Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Tema 3 de Trigonometría
Cargado por
Alexy VegasTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Tema 3 de Trigonometría
Cargado por
Alexy VegasCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
I.E.P.
“EXITU´S” “Formadores de Nuevas Generaciones”
Curso 4º Secundaria 2021
Trigonometría Separata N°3
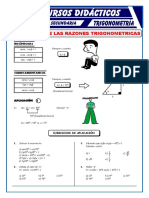
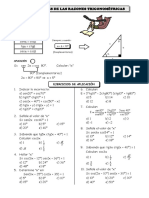
PROPIEDADES DE LAS RAZONES TRIGONOMÉTRICAS
RECÍPROCAS
Siempre y cuando:
sen . csc = 1
cos . sec = 1 =
tg . ctg = 1
COMPLEMENTARIO
sen = cos Siempre y cuando:
c
tg = ctg + = 90º a
sec = csc
(Complementarios)
APLICACIÓN 1
Si: sen 2x = cos 80º. Calcular: “x”
90º (P. Complementarios)
2x + 80º = 90º x = 5º
EJERCICIOS DE APLICACIÓN
1. Si : tg 3x . ctg(x + 40º) = 1. Calcular : Cos 3x 3. Si : sen 7x sec 2x = 1.
Calcular :
a) 1 b) 1/2 c) 3 2
E = tg 6x + tg(x + 42º - y) . tg(3x + y + 8º)
d) 3 /2 e) 3/5 a) 1 b) 3 c) 4
d) 5 e) 6
2. Hallar “x” si :
4. Determine “x” :
cos(2x – 10º) sec(x + 30º) = 1 tg 15º
sec(2x - 8) = sen 40º csc 40º +
ctg 75º
a) 10º b) 20º c) 30º a) 17º b) 20º c) 28º
d) 40º e) 50º d) 30º e) 34º
1 TRIGONOMETRÍA – 4º GRADO DE SECUNDARIA I TRIMESTRE - 2021
I.E.P. “EXITU´S” “Formadores de Nuevas Generaciones”
5. Si : sec 8x = csc 3x. 12. Si : sec(x + y + 5º) – csc(2y – x + 40º) = 0
Calcular : tg(3x - y) . ctg(2x + y) = 1
sec 2x donde “x” e “y” son agudos.
E = sen 6x sec 5x + tg 4x . tg 7x +
csc 9x
Hallar: E = sec 2x + tg(x + y) – 2 sen 2y
a) 2 b) 3 c) 6 a) 0 b) 1 c) 2
d) 1/2 e) 1/3
d) 3 e) 4
6. Si : “x” e “y” son complementarios además :
13. Si : sen(A - C) = cos (B + C).
ctg y
(tg x) = sen . A+B A+B
4 Calcular: E = 2 sen + tg
Calcular: E = 3 2
5 sen x + tg x
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3 a) 1 b) 2 c) 3
d) 4 e) 5 d) 4 e) 5
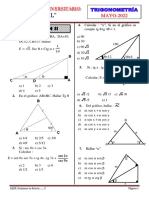
7. Si en el gráfico se cumple tg tg 4 = 1. Calcular
: “x” 14. Si : tg( + ) tg( - ) = tg
4 4 4
sen ( + sen()) = cos ( - cos())
a) 90
-1 -1
Calcular : E = +
b) 30 180
c) 90 3
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3
d) 30 3
+12º 3+6º d) 4 e) 5
e) 10 3
x
15. Si : sen(x + y) – cos(z + 2y) = 0
8. Calcular : ctg(2y - z) ctg 43º = tg(x - y) tg 47º
sen 1º + sen 2º + sen 3º + + sen 89º x
E= Calcular : sec( - z)
cos1º + cos2º + cos3º + + cos89º 2
Además : 0º < y < x < 45º
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3
a) 2 b) 2 c) 3
d) 3 e) 3 /3
d) 1 e) 5
9. Calcular : E = (5 tg 10º + 10 ctg 80º) tg 80º
a) 10 b) 12 c) 13 TAREA DOMICILIARIA Nº 4
d) 14 e) 15
10. Si : cos 4x = sen 6y. 1. Determine “x” : tg(2x + 10º) = ctg(x – 40º)
sec(3x + 2y) + tg (5x + y)
