Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Semana 3 CS
Cargado por
Anonymous 7za15o0Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Semana 3 CS
Cargado por
Anonymous 7za15o0Copyright:
Formatos disponibles
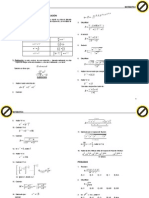
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
42 4n n2 3(2) 2n 1
SEMANA 3
OPERADORES MATEMTICOS
1. Si: m#n=3n-5m, Halle: (2#3)#(4#6) A) 0 D) 11 B) -1 E) -11 C) 1 4.
n
n n
6n 9
0
-3 -3
n=3
RPTA.: B
En la tabla:
RESOLUCIN
2#3=3(3) -5(2)=-1 4#6=3(6)-5(4)=-2 (-1)#(-2)=3(-2)-5(-1)=-1
a b a a b
c c
RPTA.: B
2. Si:
b b a c c c c a
Reducir:
p*q p*q
A) 0,5 D) 1,5
(p q) / 2, cuando p>q; (q p) / 3, cuando p<q;
B) 1 E) 3 C) -1,5
E
A) a D) c
a b a
c b c
B) 0 E) 1
Halle: (11*7) * (5*8) C) b
RESOLUCIN
11-7 11 7= 2 2 8-5 5 8= 1 3 2-1 1 2 1= 0, 5 2 2
RESOLUCIN
E
E
a b
a (b c) b c a c
a c c
0, 5na
RPTA.: E RPTA.:A
5.
n Si an & a 1
Halle: E A) 16 D) 81
81 & 27 & 16
B) 32 E) 12,5 C) 25
3.
Si: a b=3a+2b+1,
a#b=a2
Halle: n en:
ab
b2,
4#n
2 n
RESOLUCIN
B) 3 E) 4 C) 6
A) -3 D) 9
81 & 27 & 16
1 3 4 32 2 1 2 5 12, 5 2
81 & 27=34 & 33 32 & 16=25 & 24
Pgina 252
RESOLUCIN
4#n=2 * n
CICLO 2007-II
Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
E 1 2 1 2 1 3
2 2
RPTA.: E
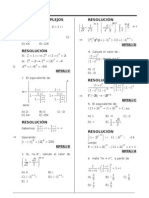
6. En la tabla
0 1 2 3 0 0 1 2 3 1 1 3 0 2 2 2 0 3 1 3 3 2 1 0
Hallar n en: 8. Si:
1 3 1 2 1 2
1 1 3 1 3 RPTA.: A
x2
= x(x+2) Halle: E=3 4 -2 6 A) 0 D) 2 B) -1 E) -2 C) 1
3 n
A) 0 D) 3
2 0
B) 1 E) 4
3 3
0
C) 2
RESOLUCIN
3 n 3 n 2 0 3 3 0 2 0 3 n 1 n 2
m2 n2 2 a b
1
RESOLUCIN
=
2 X
X
-1=x(x+2) =x + 1
RPTA.: C
4 6
=4+1=5 =6+1=7
7.
Si: m n
a b
Halle:
E = 3(5) 2 (7) =1
p#q=(p+q) p-q
E
RPTA.: C
9. Si: x =2x-6
x+2
21
21 31 3 1 2 1 #3 1
B) 0 E) 2 C) 6
=4x+4
A) 1 D) 1/6
Halle: E= 8 -5 1 A) -2 D) 0 B) 2 E) 4 C) 1
RESOLUCIN
E 1 1 2 3 1 1 1 # 3 2 3
Pgina 253
RESOLUCIN
x+2
1 2
= 2 X+2 -6 = 4x + 4 X+2 =2x + 5
Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
CICLO 2007-II
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
RESOLUCIN
a#b =
8=
6+2 =2 (6)+5 =17
1 = -1+2 =2 (-1)+5=3
E 17 5(3)
a#b
4a 4
4 4
4a 1 15
RPTA.: B
10.
