Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Formulario 2
Cargado por
Rodrigo TellezDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Formulario 2
Cargado por
Rodrigo TellezCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
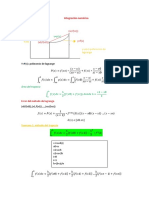
FORMULARIO
Variación numérica: valor de referencia - valor base
Variación porcentual
𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑜𝑟 𝑑𝑒 𝑟𝑒𝑓𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑖𝑎
( − 1) ∗ 100
𝑣𝑎𝑙𝑜𝑟 𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒
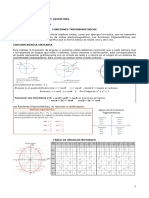
Álgebra
1⁄ 𝑛 𝑎 𝑛 𝑎𝑛 𝑎𝑚
𝑎 𝑛 = √𝑎 (𝑏 ) = 𝑏𝑛 𝑎𝑚 𝑎𝑛 = 𝑎𝑚+𝑛 𝑎0 = 1 𝑎𝑛
= 𝑎𝑚−𝑛
Productos notables-factorización
(𝑎 + 𝑏)2 = 𝑎2 + 2𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 (𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎2 − 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 )= 𝑎3 + 𝑏 3
(𝑎 + 𝑏)3 = 𝑎3 + 3𝑎2 𝑏 + 3𝑎𝑏 2 + 𝑏 3 (𝑎 − 𝑏)(𝑎2 + 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 )= 𝑎3 − 𝑏 3
(𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎 − 𝑏) = 𝑎2 − 𝑏 2 (𝑥 + 𝑎)(𝑥 + 𝑏) = 𝑥 2 + 𝑥(𝑎 + 𝑏) + 𝑎𝑏
Ecuación General de la línea recta
𝑦2 −𝑦1
𝑚= Pendiente
𝑥2 −𝑥1
y= mx + b Ecuación de la recta
𝑦 − 𝑦1 = 𝑚(𝑥 − 𝑥1) Forma punto-pendiente
Distancia o longitud entre dos puntos: 𝑑𝐴𝐵 = √(𝑥2 − 𝑥1 )2 + (𝑦2 − 𝑦1) 2
𝑥1 +𝑥2 𝑦1 +𝑦2
Punto medio: 𝑃𝑚 (𝑥𝑚 , 𝑦𝑚 ) 𝑥𝑚 = 𝑦𝑚 =
2 2
Ingreso: I = pq
Utilidad: U=I–C
Costo total: C = Cf + Cvq
CT=Cf + Cv(x)
Ingreso: I =Precio de venta por unidad
Utilidad: U = Ingreso – Costo total
Costo total: Costo total= Costos fijos + Costos variables
Formula general para ecuaciones de 2° grado
−𝑏±√𝑏 2 −4𝑎𝑐
𝑥1,2 = 2𝑎
𝑏 𝑏2
Vértice de la Parábola 𝑥 = −(2𝑎) 𝑦 = 𝑐 − (4𝑎 )
Funciones
Función lineal Función potencial
f(x) = mx + b f(x) = axn
Función exponencial Función logarítmica
f(x) = C(1 + i)x f(x) = a Log bx
f(x) = abx f(x) = [ Log (M/C) ] / [ Log (1 + x) ]
También podría gustarte
- Derivada Direccional Solución PDFDocumento24 páginasDerivada Direccional Solución PDFCarlos Eduardo Bocanegra AlbanAún no hay calificaciones
- Bma 01 Cálculo DiferencialDocumento4 páginasBma 01 Cálculo Diferencial桜内 楓羽100% (1)
- Ejemplo y Ejercicios Campos de VelocidadDocumento4 páginasEjemplo y Ejercicios Campos de VelocidadJuan Esteban Garavito BuitragoAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad Evaluativa Eje 2 Calculo Integral PDFDocumento12 páginasActividad Evaluativa Eje 2 Calculo Integral PDFSebastian Menotty100% (1)
- Actividad 2. Laboratorio. Derivadas. 408831Documento17 páginasActividad 2. Laboratorio. Derivadas. 408831Enrique100% (1)
- Ejercicios Resueltos de La Guía # 5Documento9 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de La Guía # 5José GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- Exposicion Dia Miercolesv....Documento6 páginasExposicion Dia Miercolesv....Marco AlbrichetAún no hay calificaciones
- Ep 2022 1Documento3 páginasEp 2022 1ANGELA CAMILA JIMENA BONILLA BRAVOAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 3 Herrera ArielDocumento5 páginasTarea 3 Herrera ArielAriel Patricio HerreraAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Diagnóstico de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral Ii Pae 2024-1 (Solución)Documento5 páginasExamen Diagnóstico de Cálculo Diferencial e Integral Ii Pae 2024-1 (Solución)phernroman2003Aún no hay calificaciones
- T3 Ejercicios P1MAT 2106Documento6 páginasT3 Ejercicios P1MAT 2106Luis SolizAún no hay calificaciones
- Clases. Parcial 2Documento47 páginasClases. Parcial 2Anyel doorAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Derivadas y LimitesDocumento10 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de Derivadas y LimitesSayda Cerda TenorioAún no hay calificaciones
- Elementos Finitos 1d 2nodosDocumento26 páginasElementos Finitos 1d 2nodosDEYMAR DOUGLAS AGUILAR TAPIAAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario Calculo IiDocumento1 páginaFormulario Calculo IiLinda Noelia Pantaleon DavilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Control 5 CVE Secc A y C Solución v2 PDFDocumento2 páginasControl 5 CVE Secc A y C Solución v2 PDFFiorela ArellanoAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Opc. Examen Final - SolucionarioDocumento3 páginas1 Opc. Examen Final - SolucionarioEsteban MedranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Pizarra Mat129 2.30 22y23-FebDocumento2 páginasPizarra Mat129 2.30 22y23-FebSteven GutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- METODO GENERAL DE DISCRETIZACION c2d MatlabDocumento10 páginasMETODO GENERAL DE DISCRETIZACION c2d MatlabFranzum MamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocumento3 páginasEcuaciones DiferencialesAna Paula LoorAún no hay calificaciones
- Tcin U1 A4 XxyzDocumento6 páginasTcin U1 A4 XxyzSarai VargasAún no hay calificaciones
