Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
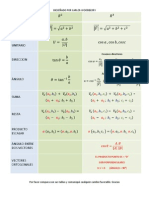
Formulas Teoremas de Calculo Trigonometria Basica Algebra
Formulas Teoremas de Calculo Trigonometria Basica Algebra
Cargado por
Yeudiel QnhamaTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Formulas Teoremas de Calculo Trigonometria Basica Algebra
Formulas Teoremas de Calculo Trigonometria Basica Algebra
Cargado por
Yeudiel QnhamaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Por Dorian Varela 2009 1
FORMULA DE LOS PRODUCTOS NOTABLES
x + y x y = x
x + y
= x
+2xy + y
x y
= x
2xy + y
x + y
= x
+ 3x
y +3xy
+ y
x y
= x
3x
y +3xy
FORMULAS DE FACTORIZACION
x
= x +yx y
x
= x yx
+ xy + y
+ y
= x +yx
xy + y
x + y = x
+ y
x
x
. y
+ y
en radical x
3
+y
3
x
2
3
x
3
. y
3
+y
2
3
x y = x
y
x
+x
. y
+ y
en radical x
3
y
3
x
2
3
+x
3
. y
3
+y
2
3
EXPONENTES Y RADICALES
EXPONENTES
RADICALES
= si n es impar ||
=
.
=
FORMULA CUADRATICA
Si a 0, la raices de ;
+ + = 0 Son: =
IDENTIDADES TRIGONOMETRICAS FUNDAMENTALES
. = 1
= 1 =
. = 1 1+
. = 1 1+
IDENTIDADES DE SUMAS Y DIFERENCIAS
+ = . + . tanu + v =
.
tanu v =
.
= . .
+ = . .
= . + .
IDENTIDADES PARA ANGULOS DOBLES Y SEMIANGULOS
2 = 2. 2 =
2 =
2 = 1 2
=
cos
2 = 2
1
Por Dorian Varela 2009 2
PROPIEDADES DE LOS LOGARITMOS Y EXPONENCIALES
Logaritmo Base a Logaritmos Comunes Logaritmos Naturales
1 = 0 1 = 0 1 = 0
= 1 10 = 1 = 1
= 10
= 10
=
Logaritmos Comunes Logaritmos Naturales
= + = +
= .
= .
Por Dorian Varela 2009 3
TEOREMAS SOBRE DIFERIENCIACION DE FUNCIONES ALGEBRAICAS
= x
= +
lim
= c. = + = .
= . = +
= . +.
=
= +
=
..
= +
.Dx +
DERIVADAS DE FUNCIONES TRIGONOMETRICAS
Dx = Dx sin = cos .
Dx = Dx = .
Dx =
Dx =
.
Dx =
Dx =
.
Dx = . Dx = . .
Dx = . Dx = . .
DERIVADAS DE FUNCIONES TRIGONOMETRICAS INVERSAS
Dx
. Dx
.
Dx
. Dx
.
Dx
. Dx
.
DERIVADAS DE FUNCIONES EXPONENCIALES Y LOGARITMICAS
.
=
.
|| =
.
Por Dorian Varela 2009 4
ALGUNAS FORMAS ELEMENTALES DE INTEGRAR
1. = + C
2. . = . + C
3. + = +
4.
. =
+1
+ 1
INTEGRALES TRIGONOMETRICAS
5. sin. = cos + 18.
= sin
+ cos
+
6. cos . = sen + 19.
1 +
= tan
cot
+
7.
. = tan + 20.
1
= sec
csc
+
8.
. = cot + 21. sin
. = sin
+
9. sec tan . = sec + 22. cos
. = cos
+
10. csc . cot . = csc + 23. tan
. = tan
ln 1 +
+
11. cot . = ln|sen| + 24. cot
. = cot
+ln 1 +
+
12. tan . = ln|sec | + 25. sec
. = sec
ln +
1 +
13. sec . = ln|sec + tan| + 30. csc
. = csc
+ ln +
1 +
14. csc . = ln|csc cot u| +
15.
= sin
+ > 0
16.
=
1
+ 0
17.
=
1
sec
+ > 0
INTEGRALES DE OTRAS FUNCIONES
31.
1
. = ln|| + 35. . v = v v
32.
. =
+
33.
. =
+ > 0 1
34. ln . = ln +
Por Dorian Varela 2009 5
INTEGRALES DE FUNCIONES TRIGONOMETRICAS
INTEGRALES QUE INVOLUCRAN SENOS Y COSENOS
CASO 1
.
Donde n o m es un nmero entero positivo impar.
En este caso se le resta 1 potencia a n (al impar)
CASO 5
.