a#b=
a(a 1) Si: a = 2
Halle: x en:
2x+1
50#65
4 50
RPTA.: E
12.
a@b3
Halle: E
b2
=21 B) 0,5 E) 4 C)1
4@27 6 2 @512
B) 45 E) 22 C) 41
A) 0,25 D) 2
A) 53 D) 14
RESOLUCIN
De afuera hacia adentro:
RESOLUCIN
4@27= 16@33
E 7@8= 49@2
3
16 32
49
2
7 8
a a 2
2x+1
21
=6
6 2 @512= 72@83
72 82
2 45 RPTA.: B
a a 2
2x+1
13.
Si: f(n) Halle: E
n 1 / n 1
f(...f(f(f(n)))...)
678 operadores
=3 A) n
a a 1 2
B) 2n D) (n
C) n
1) / n 1
2x
1 2
0, 5
E) (n
1) / n 1
RPTA.: B
11. Si: n = n
RESOLUCIN
De adentro hacia afuera: 1 Op
f(n)
a#b =4a
Halle: x=50#65 A) 30 D) 13
CICLO 2007-II
2 Op C) 14
B) 20 E) 15
n 1 n 1 n f(f(n) ) n n n
1 1 1 1
1 1
2n 2
n 1 n 1
3 Op
Pgina 254
f(f(f(n))) = f(n) =
Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
2 n = n
678 Op; como es par 14. Si:
E=n
3n n2
1
3
7 8
RPTA.: A
a #b2
Halle:
3n
b # a2
ab
n2 n2
3n 2 3n 2 0
x
A) 1 D)
31 / 4 # 2 6
B) 2 C) 3 16.
n +2 n= -2 n +1 n=-1 mximo valor: n = 1
RPTA.: D
E) 0 Si: x =2(x-16)
x+3
=8x
RESOLUCIN
a#b
a #b 3
4 2
Halle: E= 4 -2 2
2
2 2
4
a#b
2
ba
2ba a #b2
ab
ab ab
a #b 3ab
A)-4 D)-2
B) 4 E) 2
C) 0
a #b2
RESOLUCIN
x+3
3 #2
4
3#
3 #2
2
3
= 2 x
16
8x
de x:
x 4 1 3
4x 16 20
6 6
1
RPTA.: A
4(1) 16
15.
Si:
3 x =x
2 1 3 4( 1) 16 12 E 20 2 12 4 RPTA.: A
17. Sabiendo que:
1
3x
x = x2
A@ B+1
Halle: x
2A
3B
Halle el mximo valor de n en:
Si: 5@x=x@(3@1)
=-7 B) 4 E) 20 C) 2
A) 0 D) -1
RESOLUCIN
n = n2
CICLO 2007-II
32 5 37 D) 3
A)
B)
19 5
C)
28 5
E) 12
3n
Pgina 255
RESOLUCIN
Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
A & B= x+3 x2+2kx+k2 A & B= x2 8x 15 x2
15k2
20. Sabiendo que:
Dndole forma al problema:
5@ x-1 25 3 x
1 1
x@ 3@ 0+1 x@ 2 3
x@6 x@ 5+1
5 k2
30
2kx
60
13 3x 13 3x
k = 2
13 3x
28
2x
5x
35
x 28 5 RPTA.: C
RPTA.: B
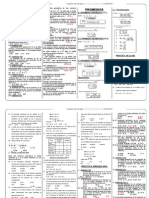
1 2 3 4 1 1 2 3 4 2 2 3 4 5 3 3 4 5 6 4 4 5 6 7
C) 0 Halle: 6 7 A) 15 D) 20
18.
