Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
15 - Continuacion de Continuidad
15 - Continuacion de Continuidad
Cargado por
moises borjas0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
7 vistas2 páginasNotas tomadas en clase
Título original
15- Continuacion de Continuidad
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoNotas tomadas en clase
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
7 vistas2 páginas15 - Continuacion de Continuidad
15 - Continuacion de Continuidad
Cargado por
moises borjasNotas tomadas en clase
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 2
MM201 1 de octubre
Seguimos el tema de continuidad.
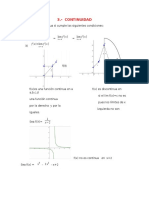
Determine si la función es continua en el punto
indicado:
x + 1 , x −1
f (x) = −1, x = −1 en x = −1
−1 − x 2 , x −1
f (−1) = −1
lim− x + 1 = −1, lim+ − 1 − x 2 = −2;
x →−1 x →−1
-1 -2 por tanto el limite no existe!
por tanto tiene discontinuidad no removible
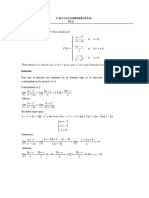
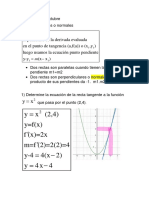
Determine los valores de a y b
tal que la función sea continua en todo su dominio:
ax + 2, x 1
2
f(x)= x − 2 x + 4,1 x 3
x − b, x 3
en x=1: f(1)=3, lim− ax + 2 = a + 2, lim+ x 2 − 2 x + 4 = 3; a+2=3 a=1
x →1 x →1
en x=3; f(3)=7, lim− x 2 − 2 x + 4 = 7, lim+ x − b = 3 − b; 3-b=7 b=-4
x →3 x →3
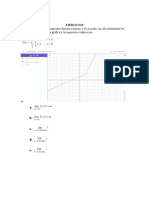
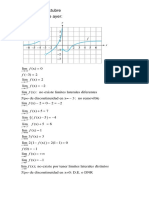
lim f (x) = 0
x →−
f (−3) = 2
lim f (x) = 2
x →−3−
lim f (x) = −2
x →−3+
lim f (x) : no existe limites laterales diferentes
x →−3
Tipo de discontinuidad en x= − 3 : no removible
lim f (x) − 2 = 0 − 2 = −2
x →−1
lim f (x) + 5 =
x →−3−
lim
x →−3−
4
3 ( f (x) − 5 ) =
lim f (x) + 5 =
x →−3−
lim f (x) =
x →+
lim 3 f (x) =
x →+
lim 2 (1 − f (x) ) =
x →+
f (0) =
lim f (x) =
x → 0−
lim f (x) =
x → 0+
lim f (x) =
x →0
Tipo de discontinuidad en x=0:
También podría gustarte
- Repartido 07 Funciones ContinuasDocumento1 páginaRepartido 07 Funciones Continuasjonatan juarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Casos Veridicos de Corrupcion en HondurasDocumento6 páginasCasos Veridicos de Corrupcion en Hondurasmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios 2. LímitesDocumento4 páginasEjercicios 2. LímitesIgnacioAún no hay calificaciones
- Entrega 2Documento5 páginasEntrega 2Jose londoñoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de Análsis MatemáticoDocumento4 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de Análsis MatemáticoMamunia MorrocoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Propuestos. ContinuidadDocumento3 páginasEjercicios Propuestos. ContinuidadMario ZañartuAún no hay calificaciones
- Algunos Ejercicios Resueltos de MatemáticaDocumento4 páginasAlgunos Ejercicios Resueltos de MatemáticaMamunia MorrocoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Varios de DerivacionDocumento8 páginasEjercicios Varios de DerivacionalexAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo DiferencialDocumento10 páginasCalculo DiferencialKaren VasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- 3.4.5.6 (Falta) 7.8, 9,10 .11.12.13 .14 .15 .16.17.18.19Documento109 páginas3.4.5.6 (Falta) 7.8, 9,10 .11.12.13 .14 .15 .16.17.18.19Carlita MelisaAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo Dif2Documento1 páginaCalculo Dif2HugoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1Documento11 páginasTarea 1Abdul OnofaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía No 2 - Límites Laterales y Continuidad PDFDocumento9 páginasGuía No 2 - Límites Laterales y Continuidad PDFLeo RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Limites Infinitos y Asintotas Verticales - Grupo Daniel Leon, Viviana Rodriguez, Andrea Valencia, Nataly RomeroDocumento8 páginasTaller Limites Infinitos y Asintotas Verticales - Grupo Daniel Leon, Viviana Rodriguez, Andrea Valencia, Nataly RomeroMARITZA NIPIAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia AnalisisDocumento5 páginasGuia AnalisisdavidAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctico III Funciones y Gráficas I-2023Documento3 páginasPráctico III Funciones y Gráficas I-2023MALDONADO ARRAYASA JOHN JOSIASAún no hay calificaciones
