Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
20 VALORES EXTREMOS Fxy 1CONDICION PDF
20 VALORES EXTREMOS Fxy 1CONDICION PDF
Cargado por
Carlito's OcampoTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
20 VALORES EXTREMOS Fxy 1CONDICION PDF
20 VALORES EXTREMOS Fxy 1CONDICION PDF
Cargado por
Carlito's OcampoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
05/10/2014
CÁLCULO VECTORIAL
CAPÍTULO II
SESIÓN 21
Joseph-Louis Lagrange
VALORES EXTREMOS CON
UNA CONDICIÓN
MÉTODO DE LAGRANGE
∇ f (P) = λ ∇ g ( P) y g (P) = 0
1736 -1813
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 2
MÁXIMO ABSOLUTO Y MÁXIMO CON UNA Función objetivo: f (x, y) = 9 - x2 - y2 (Paraboloide)
CONDICIÓN Condición: x + y = 3 (segmento recto)
Determine geométricamente si la función
f (x, y) = 9 - x2 - y2 tiene un valor
extremo cuando las variables x e y están
restringidas a x + y = 3
Función objetivo: f (x, y) = 9 - x2 - y2 (Paraboloide)
Condición: x + y = 3 (segmento recto)
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 3 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 4
TEOREMA DE LAGRANGE Determinar los valores extremos de una función z = f (x, y)
sujeta a una restricción dada por g(x, y) = 0
Supongamos que la función z = f (x, y) tiene un
extremo en el punto P sobre la gráfica de la
ecuación restricción g(x, y) = 0. Si f y g tienen
primeras derivadas parciales continuas en un
conjunto abierto que contiene la gráfica de la
ecuación restricción y ∇ g (P ) ≠ 0 , entonces
existe un número real λ (multiplicador de
Lagrange) tal que
∇ f ( P ) = λ∇ g ( P )
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 5 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 6
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
05/10/2014
Determinar los valores extremos de una función z = f (x, y) INTERPRETACIÓN GEOMÉTRICA
sujeta a una restricción dada por g(x, y) = 0
MÉTODO DE LAGRANGE
Sea S la superficie definida por z = f (x, y)
Curvas de nivel f (x, y) = c , c = 7, 8, 9, 10, 11.
Condición g (x, y) = 0
Curva de nivel g(x, y) = 0 de la superficie w =g(x, y)
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 7 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 8
Curvas de nivel f (x, y) = c , c = 7, 8, 9, 10, 11. Curvas de nivel f (x, y) = c , c = 7, 8, 9, 10, 11.
∇ f (P0 )
∇ g(P0 )
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 9 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 10
VALORES EXTREMOS CON UNA CONDICIÓN INTERPRETACIÓN GEOMÉTRICA
MÉTODO DE LAGRANGE
MÉTODO DE LAGRANGE
Sea S la superficie definida por z = f (x, y)
Curvas de nivel f (x, y) = c
∇ f (P) = λ ∇ g (P) y g (P) = 0
1424 3
CONDICION c = 200, 300, 400, 500, 600, 700
Condición g (x, y) = 0
Curva de nivel g(x, y) = 0
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 11 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 12
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
05/10/2014
INTERPRETACIÓN GEOMÉTRICA VALORES EXTREMOS CON UNA CONDICIÓN
MÉTODO DE LAGRANGE
∇f ( P0 ) = λ0 ∇g ( P0 )
∇ f ( P1 ) = λ1 ∇g ( P1 )
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 13 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 14
MÉTODO DE MULTIPLICADORES MÉTODO DE MULTIPLICADORES
DE LAGRANGE (una condición) DE LAGRANGE (una condición)
Si f tiene un valor extremo con condición en el punto
Si f tiene un valor extremo con condición en el punto P, entonces
P, entonces
∂f ∂g
( P) = λ ( P)
∂x ∂x
∇ f (P) = λ ∇ g (P)
SISTEMA DE ∂f ∂g
ECUACIONES
( P) = λ ( P)
∂y ∂y
g ( P ) = 0 condición o restricció n
g ( P) = 0 condición o restricción
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 15 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 16
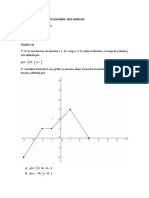
EJEMPLO 1 SOLUCIÓN
¿Cuál es el área máxima que puede tener un
rectángulo si la longitud de su diagonal es 2? • Función Objetivo :f (x, y) = x y
Función área
y (Superficie)
(x , y)
2 • Condición : g(x, y) = x2 + y2 – 4 = 0
Longitud diagonal
x
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 17 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 18
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
05/10/2014
Función Área
f(x,y)=xy
x = 2 cos t
C : y = 2 sent t ∈ [0, π / 2]
z = 4 cos t sent
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 19 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 20
SOLUCIÓN SOLUCIÓN
MÉTODO DE MULTIPLICADORES DE LAGRANGE
f (x, y) = x y, función área
g(x, y) = x2 + y2 – 4 = 0, condición ∇f ( x, y) = λ∇g ( x, y )
g ( x, y) = 0
MÉTODO DE MULTIPLICADORES DE LAGRANGE
y = λ (2 x )
∇f ( x, y) = λ∇g ( x, y )
SISTEMA DE
x = λ ( 2 y)
ECUACIONES
g ( x, y) = 0 x 2 + y 2 = 4 condición
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 21 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 22
Interpretación Geométrica del Ejemplo 1
Resolviend o el sistema
x = y = 2 ; λ = 1/ 2
Curvas de Nivel de la funcion Area: f(x, y)=xy
3 12 14 16
4
3.5
Curva Condición
Area = 2 3 (sqrt(2) ,sqrt(2))
2.5
1 Curva de Nivel
Maximo
El rectángulo de máxima área con
2
Y
1.5
diagonal 2 es el cuadrado cuyos lados 1
k=3
k=4
miden √ 2. Su área es 2.
