Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Formulario Identidades
Cargado por
LIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Formulario Identidades
Cargado por
LIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
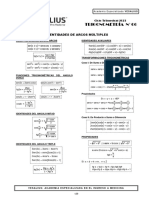
Identidades trigonométricas
1 1 senx
sen2 x +cos 2 x=1 senx= cosx= tanx=
cscx secx cosx
1 cosx
tan 2 x +1=sec 2 x tanx = ctgx=
ctgx senx
ctg 2 x+1=csc 2 x senx . cscx=1 senx . cscx=1
Funciones de la suma y diferencia de los ángulos
sen ( x+ y ) =senX . cosY + cosX . senY tanX −tanY
tan ( x− y )=
1+tanX .tanY
sen ( x− y )=senX . cosY −cosX . senY
ctgX . ctgY −1
cos ( x + y )=cosX . cosY −senX . senY ctg ( x+ y )=
ctgY +ctgX
cos ( x− y )=cosX . cosY + senX . senY ctgX . ctgY +1
ctg ( x− y )=
tanX +tanY ctgY −ctgX
tan ( x + y )=
1−tanX .tanY
Funciones del ángulo doble
sen 2 X=2 senX . cosX
cos 2 X =cos2 X −sen 2 X cos 2 X =2 cos2 X−1 cos 2 X =1−sen2 X
2 tanX
tan2 X =
1−tan 2 X
Funciones del ángulo mitad
x 1−cosX x 1+ cosX
sen =±
2 2 √ cos =±
2 √
2
x 1−cosX senX 1−cosX
tan =±
2 √ =
1+cosX 1+cosX
=
senX
x 1+cosX 1+ cosX senX
ctg =±
2 √
1−cosX
=
senX
=
1−cosX
Ángulos negativos
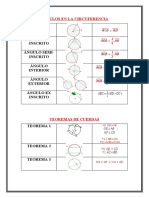
De Producto a Suma
cos ( x− y )−cos ( x+ y)
senXsenY =
2
cos ( x+ y )+ cos ( x− y)
cosXcosY =
2
sen ( x+ y ) + sen ( x− y)
senXcosY =
2
sen ( x + y )−sen (x− y )
cosXsenY =
2
De Suma a Producto
senX + senY =2 sen ( x+2 y ) cos( x−2 y )
x+ y x− y
senX−senY =2 cos ( ) sen (
2 2 )
x+ y x− y
cosX + cosY =2 cos ( ) cos (
2 2 )
x+ y x− y
cosX −cosY =−2 sen ( ) sen (
2 2 )
De diferencia de cuadrados a Producto
sen2 x −sen 2 y=sen ( x + y ) sen ( x− y )
cos 2 x−sen2 y=cos ( x + y ) cos ( x− y )
Eliminar seno y coseno
1
x x
senX=2 sen ( ) cos ( )=
( 2 )
2 tan
x
2 2 1
1+tan ( x ) 2
2
1
1−tan ( x ) 2
x 2
cosX =2 cos ( )−1=
2
2 1
1+ tan ( x )
2
2
También podría gustarte
- Formulario IdentidadesDocumento2 páginasFormulario IdentidadesLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- 06 Trigonometría - Identidades de Arcos Multiples 129 - 132Documento4 páginas06 Trigonometría - Identidades de Arcos Multiples 129 - 132Francisco Bocanegra CiudadAún no hay calificaciones
- FORMULARIODocumento2 páginasFORMULARIOJhon Brayan Quisbert CalderónAún no hay calificaciones
- IdentidadesTrigonómicasDocumento1 páginaIdentidadesTrigonómicasAlessandro HaroAún no hay calificaciones
- Relaciones trigonométricas y sus aplicacionesDocumento2 páginasRelaciones trigonométricas y sus aplicacionesMateoGP0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones Trigonometricas ResumenDocumento1 páginaFunciones Trigonometricas ResumenFotografiArtisticaAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario de TrigonometríaDocumento1 páginaFormulario de TrigonometríaBrayan CanquiAún no hay calificaciones
- Sin 2x 2sin X Cos X: Formulele TrigonometriceDocumento1 páginaSin 2x 2sin X Cos X: Formulele TrigonometriceGabi annAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones, Razones e Identidades TrigonométricasDocumento2 páginasFunciones, Razones e Identidades TrigonométricasYohana Delgado RodallegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario Completo Mate 2Documento3 páginasFormulario Completo Mate 2Luis Fer BailonAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades TrigonométricasDocumento2 páginasIdentidades TrigonométricasEstefania Ortiz AriasAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas de funciones trigonométricas directas e inversasDocumento4 páginasDerivadas de funciones trigonométricas directas e inversasMagaly ChilamaAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades TrigonometricasDocumento1 páginaIdentidades TrigonometricasFabiola RamírezAún no hay calificaciones
- Pertemuan 4 Kalkukulus 2Documento11 páginasPertemuan 4 Kalkukulus 2Jihad Mufry AnnahlAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo IDocumento5 páginasCalculo IDanny QuishpiAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios A Resolver en Sesiones de Derivadas Trigonométricas DirectasDocumento2 páginasEjercicios A Resolver en Sesiones de Derivadas Trigonométricas DirectasYos CoconiAún no hay calificaciones