- Sea F La Función Definidacomo: F (X) Ax BX, X 1Documento3 páginasSea F La Función Definidacomo: F (X) Ax BX, X 1Axel LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 2-Límites AsisntotasDocumento2 páginasSemana 2-Límites AsisntotasPatrik SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Pc2-Solucionario Profesor 2021-2Documento5 páginasPc2-Solucionario Profesor 2021-2Marcos E Inga GuzmanAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 2 Calculo DiferencialDocumento7 páginasTaller 2 Calculo DiferencialCrIstianDaVidThOmasAún no hay calificaciones
- Limites (General)Documento11 páginasLimites (General)Luis Abel Martinez RiquelmeAún no hay calificaciones
- Primera Pr+íctica Integrada de 2015-2Documento4 páginasPrimera Pr+íctica Integrada de 2015-2Jose Ames LauraAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase Practica SEM-.2Documento3 páginasClase Practica SEM-.2Sebastian F. VillarrealAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 2 Calculo I.pdf EMIDocumento6 páginasPractica 2 Calculo I.pdf EMIRosana FactorAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Limites de Funciones 1Documento4 páginasGuia Limites de Funciones 1evaristoAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia de ContinuidadDocumento2 páginasGuia de ContinuidadCara ReforzamientoAún no hay calificaciones
- mr2 178 179 2008 1Documento6 páginasmr2 178 179 2008 1Anya GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Fin Del Bloque IDocumento6 páginasFin Del Bloque Ibadreddine gomiAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 3Documento11 páginasGuia 3Camila Marmolejo VergaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Lim Sol 1Documento8 páginasLim Sol 1Denis GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia ContinuidadDocumento3 páginasGuia Continuidadboris peñaAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivabilidad de Una FunciónDocumento4 páginasDerivabilidad de Una FunciónJose Llamas AragonésAún no hay calificaciones
- ExtremosDocumento12 páginasExtremosdanAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller N10Documento3 páginasTaller N10Camila Valeria Ruiz RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de DerivadasDocumento11 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de Derivadasgergo_351Aún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Practica 9-Ing. Industrial 2022-IDocumento3 páginasGuía Practica 9-Ing. Industrial 2022-IEl Lol :v :vAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo Diferencial Estudiante 4Documento8 páginasCalculo Diferencial Estudiante 4GERARSDOAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo de Aula. Derivada Aplicada A Los Negocios - Máximos y MínimosDocumento4 páginasTrabajo de Aula. Derivada Aplicada A Los Negocios - Máximos y MínimosJean CordovaAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica 2 (Matemática I - UNSAM)Documento7 páginasPráctica 2 (Matemática I - UNSAM)Eugenia De PalmaAún no hay calificaciones
- MAT-I Límites y Continuidad - Ejercicios PropuestosDocumento11 páginasMAT-I Límites y Continuidad - Ejercicios PropuestosmarlinAún no hay calificaciones
- Hoja 5 ContinuidadDocumento3 páginasHoja 5 ContinuidadSteven JosueAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematicas Resueltos (Soluciones) Límites de Funciones - Continuidad 1º BachilleratoDocumento36 páginasMatematicas Resueltos (Soluciones) Límites de Funciones - Continuidad 1º Bachilleratomanuel_valle_433% (9)
- TP 2 LimiteDocumento7 páginasTP 2 Limiteguido pavanelAún no hay calificaciones
- Respuestas 2023 2C 1parcial Tema4Documento2 páginasRespuestas 2023 2C 1parcial Tema4Sara SiebenharAún no hay calificaciones
- TP1 Mii 2018 PDFDocumento2 páginasTP1 Mii 2018 PDFmarianaAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen de Límites y ContinuidadDocumento1 páginaExamen de Límites y ContinuidadsecretariaiesvilladevicarAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 Lim Cont EbauDocumento7 páginas5 Lim Cont EbauCARLOS MOLINAAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Aplicativos Cáalculo DiferencialDocumento5 páginasEjercicios Aplicativos Cáalculo DiferencialMarden Puerta ChoctalinAún no hay calificaciones
- MateDocumento10 páginasMate3333Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Estudiante 2 Tarea 4.Documento6 páginasEjercicios Estudiante 2 Tarea 4.Caro ParraAún no hay calificaciones
- Dcdi U2 A3 JufmDocumento5 páginasDcdi U2 A3 JufmJuan Alberto Frías MajulAún no hay calificaciones
