaramilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Radicacion Preagraria 2022 - IIDocumento26 páginasRadicacion Preagraria 2022 - IIshelle yetteAún no hay calificaciones
- Potenciacion - RadicacionDocumento17 páginasPotenciacion - Radicacionedith miriam sotelo uretaAún no hay calificaciones
- Matemáticas 3ro - Sec.ib - PamerDocumento130 páginasMatemáticas 3ro - Sec.ib - PamerCristian Edgardo Portocarrero GutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- 0D - Al - Intro IvDocumento2 páginas0D - Al - Intro IvKEVIN STEVEN TOMAS SALINASAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Anual Uni 2015Documento113 páginasAlgebra Anual Uni 2015Angel Alfredo Guillen Urrutia100% (1)
- Álgebra 01 Refor 2022-IDocumento2 páginasÁlgebra 01 Refor 2022-IFrancisco CentenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Listado 5 AT 2023 1Documento2 páginasListado 5 AT 2023 1Paulo MederoAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen MensualDocumento5 páginasExamen MensualCÉSAR AUGUSTO RUMICHE AMAYAAún no hay calificaciones
- Teorema de Pitágoras y Triángulos NotablesDocumento2 páginasTeorema de Pitágoras y Triángulos NotablesDennis Lee Caballon ArevaloAún no hay calificaciones
- 3ºAÑO - ANÁLISIS COMBINATORIO - Solución de La Ficha de Aplicación.Documento9 páginas3ºAÑO - ANÁLISIS COMBINATORIO - Solución de La Ficha de Aplicación.jtoledotasaico0101109Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fichas Refuerzo MatematicaDocumento83 páginasFichas Refuerzo MatematicarylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha 2 - PolinomiosDocumento1 páginaFicha 2 - PolinomiosrylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Protocolo BIAE JEC 2020Documento2 páginasProtocolo BIAE JEC 2020rylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- D-Ficha 4 - División de Polinomios y Cocientes NotablesDocumento1 páginaD-Ficha 4 - División de Polinomios y Cocientes NotablesrylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- PLAN DE TUTORIA 2020 4to ADocumento4 páginasPLAN DE TUTORIA 2020 4to ArylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha 3 - Productos NotablesDocumento1 páginaFicha 3 - Productos NotablesrylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Fichas Refuerzo RMDocumento53 páginasFichas Refuerzo RMrylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Cript Oar It Me TicaDocumento2 páginasCript Oar It Me TicarylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Infracciones Frecuentes de InmobiliariasDocumento3 páginasInfracciones Frecuentes de InmobiliariasrylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Aritmetica Ciencias 2014Documento23 páginasAritmetica Ciencias 2014rylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Aritmética Segundo Grado II Trimestre 2014Documento7 páginasAritmética Segundo Grado II Trimestre 2014rylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Gestionderiesgosenlaie 100419203539 Phpapp01Documento90 páginasGestionderiesgosenlaie 100419203539 Phpapp01roxamarAún no hay calificaciones
- Aritmética Primer Grado 2014 II TrimestreDocumento7 páginasAritmética Primer Grado 2014 II Trimestrerylexs0% (1)
- Aritmetica Ciencias 2014Documento23 páginasAritmetica Ciencias 2014rylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Aritmética Primer Grado 2014Documento11 páginasAritmética Primer Grado 2014rylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- 03 RelacionesDocumento66 páginas03 RelacionesbraminsaluzAún no hay calificaciones
- Matemáticas Evaluacion Diagnóstica PrimariaDocumento28 páginasMatemáticas Evaluacion Diagnóstica PrimariarylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Educación en Los Países de PerúDocumento22 páginasEducación en Los Países de PerúrylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- VII Olimpiada Nacional Escolar de Matem AticaDocumento5 páginasVII Olimpiada Nacional Escolar de Matem AticarylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso de Transicion Pedagogica 2014Documento9 páginasCurso de Transicion Pedagogica 2014rylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso de Transicion Pedagogica 2014Documento9 páginasCurso de Transicion Pedagogica 2014rylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Con ConjuntosDocumento1 páginaProblemas Con ConjuntosrylexsAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentación 1Documento13 páginasPresentación 1rylexsAún no hay calificaciones