Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Cálculo de La Ganancia Phi
Cargado por
Agera RS0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
27 vistas1 páginaEste documento presenta los cálculos para resolver un polinomio deseado p(z)=z^2-z+0.29 igualando coeficientes. Se obtienen las soluciones x=-26.42 y y=2.8129. Luego se verifica que el polinomio original evaluado en estas soluciones es igual al polinomio deseado, completando así la resolución.
Descripción original:
Ganancia PHI en Sistemas de Control.
Título original
Cálculo De La Ganancia Phi
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoEste documento presenta los cálculos para resolver un polinomio deseado p(z)=z^2-z+0.29 igualando coeficientes. Se obtienen las soluciones x=-26.42 y y=2.8129. Luego se verifica que el polinomio original evaluado en estas soluciones es igual al polinomio deseado, completando así la resolución.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
27 vistas1 páginaCálculo de La Ganancia Phi
Cargado por
Agera RSEste documento presenta los cálculos para resolver un polinomio deseado p(z)=z^2-z+0.29 igualando coeficientes. Se obtienen las soluciones x=-26.42 y y=2.8129. Luego se verifica que el polinomio original evaluado en estas soluciones es igual al polinomio deseado, completando así la resolución.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 1
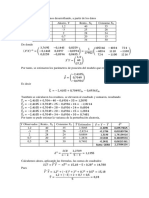
Calculo de
z − 0. 9761 − 0. 0398x −0. 1981 − 0. 0398y
z 2 − 1.
0. 2378 − 0. 0363x z − 0. 9733 − 0. 0363y
949 4z − 0. 036 3zy 0. 997 15 4. 489 7 10 −2 y − 0. 039 8xz 3. 154 6 10 −2 x
z 2 −1. 949 4 − 0. 039 8x − 0. 036 3yz 4. 489 7 10 −2 y 3. 154 6 10 −2 x 0. 997 15
Polinomio deseado pz z 2 − z 0. 29 Luego se igualan terminos, coeficiente a
coeficiente:
−1. 949 4 − 0. 039 8x − 0. 036 3y −1, Solution is:
y −26. 154 − 1. 096 4x
4. 489 7 10 y 3. 154 6 10 −2 x 0. 997 15 0. 29 Se sustituye el valor de y en la
−2
ec. anterior:
4. 489 7 10 −2 −26. 154 − 1. 096 4x 3. 154 6 10 −2 x 0. 997 15 0. 29, Solution is:
x −26. 42
Entonces el valor de
y −26. 154 − 1. 096 4−26. 42 2. 812 9,
z − 0. 9761 − 0. 0398−26. 42 −0. 1981 − 0. 03982. 812 9
Verificación
0. 2378 − 0. 0363−26. 42 z − 0. 9733 − 0. 03632. 812 9
z 2 − 0. 999 99z 0. 289 98 Por lo que la ganancia −26. 42 2. 812 9
También podría gustarte
- Ejercicios Primer Parcial ProcesosDocumento8 páginasEjercicios Primer Parcial Procesosleondavid94Aún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de EngranajesDocumento22 páginasProblemas de EngranajesJohnnyChateSulcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Determinacion de Los Periodos y Formas D PDFDocumento14 páginasDeterminacion de Los Periodos y Formas D PDFLoberon GamerAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Ejercicios+sobre+numeros+complejos+FORMAS+TPEDocumento2 páginasAlgebra Ejercicios+sobre+numeros+complejos+FORMAS+TPEManuel MorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 7 Juan Chávez OrozcoDocumento10 páginasTarea 7 Juan Chávez OrozcoJuan Chavez OrozcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Proyecto Integrador. Métodos Numéricos. Matematicas Aplicadas IIIDocumento26 páginasProyecto Integrador. Métodos Numéricos. Matematicas Aplicadas IIIfrancisAún no hay calificaciones
- Descarga Por OrificiosDocumento7 páginasDescarga Por Orificiosalfbol2003Aún no hay calificaciones
