Tema 8: Productos Notables
PRODUCTOS NOTABLES:
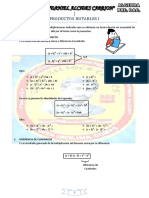
I.- Binomio al Cuadrado:
a) (a+b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2 b) (a-b)2 = a2 - 2ab + b2
II.- Binomio al Cubo:
a) (a+b)3 = a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3 b) (a-b)3 = a3 - 3a2b + 3ab2 - b3
III.- Suma por Diferencia:
a) (a+b)(a-b) = a2 - b2
IV.- Suma y Diferencia de Cubos:
a) (a+b)(a2 - ab + b2) = a3 + b3 b) (a-b)(a2 + ab + b2) = a3 - b3
V.- Producto de dos Binomios:
a) (x+a)(x+b) = x2 + (a+b)x + ab
VI.- Identidades de Legendre:
a) (a+b)2 + (a-b)2 = 2(a2 + b2) b) (a+b)2 - (a-b)2 = 4ab
VII.- Trinomio al cuadrado
a) (a+ b+c) 2 = a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2ac + 2 bc
VIII.- Trinomio al cubo
a) (a + b + c) 3 = a3 + b3 + c3 + 3(a+b)(b+c)(a+c)
b) (a + b+ c) 3 = a3 + b3 + c3 + 3(a+b+c)(ab+bc+ca) - 3ab
c) (a + b+ c) 3 = a3 + b3 + c3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + 3b2c + 3bc2 + 3c2a + 3ca2 + 6abc
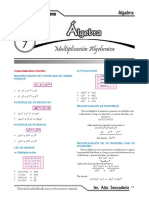
1. Simplificar la expresión algebraica: [(x+1)2(x-1)2(x2-1)3(x2+1)5(x4+1)5(x8-1)3]1/8 +1
A) 2 B) 0 C) -1 D) 3 E) x8
1
[(𝑥 + 1)2 (𝑥 − 1)2 (𝑥 2 − 1)3 (𝑥 2 + 1)5 (𝑥 4 + 1)5 (𝑥 8 − 1)3 ] 8 + 1
1
= [(𝑥 2 − 1)2 (𝑥 2 − 1)3 (𝑥 2 + 1)5 (𝑥 4 + 1)5 (𝑥 8 − 1)3 ] 8 + 1
1
= [(𝑥 2 − 1)5 (𝑥 2 + 1)5 (𝑥 4 + 1)5 (𝑥 8 − 1)3 ] 8 + 1
1
= [(𝑥 4 − 1)5 (𝑥 4 + 1)5 (𝑥 8 − 1)3 ] 8 + 1
1
= [(𝑥 8 − 1)5 (𝑥 8 − 1)3 ] 8 + 1
1
= [(𝑥 8 − 1)8 ] 8 + 1
= ( 𝑥 8 − 1) + 1
= 𝑥8
�2. Determinar el valor de "m" con la condición de que el término independiente del
siguiente producto: (x+2)3(x-m)2(x2+5)(x+3)2 sea 1440.
A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 6 E) 8
(𝑥 + 2)3 (𝑥 − 𝑚)2 (𝑥 2 + 5)(𝑥 + 3)2 (𝑇. 𝑖𝑛𝑑𝑒𝑝 = 1440)
𝑥=0
(0 + 2)3 (0 − 𝑚)2 (02 + 5)(0 + 3)2 = 1440
(2)3 (−𝑚)2 (5)(3)2 = 1440
𝑚2 = 4
𝑚 = ±2
3. Simplificar la siguiente expresión: (x+1)(x-1)(x+2)(x+4) + 2x(x+3) - x2(x+3)2
A) x2+x-8 B) x-8 C) 8 D) -8 E) N.A.