Si: F x
Fx
3x
F0
A) 2 D) -1
1;Halle F 2
B) 1 E) 4
3 5
B) 17 E) 16 C) 18
RESOLUCIN
F2 F2 F1 F1 F1 F1 F0 F0
1 1 1 1
F1 F1 F0 F0 1 0
3(1) 2 1.......(I) 3(0) 2 2 F1 1
RESOLUCIN
De tablas se obtiene:
1 2 2 3 4 3 6 7 3 5 12 7
21. Si
2 4 6 6
1 2 2 4 7 3 3 1 1
1 1 1 12 7 1 18 RPTA.: C
R
Cmo F 0
Reemplazando en (I):
F2
1 1
RPTA.: C
19. Si se define: A&B= AB2 A
3 5 12 7
x
Adems: A=x+3 y B=x+k Halle: K>0, si el trmino independiente de A&B es 60. A) 1 D) 4 B) 2 E) 5 C) 3
x2
x3; x
Calcule: A) -1 D)
1
B) 0 E) C) 1
1 2
-1 2
RESOLUCIN
A & B= x+3 x+k
CICLO 2007-II
2
RESOLUCIN
x 3 2
Pgina 256
x2
x3 y
( 1)
Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
* Clculo de elemento a 1 ; para cada letra inverso
Igualamos los argumentos:
x x x x 1
2
1
ambos miembros
Multiplicando por x 1 :
a1 b1
a d
c1 d1
1
c b
E
E
d a
d1 d
d
1
x x 1 x 1
x x2
x
3
1 x 1
x 1
23.
b d
1
x 1
E
Se
a1
a
define en
x x3
1
RPTA.: C
la siguiente operacin:
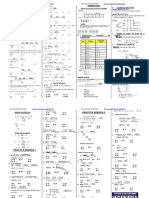
RPTA.: A A= a,b,c
22.
Se
define
en
A= a,b,c,d , la
a b c a b c a b c a b c a b c
Cules de las siguientes proposiciones son verdaderas? I. Si: (b*x) (b*c)=(c*a)*b x=a II. Se cumple la propiedad de clausura III. Se cumple la propiedad conmutativa IV. El elemento neutro es b V. a1=b A) I, II, IV C) II, III, V E) Todas B) II, III, IV D) II, IV, V
siguiente operacin:
a b c d a a b c d b b c d a c c d a b d d a b c
Halle: E A) a D) d
d a1
B) b E) e
C) c
RESOLUCIN
* Clculo del elemento neutro (e): de la tabla: e=a
RESOLUCIN
a b c d a a b c d b b c d a c c d a b d d a b c
I.
b x b x b x
b c b b a b c
a b
c a
II.
F S se cumple la propiedad de clausura. V
Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
b x x
CICLO 2007-II
Pgina 257
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
P4 P2 P4 P4
2
III. IV. V.
S se cumple la propiedad asociativa V El elemento neutro es C F 1 V a b
RPTA.:C
24. Se define: a b Calcule: 3 1
1
P4 P2
P2 P4
P4 P4
P4 P4
21
a b 4 41
P2
P2 P2 P4
Invirtiendo:
a es el elemento inverso de a
A) 4 D) 7 B) 5 E) 8 C) 6
2
P4 P2
P2 P4
2
RESOLUCIN *
Clculo del elemento neutro e: a e=a a +e - 4 = a e=4 Clculo del elemento inverso "a 1 ":
RPTA.: B
26. Se define:
a a1 e a a1 4 a1 31 21 41
a b a
a b ; a b
4 8 8 8 8
Calcule: 16 2
a 3 5 2 6 4 4
A)2 D) 8
B)4 E) 2 2
C) 6
RESOLUCIN
4 4 7
a b
a b
a b
2
31 21 31 21 3
1
41 41 7 4
5 6
a b a ;b a
a
a
b a b
5 6 4 7 4 4
b a b
b a b
RPTA.: D
25. Si: P x / y Calcule:
P x
P y
a b
a2 b a b
P4 P2
B) 2 E) C) 3 27.
a b
a2 b
3
a b 16 2
1 2
a2b
3
162 x2
8
RPTA.: D
A) 1 D) 4
Si:
n; x Z;
n
Pgina 258
n 1
RESOLUCIN
CICLO 2007-II Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
K
=k+1 =2+1=3 = 12 =
Halle: F
3 en:
3, 2 a 0, 95
B) -2 E)Ind.