k=2
2
0.5
k=1
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4
X
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 23 Rosa Ñique Alvarez 24
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
05/10/2014
MÉTODO DE LAGRANGE PARA TRES
VARIABLES INDEPENDIENTES
w = f (x, y, z) y g(x, y, z) = 0
∂f ∂g
=λ
∂x ∂x
∂f ∂g
=λ
∂y ∂y
∂f ∂g
=λ
∂z ∂z
g ( x, y , z ) = 0 condición o restricció n
Rosa Ñique Alvarez 25
PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com
También podría gustarte
- Unidad 1.3 Calculo DiferencialDocumento3 páginasUnidad 1.3 Calculo DiferenciallauraAún no hay calificaciones
- Tipos de Izaje de Un BuqueDocumento8 páginasTipos de Izaje de Un BuqueCharlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de FuncionesDocumento10 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de FuncionesFabián Sánchez Parrines100% (1)
- Simulacion de Pernos de AnclajeDocumento15 páginasSimulacion de Pernos de AnclajeKervin CaerdaAún no hay calificaciones
- TransfeDocumento6 páginasTransfeCharlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Mapa Mental-Cotas y Diseño en AutocadDocumento1 páginaMapa Mental-Cotas y Diseño en AutocadJeisson Duarte25% (4)
- Unid - Ii.funciones Varias Variables 2018Documento79 páginasUnid - Ii.funciones Varias Variables 2018Raul Victor Velasquez JaqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Costo Pozo PetroleroDocumento130 páginasCosto Pozo Petrolerocontradictorio_alexAún no hay calificaciones
- Resistencia de Los Materiales - Abraham Lassaube - Tarea 1Documento5 páginasResistencia de Los Materiales - Abraham Lassaube - Tarea 1abraham esteban lassaube lopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoría de cuerpos y teoría de GaloisDe EverandTeoría de cuerpos y teoría de GaloisCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- EntregableDocumento5 páginasEntregableDenissAún no hay calificaciones
- Situación Vamos A MedirDocumento11 páginasSituación Vamos A MedirRaquel Cuevas89% (18)
- Calculo Vectorial Unidad 4 (Completo)Documento38 páginasCalculo Vectorial Unidad 4 (Completo)AlejandroAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica Grupo 5Documento20 páginasPractica Grupo 5Wily Quispe CopariAún no hay calificaciones
- Campo Escalar GuiaDocumento29 páginasCampo Escalar GuiaAida AcostaAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivacion y Diferenciacion de Funciones EscalaresDocumento112 páginasDerivacion y Diferenciacion de Funciones EscalaresMario CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo Vectorial Extremos de FuncionesDocumento26 páginasCalculo Vectorial Extremos de FuncionesCésar PilarAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo Vectorial Extremos de FuncionesDocumento39 páginasCalculo Vectorial Extremos de Funcionesayanez22Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tema22 Funciones Pares e Impares, Algebra de FuncionesDocumento4 páginasTema22 Funciones Pares e Impares, Algebra de FuncionesSEBAS OLARTEAún no hay calificaciones
- 22valores Extremos Condicionados Metodo de LagrangeDocumento10 páginas22valores Extremos Condicionados Metodo de LagrangeJesus Ernesto Peralta HuasasquicheAún no hay calificaciones
- Primera Fase Ejercicios CalDocumento19 páginasPrimera Fase Ejercicios CalFernando Ovalle BlancoAún no hay calificaciones
- 22 - Algebra de Funciones y Funcion InversaDocumento8 páginas22 - Algebra de Funciones y Funcion InversaCamilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Acetatos Unidad 2 Calculo AvanzadoDocumento54 páginasAcetatos Unidad 2 Calculo AvanzadoJ EnriQue AlcAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía 4 - FuncionesDocumento4 páginasGuía 4 - FuncionesnicolepinozamoranoAún no hay calificaciones
- AMIII Trabajo Practico N2Documento4 páginasAMIII Trabajo Practico N2cordobezaldana29Aún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo 4a FuncionesDocumento2 páginasTrabajo 4a FuncionesArielCusipumaOrtegaAún no hay calificaciones
- GUIA N° 5 ALGEBRA DE FUNCIONESDocumento7 páginasGUIA N° 5 ALGEBRA DE FUNCIONESRaúl edgardo Cardona lafaurieAún no hay calificaciones
- VALORES EXTREMOS F (X, Y) 1CONDICIODocumento6 páginasVALORES EXTREMOS F (X, Y) 1CONDICIOJordan ZavaletaAún no hay calificaciones