2
(𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 − 1)(𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 + 4) + 2𝑥(𝑥 + 3) − 𝑥2 (𝑥 + 3)
=[(𝑥 + 1)(𝑥 + 2)][(𝑥 − 1)(𝑥 + 4)] + 2[𝑥(𝑥 + 3)] − [𝑥 (𝑥 + 3)]2
=(𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 − 4) + 2(𝑥 2 + 3𝑥) − (𝑥 2 + 3𝑥)2
Cambio de variable
*𝑥 2 + 3𝑥
= (𝑎 + 2)(𝑎 − 4) + 2𝑎 − 𝑎2
= 𝑎2 − 2𝑎 − 8 + 2𝑎 − 𝑎2
= −8
x 1 2 x 2 x 1 2 x 1 2 x 2 x 1 2
4. Si "x" no es 1 ni (-1) el producto:
x 3 1 2 x 3 1 2
A) (x+1)4 B) 1 C) (x3+1)4 D) [(x3+1)(x3-1)]2 E) [(x3-1)2]2
( 𝑥 + 1)2 (𝑥 2 − 𝑥 + 1)2 (𝑥 − 1)2 (𝑥 2 + 𝑥 + 1) 2
= [ ][ ]
(𝑥 3 + 1)2 (𝑥 3 − 1)2
(𝑥 3 + 1)2 (𝑥 3 − 1)2
= [ 3 ][ ] = (1)(1) = 1
(𝑥 + 1)2 (𝑥 3 − 1)2
5. Si: (a+1/a)2 = 3 ; a3+1/a3 valdrá:
A) 27 B) 6 C) 12 D) 4,3758 E) 0
1 2 1 1 1 1
(𝑎 + ) = 3 𝑎3 + = (𝑎 + ) [𝑎 2
− ( 𝑎 ) ( ) + ]
𝑎 𝑎3 𝑎 𝑎 𝑎2
1 1 1 1
𝑎 2 + 2(𝑎 ) ( ) + 2 = 3 = (𝑎 + ) [(𝑎2 + 2 ) − 1]
𝑎 𝑎 𝑎 𝑎
1 1
𝑎2 + 2 + =3 = (𝑎 + ) [1 − 1]
𝑎2 𝑎
1 1
𝑎2 + =1 = (𝑎 + ) (0)
𝑎2 𝑎
1
𝑎3 + =0
𝑎3
� x y x y 3x 2 y 2 4
6. Si: 3 ; hallar el valor de: .
y x 4x 2 y 2
A) 1 B) 3 C) 7 D) 9 E) 5
𝑥 𝑦
+ =3 (𝑥 + 𝑦)4 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2 [(𝑥 + 𝑦)2 ]2 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2
=
𝑦 𝑥 4𝑥 2 𝑦 2 4𝑥 2 𝑦 2
𝑥 2 +𝑦 2 (𝑥 + 𝑦)4 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2 [(𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 ) + 2𝑥𝑦]2 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2
=3 4𝑥 2 𝑦 2
=
4𝑥 2 𝑦 2
𝑦𝑥
(𝑥 + 𝑦)4 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2 [3𝑥𝑦 + 2𝑥𝑦]2 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2
𝑥 + 𝑦 2 = 3𝑥𝑦
2
4𝑥 2 𝑦 2
=
4𝑥 2 𝑦 2
(𝑥 + 𝑦)4 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2 [5𝑥𝑦] + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2
2
=
4𝑥 2 𝑦 2 4𝑥 2 𝑦 2
(𝑥 + 𝑦)4 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2 25𝑥 𝑦 2 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2
2
=
4𝑥 2 𝑦 2 4𝑥 2 𝑦 2
(𝑥 + 𝑦)4 + 3𝑥 2 𝑦 2 28𝑥 2 𝑦 2
=
4𝑥 2 𝑦 2 4𝑥 2 𝑦 2
= 7
7. Simplificar: P = (x+8)2 (x-5)2 - (x+2)2(x+1)2 + 84x(x+3)
A) 1396 B) 1596 C) 1286 D) 1046 E) 1536
(𝑥 + 8)2 (𝑥 − 5)2 − (𝑥 + 2)2 (𝑥 + 1)2 + 84𝑥 (𝑥 + 3)
= [(𝑥 + 8)(𝑥 − 5)]2 − [(𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 + 1)]2 + 84[𝑥(𝑥 + 3)]
= (𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 − 40)2 − (𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 + 2)2 + 84(𝑥 2 + 3𝑥)