F a
A)-1 D) 0
a2
2, 8 3, 4
8, 01 1
2
1
C) +1
1
RESOLUCIN
De la definicin, tenemos: 3,2 3 ; 3 3,2 4
2,8 8,01 0,95 3, 4 3; 9; 0; 4; 0 3 9 0,95 4 2,8 8,1 1 3 3, 4 2 8
0
+
1
=0+1=1
=3 + 1 = 4 RPTA.: E
Fa
Fa
a2 3 3 9 a 0 4 1 a2 9 a 3
3
3
3 3
= k2
0 0
Ind
RPTA.: E
28.
k
Halle:
= k (k+2)
2 +
A) 5 D) 2
1
B) 7 E) 4 C) 3
RESOLUCIN
K
2 K
CICLO 2007-II
2 K - 1 = k (k + 2)
= k2 2k 4 1
Pgina 259
Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DEL CALLAO CENTRO PREUNIVERSITARIO
Aptitud Matemtica
30. Si: =x-x+x-x+.. Calcule el valor de:
29.
Si:
x-1
m +1
=3x+2 =4 +3
m+1
Calcule:
E
A) 3 D) 2
2
B) -1 E) 1
20
21 operadores
C) 0
A) Ind D) 2 20
B) 2 8 E) 2 21
C) 2
19
RESOLUCIN
m +1
RESOLUCIN
x x x 2
1 Op. 2 1
x ...
= 4 m+1 +3
forma de la 1
Dndole la operacin
1= 4 m
2 Op.
2 2 1 2
1 2
1
3 m
4 3 m 2
3
3 Op.
1 2 1 22 2
1 2 2
1 22 1 23
3 m +8 =4 3m+8
3
1 4 Op. 2 2
-2
m
= 4m + 9
=4 2
1
21Op.
1
RPTA.: E
2 20
RPTA.: D
CICLO 2007-II
Pgina 260
Prohibida su Reproduccin y Venta
También podría gustarte
- Geometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designDe EverandGeometric modeling in computer: Aided geometric designAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 3 CS-operadoresDocumento9 páginasSemana 3 CS-operadoresGrety TorresAún no hay calificaciones
- Operadores 11/01/12Documento9 páginasOperadores 11/01/12Academiapre CygnusAún no hay calificaciones
- Preguntas de Examenes de Admision San Marcos GSMDocumento1372 páginasPreguntas de Examenes de Admision San Marcos GSMA94leo14hsetma100% (2)
- Algebra Preuniversitario (600 Ejercicios Resueltos)Documento148 páginasAlgebra Preuniversitario (600 Ejercicios Resueltos)Jean Hernandez79% (61)
- ALGEBRA 9asDocumento7 páginasALGEBRA 9asLuigi Ruiz SalvadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Acv 2015 RM 05Documento16 páginasAcv 2015 RM 05Jose Luis Roca Cordova100% (1)
- Algebra 1Documento3 páginasAlgebra 1Frank Fasanando0% (1)
- AlgebraDocumento83 páginasAlgebraJPabloCLeoAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra 1Documento12 páginasAlgebra 1Pérez JairoAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 8 CS CIRCUNFERENCIA TRIGONOMÉTRICADocumento12 páginasSemana 8 CS CIRCUNFERENCIA TRIGONOMÉTRICAelioAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de AlgebraDocumento13 páginasProblemas de AlgebraAlexander TasaycoAún no hay calificaciones
- Acv 2016 X 01Documento12 páginasAcv 2016 X 01alter147Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aritmetica 7Documento7 páginasAritmetica 7vegacarlos89Aún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra 1Documento23 páginasAlgebra 1Kevin CajachuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Operadores Matemáticos - PrácticaDocumento2 páginasOperadores Matemáticos - PrácticaNancy Lilly ParedesAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 SCPM Rma 162002Documento2 páginas2 SCPM Rma 162002Edinsson R. Javier VillanuevaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1er Año - Guia Nº7 - Operadores MatemáticosDocumento6 páginas1er Año - Guia Nº7 - Operadores MatemáticosmariaquirozAún no hay calificaciones
- MATEMÁTICADocumento18 páginasMATEMÁTICAteodomiroariasAún no hay calificaciones
- Aritmética I 1 CSDocumento7 páginasAritmética I 1 CSvegacarlos89Aún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Semestral Integral 2016Documento48 páginasAlgebra Semestral Integral 2016KimmerQuispeAún no hay calificaciones