- Limites TrigonometricosDocumento3 páginasLimites TrigonometricosBriyhit QuispeAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo lineal: Tarea 1 de álgebra, trigonometría e integralesDocumento5 páginasCalculo lineal: Tarea 1 de álgebra, trigonometría e integralesyuranyAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrales TrigonométricasDocumento5 páginasIntegrales TrigonométricasGiovana Barbara Aguilar MamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario Alg TrigoDocumento3 páginasFormulario Alg TrigoNick RiveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades trigonométricas fundamentalesDocumento11 páginasIdentidades trigonométricas fundamentalesLuz Dary Caro Jimenez100% (1)
- Ecuaciones diferenciales de RiccatiDocumento8 páginasEcuaciones diferenciales de RiccatiRodrigo Miguel Moina SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometría: identidades y problemasDocumento6 páginasTrigonometría: identidades y problemasNando AlarconAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas de funciones compuestas y explícitasDocumento8 páginasDerivadas de funciones compuestas y explícitasdanitza ortizAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFDaniel CabarcasAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFcesamav0% (1)
- Identidades TrigonometricasDocumento19 páginasIdentidades TrigonometricasJosé Natalio Guerrero CoxcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFJosé Natalio Guerrero CoxcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFu3erAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFPrincesa MedinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFRobertoAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFAdony LunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDF1979jccmAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades TrigonometricasDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricascarlos loaizaAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFFreddy AndrangoAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades trigonométricas fundamentalesDocumento19 páginasIdentidades trigonométricas fundamentalesAriel GalvanAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFluzAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades TrigonometricasDocumento19 páginasIdentidades Trigonometricasjareneuyate100% (1)
- 4_Trig_Cap4_V_UNI_TareaDocumento1 página4_Trig_Cap4_V_UNI_Tareajeanpierrellantocanales2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fórmulas de Funciones e Identidades TrigonométricasDocumento2 páginasFórmulas de Funciones e Identidades TrigonométricasMario VilcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades TrigonometricasDocumento1 páginaIdentidades TrigonometricasKevin Andrés Garzón MijaresAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades TrigonometricasDocumento1 páginaIdentidades TrigonometricasNaomi RangelAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades TrigonometricasDocumento1 páginaPropiedades TrigonometricasAlonso GutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tabla1 A PDFDocumento1 páginaTabla1 A PDFHilda HMAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades de ÁlgebraDocumento1 páginaIdentidades de ÁlgebraEvelyn SaucedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario Identidades TrigonometricasDocumento1 páginaFormulario Identidades TrigonometricasJosé HernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tab TrigDocumento1 páginaTab TrigAngelica RiozAún no hay calificaciones
- Tabla TrigonometriaDocumento1 páginaTabla TrigonometriaJairo GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- IdentiTrigoDocumento1 páginaIdentiTrigoReynaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tab Trig PDFDocumento1 páginaTab Trig PDFFranz Leonard NayyarAún no hay calificaciones
- IdentidadesTrigonometricasDocumento1 páginaIdentidadesTrigonometricasVictor RolónAún no hay calificaciones
- Tab Trig PDFDocumento1 páginaTab Trig PDFBrandon RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tabela de Derivadas e IntegraisDocumento2 páginasTabela de Derivadas e IntegraisMaria Eduarda GnoattoAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades Trigonometricas PDFDocumento1 páginaIdentidades Trigonometricas PDFYuliiana Hernandez100% (1)