Donde m es un numero entero positivo par
En este caso se le resta 2 potencias a m ( al par ) y se utilizan
la identidades :
a)
+ 1 =
b)
+1=
CASO 2
.
Donde m y n son nmeros enteros positivos pares.
En este caso se utiliza la identidades :
CASO 6
.
Donde n es un nmero entero positivo impar y m .
En este caso se le resta 1 potencia a n y m y se utilizan las
identidades:
a)
+ 1 =
b)
+1=
CASO 3
.
Donde n es un numero entero positivo
En este caso se le resta 2 potencias a n y se utilizan las
identidades;
a) 1+
b) 1+
CASO7.
.
Donde n es un numero entero positivo impar
Las cuales se resuelven con integracin por partes.
Puede aplicar formulas de reduccin 77 y 78 de tablas de
integrales del libro de Leithold.
a) Considere u =
y dv =
.
b) Considere u =
y dv =
.
CASO 4.
.
Donde n es un nmero entero positivo par.
En este caso se le resta 2 potencias a n y se utilizan la
identidades
a)
+ 1 =
b)
+ 1=
CASO 8
.
Donde n es un nmero entero positivo par y m es un nmero
entero positivo impar.
Exprese el integrando en trminos de potencias impares de la
Secante o Cosecante.
Las Cuales se resuelven con integracin por partes.
a) Considere u =
y dv =
.
b) Considere u =
y dv =
.
CASO ESPECIAL
. .
En este caso que los argumentos son diferentes se aplica
la identidad trigonomtrica a:
. =
1
2
+
1
2
+
Y luego integramos.
Por Dorian Varela 2009 6
"No s cmo puedo ser visto por el mundo, pero en mi opinin, me he comportado como un
Nio Que juega al borde del mar, y que se divierte buscando de vez en cuando una piedra
ms pulida y una concha ms bonita de lo normal, mientras que el gran ocano de la
verdad se expona ante m completamente desconocido."
SIR ISAAC NEWTON
También podría gustarte
- Caso Krispy KremeDocumento3 páginasCaso Krispy KremeAnny Zhang ChengAún no hay calificaciones
- Geometria PlanaDocumento3 páginasGeometria Planaanon-144933100% (45)
- Ecuaciones de 1º GradoDocumento6 páginasEcuaciones de 1º GradoAlejandro Guillen BetancourtAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario Matematicas IIIDocumento3 páginasFormulario Matematicas IIIJoshuaAún no hay calificaciones
- MEMORIA AUTOCAD Expresión Gráfica Electrónica Industrial y AutomáticaDocumento22 páginasMEMORIA AUTOCAD Expresión Gráfica Electrónica Industrial y AutomáticaF Ricardo PintoAún no hay calificaciones
- Bloque #2Documento8 páginasBloque #2Fernando SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- TalleresMatematicasI SRDocumento134 páginasTalleresMatematicasI SREdwin Hernandez CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Prueba de Historia 8 BásicoDocumento3 páginasPrueba de Historia 8 BásicoCassiel2000Aún no hay calificaciones
- Libro para ColorearDocumento28 páginasLibro para ColorearGaby Gomez de LinaresAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario de Matemáticas (IV)Documento20 páginasFormulario de Matemáticas (IV)JUGMANAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario de Algebra LinealDocumento1 páginaFormulario de Algebra LinealFicciones BrevesAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio As de Áreas y PerímetrosDocumento3 páginasEjercicio As de Áreas y PerímetrosMaría Inmaculada Juárez Alonso0% (1)
- Formulario de TrigonometriaDocumento4 páginasFormulario de Trigonometriaprofe.alex100% (3)
- SCV 2015 RM 04Documento24 páginasSCV 2015 RM 04Jose Luis Roca CordovaAún no hay calificaciones
- Geometría Analítica 25 Ejercicios ResueltosDocumento32 páginasGeometría Analítica 25 Ejercicios ResueltosRene Alfredo Quispe CoaquiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Fórmulas GeometríaDocumento5 páginasFórmulas Geometríaspablo88100% (1)
- Aprendiendo Maple 10Documento58 páginasAprendiendo Maple 10Cheko LunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario MatematicasDocumento15 páginasFormulario Matematicasrocady75100% (1)
- Guía de Trigonometria, Cálculo de Área y VolumenDocumento4 páginasGuía de Trigonometria, Cálculo de Área y Volumencdavila100% (36)
- Analisis Combinatorio 01 PDFDocumento12 páginasAnalisis Combinatorio 01 PDFMarlene NavarreteAún no hay calificaciones
- Hoja Logaritmos ResueltaDocumento3 páginasHoja Logaritmos Resueltamarihelen60Aún no hay calificaciones
- MatemáticaDocumento38 páginasMatemáticaThais M. Batista V.100% (1)