- Intervalos de Confianza (Cap I)Documento48 páginasIntervalos de Confianza (Cap I)Deymer Nicson RUiz TiradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Constrastacion Por El Metodo de CaineDocumento2 páginasConstrastacion Por El Metodo de CaineAnthony Quiroz LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen 3 Analisis NumericoDocumento12 páginasExamen 3 Analisis Numericothewolft21Aún no hay calificaciones
- 02 Ejercicios Prog Lineal Recintos SolucionesDocumento13 páginas02 Ejercicios Prog Lineal Recintos SolucionesMargarita Lopez AlonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- Solución Pista 7Documento2 páginasSolución Pista 7camilo robayo gomezAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Resueltos Tema1 PDFDocumento14 páginasProblemas Resueltos Tema1 PDFTamara CalleAún no hay calificaciones
- Ocw - Usal.es Ensenanzas Tecnicas Resistencia de Materiales Ingeniero Tecnico en Obras Publicas Contenidos Problemas Resueltos Tema1Documento14 páginasOcw - Usal.es Ensenanzas Tecnicas Resistencia de Materiales Ingeniero Tecnico en Obras Publicas Contenidos Problemas Resueltos Tema1notesinwinAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de Estadistica Inferencial Unidad 3Documento5 páginasActividad de Estadistica Inferencial Unidad 3MAIRA ALEJANDRA DE LA OSSA CASTILLO Estudiante100% (1)
- Serie 4 EntrDocumento25 páginasSerie 4 EntrLeo CondeAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Resueltos de Cap 16Documento15 páginasProblemas Resueltos de Cap 16ElkinAún no hay calificaciones
- LOs 6 Metodos de MatlabDocumento5 páginasLOs 6 Metodos de MatlabJose Paucara Villca0% (1)
- Método de Mínimos CuadradosDocumento18 páginasMétodo de Mínimos CuadradosMarcelino CordovaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 2 Ejemplo ModeloDocumento2 páginasTema 2 Ejemplo ModeloPAOLA RIVAS GARCIAAún no hay calificaciones
- Mecánica - Serie de Ejercicios 2Documento8 páginasMecánica - Serie de Ejercicios 2Jorge Eithan Treviño SellesAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario Practica de MedidasDocumento15 páginasSolucionario Practica de MedidasGermanico UsandivaresAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculos Final-1Documento6 páginasCalculos Final-1Oliver ZamoraAún no hay calificaciones
- Pruebas y Exámenes de Calculo VectorialDocumento32 páginasPruebas y Exámenes de Calculo VectorialJhonatanAlexis100% (3)
- Ejercicio 2Documento19 páginasEjercicio 2Jose Luis Huincho EscalanteAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Estadística Inferencial II Wapole y OtrosDocumento36 páginasEjercicios de Estadística Inferencial II Wapole y OtrosEstudiante INGAún no hay calificaciones
- ANALISIS 4 GDL - BBDocumento5 páginasANALISIS 4 GDL - BBALANAún no hay calificaciones
- Verificación de VigaDocumento6 páginasVerificación de VigapablobonvinAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis 4 GDL - BDocumento5 páginasAnalisis 4 GDL - BALANAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis 4 GDL - BDocumento5 páginasAnalisis 4 GDL - BALANAún no hay calificaciones
- Cert2 - Estatica - Centroide PautaDocumento2 páginasCert2 - Estatica - Centroide PautaEnrique Andres Catalan HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen 2Documento10 páginasExamen 2hi im adcAún no hay calificaciones
- TZ222Documento6 páginasTZ222Kevin SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Aproximaciones de Límites ResueltoDocumento4 páginasEjercicios Aproximaciones de Límites ResueltoJosi Llanes GonzálezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 1 ALGEBRA LINEAL - FDocumento8 páginasEjercicio 1 ALGEBRA LINEAL - FbiancaAún no hay calificaciones