- Graficar en GeoGebra La Siguiente Función A TrozosDocumento9 páginasGraficar en GeoGebra La Siguiente Función A TrozosDarwin Andres Beleño GuillenAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 2b - Estudiante 3Documento12 páginasTarea 2b - Estudiante 3andres SuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplos de continuidad de funciones por partes: ayb x=−1 y x=2. xϵ f x xϵ xϵ f x x x=−1Documento3 páginasEjemplos de continuidad de funciones por partes: ayb x=−1 y x=2. xϵ f x xϵ xϵ f x x x=−1eduardo rodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Exam Enc Ál CuloDocumento6 páginasExam Enc Ál CuloMiky SaezAún no hay calificaciones
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDe EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesAún no hay calificaciones
- Respuestas Del Capitulo 1Documento5 páginasRespuestas Del Capitulo 1moises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Repaso de Cápitulo 3Documento5 páginasRepaso de Cápitulo 3moises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 24 - Derivacion LogaritmicaDocumento2 páginas24 - Derivacion Logaritmicamoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen de Contabilidad 2Documento2 páginasExamen de Contabilidad 2moises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 18 - Formulas Basicas de DerivacionDocumento2 páginas18 - Formulas Basicas de Derivacionmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Encuesta A Los ClientesDocumento3 páginasEncuesta A Los Clientesmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Lineamientos Investigación A01Documento1 páginaLineamientos Investigación A01moises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Conceptos para EstudiarDocumento2 páginasConceptos para Estudiarmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 16 - Continuidad (Graficas)Documento3 páginas16 - Continuidad (Graficas)moises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 27 - Repaso de Implicita y LogaritmicaDocumento3 páginas27 - Repaso de Implicita y Logaritmicamoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 13 - Limites Trigonometricos (Ejercicios de La Guia Metodologica)Documento1 página13 - Limites Trigonometricos (Ejercicios de La Guia Metodologica)moises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 43 - Integrales de Funciones ExponencialesDocumento2 páginas43 - Integrales de Funciones Exponencialesmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 29 - Rectas Tangentes o NormalesDocumento3 páginas29 - Rectas Tangentes o Normalesmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 14 - ContinuidadDocumento2 páginas14 - Continuidadmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 22 - Repaso de FTI y Funciones ExponencialesDocumento2 páginas22 - Repaso de FTI y Funciones Exponencialesmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 9 - Ejercicios Con Limites Al InfnitoDocumento1 página9 - Ejercicios Con Limites Al Infnitomoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 30 - Continuacion de Rectas Tangentes o NormalesDocumento2 páginas30 - Continuacion de Rectas Tangentes o Normalesmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 - Mayor Entero y Limites Al InfinitoDocumento3 páginas7 - Mayor Entero y Limites Al Infinitomoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 - Limites y ContinuidadDocumento5 páginas2 - Limites y Continuidadmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 44 - Segunda Formula Fundamental de Calculo (Integral Definida)Documento4 páginas44 - Segunda Formula Fundamental de Calculo (Integral Definida)moises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Levic Borjas - Guía #1Documento7 páginasLevic Borjas - Guía #1moises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- 45 - Area Entre CurvasDocumento8 páginas45 - Area Entre Curvasmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- La Carta de La TierraDocumento7 páginasLa Carta de La Tierramoises borjas100% (1)
- Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Honduras Facultad de Ciencias EconómicasDocumento3 páginasUniversidad Nacional Autónoma de Honduras Facultad de Ciencias Económicasmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tipos de Computadoras CuánticasDocumento4 páginasTipos de Computadoras Cuánticasmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Chuck HallDocumento2 páginasChuck Hallmoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones
- Centro de ComputoDocumento2 páginasCentro de Computomoises borjasAún no hay calificaciones