- CepreDocumento8 páginasCepreMarco Cisneros PachecoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Geometría Plana ResueltosDocumento10 páginasEjercicios de Geometría Plana ResueltosMateo SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades TrigonométricasDocumento1 páginaIdentidades TrigonométricasAlessandro HaroAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia MRU y MRUADocumento2 páginasGuia MRU y MRUACristina Pino ParraAún no hay calificaciones
- Inecuaciones Con Valor AbsolutoDocumento8 páginasInecuaciones Con Valor Absolutomielmach2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tercero MedioDocumento7 páginasTercero Mediomaestralorena2566Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocumento30 páginasEcuaciones DiferencialesRonald FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Estatica-Fichas de RefuerzoDocumento2 páginasEstatica-Fichas de RefuerzoSANSIMON1968Aún no hay calificaciones
- Trucos MatematicosDocumento6 páginasTrucos MatematicosminodanAún no hay calificaciones
- RaicesDocumento2 páginasRaicesDaniela Nicole Vasquez RiquelmeAún no hay calificaciones
- 2do Examen de Cálculo I (UNSL)Documento8 páginas2do Examen de Cálculo I (UNSL)Miguel Berardi Alfonso100% (1)
- Test Simulacro 2000 Becas de Itaipu - MateDocumento3 páginasTest Simulacro 2000 Becas de Itaipu - MateMelissa FernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fórmulas de Algebra Trigonometria y CálculoDocumento14 páginasFórmulas de Algebra Trigonometria y CálculoJared PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de Olimpiadas Internacionales Resueltos 43Documento4 páginasProblemas de Olimpiadas Internacionales Resueltos 43JALS100% (1)
- Libros Buenos de CaldereriaDocumento1 páginaLibros Buenos de Caldereriamarco31416Aún no hay calificaciones
- AlgebraDocumento82 páginasAlgebraantony alarcnAún no hay calificaciones
- CLASE 2. Ejercicios Sobre Conversion de UnidadesDocumento3 páginasCLASE 2. Ejercicios Sobre Conversion de UnidadesahalonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- SOLUCIONARIO Limites 6dDocumento11 páginasSOLUCIONARIO Limites 6dMarco Antonio FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario AlgebraDocumento2 páginasFormulario Algebraj288% (8)
- 04 - Matematica (Funciones) (Respuestas)Documento12 páginas04 - Matematica (Funciones) (Respuestas)Edson Ugarte GamboaAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario de AlgebraDocumento6 páginasFormulario de AlgebraRosalba MuñozAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulario F1Documento1 páginaFormulario F1AlfonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- Series - Ejercicios ResueltosDocumento9 páginasSeries - Ejercicios Resueltosprofe.alexAún no hay calificaciones
- Pepe Aranda. Apuntes de Matemáticas. SolucionesDocumento20 páginasPepe Aranda. Apuntes de Matemáticas. SolucionesPepealej100% (2)
- Cap3 Funciones Vectoriales de Variable RealDocumento16 páginasCap3 Funciones Vectoriales de Variable RealJhulisa Torrez CondoriAún no hay calificaciones
- PSU Matematicas, Capitulo 8, FuncionesDocumento28 páginasPSU Matematicas, Capitulo 8, FuncionespanchomoyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Logaritmos PDFDocumento2 páginasLogaritmos PDFelenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodo Simbolico Funciones GeneratricesDocumento37 páginasMetodo Simbolico Funciones Generatricesshabedekam100% (2)
- Formulario de DerivadasDocumento2 páginasFormulario de DerivadasGerall Garces AraosAún no hay calificaciones
- Silabos de Geometria - Cepre UntrmDocumento5 páginasSilabos de Geometria - Cepre UntrmDonald Cubas HurtadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tabla de Conversión de Unidades-2019Documento4 páginasTabla de Conversión de Unidades-2019cristofer lucasAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos Notables FactorizacionDocumento4 páginasProductos Notables FactorizacionJorge CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Formulas de Fisica IDocumento3 páginasFormulas de Fisica ISoka Díaz OchoaAún no hay calificaciones
- S09.s1 - Productos Notables 1 UCVDocumento15 páginasS09.s1 - Productos Notables 1 UCVcesar godAún no hay calificaciones
- ICYA4414 Final TDocumento3 páginasICYA4414 Final TVictoria YakryAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía de CurvasDocumento3 páginasGuía de CurvasEduardo HidalgoAún no hay calificaciones
- Labo 5 Fisica IiDocumento6 páginasLabo 5 Fisica IiJean Carla PuenteAún no hay calificaciones
