0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
341 vistas21 páginasProductos Notables en Matemáticas
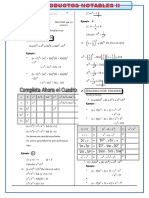
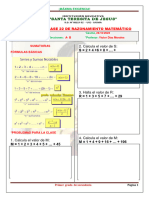
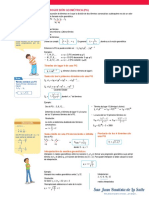
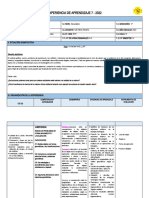
El documento presenta varios productos notables como el binomio al cuadrado, la diferencia de cuadrados, el binomio al cubo, la suma y diferencia de cubos, el trinomio al cuadrado, y las identidades de Legendre. Incluye ejemplos para ilustrar cómo aplicar estas fórmulas a problemas algebraicos.
Cargado por
DhiX -1992Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd
0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
341 vistas21 páginasProductos Notables en Matemáticas
El documento presenta varios productos notables como el binomio al cuadrado, la diferencia de cuadrados, el binomio al cubo, la suma y diferencia de cubos, el trinomio al cuadrado, y las identidades de Legendre. Incluye ejemplos para ilustrar cómo aplicar estas fórmulas a problemas algebraicos.
Cargado por
DhiX -1992Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Nos tomamos en serio los derechos de los contenidos. Si sospechas que se trata de tu contenido, reclámalo aquí.
Formatos disponibles
Descarga como PDF, TXT o lee en línea desde Scribd