Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
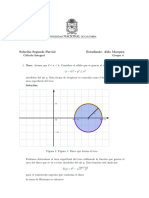
Apuntes Fracciones Parciales Caso 2
Cargado por
Daniel Felipe Quintero Jimenez0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
66 vistas3 páginasEste resumen describe el caso 2 de fracciones parciales con factores lineales repetidos. Se presentan las ecuaciones para formar las integrales parciales y luego las ecuaciones lineales para identificar los valores de los coeficientes A, B y C.
Descripción original:
Título original
apuntes fracciones parciales caso 2
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoEste resumen describe el caso 2 de fracciones parciales con factores lineales repetidos. Se presentan las ecuaciones para formar las integrales parciales y luego las ecuaciones lineales para identificar los valores de los coeficientes A, B y C.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
66 vistas3 páginasApuntes Fracciones Parciales Caso 2
Cargado por
Daniel Felipe Quintero JimenezEste resumen describe el caso 2 de fracciones parciales con factores lineales repetidos. Se presentan las ecuaciones para formar las integrales parciales y luego las ecuaciones lineales para identificar los valores de los coeficientes A, B y C.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 3
𝐹𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑒𝑠 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑐𝑖𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑐𝑎𝑠𝑜 2 Caso 2: Factores lineales repetidos
𝑥 4 − 2𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 + 1 5. Formar las fracciones parciales
න 3 𝑑𝑥
𝑥 − 𝑥2 − 𝑥 + 1 DENOMINADOR 4𝑥 4𝑥 4𝑥
1. DIVISIÓN = =
𝑥 3 −𝑥 2 −𝑥+1 (x−1)(x−1)(x+1) (x−1)2 (x+1)
𝑥4 + −2𝑥 2 + 4𝑥 + 1 𝑥 3 − 𝑥 2 − 𝑥 + 1
4𝑥 𝐴 𝐵 𝑐
−𝑥 4 + 𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 -x X +1 =
(x−1)
+ 2 +
𝑥 3 -𝑥 2 +3x +1
COCIENTE (x−1)2 (x+1) x−1 (x+1)
−𝑥 3 + 𝑥 2 + 𝑥 − 1 4𝑥 𝐴 𝑐 𝐷 𝐵 𝐸 𝑓
4𝑥 = + + + 2 ++
3 x−1 4 (x+1) x+1 2
2 (x−1) x−1 x−1
2. Formar las integrales (x−1) x+1
4
4𝑥 EXPLICACIÓN DE OTRO EJERCICIO
න𝑋 + 1 + 3 2 dx
𝑥 −𝑥 −𝑥+1 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑜𝑟
4𝑥 4𝑥 𝐴 𝐵 𝐶
(x−1)2 (x+1) = (x−1) + x−1 2 (x+1)
න𝑋𝑑𝑥 +න1𝑑𝑥 + dx + x−1 4 x+1 2
𝑥 3 −𝑥 2 −𝑥+1
3. Resolver las integrales que se puedan
En el denominador solamente
𝑥1+1 (x+1) x−1 2 4𝑥 𝐴(x+1)(x−1) +B(x+1)+C x−1 2
se multiplica los factores que
+ 1 න𝑑𝑥 = 2 tengan la potencia mayor y
1+1 (x−1) (x−1)2 (x+1) x−1 (x+1) que no se repitan
𝑥2 x (x+1) x−1 2 4𝑥 = A(x+1)(x-1)+B(x+1)+C x−1 2
+ 𝑥3 − 𝑥2 − 𝑥 + 1
2 (x−1)
𝑥 2 (x-1) - 1(x-1) 4𝑥 = A(𝑥 2 -x +x −1) +Bx+B+C(𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 + 1)
(x+1)(x-1) 4𝑥 = A(𝑥 2 −1) +Bx+B+C(𝑥 2 − 2𝑥 + 1)
4. Identificar (x-1) (𝑥 2 −1)
el caso
(x-1) (x-1)(x+1) 4𝑥 = A𝑥 2 −A + Bx +B +C𝑥 2 − 2𝐶𝑥 + 𝐶
4𝑥 = A𝑥 2 +C𝑥 2 + B𝑥 − 2𝐶𝑥 − A +B + 𝐶
4𝑥 = 𝑥 2 (A+C)+ x(B − 2𝐶) − A +B + 𝐶
𝐹𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑒𝑠 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑐𝑖𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑐𝑎𝑠𝑜 2
3. FORMAR LAS ECUACIONES LINEALES
Caso 2: Factores lineales repetidos CASO 2
4𝑥
4𝑥 = 𝑥 2 (A+C)+ x(B − 2𝐶) − A +B + 𝐶 න𝑋𝑑𝑥 + න1𝑑𝑥 + 𝑥 3 −𝑥 2 −𝑥+1 dx
0 = A+C 0 = A 0 +C 𝐴 𝐵 𝑐
𝑥2 + x + ( x−1) + +
4 = B − 2𝐶 4 = 0 + B − 2𝐶 2 x−1 2
(x+1) dx
0 = − A +B + 𝐶 0 =−A+B +𝐶 𝑥2 1 2 −1
+ x + ( x−1) 𝑑𝑥 + 2 dx + 𝑥 +1dx
2 x−1
0 = A+C 𝑢 = 𝑥−1 𝑢 = 𝑥−1 𝑢 = 𝑥+1
−𝐶 = A 𝑑𝑢 𝑑𝑢
=1
𝑑𝑢
=1
=1 𝑑𝑥
𝑑𝑥 𝑑𝑥
0 = − A +B + 𝐶
du= 𝑑𝑥 du= 𝑑𝑥 du= 𝑑𝑥
0 = − (−C) +B + 𝐶 1 2 −1
න 𝑑𝑢
𝑢 + න
𝑢2
𝑑𝑢 + න
𝑢
𝑑𝑢
0 = +C +B + 𝐶 න 𝑢−1 𝑑𝑢 2 න 𝑢−2 𝑑𝑢 − න 𝑢−1 𝑑𝑢
𝑢 −2+1
0 = +2C +B Ln u + 2 −2+1 -Ln u
−2𝐶 = B 2
𝑢 −1
−2𝐶 = B −1
−2(−1) = B Ln (x-1) +c -Ln (x+1) +c
−2𝑢−1