- Preguntas de Algebra - SELECCIONADOSDocumento15 páginasPreguntas de Algebra - SELECCIONADOSManasésAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminario Raz. Matematico - Cpu - Unasam 2011 - IIDocumento2 páginasSeminario Raz. Matematico - Cpu - Unasam 2011 - IIerickesmeAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometría Iii PDFDocumento12 páginasTrigonometría Iii PDFArturo Rubén Lozano PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra 1Documento56 páginasAlgebra 1Bladimir Wilder BritoAún no hay calificaciones
- Maraton AlgebraDocumento4 páginasMaraton AlgebraJennifer RSAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica Ok 1 2Documento101 páginasMatematica Ok 1 2lazartezerpa50% (2)
- Semana 13Documento7 páginasSemana 13Ayasta KstroAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Examen de Algebra 2Documento7 páginas2 Examen de Algebra 2SesyGuisSesyamAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion 01 Habilidad OperativaDocumento4 páginasSesion 01 Habilidad Operativamoi19Aún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometria RepasoDocumento15 páginasTrigonometria RepasoBladimir Wilder Brito100% (3)
- Aritmetica 11Documento6 páginasAritmetica 11vegacarlos89Aún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 7 Aritmetica Divisibilidad IDocumento7 páginasSemana 7 Aritmetica Divisibilidad IRolando Laura50% (2)
- PRUEBA Supletorio Matemática 9noDocumento7 páginasPRUEBA Supletorio Matemática 9noricard666Aún no hay calificaciones
- ALGEBRA CpuDocumento4 páginasALGEBRA CpuFrank Alex RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- 4 ÁlgebraDocumento30 páginas4 ÁlgebraRolando Antonio Escobar RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Teoria de Exponentes-1Documento6 páginasTeoria de Exponentes-1Jose Quiñonez Choquecota0% (1)
- Cepuns 2013-II Semana 11Documento5 páginasCepuns 2013-II Semana 11boc_55Aún no hay calificaciones
- Cuaderno Nivel Uno Crsito RedentorDocumento150 páginasCuaderno Nivel Uno Crsito RedentorMiguel Barba MontesAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica 2° Secundaria Coveñas SolucionarioDocumento148 páginasMatematica 2° Secundaria Coveñas SolucionarioLuis Armando Cuzco Trigozo78% (23)
- Solucionario Numeros ComplejosDocumento5 páginasSolucionario Numeros ComplejosAcademiapre CygnusAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesDe EverandProblemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (7)
- Métodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABDe EverandMétodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- La guía definitiva en Matemáticas para el Ingreso al BachilleratoDe EverandLa guía definitiva en Matemáticas para el Ingreso al BachilleratoCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (9)
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDe EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesAún no hay calificaciones
- La Guía Definitiva en Matemáticas para el Ingreso a la UniversidadDe EverandLa Guía Definitiva en Matemáticas para el Ingreso a la UniversidadCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (11)
- Petroglifos del Norte de Chile: Interpretación gráfica para su aplicación en Diseño, Arte y Artesanía.De EverandPetroglifos del Norte de Chile: Interpretación gráfica para su aplicación en Diseño, Arte y Artesanía.Aún no hay calificaciones