Hallar: E =
csc(x + 4 y) + ctg(5y − x) a) 10º b) 20º c) 30º
d) 40º e) 60º
a) 1 b) -1 c) 1/2
d) 2 e) 4
2. Si : tg x . tg 2x = 1.
3x
11. Si : sen x cos2x sen
Calcular: E = 2
3x
4sec(2x + 10º) – 2csc(80º - 2x) = sec csc(3x – 10º) tg 37º ctg . tg x
3 2
sen x sen 2x
Calcular : E = +
cos 4 x cos3x
a) 2 /2 b) 3 /3 c) 6 /6
a) 2 b) 5/2 c) 7/3
d) 5 /5 e) 1
d) 25/12 e) 4
2 TRIGONOMETRÍA – 4º GRADO DE SECUNDARIA I TRIMESTRE - 2021
I.E.P. “EXITU´S” “Formadores de Nuevas Generaciones”
3. Determine el valor de “x” :
sen(3x – 42º) csc(18º - 2x) = 1 3x + 2 x+1
10. Si: cos A = y sen B = . Determinar
3x + 1 x+2
a) 6º b) 12º c) 15º el valor de tg A si A y B son complementarios.
d) 20º e) 24º
a) 5 b) 2 6 c) 2 5
4. Sabiendo que : tg 5x . ctg (x + 40º) = 1. d) 6 /8 e) 3/4
Calcular : cos 3x
11. Si : tg (2y – 3º) sen (93º - 2y) = cos (4x + y).
a) 1 b) 1/2 c) 2 /2 sec 4x − csc 3( y − 1º )
Calcular : E =
d) 3 e) 2/3 sen 6x
5. Calcular :
a) 2 b) 2 3 c) 6
E = (tg 20º + ctg 70º) (ctg 20º + tg 70º)
d) 1 e) 0
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3
12. Si : sen 2x + tg 2y = cos 2y + ctg 2x. Calcular :
d) 4 e) 8
E = tg (x + y) tg 2x – ctg 2y ctg (x + y)
Si además “x” e “y” son ángulos agudos.
6. Reducir : E = (3 sen 40º + 4 cos 50º) csc 40º
a) 1 b) 3 c) 4
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3
d) 2 3 e) 0
d) 4 e) 7
7. Calcular : 13. Si : sen (2)csc ( + 30º) = 1
sec 1º + sec 2º + sec 3º + + sec 89º tg ( + 20º) = ctg ( - 20º)
E=
csc 1º + csc 2º + csc 3º + + csc 89º Calcular :
E = sen ( - 10º) sec + tg ( - 5º) tg ( + 5º)
a) 1 b) -1 c) 2
a) 5 b) 4 c) 3
d) 3 e) 2 /2
d) 2 e) 1
x y
8. Se sabe que : tg = ctg . Calcular:
m m 14. Si: sen (3x + 10º) = cos (6x – 10º).
x+y x+y 9x
E = tg ctg Calcular : E = tg + sec (3x + 7º )
2m 3m 2
a) 1/2 b) 1 c) 1/12
a) 3 /3 b) 3 c) 1/2
d) 9/4 e) 3/2
d) 1 e) 2 3
tg x tg 2x tg 3x tg 8x
9. Si : sen (7x – 20º) = cos (3x + 10º) 15. Calcular: E = siendo:
sen 3x + cos6x
tg (2y – 30º) . ctg (30º - y) = 1
tg (3x – 10º) = cos (100º - 3x) csc 7x
Calcular: E = 2 sen (x + y) + sec 3y
a) 1 b) 2 c) 1/2
a) 1 b) 2 c) 3
d) 4 e) 5 d) 3 /2 e) 3 /3 Sec21-4 Trig 3
Exitu´s
3 TRIGONOMETRÍA – 4º GRADO DE SECUNDARIA I TRIMESTRE - 2021
También podría gustarte
- Propiedades de Las R.T. para Quinto de SecundariaDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las R.T. para Quinto de Secundariajhon cesarAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 4 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento3 páginasGuia 4 - Propiedades de Las Razones Trigonométricasrcartolin8245100% (3)
- Propiedades de Las R.T. para Quinto de SecundariaDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las R.T. para Quinto de SecundariaJunior AlReAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 4 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento3 páginasGuia 4 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasNéstor Ventura Dávila FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 4 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento3 páginasGuia 4 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasJhilson Hazaeel Ipanaque JuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- TEMA 03 Propiedades de Razones Trigonometricos PDFDocumento3 páginasTEMA 03 Propiedades de Razones Trigonometricos PDFAteez DanielAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 4 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento4 páginasGuia 4 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasJhon Castro100% (1)
- Propiedades de Las R.T. para Quinto de SecundariaDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las R.T. para Quinto de Secundariaangelmc80Aún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 6 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento4 páginasGuia 6 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasFrancisco MarcasAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 6 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento4 páginasGuia 6 - Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasYelena Vasquez ValenzuelaAún no hay calificaciones