- 56 - 100411 - 56 - Fase 2 - Trabajo PDFDocumento17 páginas56 - 100411 - 56 - Fase 2 - Trabajo PDFmilenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculo Integral TVDocumento3 páginasCálculo Integral TVbialiarenas5Aún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo ContienentalDocumento11 páginasCalculo ContienentalJulioOseda100% (1)
- Métodos de IntegraciónDocumento59 páginasMétodos de IntegraciónBrandon MelendezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculo 3Documento3 páginasCálculo 3Roberto MarceliAún no hay calificaciones
- BCMV U3 Ea JebrDocumento5 páginasBCMV U3 Ea JebrJesús BuenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ev 1mpiDocumento13 páginasEv 1mpiIssachar Roberto Garcia HinojosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fase 3Documento14 páginasFase 3Cesar Augusto Pacco GuerraAún no hay calificaciones
- Repaso Final - Ejercicios ResueltosDocumento16 páginasRepaso Final - Ejercicios ResueltosJbc DrillerAún no hay calificaciones
- SOLUCION - Taller Tercer Corte 2021-1Documento5 páginasSOLUCION - Taller Tercer Corte 2021-1Catherine Andrea Cruz MolinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Resolución: Quinta Práctica Calificada de Cálculo Diferencial - Bma-01Documento3 páginasResolución: Quinta Práctica Calificada de Cálculo Diferencial - Bma-01Caff LlontopAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformaciones LinealesDocumento3 páginasTransformaciones LinealesDaniel OyolaAún no hay calificaciones
- Perfil de TemperaturaDocumento3 páginasPerfil de Temperaturayitoarigarcia2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Matematicas II Selectividad Julio Extraordinaria 2021 EnunciadoDocumento8 páginasExamen Matematicas II Selectividad Julio Extraordinaria 2021 EnunciadoVanessa Menchén FernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Asqui Vaca Hector DanielDocumento6 páginasAsqui Vaca Hector DanielJairo JoelAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario ComplejosDocumento1 páginaFormulario ComplejosMata López Antonio DavidAún no hay calificaciones
- J K LDocumento6 páginasJ K LYenny Alexandra Bacca CuasapazAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Matematicas II Selectividad Junio 2019 Opcion A y B SolucionDocumento6 páginasExamen Matematicas II Selectividad Junio 2019 Opcion A y B SolucionFRANCISCO JAVIER FERNANDEZ JIMENEZAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 4 Calculo Multivariable1Documento3 páginasTarea 4 Calculo Multivariable1carlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario GeoDocumento5 páginasFormulario GeoEdith Cayo VicenteAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller DiferencialDocumento10 páginasTaller DiferencialLuz Ángela Gómez Garzón0% (1)
- Examen Casa Variable ComplejaDocumento1 páginaExamen Casa Variable ComplejaLUIS CAEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Calculo 3Documento13 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de Calculo 3Alexander Bryan Delgado Silverio50% (2)
- 2°guia Materia Trigonometría FG Prim 2022Documento4 páginas2°guia Materia Trigonometría FG Prim 2022Miguel YuclaAún no hay calificaciones
- EJEMPLO S PARÁBOLA VERTICE (H, K) GeoDocumento9 páginasEJEMPLO S PARÁBOLA VERTICE (H, K) Geoestefania salazar gutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Antiderivada e Integrales IndefinidaDocumento13 páginasAntiderivada e Integrales IndefinidajuanAún no hay calificaciones
- (Ama Resuelto) 3º Totalizador Marzo 2021Documento4 páginas(Ama Resuelto) 3º Totalizador Marzo 2021Mar MoralesAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluacion PermanenteDocumento4 páginasEvaluacion Permanentejhosep0902 franshesco0209Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios GeoDocumento5 páginasEjercicios GeoJhon AcevedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluacion4 GrupoDDocumento8 páginasEvaluacion4 GrupoDNora Andrea Carrasco PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Desarrollo de Los Ejercicios de Análisis Matemático IIDocumento52 páginasDesarrollo de Los Ejercicios de Análisis Matemático IILeonardo Javier Díaz AguilarAún no hay calificaciones
- Limit EsDocumento14 páginasLimit EsFernando RamiroAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1Documento13 páginasTarea 1Gerardo Chavez CovarrubiasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ta A A A RRRRR Eeeeeee A AaaaaaaaaaDocumento2 páginasTa A A A RRRRR Eeeeeee A AaaaaaaaaaJefferson CandoAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario Tercer ParcialDocumento3 páginasSolucionario Tercer ParcialMireyra Belén L.MAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos Funciones Trigonométricas Inversas. 21-12-30.Documento4 páginasEjercicios Resueltos Funciones Trigonométricas Inversas. 21-12-30.Vladimil MellaAún no hay calificaciones