4 = B − 2𝐶 𝑥2 −2
2 = B + x +Ln (x-1) -Ln (x+1) +c
2 𝑢
4 = −2C − 2𝐶 −2
𝑥2 + x +Ln (x-1) -Ln (x+1) +c
𝑥−1
4 = −4C −𝐶 = A 2
4 −(−1)= A
=C 𝑥2 x−1 2
−4
1= A + x Ln − 𝑥−1 +c
-1= C 2 𝑥+1
https://www.calculadora-de-integrales.com/ https://es.symbolab.com/
7 𝐹𝑟𝑎𝑐𝑐𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑒𝑠 𝑝𝑎𝑟𝑐𝑖𝑎𝑙𝑒𝑠 𝑐𝑎𝑠𝑜 1 𝑥 2 + 3𝑥 − 10
න 2 𝑑𝑥
𝑥 + 3𝑥 − 10 DENOMINADOR 𝑥−2 𝑥+5
Caso 1:Factores lineales no repetidos
𝑥
Caso 1:Factores lineales no repetidos
Caso 3 𝑥2 + 5 𝑥−2
Caso 2 𝑥 + 5 2
Caso 2:Factores lineales repetidos 𝑥−2
Caso 2 𝑥 2 + 10𝑥 + 25 𝑥−2
Caso 3:Factores cuadráticos no repetidos
Caso 2 𝑥 + 5 𝑥 + 5 𝑥−2
Caso 4:Factores cuadráticos repetidos
Caso 1 𝑥+5 𝑥−2 𝑥+3 𝑥−7
Caso 2 10𝑥 𝑥−2 𝑥−2 𝑥−7
(x-1) (x-1) (x+1) Caso 4 𝑥2 + 5 4 𝑥−2
Caso 4 𝑥2 + 5 𝑥2 + 5 𝑥2 + 5 𝑥2 + 5 𝑥−2
𝑥2 − 4 3 𝑥−2
𝑥2 − 4 𝑥2 − 4 𝑥2 − 4 𝑥−2
𝑥−2 𝑥+2 𝑥−2 𝑥+2 𝑥−2 𝑥+2 𝑥−2
También podría gustarte
- Integración por sustitución y fracciones parciales: Ejercicio eDocumento8 páginasIntegración por sustitución y fracciones parciales: Ejercicio eAna DonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- 9 Tarea Intermedia 1Documento18 páginas9 Tarea Intermedia 1Anonymous TGUj4mSx0% (1)
- Calculo IntegralDocumento8 páginasCalculo Integralandres SuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- MA1111 2024 Ene-Mar 1ro SoluciónDocumento6 páginasMA1111 2024 Ene-Mar 1ro Solución22-10085Aún no hay calificaciones
- PRACTICA Nro 4 DERIVADASDocumento3 páginasPRACTICA Nro 4 DERIVADASed.l.deathnoteAún no hay calificaciones
- 2do - Parcial de Repaso MónicaDocumento3 páginas2do - Parcial de Repaso MónicaNico gianniciAún no hay calificaciones
- Apuntes Fracciones Parciales Caso 2Documento3 páginasApuntes Fracciones Parciales Caso 2Juan Waldo Gonzalez VacaAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo IntegralDocumento3 páginasCalculo IntegralGuillermo ChoezAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo StevensonDocumento6 páginasTrabajo StevensonJohn Stevenson Retalloud RinconAún no hay calificaciones
- Retroalimentacion Examen FinalDocumento6 páginasRetroalimentacion Examen Finalbryantesla98Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1-PRACTICO 1 Cálculo II 2022Documento2 páginas1-PRACTICO 1 Cálculo II 2022Valentin BeltranAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas de funciones algebraicas, exponenciales y logaritmosDocumento6 páginasDerivadas de funciones algebraicas, exponenciales y logaritmosRebe Ortega Miry PicadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones diferenciales: métodos de variables separables y homogéneasDocumento3 páginasEcuaciones diferenciales: métodos de variables separables y homogéneasDavid Mauricio RojasAún no hay calificaciones
- Integración por fracciones parciales y sustitución trigonométricaDocumento16 páginasIntegración por fracciones parciales y sustitución trigonométricaPablo UrbanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller de Derivadas.Documento7 páginasTaller de Derivadas.Alejandra VeraAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea Guia MM-411Documento14 páginasTarea Guia MM-411Willian Josue Ortez EucedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Integración de Funciones Racionales Por Fracciones ParcialesDocumento13 páginasIntegración de Funciones Racionales Por Fracciones ParcialesKeina SalinasAún no hay calificaciones
- Operaciones Con Funciones 2022Documento29 páginasOperaciones Con Funciones 2022Liceth Rosario Mamani SalvatierraAún no hay calificaciones