- NumeracionDocumento24 páginasNumeracionAnonymous 7za15o0100% (1)
- Copia de Promedios Verano 2014Documento3 páginasCopia de Promedios Verano 2014Anonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Certezas 2014Documento3 páginasCertezas 2014Anonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- NumeracionDocumento24 páginasNumeracionAnonymous 7za15o0100% (1)
- Certezas 2014Documento3 páginasCertezas 2014Anonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Numeracion Academia Circulo 2014Documento3 páginasNumeracion Academia Circulo 2014Anonymous 7za15o0100% (1)
- Numeracion Academia Circulo 2014Documento3 páginasNumeracion Academia Circulo 2014Anonymous 7za15o0100% (1)
- PorcentajeDocumento2 páginasPorcentajeAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ultimo NumeracionDocumento4 páginasUltimo NumeracionAnonymous 7za15o00% (1)
- Certeza SDocumento3 páginasCerteza SAnonymous 7za15o075% (8)
- Regla de TresDocumento4 páginasRegla de TresFranky Tello Buitrón43% (7)
- PROMEDIOSDocumento6 páginasPROMEDIOSAnonymous 7za15o067% (3)
- Suce SionesDocumento9 páginasSuce SionesBenito Quispe ValerianoAún no hay calificaciones
- NUMERACIONDocumento4 páginasNUMERACIONAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fracciones 2013 JulioDocumento3 páginasFracciones 2013 JulioAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Probabilidad e Inferencia Estadistica, Luis Santaló PDFDocumento140 páginasProbabilidad e Inferencia Estadistica, Luis Santaló PDFLuis CabreraAún no hay calificaciones
- Divisibilidad 3 Nivel UniDocumento3 páginasDivisibilidad 3 Nivel UniAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- COMPENDIO DE PSICOLOGiA PDFDocumento92 páginasCOMPENDIO DE PSICOLOGiA PDFDavid MeloAún no hay calificaciones
- Fracciones 2 2013Documento3 páginasFracciones 2 2013Anonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Conjunto SDocumento6 páginasConjunto SAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- DivisibilidadDocumento7 páginasDivisibilidadAnonymous 7za15o050% (4)
- 4 OperacionesDocumento3 páginas4 OperacionesAnonymous 7za15o0100% (3)
- Suce SionesDocumento9 páginasSuce SionesBenito Quispe ValerianoAún no hay calificaciones
- Conjunto SDocumento6 páginasConjunto SAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- PorcentajeDocumento2 páginasPorcentajeAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Certezas FEBREO 2013 ScribdDocumento5 páginasCertezas FEBREO 2013 ScribdAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- NUMERACIONDocumento4 páginasNUMERACIONAnonymous 7za15o0Aún no hay calificaciones
- PROMEDIOSDocumento6 páginasPROMEDIOSAnonymous 7za15o067% (3)
- Regla de TresDocumento4 páginasRegla de TresFranky Tello Buitrón43% (7)
- COMPENDIO DE PSICOLOGiA PDFDocumento92 páginasCOMPENDIO DE PSICOLOGiA PDFDavid MeloAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller MatematicasDocumento15 páginasTaller MatematicasEstiven AceroAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 1 Matematica 2do ModificadaDocumento1 páginaUnidad 1 Matematica 2do ModificadajuangabrieelAún no hay calificaciones
- Desafio Matematicos Media IIDocumento15 páginasDesafio Matematicos Media IIFabioLa Antonela Villena VillalobosAún no hay calificaciones
- Matemáticas Aplicadas A La Economía Y La AdministraciónDocumento93 páginasMatemáticas Aplicadas A La Economía Y La AdministraciónTesoreria LigaAún no hay calificaciones
