Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Problemas Tema 09 01
Cargado por
Edward LeoDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Problemas Tema 09 01
Cargado por
Edward LeoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
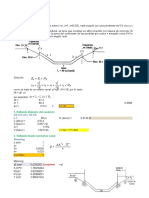
Ejercicio 1: Calcular la lectura de los tres amperímetros:
I1
R A1
I2
S A2
I3
T A3
230 V
50 Hz
M M
3
10 CV 2 CV
cos ϕ = 0,8 cos ϕ = 0,9
η = 0,9 η=1
Solución:
UL = 230 V
R R
S S
T T
N N
R S
230 V 230 120 V
P = 8177,8 W CV 10 P= 1472 W CV 2
fdp= 0,8 h= 0,9 fdp = 0,9 h= 1
UL = 230 V UL = 230 V
P= 8177,8 W j = 0,644 rad P= 1472 W j = 0,451 rad
Q= 6133,3 Var j = 36,87 º Q = 712,92 Var j = 25,842 º
S= 10222 VA IL= 25,66 A S = 1635,6 VA IL= 7,1111 A
Estrella equivalente Z = 32,344 25,84 º = 29,109 + 14,1 j
UF = 132,79 V IF = 25,66 A
ZE = 5,175 36,8699 º = 4,14 + 3,105 j URS = 230 120 º = -115 + 199,2 j
Triangulo equivalente IRS = 7,1111 94,16 º = -0,516 + 7,092 j
UF = 230 V IF = 14,81 A
ZT = 15,525 36,8699 º = 12,42 + 9,315 j
I1 = 25,66 53,1301 º = 15,40 + 20,53 j I1 = 7,1111 94,16 º = -0,516 + 7,092 j
I2 = 25,66 -66,8699 º = 10,08 + -23,60 j I2 = 7,1111 274,2 º = 0,5156 + -7,092 j
I3 = 25,66 -186,87 º = -25,48 + 3,07 j I3 = 0 0º = 0 + 0j
Aplicando el primer lema a cada fase obtenemos las intensidades totales:
IT1 = 31,374 61,69 º = 14,88 + 27,62 j Lectura de A1: 31,4 A
IT2 = 32,467 289,05 º = 10,60 + -30,69 j Lectura de A2: 32,5 A
IT3 = 25,660 173,13 º = -25,48 + 3,07 j Lectura de A3: 25,7 A
También podría gustarte
- Problemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesDe EverandProblemas resueltos de Hidráulica de CanalesCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (7)
- Problemas de Conceptos Basicos Unidad 1 StenvensonDocumento11 páginasProblemas de Conceptos Basicos Unidad 1 StenvensonLaex ChepAún no hay calificaciones
- Problema de TransformadorDocumento8 páginasProblema de TransformadorRicardo NuñezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 05 GrupoDocumento14 páginasTarea 05 GrupoPiero Molina100% (2)
- Tarea 4 de Arquitectura Sistemas - CorreccionesDocumento8 páginasTarea 4 de Arquitectura Sistemas - CorreccionesAlejandro ZapataAún no hay calificaciones
- Tutorial para Resolver Ecuaciones Diferenciales Usando MATLABDocumento7 páginasTutorial para Resolver Ecuaciones Diferenciales Usando MATLABAkademus GalileoAún no hay calificaciones
- Prob Trifasicos AlumnosDocumento14 páginasProb Trifasicos AlumnosEdwin SalomónAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase Junio 30 Ejercicio Pruebas de Transformador MonofásicoDocumento10 páginasClase Junio 30 Ejercicio Pruebas de Transformador MonofásicoEdward David Martinez RuizAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario Febrero 2024Documento78 páginasSolucionario Febrero 2024pevire81Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electrotecnia Solucionario Electrotecnia ParaninfoDocumento75 páginasElectrotecnia Solucionario Electrotecnia ParaninfoLuis LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Problema 11 Circuitos 2 TrifasicosDocumento7 páginasProblema 11 Circuitos 2 TrifasicosxrexAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios TransformadorDocumento4 páginasEjercicios TransformadorLeonardo Núñez LópezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cap. 1 SMRDocumento3 páginasCap. 1 SMRJack MondragonAún no hay calificaciones
- Parcial 11 ResolucionDocumento5 páginasParcial 11 ResolucionFede CasconAún no hay calificaciones
- Problema #28Documento3 páginasProblema #28rodrigo.nievasAún no hay calificaciones
- TP 6 ElectrotecniaDocumento9 páginasTP 6 Electrotecnialucas100% (1)
- Informe CircuitoDocumento21 páginasInforme CircuitoKatymax ArguelloAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Fisicoquimica 2.1Documento7 páginasEjercicios Fisicoquimica 2.1Jefersson Asis LunarejoAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 20. Potencia en Circuitos de CDDocumento7 páginasActividad 20. Potencia en Circuitos de CDJesus MateoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica DirigidaDocumento5 páginasPractica DirigidaMB LegendsAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Final Electronica de Potencia AndresDocumento23 páginasTaller Final Electronica de Potencia AndresgerardogusiAún no hay calificaciones