- TRIANGULACION Método de Mínimos Cuadrados - Parte 04Documento19 páginasTRIANGULACION Método de Mínimos Cuadrados - Parte 04Rolando Sosa100% (1)
- Torsión en Ejes Huecos de Pared DelgadaDocumento3 páginasTorsión en Ejes Huecos de Pared DelgadaAlvaro TitiricoAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo de Una Curva de RemansoDocumento5 páginasCalculo de Una Curva de RemansoEdith LemaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 11 Taller Practico Aplicado Eliminacion Gaussiana y Gauss JordanDocumento18 páginasActividad 11 Taller Practico Aplicado Eliminacion Gaussiana y Gauss Jordanpedreros2012Aún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Mejoramiento-Lab 4Documento6 páginasGuia Mejoramiento-Lab 4Benjamin Romero AranaAún no hay calificaciones
- Solución Parcial Sistemas de Potencia Jairo Fabian Jaimes (JJ)Documento7 páginasSolución Parcial Sistemas de Potencia Jairo Fabian Jaimes (JJ)Fernando SanjuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual de Algebra2 05.10.2023Documento11 páginasManual de Algebra2 05.10.2023loreto.cruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad Transf de MasaDocumento6 páginasActividad Transf de Masalissette alvaradoAún no hay calificaciones
- TAREA 16-06-2022 MauricioDocumento12 páginasTAREA 16-06-2022 MauricioMauricio Alejandro Moncayo ReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisis 4 GDL - B PDFDocumento5 páginasAnalisis 4 GDL - B PDFALANAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica de Energia y Fuerza Especifica2Documento7 páginasPractica de Energia y Fuerza Especifica2Chris wlAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplo de Cálculo de Frenos de Zapata, Tambor y Pivotante 04.12.23Documento8 páginasEjemplo de Cálculo de Frenos de Zapata, Tambor y Pivotante 04.12.23Aurora Carrión AdrianzénAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 3 Practica 2Documento3 páginasEjercicio 3 Practica 2camilefuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo de CoordenadasDocumento9 páginasCalculo de CoordenadasCésar ChiclayoAún no hay calificaciones
- Caso Practico 2 MatematicasDocumento6 páginasCaso Practico 2 Matematicasmelani vargasAún no hay calificaciones
- Topografia BasicaDocumento7 páginasTopografia BasicaJavier MaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Estadistica KellyDocumento9 páginasTaller Estadistica KellyEduardo CiroAún no hay calificaciones
- Fitxa 4 - Ecuaciones Bicúbicas y TricuadrádasDocumento2 páginasFitxa 4 - Ecuaciones Bicúbicas y Tricuadrádasclaudia tocuAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 3 EstadisticaDocumento7 páginasActividad 3 EstadisticaJuan Andres Arenas SaltosAún no hay calificaciones
- Compendio N3 Mecanica AplicadaDocumento47 páginasCompendio N3 Mecanica AplicadaLUIS BRYAN VENTOSILLA PORTOCARREROAún no hay calificaciones
- Parte 0 - Inicios Del CineDocumento16 páginasParte 0 - Inicios Del CineAgera RSAún no hay calificaciones
- Ávila CamachoDocumento7 páginasÁvila CamachoAgera RSAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplo (Sistema Discreto)Documento2 páginasEjemplo (Sistema Discreto)Agera RSAún no hay calificaciones
- Primer Examen ParcialDocumento2 páginasPrimer Examen ParcialAgera RSAún no hay calificaciones
- Test de Temperamento (2020)Documento4 páginasTest de Temperamento (2020)Agera RS100% (1)
- FANUC M-710iC/50EDocumento6 páginasFANUC M-710iC/50EAgera RSAún no hay calificaciones
- 3er. Examen ParcialDocumento16 páginas3er. Examen ParcialAgera RSAún no hay calificaciones