- TAREA 1 - Ejercicios B 1604Documento8 páginasTAREA 1 - Ejercicios B 1604Karen CabalAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometría (Fórmulas)Documento1 páginaTrigonometría (Fórmulas)Diego ArosemenaAún no hay calificaciones
- FormularioDocumento7 páginasFormularioDominique TrevisanAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo 3Documento5 páginasTrabajo 3MIGUEL ANGEL AHUMADAAún no hay calificaciones
- Precision SemanticaDocumento20 páginasPrecision Semanticaemily mtlAún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamentos Filosóficos e Históricos de La Educación Actividad Semana VIIIDocumento3 páginasFundamentos Filosóficos e Históricos de La Educación Actividad Semana VIIIrobertoAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 7 - GPDocumento16 páginasSemana 7 - GPRojas SharonAún no hay calificaciones
- MentirasDocumento2 páginasMentirasPau TldAún no hay calificaciones
- Cómo Escribir Un Ensayo Reflexivo EficazDocumento2 páginasCómo Escribir Un Ensayo Reflexivo EficazDaniel Castillo100% (1)
- Conversión de Pena Efectiva Impuesta A Prestación de Servicios A La Comunidad - RESOLUCION NULIDAD - ROBODocumento7 páginasConversión de Pena Efectiva Impuesta A Prestación de Servicios A La Comunidad - RESOLUCION NULIDAD - ROBOJIMMYHTAún no hay calificaciones
- idUS - Actitud de Los Estudiantes de La Universidad Autónoma Juan Misael Saracho Hacia La Educación AmbientalDocumento3 páginasidUS - Actitud de Los Estudiantes de La Universidad Autónoma Juan Misael Saracho Hacia La Educación AmbientalWilber Siles CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Donar SangreDocumento10 páginasDonar SangreasidhasdAún no hay calificaciones
- Balsas LipídicasDocumento4 páginasBalsas LipídicasRosa Marcela Rojas CorralesAún no hay calificaciones
- Técnicas Proyectivas Gráficas: Evolutiva Gráfica Mg. Ps. Lucía Puentes MatamalaDocumento82 páginasTécnicas Proyectivas Gráficas: Evolutiva Gráfica Mg. Ps. Lucía Puentes MatamalaKristenAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Caso Problema (Contabilidad) Empresa Nebulosa S.a.formato NuevoDocumento8 páginas1 Caso Problema (Contabilidad) Empresa Nebulosa S.a.formato NuevoLeni Castellon LinaresAún no hay calificaciones
- Purgatorio - Raul Zurita PDFDocumento65 páginasPurgatorio - Raul Zurita PDFFederico SamosAún no hay calificaciones
- PresentacionDocumento15 páginasPresentacionGRISERLY ROSARIO SANTOSAún no hay calificaciones
- Perdida de Carga en TuberíasDocumento19 páginasPerdida de Carga en TuberíasJose Luis Zapata FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Relación de Misioneros Que Sirvieron en La Misión Mexicana SUD1945-1955Documento41 páginasRelación de Misioneros Que Sirvieron en La Misión Mexicana SUD1945-1955taxamaranchiAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Sechura UltimoDocumento45 páginasTrabajo Sechura UltimoJose Luis Ayala Yarleque50% (2)
- Fragmentos de Dignidad y Una Mujer DesesperadaDocumento7 páginasFragmentos de Dignidad y Una Mujer DesesperadaWady Andres Semanate CabreraAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluación Unidad #5 TRANSITORIOS LenguajeDocumento5 páginasEvaluación Unidad #5 TRANSITORIOS Lenguajejosefina pachecoAún no hay calificaciones
- CUESTIONARIODocumento4 páginasCUESTIONARIOLuis Fernando Garcia candeleroAún no hay calificaciones
- IdeaciónDocumento16 páginasIdeaciónMarilut Maldonado VillcaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad - Coherencia y CohesiónDocumento8 páginasActividad - Coherencia y CohesiónKaren Bobadilla0% (2)
- Octeto OminosoDocumento4 páginasOcteto OminosomurilloAún no hay calificaciones
- 14 Via Docente n1Documento6 páginas14 Via Docente n1Jose Luis NavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Triptico Aymara Terminado para Imprimir Cara 2Documento2 páginasTriptico Aymara Terminado para Imprimir Cara 2Anonymous NILfmfr0100% (1)
- Reale II-5-Revolucion - Cientifica PDFDocumento34 páginasReale II-5-Revolucion - Cientifica PDFJuan Ignacio CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Sub 4Documento21 páginasSub 4Alexsander SarmientoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ciencias Naturales Planificacion - 2 BasicoDocumento5 páginasCiencias Naturales Planificacion - 2 BasicoErwin AlonsoAún no hay calificaciones