- Composicion: DE FuncionesDocumento17 páginasComposicion: DE FuncionesPaul Anderson Bardales MilianAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller10 2015Documento2 páginasTaller10 2015hernan estradaAún no hay calificaciones
- Briozzo-Calculo Difer y OptimizacionDocumento25 páginasBriozzo-Calculo Difer y OptimizacionLuis AlvearAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo - Funciones de Varias VariablesDocumento6 páginasCalculo - Funciones de Varias VariablesSergio Cerda SabugoAún no hay calificaciones
- Extremos RestringidosDocumento12 páginasExtremos RestringidosjemmyjimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Final Cálculo II 21 - 12 - 18Documento2 páginasFinal Cálculo II 21 - 12 - 18Vanesa MendezAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 01Documento9 páginasSemana 01Josseling Huamán EncoAún no hay calificaciones
- Universidad de Concepci On Facultad de Ciencias F Isicas y Matem Aticas Departamento de Matem AticaDocumento2 páginasUniversidad de Concepci On Facultad de Ciencias F Isicas y Matem Aticas Departamento de Matem AticaMarco Cuevas SepulvedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivacion y Diferenciacion de Funciones EscalaresDocumento106 páginasDerivacion y Diferenciacion de Funciones EscalaresBercho PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de FuncionesDocumento1 páginaEjercicios de Funciones130 Rodriguez Mendoza Herlan NelsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 5 C 32020Documento1 páginaPractica 5 C 32020Marcelo SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- FuncionesDocumento7 páginasFuncionesDora Anita Mamani ChuraAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones Parte3 UvirtualDocumento14 páginasFunciones Parte3 UvirtualepmelsAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Propuestos Funcion Compuesta, Inversa, ImplicitaDocumento3 páginasEjercicios Propuestos Funcion Compuesta, Inversa, ImplicitaJulio MayaudonAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones PDFDocumento30 páginasFunciones PDFSara GomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 10Documento8 páginasClase 10Isocrack FelizAún no hay calificaciones
- Facultad de Ciencias Fisicas Y MatematicasDocumento11 páginasFacultad de Ciencias Fisicas Y MatematicasBenjamin FigueroaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion 3Documento15 páginasSesion 3ErickRojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 2Documento10 páginasTema 2anaprarodAún no hay calificaciones
- ListaDeEjercicios4Respuestas 23 2Documento8 páginasListaDeEjercicios4Respuestas 23 2Vico HuacchaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios 1CAVDocumento8 páginasEjercicios 1CAVRafael AntonioAún no hay calificaciones
- La Integral DefinidaDocumento13 páginasLa Integral DefinidaMario Orlando Suárez IbujésAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía - HT - Sem 14Documento7 páginasGuía - HT - Sem 14MiguelAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones LaTeXDocumento3 páginasFunciones LaTeXMarcelo CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 Analisis Vectorial PDFDocumento41 páginas7 Analisis Vectorial PDFR16QAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica Dirigida 02-Cálculo I-2023-I PDFDocumento3 páginasPráctica Dirigida 02-Cálculo I-2023-I PDFYxjjk.01Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 7 Funciones Notables y Operaciones Con FuncionesDocumento14 páginasTema 7 Funciones Notables y Operaciones Con FuncionesAlexandra Zevallos SaavedraAún no hay calificaciones
- Condicion de Segundo OrdenDocumento18 páginasCondicion de Segundo OrdenJuan Carlos Giron RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- TP7 DiferenciabilidadDocumento3 páginasTP7 DiferenciabilidadmarianelaAún no hay calificaciones
- FuncionesDocumento51 páginasFuncionesZurianis RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Relación 1 AmpliaciónDocumento2 páginasRelación 1 AmpliaciónThe Nick ChannelAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones Límite Cálculo DiferencialDocumento48 páginasFunciones Límite Cálculo DiferencialJuan Angel Rivera ReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodo de Lagrange UbDocumento6 páginasMetodo de Lagrange UbChristian PatiñoAún no hay calificaciones