- 2propiedades de Las RT.Documento3 páginas2propiedades de Las RT.frankalesandroaraujoleonAún no hay calificaciones
- Raznones Trigonometrica Reciprocas y ComplementariasDocumento4 páginasRaznones Trigonometrica Reciprocas y ComplementariasAnttonyCastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Razones TrigonometricasDocumento4 páginasPropiedades de Razones TrigonometricasRichard SalinasAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonometricasDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las Razones TrigonometricasSF CesarAún no hay calificaciones
- Razones TrigonometricasDocumento3 páginasRazones TrigonometricasrichardAún no hay calificaciones
- Razones TrigonométricasDocumento2 páginasRazones TrigonométricasAlejandroEspinozaChumánAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricaskeateAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricaskeateAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasJORGE LUIS HUAMANGUILLAS HUAMANAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las Razones Trigonométricas para Cuarto de SecundariaDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las Razones Trigonométricas para Cuarto de SecundariaYane Rojas ZevallosAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las Razones Trigonométricas para Cuarto de SecundariaDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las Razones Trigonométricas para Cuarto de SecundariaYane Rojas ZevallosAún no hay calificaciones
- RT Complementarias y RecíprocasDocumento3 páginasRT Complementarias y RecíprocasKOKO CABALLEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 7 - Trigo - 5° - Prop RTDocumento3 páginasSemana 7 - Trigo - 5° - Prop RTJean Rios EspinozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Prop. de Las Razones TriDocumento3 páginasProp. de Las Razones TriEder Murillo CobeñasAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las Razones Trigonométricas para Cuarto de SecundariaDocumento4 páginasPropiedades de Las Razones Trigonométricas para Cuarto de SecundariaChristian GuillmarAún no hay calificaciones
- Raz Trigo 4Documento2 páginasRaz Trigo 4Reyna EchaccayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las R.TDocumento3 páginasPropiedades de Las R.TCristian CustodioAún no hay calificaciones
- R.T Ángulos AgudosDocumento2 páginasR.T Ángulos Agudosluigui alexis chero nunuraAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasDocumento4 páginasPropiedades de Las Razones TrigonométricasMercedesMorenoTAún no hay calificaciones
- Angulo Compuesto 2021Documento2 páginasAngulo Compuesto 2021Jorge MedinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 03 Razones Trigonometrica Reciprocas y Complemtarias - R.T de Triángulo RectánguloDocumento3 páginasTema 03 Razones Trigonometrica Reciprocas y Complemtarias - R.T de Triángulo RectánguloLuis Enrique Coca RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigo 1Documento3 páginasTrigo 1Genaro HuamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- 12 Sem TrigonometríaDocumento2 páginas12 Sem TrigonometríaJazmin HuamanAún no hay calificaciones
- TRIG 4 - RepasoDocumento3 páginasTRIG 4 - RepasoHeber FallenAún no hay calificaciones
- Propiedades de RT - PrimeroDocumento2 páginasPropiedades de RT - PrimeroLeonel Mamani MamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluacion de Trigonometria-4toDocumento2 páginasEvaluacion de Trigonometria-4toRomero Diaz PieroAún no hay calificaciones
- ÁNGULOS COMPUESTOS OkDocumento3 páginasÁNGULOS COMPUESTOS OkChristian John Veliz AlvercaAún no hay calificaciones
- PROPIEDADES de Razones TrigonométricasDocumento3 páginasPROPIEDADES de Razones TrigonométricasAnderson Lionel QUISPE HUAYTAAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Razones Trigonométricas para Cuarto de SecundariaDocumento4 páginasEjercicios de Razones Trigonométricas para Cuarto de Secundariawawa ñaupa ricraAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Propuestos de Razones Trigonometricas RT5-Ccesa007Documento3 páginasProblemas Propuestos de Razones Trigonometricas RT5-Ccesa007Demetrio Ccesa RaymeAún no hay calificaciones