∗ 𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 = 𝑎 cambio de variable
=(𝑎 − 40)2 − (𝑎 + 2)2 + 84𝑎
= 𝑎2 − 80𝑎 + 1600 − (𝑎2 + 4𝑎 + 4) + 84𝑎
=1596
8. Efectuar: (a+b+c-d)2 + (a+b-c+d)2 + (a-b+c+d)2 + (b+c+d-a)2
A) 4abcd B) a2b2c2d2 C) 4a2b2c2d2 D) 4(a2+b2+c2+d2) E) 4(a2+b2-c2-d2)
= {[(𝑎 + 𝑏) + (𝑐 − 𝑑 )]2 + [(𝑎 + 𝑏) − (𝑐 − 𝑑 )]2 } + {[(𝑐 + 𝑑 ) + (𝑎 − 𝑏)]2 + [(𝑐 + 𝑑 ) − (𝑎 − 𝑏)]2 }
= 2[(𝑎 + 𝑏)2 + (𝑐 − 𝑑 )2 ] + 2[(𝑐 + 𝑑 )2 + (𝑎 − 𝑏)2 ]
=2[(𝑎 + 𝑏)2 + (𝑐 − 𝑑 )2 + (𝑎 − 𝑏)2 + (𝑐 − 𝑑 )2 ]
= 2{[(𝑎 + 𝑏)2 + (𝑎 − 𝑏)2 ] + [(𝑐 + 𝑑 )2 + (𝑐 − 𝑑 )2 ]}
= 2[2(𝑎2 + 𝑏2 ) + 2(𝑐 2 + 𝑑 2 )]
= 4(𝑎2 + 𝑏2 ) + 4(𝑐 2 + 𝑑 2 )
= 4(𝑎 2 + 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 + 𝑑 2 )
2 2
a b 2 a b 2 a 2 b 2
9. Simplificar: 4
b a b a b a
A) 0 B) 1 C) 24 D) 8 E) 16
2 2
𝑎 𝑏 2 𝑎 𝑏 2 𝑎 2 𝑏 2
[( + ) + ( − ) ] − 4 [( ) − ( ) ]
𝑏 𝑎 𝑏 𝑎 𝑏 𝑎
2 2
𝑎 2 𝑏 2 𝑎 2 𝑏 2
= { 2 [( ) + ( ) ]} − 4 [( ) − ( ) ]
𝑏 𝑎 𝑏 𝑎
2 2 2
𝑎 2 𝑏 𝑎 2 𝑏 2
= 4 [( ) + ( ) ] − 4 [( ) − ( ) ]
𝑏 𝑎 𝑏 𝑎
2 2
𝑎 2 𝑏 2 𝑎 2 𝑏 2
= 4 {[( ) + ( ) ] − [( ) − ( ) ] }
𝑏 𝑎 𝑏 𝑎
� 𝑎 2 𝑏 2
= 4 [4 ( ) ( ) ]
𝑏 𝑎
𝑎 2 𝑏 2
= 16 ( ) ( )
𝑏 𝑎
𝑎 𝑏2
2
= 16 ( 2 · 2 )
𝑏 𝑎
= 16
10. Efectuar: P = (x-2)(x+2)(x2+22)(x4+24)(x8+28)…. hasta 50 factores
A) x 2 2 2 B) x 2 2 2 C) x 2 2 2 D) x 2 2 2 E) x 2 2 2
50 50 50 50 49 49 50 49 49 49
= (𝑥 − 2)(𝑥 + 2)(𝑥 2 + 22 )(𝑥 4 + 24 )(𝑥 8 + 28 ) … 50 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑠
= (𝑥 2 − 22 )(𝑥 2 + 22 )(𝑥 4 + 24 )(𝑥 8 + 28 ) … 49 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑠
0 0 0 0 1 1 2 2 3 3 48 48
=(𝑥 2 − 22 )(𝑥 2 + 22 )(𝑥 2 + 22 )(𝑥 2 + 22 )(𝑥 2 + 22 ) … (𝑥 2 + 22 ) 50 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑠
49 𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟𝑒𝑠
49 49
=> 𝑃 = 𝑥 2 − 22
11. Determinar el V.N de: R a 2 2a 3 a 12 a 1a 3 8aa 2 para
2
a = 200
R a 2 2a 3 a 1 a 1 a 3 8a a 2
2 2
2
R a 2 2a 3 a 2 2a 1 a 2 2a 3 8 a 2 2a cambio de var iable
x x x x
R ( x 3) ( x 1)( x 3) 8 x
2
R x 2 6 x 9 ( x 2 2 x 3) 8 x
R x2 6 x 9 x2 2 x 3 8x
R 12
12. Calcular el valor de : 8 1 24(26)(626)
8 1 24(26)(626) 8 1 (52 1)(52 1)(626) 8 1 (54 1)(626) 8 1 (54 1)(54 1)
8 1 58 1 8 58 5
13. Efectuar : S 8 1 3(5)(17)(257)
S 8 1 3(5)(17)(257) 8 1 (22 1)(22 1)(17)(257) 8 1 (24 1)(17)(257) 8 1 (24 1)(24 1)(257)
8 1 (28 1)(257) 8 1 (28 1)(28 1) 8 1 216 1 8 216 2 2 4