- Identidades Fundamentales-1Documento1 páginaIdentidades Fundamentales-1MayraCaceresAún no hay calificaciones
- IdentiTrigoDocumento1 páginaIdentiTrigojaime hernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tab TrigDocumento1 páginaTab TrigAlberto JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tablas TrigonometricasDocumento1 páginaTablas TrigonometricasYEIMY MARISOL CRUZ ALARCONAún no hay calificaciones
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDe EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesAún no hay calificaciones
- G9 - NRC - 7833 - Flexibilidad en OrigenDocumento4 páginasG9 - NRC - 7833 - Flexibilidad en OrigenLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Completar Todos Los Campos RequeridosDocumento3 páginasCompletar Todos Los Campos RequeridosLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Sistemas BlockchainDocumento1 páginaTaller Sistemas BlockchainLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Innovacion Actividad Aprendizaje 2-3PDocumento1 páginaInnovacion Actividad Aprendizaje 2-3PLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Pbis PaisesDocumento93 páginasPbis PaisesJoseAún no hay calificaciones
- Innovacion Actividad Aprendizaje 3Documento1 páginaInnovacion Actividad Aprendizaje 3LIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- DEBER 1uisnkDocumento1 páginaDEBER 1uisnkLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Ofimatica DocdhlkncDocumento1 páginaOfimatica DocdhlkncLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Preguntas de Base EstructuradaDocumento3 páginasPreguntas de Base EstructuradaLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Conectividad estudiantes turismo ESPEDocumento1 páginaConectividad estudiantes turismo ESPELIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- FORMULASns, MDocumento2 páginasFORMULASns, MLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- COMUNICACIÓN ORAL Y ESCRITA TurskñDocumento2 páginasCOMUNICACIÓN ORAL Y ESCRITA TurskñLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea1 Capitulo1y2 6958 LizbethsarangoDocumento7 páginasTarea1 Capitulo1y2 6958 LizbethsarangoLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- ANDITECHDocumento22 páginasANDITECHLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Matricula Ordinaria ManualDocumento2 páginasMatricula Ordinaria ManualLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Qué Son Las NIIFDocumento3 páginasQué Son Las NIIFLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis de Las Principales Obligaciones TributariasDocumento3 páginasAnalisis de Las Principales Obligaciones TributariasLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 - Guion - Retrato de Dorian GrayDocumento15 páginas4 - Guion - Retrato de Dorian GrayLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANO100% (2)
- Tarea2 Capitulo3y4 6958 LizbethsarangoDocumento5 páginasTarea2 Capitulo3y4 6958 LizbethsarangoLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Propósito de Los Principios UNIDROITDocumento11 páginasPropósito de Los Principios UNIDROITLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Exposicionincoterms Grupo5 6958Documento17 páginasExposicionincoterms Grupo5 6958LIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Compras Sin Deficit EoqDocumento3 páginasCompras Sin Deficit EoqLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Banco de Preguntas - Grupo5Documento9 páginasBanco de Preguntas - Grupo5LIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis de Las Principales Obligaciones TributariasDocumento3 páginasAnalisis de Las Principales Obligaciones TributariasLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuestionario de SocialesDocumento2 páginasCuestionario de SocialesLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Qué Son Las NIIFDocumento3 páginasQué Son Las NIIFLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- FORMULARIO CIRCUNFERENCUA BDocumento2 páginasFORMULARIO CIRCUNFERENCUA BLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- SupCías controla sociedadesDocumento3 páginasSupCías controla sociedadesLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Salario Mensual Básico UnificadoDocumento1 páginaSalario Mensual Básico UnificadoLIZBETH NOEMI SARANGO ZAMBRANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Segundo Parcial - Geometria AnaliticaDocumento6 páginasSegundo Parcial - Geometria AnaliticaSandra Ibeth Vazquez RecobaAún no hay calificaciones