- De Ángulos ComplementariosDocumento2 páginasDe Ángulos Complementariosenrique soto lucero100% (1)
- RT NucleoDocumento2 páginasRT NucleoAndy HuillcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometria Semana 5-5Documento2 páginasTrigonometria Semana 5-5Giyuu TomiokaAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica Mañana 3Documento3 páginasPractica Mañana 3Frank Del carpioAún no hay calificaciones
- Reducción Al Primer Cuadrante Preu EjerciciosDocumento2 páginasReducción Al Primer Cuadrante Preu EjerciciosRomulo Wilder PACHECO MODESTOAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica Mañana 1Documento2 páginasPractica Mañana 1Frank Del carpioAún no hay calificaciones
- PropiDocumento1 páginaPropiJose Huere ZuñigaAún no hay calificaciones
- Reducción Al Primer Cuadrante: Fredy Rios PerezDocumento3 páginasReducción Al Primer Cuadrante: Fredy Rios PerezDEMBER FREDY RIOS PEREZAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigo 2Documento2 páginasTrigo 2Genaro HuamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- GUÍA DE EJERCICIOS RAZONES TRIGONOMETRICAS II 4ta ClaseDocumento2 páginasGUÍA DE EJERCICIOS RAZONES TRIGONOMETRICAS II 4ta Clasejavier cordova floresAún no hay calificaciones
- Razones TrigonometricasDocumento2 páginasRazones TrigonometricasmatecapristanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Repaso TrigonometriaDocumento2 páginasRepaso TrigonometriaSharonCuevadelAguilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 09 - Ángulo CompuestoDocumento2 páginasSemana 09 - Ángulo CompuestoCarito Naz LuAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Razones TrigonométricasDocumento2 páginasEjercicios Razones TrigonométricasKatshiumy Strella Porras PaitanAún no hay calificaciones
- Angulos Compuestos OkDocumento2 páginasAngulos Compuestos OkDaniela SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- ÁNGULOS COMPUESTOS OkDocumento2 páginasÁNGULOS COMPUESTOS OkChristian John Veliz Alverca0% (1)
- Métodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABDe EverandMétodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Proyecto 02: "Juntos y Juntas Nos Preparamos para Celebrar Con Optimismo El Aniversario de Nuestra Institución"Documento12 páginasProyecto 02: "Juntos y Juntas Nos Preparamos para Celebrar Con Optimismo El Aniversario de Nuestra Institución"Alexy VegasAún no hay calificaciones
- Proyecto 02: "Juntos y Juntas Nos Preparamos para Celebrar Con Optimismo El Aniversario de Nuestra Institución"Documento12 páginasProyecto 02: "Juntos y Juntas Nos Preparamos para Celebrar Con Optimismo El Aniversario de Nuestra Institución"Alexy VegasAún no hay calificaciones
- Proyecto 02: "Juntos y Juntas Nos Preparamos para Celebrar Con Optimismo El Aniversario de Nuestra Institución"Documento15 páginasProyecto 02: "Juntos y Juntas Nos Preparamos para Celebrar Con Optimismo El Aniversario de Nuestra Institución"Alexy VegasAún no hay calificaciones
- Proyecto 01: "Juntas y Juntos Nos Embarcamos en Una Aventura de Nuevos Aprendizajes para Trasformar Vidas"Documento20 páginasProyecto 01: "Juntas y Juntos Nos Embarcamos en Una Aventura de Nuevos Aprendizajes para Trasformar Vidas"Alexy VegasAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 de CTDocumento16 páginas1 de CTAlexy VegasAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 - 3roDocumento16 páginas4 - 3roAlexy VegasAún no hay calificaciones
- 3ro - Actividad de Aprendizaje 10 - Emanuel VegasDocumento6 páginas3ro - Actividad de Aprendizaje 10 - Emanuel VegasAlexy VegasAún no hay calificaciones
- 3ro - Actividad de Aprendizaje 4 - Emanuel VegasDocumento8 páginas3ro - Actividad de Aprendizaje 4 - Emanuel VegasAlexy VegasAún no hay calificaciones