- Planos TangentesDocumento27 páginasPlanos TangentesFleetAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Traslacion y Rotacion de EjesDocumento77 páginasEjercicios de Traslacion y Rotacion de EjesPedro Alonso Machuca GarcíaAún no hay calificaciones
- A.A. Integradora 3Documento17 páginasA.A. Integradora 3Miriam Elizabeth ColinAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de PorcentajesDocumento9 páginasEjercicios de PorcentajesMarianela Andrea Reyes Delgado33% (3)
- Curriculo Educacion Primaria Bolivariana. 2007Documento119 páginasCurriculo Educacion Primaria Bolivariana. 2007jorgelina bolivarAún no hay calificaciones
- Prueba Matemática NT2Documento10 páginasPrueba Matemática NT2Nicole ZapataAún no hay calificaciones
- .Lab Mate IiDocumento6 páginas.Lab Mate IiJackeline Leshuga AzulAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuaderno de Trabajo 3 Matematicas Diarioeducacion Blog PDFDocumento214 páginasCuaderno de Trabajo 3 Matematicas Diarioeducacion Blog PDFmariveanAún no hay calificaciones
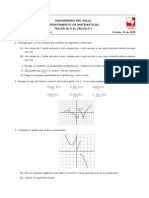
- Taller No 6. LimitesDocumento2 páginasTaller No 6. LimitesferAún no hay calificaciones
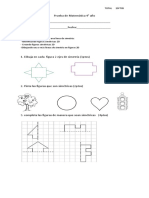
- Prueba de Matemática 4Documento2 páginasPrueba de Matemática 4Flor RomanAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller IIIDocumento5 páginasTaller IIICrizz CRAún no hay calificaciones
- DeterminantesDocumento9 páginasDeterminantesAlgebra Lineal(gr5)Aún no hay calificaciones
- 05 BacktrackingDocumento75 páginas05 BacktrackingPedro MenéndezAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 Matematicos y Sus AportesDocumento5 páginas5 Matematicos y Sus AportesYissel Taveras VillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Campos Escalares - 5Documento31 páginasCampos Escalares - 5Julian ScortechiniAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1 - S3 (Indicaciones)Documento1 páginaTarea 1 - S3 (Indicaciones)M Anuel Pc PorrasAún no hay calificaciones
- Expresiones AlgebraicasDocumento6 páginasExpresiones AlgebraicasEduardo AvicottAún no hay calificaciones
- Super Cies Cuadráticas: César BarrazaDocumento39 páginasSuper Cies Cuadráticas: César BarrazaJULIO CESAR BARRAZA BERNAOLAAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 Big DataDocumento2 páginasTaller 1 Big DataArley ValenzuelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematicas para Economistas Capitulo 6Documento23 páginasMatematicas para Economistas Capitulo 6Alvaro ChevalierAún no hay calificaciones
- Topología en Espacios MétricosDocumento5 páginasTopología en Espacios MétricosluisarbertosilvaAún no hay calificaciones
- Mentes BrillantesDocumento4 páginasMentes BrillantesSilvia Stella CARO CARDONAAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 5Documento6 páginasTaller 5Fundacion SireAún no hay calificaciones
- Cap 1 Al 6 PDFDocumento110 páginasCap 1 Al 6 PDFMaria RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de Puntos Evaluables - Escenario 6 - PRIMER BLOQUE-CIENCIAS BASICAS - VIRTUAL - MÉTODOS NUMÉRICOS - (GRUPO B01) 2Documento7 páginasActividad de Puntos Evaluables - Escenario 6 - PRIMER BLOQUE-CIENCIAS BASICAS - VIRTUAL - MÉTODOS NUMÉRICOS - (GRUPO B01) 2Carlos Yesid Ascencio CelyAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratorio Cali 2022Documento8 páginasLaboratorio Cali 2022Nikol CubidesAún no hay calificaciones