- División de Polinomios Resumen de ClaseDocumento5 páginasDivisión de Polinomios Resumen de ClasejuangeomaAún no hay calificaciones
- Apuntes CALCULO VECTORIAL PDFDocumento5 páginasApuntes CALCULO VECTORIAL PDFYeyei Rodríguez LeónAún no hay calificaciones
- Proporciones, razones y promediosDocumento5 páginasProporciones, razones y promediosErick Gabriel ChuquimiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion de Matematica Martes 27Documento9 páginasSesion de Matematica Martes 27Vanessa Sandoval FernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Mediatriz de un triánguloDocumento6 páginasMediatriz de un triánguloAbraham :v na masAún no hay calificaciones
- Lenguaje AlgebraicoDocumento2 páginasLenguaje Algebraicojoseangelmadrid97% (69)
- Levantamiento Planimetrico de Wincha y CordelDocumento9 páginasLevantamiento Planimetrico de Wincha y CordelKevin Richard Balbuena HuacacAún no hay calificaciones
- Síntesis Matemática Segundo SemestreDocumento2 páginasSíntesis Matemática Segundo SemestreHumberto Bustos CalabaceroAún no hay calificaciones
- Ctrmat 5s IpDocumento13 páginasCtrmat 5s IpAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- MA-1112 Farith Guías 7-11 2016 PDFDocumento240 páginasMA-1112 Farith Guías 7-11 2016 PDFfernando_alvrzAún no hay calificaciones
- S-3B-versià N 1-1Documento10 páginasS-3B-versià N 1-1Data BossAún no hay calificaciones
- Matemática - 3er Grado - Unidad 3Documento44 páginasMatemática - 3er Grado - Unidad 3leticia laraAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesiã N 4-Clase33Documento45 páginasSesiã N 4-Clase33Tati Diaz MontenegroAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica Ensayo General 3Documento46 páginasMatematica Ensayo General 3Karma_2006Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadros de Doble Entrada para Segundo de SecundariaDocumento6 páginasCuadros de Doble Entrada para Segundo de SecundariaJimmy AngelAún no hay calificaciones
- EJRCICIOS TAREA - Liliana - Ballen - UNADDocumento17 páginasEJRCICIOS TAREA - Liliana - Ballen - UNADEnzon Eduardo Porras MaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Álgebra para Niños de Primaria - SmartickDocumento6 páginasÁlgebra para Niños de Primaria - SmartickWilliam MoraAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 2 - Funciones Reales - Luis ZegarraDocumento56 páginasCapitulo 2 - Funciones Reales - Luis ZegarrajuandeugarteAún no hay calificaciones
- 07 Patrones Regex 01Documento33 páginas07 Patrones Regex 01pineidenAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo pendiente ángulo inclinaciónDocumento12 páginasCalculo pendiente ángulo inclinaciónLuis ReynosoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practicas de ParalelasDocumento3 páginasPracticas de ParalelasDarwin Jose Angulo Suarez100% (1)
- BC1 06 FuncionesDocumento56 páginasBC1 06 FuncionesMaria Isabel Rodriguez MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- PREGUNTAS RAZONAMIENTO MATEMATICOo UnprgDocumento16 páginasPREGUNTAS RAZONAMIENTO MATEMATICOo UnprgGERSSON DANIEL SANCHEZ MEJIAAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica de Ecuaciones Cuadráticas PDFDocumento6 páginasPráctica de Ecuaciones Cuadráticas PDFAngela SimpsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Capítulo 5 Vertedores VFDocumento29 páginasCapítulo 5 Vertedores VFEver OrtizAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 Matematica - Aritmetica - AlgebraDocumento3 páginas5 Matematica - Aritmetica - AlgebraValentín NoyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Cuadrado de BinomioDocumento5 páginasGuia Cuadrado de BinomioninoskagcAún no hay calificaciones
- Sistemas de ecuaciones linealesDocumento7 páginasSistemas de ecuaciones linealesNathaliReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- Logaritmos LexDocumento16 páginasLogaritmos LexJuver Olmos HuallpaAún no hay calificaciones