- Araucano Manual de Definiciones Conceptuales y OperativasDocumento28 páginasAraucano Manual de Definiciones Conceptuales y Operativasmotiv31Aún no hay calificaciones
- NUEVA Tutoría PresencialDocumento30 páginasNUEVA Tutoría PresencialMiguel Angel SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- La Educación Secundaria A Debate PDFDocumento497 páginasLa Educación Secundaria A Debate PDFNorikAún no hay calificaciones
- Álgebra - Semana 7Documento7 páginasÁlgebra - Semana 7Odalis VargasAún no hay calificaciones
- Estado Nutricional en El AdolescenteDocumento2 páginasEstado Nutricional en El AdolescenteAnyela AlvaradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Desigualdades Persistentes y Promesas IncumplidasDocumento32 páginasDesigualdades Persistentes y Promesas IncumplidasEduardo Vizcaino CruzadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuestionario Sobre Ambientes de Aprendiz PDFDocumento5 páginasCuestionario Sobre Ambientes de Aprendiz PDFInformatica terceroAún no hay calificaciones
- ¿Seleccionar o Segregar? Las Vacantes PUCP para El 2014Documento7 páginas¿Seleccionar o Segregar? Las Vacantes PUCP para El 2014Coherencia UniversitariaAún no hay calificaciones
- Plan de Trabajo de Comision de Clausura 2020Documento3 páginasPlan de Trabajo de Comision de Clausura 2020evelyn0% (1)
- Bibliografía RecomendadaDocumento3 páginasBibliografía RecomendadaJuliana0% (1)
- Port AdaDocumento4 páginasPort AdaRaul Quincho ApumaytaAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual de Arit. 2Documento76 páginasManual de Arit. 2Nataly H Taipe C100% (1)
- Área Del Triangulo Esférico, Triangulos Polares Resolución de Problemas S2Documento24 páginasÁrea Del Triangulo Esférico, Triangulos Polares Resolución de Problemas S2ESMERALDAAún no hay calificaciones
- Curriculum Vitae 4 - 4Documento6 páginasCurriculum Vitae 4 - 4DenisseAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.2 Clasificación NuméricaDocumento3 páginas1.2 Clasificación Numéricastefany ArévaloAún no hay calificaciones
- 6.-Funcion Exponencial y LogaritmicaDocumento20 páginas6.-Funcion Exponencial y LogaritmicaWashington Enrique Perez BenitesAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodos de Integracion CecytemDocumento9 páginasMetodos de Integracion CecytembernardsanzAún no hay calificaciones
- Manuel Encarnacion Saavedra PerezDocumento2 páginasManuel Encarnacion Saavedra Perezluissebastianulloaruiz9Aún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 2 Julen Sorazu LucioDocumento2 páginasActividad 2 Julen Sorazu LucioSolete LeteAún no hay calificaciones
- Palabras Pendientes 11 La Disputa Por La Educación SuperiorDocumento76 páginasPalabras Pendientes 11 La Disputa Por La Educación SuperiorRomel CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Geometría - Introductorio 2A - Triángulos - Propiedades 1 - TareaDocumento5 páginasGeometría - Introductorio 2A - Triángulos - Propiedades 1 - TareaDiego PcAún no hay calificaciones
- TEXTO 2 - OkDocumento73 páginasTEXTO 2 - OkJenny MaricelAún no hay calificaciones
- Terapia Sistémica y Problemas de AprendizajeDocumento5 páginasTerapia Sistémica y Problemas de AprendizajeVanessa Ballestero López50% (2)
- Repaso 05 - AcemDocumento1 páginaRepaso 05 - AcemAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica 20 Marzo 2021Documento15 páginasMatematica 20 Marzo 2021marit A TibreyAún no hay calificaciones
- Repàs PROBLEMES 1r ESO 16-17 PDFDocumento8 páginasRepàs PROBLEMES 1r ESO 16-17 PDFAnonymous Hq51w6UvAún no hay calificaciones
- Or. Acuario CambioDocumento1 páginaOr. Acuario CambioOlga María GaytanAún no hay calificaciones
- Res 1540 UaderDocumento75 páginasRes 1540 UaderWalter SerranoAún no hay calificaciones
- 1351 Dibujo y FormaDocumento10 páginas1351 Dibujo y FormaVanesa Vega Garcia100% (1)
- Diagnostico Institucional Escuela Ep NDocumento12 páginasDiagnostico Institucional Escuela Ep NfernandoAún no hay calificaciones