- DLT115 Examen2-2019-Repetido-SolucionDocumento4 páginasDLT115 Examen2-2019-Repetido-Solucionnoel antonio Ramos100% (1)
- Maq Elect P1 SoluciónDocumento12 páginasMaq Elect P1 SoluciónMarcos Huaman AarujoAún no hay calificaciones
- Circuitos RL y RC en paraleloDocumento12 páginasCircuitos RL y RC en paraleloLaura Valentina ARTEAGA FUENTESAún no hay calificaciones
- Efis U2 A2 JucaDocumento8 páginasEfis U2 A2 JucaJulio C. Chan AngelesAún no hay calificaciones
- Cap. 7 de La Electrotecnia de José RedondoDocumento10 páginasCap. 7 de La Electrotecnia de José RedondoGilber MesiasAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Laboratorio 8 OR19020 SS19035Documento17 páginasGuia Laboratorio 8 OR19020 SS19035Samuel Elias Osorto RiveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Alex Herrera Soto 15896610 CORRIENTE ALTERNA EnviadoDocumento7 páginasAlex Herrera Soto 15896610 CORRIENTE ALTERNA EnviadoAlex Andres Herrera SotoAún no hay calificaciones
- TP 2 CompletoDocumento9 páginasTP 2 CompletolucasAún no hay calificaciones
- Transformador 50 KVADocumento8 páginasTransformador 50 KVAMarcos Huaman AarujoAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculos eléctricos de receptores trifásicosDocumento6 páginasCálculos eléctricos de receptores trifásicosOscar PradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Zener, Filtros, Reguladores y TrifásicosDocumento43 páginasZener, Filtros, Reguladores y TrifásicosmkjAún no hay calificaciones
- Vacio y Corto de 3fsicoDocumento10 páginasVacio y Corto de 3fsicoLuis miguelAún no hay calificaciones
- Deasarrollo de Puntos Tarea 3Documento19 páginasDeasarrollo de Puntos Tarea 3victorever01Aún no hay calificaciones
- AdsfasdfasdasdDocumento8 páginasAdsfasdfasdasdÁngel Peinado DíazAún no hay calificaciones
- Circuitos en serie y paraleloDocumento10 páginasCircuitos en serie y paraleloJeisson MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario Electrotecnia PDFDocumento72 páginasSolucionario Electrotecnia PDFTina Norris100% (1)
- Codigo V15284373 326Documento9 páginasCodigo V15284373 326HEDDIE ELIZABETH MONASTERIO MEDINAAún no hay calificaciones
- Sifon InvertidoDocumento7 páginasSifon Invertidosamir0% (1)
- Diseño de Maquinas, TrabajoDocumento4 páginasDiseño de Maquinas, TrabajoOmar MontufarAún no hay calificaciones
- Diodo de Libre Circulación 3.14Documento4 páginasDiodo de Libre Circulación 3.14Jonathan Vasquez LAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen EjerciciosDocumento20 páginasExamen EjerciciosAnthony CabezasAún no hay calificaciones
- InformeDocumento12 páginasInformeFabianAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Terminado Corriente Alterna n-3Documento16 páginasTrabajo Terminado Corriente Alterna n-3ORLANDOAún no hay calificaciones
- William Sneyder Suarez Leon Taller de Circuitos RLDocumento26 páginasWilliam Sneyder Suarez Leon Taller de Circuitos RLSneyder SuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1Documento5 páginasTarea 1Sergio GutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- C14 T AGuaman ESulcaDocumento5 páginasC14 T AGuaman ESulcaEdwin SuárezAún no hay calificaciones
- Escenario 6 Fisica II FinalDocumento21 páginasEscenario 6 Fisica II FinalLeidy AyalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe Práctica 1 Electro 2 FinalDocumento19 páginasInforme Práctica 1 Electro 2 Finalhenrycash23Aún no hay calificaciones
- Resolucion de Ejercicios de CondensadoresDocumento3 páginasResolucion de Ejercicios de CondensadoresAntonio Gonzalo Arispe PatonAún no hay calificaciones
- 20 Ejercicios 1Documento4 páginas20 Ejercicios 1alvaro huamánAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe 7 Velarde y ClodomiroDocumento37 páginasInforme 7 Velarde y ClodomiroSebastiam VelardeAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuestionario 6Documento4 páginasCuestionario 6Giovanna Antonella Adorno BogadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 2 Lab ElectrotecniaDocumento16 páginasPractica 2 Lab ElectrotecniastephanyAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos-1-28Documento26 páginasEjercicios Resueltos-1-28alder anthony anahueAún no hay calificaciones