- 10 AyT - Relaciones y Funciones 2Documento21 páginas10 AyT - Relaciones y Funciones 2Pablo GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra de FuncionesDocumento4 páginasAlgebra de FuncionesCesar Gallardo BrionesAún no hay calificaciones
- c3 - Cálculo VectorialDocumento15 páginasc3 - Cálculo VectorialVANESSA ALEXANDRA BLANCO MEDINAAún no hay calificaciones
- Estudio de Las Estudiode Las Funciones RealesDocumento8 páginasEstudio de Las Estudiode Las Funciones RealesLeny LauraAún no hay calificaciones
- Francobordo PT1Documento7 páginasFrancobordo PT1Charlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tubo de Reynolds Labo 3Documento4 páginasTubo de Reynolds Labo 3Charlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Temas y Nombres ActualizadosDocumento3 páginasTemas y Nombres ActualizadosCharlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- fONDEO Anclajes y CadenasDocumento25 páginasfONDEO Anclajes y CadenasCharlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas PropuestosDocumento4 páginasProblemas PropuestosCharlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Luces de NavegacionDocumento15 páginasLuces de NavegacionCharlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- James WattDocumento7 páginasJames WattCharlie Aguero PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Ambiental para El Manejo de CianuroDocumento26 páginasGuía Ambiental para El Manejo de CianuroBianny Gempell Velarde PazAún no hay calificaciones
- Diapositivas CapacitanciaDocumento11 páginasDiapositivas CapacitanciaCesar Carlos Caballero Cardenas100% (1)
- RESL. #04201 DIC 27 de 2018 PDFDocumento37 páginasRESL. #04201 DIC 27 de 2018 PDFJorge CuervoAún no hay calificaciones
- Elementos de Las LíneasDocumento24 páginasElementos de Las LíneasSiul VegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clasificacion de Los Materiales en Las Ingenieria (Sintesis)Documento4 páginasClasificacion de Los Materiales en Las Ingenieria (Sintesis)fernandoAún no hay calificaciones
- Catalogo Tecnico ContiDocumento116 páginasCatalogo Tecnico Contiaster100% (1)
- B2-Problemas Resueltos Tema 1Documento7 páginasB2-Problemas Resueltos Tema 1Elvis PulgarAún no hay calificaciones
- Problem As Campo Magnetic oDocumento2 páginasProblem As Campo Magnetic oQuistian Jonathan0% (2)
- Parcial en MatlabDocumento6 páginasParcial en MatlabZorielys RamírezAún no hay calificaciones
- Capítulo 9. Ecuaciones Diferenciales de Primer OrdenDocumento6 páginasCapítulo 9. Ecuaciones Diferenciales de Primer OrdenMayra Alejandra Torres AlfonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- Entrenamiento Media MaratonDocumento7 páginasEntrenamiento Media MaratonJorge Díaz BúquezAún no hay calificaciones
- DMPDDocumento2 páginasDMPDJeanPaul FalquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluación - Examen Parcial - Semana Fisica4Documento6 páginasEvaluación - Examen Parcial - Semana Fisica4Nicolas GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Conversor DC-DC (Reductor)Documento5 páginasConversor DC-DC (Reductor)Manuel SagbayAún no hay calificaciones
- Fenomenos EspecialesDocumento25 páginasFenomenos EspecialespaulapincheiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodo SimplexDocumento12 páginasMetodo SimplexYeinyAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Fisica Mecanica - Momento 3Documento10 páginasTaller Fisica Mecanica - Momento 3Wot BlitzAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe Electronica PlacaDocumento5 páginasInforme Electronica PlacaManuel Enrique Alarcon Castillo100% (1)
- 2ER INFOrmeDocumento9 páginas2ER INFOrmeLinda Sanchez RominaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 2.38Documento4 páginasEjercicio 2.38Maria Cristina Pacheco SuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Introducción A La Ingeniería SísmicaDocumento20 páginas1 Introducción A La Ingeniería SísmicaGiselleAún no hay calificaciones
- Álgebra 5°Documento34 páginasÁlgebra 5°Eduardo MagicworldAún no hay calificaciones
- Salas de ExposicionesDocumento39 páginasSalas de ExposicionesrodrigoAún no hay calificaciones
- Multimetro DigitalDocumento2 páginasMultimetro DigitalAnderson Ocan HuamanAún no hay calificaciones