- Grupal - 2150502 - 5 2 ELECTRICIDADDocumento32 páginasGrupal - 2150502 - 5 2 ELECTRICIDADlina marcela arias jaramilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Circuitos 1.8 A 1.24Documento8 páginasCircuitos 1.8 A 1.24Isabela VázquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos IieeDocumento41 páginasEjercicios Resueltos IieeJavier Quispe ValenciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario 2da Práctica de Máquinas Eléctricas EE-211 2019-IIDocumento8 páginasSolucionario 2da Práctica de Máquinas Eléctricas EE-211 2019-IILucho_del_PeruAún no hay calificaciones
- Diagrama Cuerpo LibreDocumento7 páginasDiagrama Cuerpo LibrearmandoAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucion Examen 14 ADocumento4 páginasSolucion Examen 14 AMimi KaAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual Tecnico de Instalaciones ElectricasDocumento614 páginasManual Tecnico de Instalaciones ElectricasWilmer Susano100% (5)
- Área Transversal de Un Cable y Su Calibre AWG (American Wire Gauge)Documento5 páginasÁrea Transversal de Un Cable y Su Calibre AWG (American Wire Gauge)didioAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia para La Presentacion de Proyectos V2 15 Enero 2018Documento33 páginasGuia para La Presentacion de Proyectos V2 15 Enero 2018Jose RicardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Transform AdoresDocumento93 páginasTransform AdoresLuceroMilagrosCubaMirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- PROBLEMAS DE CIRCUITOS Y SISTEMAS DIGITALES (Carmen Baena - Varios) - (LIBRO - ESP - SCAN)Documento396 páginasPROBLEMAS DE CIRCUITOS Y SISTEMAS DIGITALES (Carmen Baena - Varios) - (LIBRO - ESP - SCAN)Juan Pablo Argote Ortiz100% (7)
- Métodos Numéricos Con MATLAB - Mathews-FinkDocumento730 páginasMétodos Numéricos Con MATLAB - Mathews-FinkGonzalo195996% (25)
- TransformadoresDocumento37 páginasTransformadoresFernando Tato UriburuAún no hay calificaciones
- Ra8 030 Selección Conexión Medidores Transformadores MedidaDocumento54 páginasRa8 030 Selección Conexión Medidores Transformadores MedidaLuis Cesar VaPi100% (1)
- Apuntes MATLABMOMDocumento142 páginasApuntes MATLABMOMJuan Ruiz TelloAún no hay calificaciones
- Transform AdoresDocumento93 páginasTransform AdoresLuceroMilagrosCubaMirandaAún no hay calificaciones
- El Método de La Secante y Secante ModificadoDocumento15 páginasEl Método de La Secante y Secante ModificadoJhonnatan PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodos Numericos Con Aplicaciones en MatlabDocumento13 páginasMetodos Numericos Con Aplicaciones en MatlabEdgarGuerrero2140% (5)
- An Lisis Transitorio de Circuitos Primer y Segundo OrdenDocumento46 páginasAn Lisis Transitorio de Circuitos Primer y Segundo OrdenNeorgi O. GAún no hay calificaciones
- PROBLEMAS PROPUESTOSportada - TransformadoresDocumento74 páginasPROBLEMAS PROPUESTOSportada - TransformadoresJulián FumarolaAún no hay calificaciones
- InterpolaciónDocumento17 páginasInterpolaciónEdward LeoAún no hay calificaciones
- Asociación muelles serie paraleloDocumento3 páginasAsociación muelles serie paraleloEdward LeoAún no hay calificaciones
- U4 Medicion de NIVELDocumento14 páginasU4 Medicion de NIVELGustavo WilVen VelasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- MA-1112 Mike Guía de Ejercicios PDFDocumento33 páginasMA-1112 Mike Guía de Ejercicios PDFredrogo1234Aún no hay calificaciones
- U4 Medicion de NIVELDocumento14 páginasU4 Medicion de NIVELGustavo WilVen VelasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Factores IntegrantesDocumento3 páginasFactores IntegrantesMamuchis PolancoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sistema de Ecuaciones No LinealesDocumento6 páginasSistema de Ecuaciones No LinealesEdward LeoAún no hay calificaciones
- Métodos Numéricos en Los Lenguajes Matlab y Microsoft Visual CDocumento403 páginasMétodos Numéricos en Los Lenguajes Matlab y Microsoft Visual CAndrew MylesAún no hay calificaciones
- Asociación muelles serie paraleloDocumento3 páginasAsociación muelles serie paraleloEdward LeoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tranformador TrifasicoDocumento9 páginasTranformador TrifasicoCesar KwAún no hay calificaciones
- Comandos Ejemplo MatlabDocumento46 páginasComandos Ejemplo MatlabBlady Blady PAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejemplos SimulinkDocumento99 páginasEjemplos SimulinkMax SantiagoAún no hay calificaciones
- 01 Estudio General de Corto Circuito PDFDocumento12 páginas01 Estudio General de Corto Circuito PDFCarlos AimaAún no hay calificaciones