- Jonathan Riveros Tarea4Documento4 páginasJonathan Riveros Tarea4fabian riverosAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1 El Concepto IntegralDocumento21 páginasTarea 1 El Concepto IntegralManuela Bran RuedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo I Tarea 1Documento8 páginasCalculo I Tarea 1Lisette Johana Silva ManosalvaAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo semana N°4Documento5 páginasTrabajo semana N°4guillermo valenzuelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Suma de Riemann para integral definidaDocumento33 páginasSuma de Riemann para integral definidaJARITZA SANTAMARIA ARIZAAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller No. 1 MatematicaDocumento7 páginasTaller No. 1 Matematicabridis vasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1Documento6 páginasTarea 1Liliana GutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 3 Calculo Diferencial Luis Gael Lopez SalazarDocumento4 páginasActividad 3 Calculo Diferencial Luis Gael Lopez SalazarDylan López100% (1)
- Funciones Por TramosDocumento5 páginasFunciones Por TramosnadinanicAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Colaborativo Tarea 1Documento25 páginasTrabajo Colaborativo Tarea 1juliana combarizaAún no hay calificaciones
- Universidad Privada de Tacna Facultad de IngenieríaDocumento4 páginasUniversidad Privada de Tacna Facultad de IngenieríaDennise PazAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculo integral: Concepto de integral y métodos de resoluciónDocumento9 páginasCálculo integral: Concepto de integral y métodos de resoluciónLizeth Andrade AlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Jordan Pizarro Tareas4Documento5 páginasJordan Pizarro Tareas4Jordan PizarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 1 Ejercicios Derivadas - ResueltasDocumento4 páginasGuia 1 Ejercicios Derivadas - ResueltasLoreto PeñalozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Funciones UdDocumento2 páginasTaller Funciones Udandres felipe galindo duquinoAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo 6Documento19 páginasTrabajo 6Yelena Olivo Mora100% (1)
- Anexo 1. Ejemplos para EjerciciosDocumento4 páginasAnexo 1. Ejemplos para EjerciciosEmisora Comunitaria la UvitaAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas Estudiante 5 (Autoguardado)Documento7 páginasDerivadas Estudiante 5 (Autoguardado)Edilbeto SambonyAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesión 15 Integración Por Fracciones ParcialesDocumento26 páginasSesión 15 Integración Por Fracciones ParcialesAldair Edgar Verastegui RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas 2020 2 PDFDocumento3 páginasDerivadas 2020 2 PDFSherwin Brayan Barboza VasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas e integralesDocumento2 páginasDerivadas e integralesSantiago VarelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aporte Individual Martin Navas Ejercicios 2, 6 y 10Documento6 páginasAporte Individual Martin Navas Ejercicios 2, 6 y 10Martin NavasAún no hay calificaciones
- Dirección de Una CurvaDocumento10 páginasDirección de Una CurvaVane SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo ColaborativoDocumento7 páginasCalculo ColaborativoRuby Garnica GarnicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aporte 1Documento4 páginasAporte 1Fernanda CristanchoAún no hay calificaciones
- Listado 1 C1 (2023-2)Documento3 páginasListado 1 C1 (2023-2)AlexMvAún no hay calificaciones
- Grupo N°5 Actividad 4 FuncionesDocumento13 páginasGrupo N°5 Actividad 4 FuncionesBrayan stiven Torres sarayAún no hay calificaciones
- La Derivada de Un CocienteDocumento3 páginasLa Derivada de Un CocienteFernando GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1-Daniela Victoria DelgadoDocumento9 páginasTarea 1-Daniela Victoria DelgadoYesica Maria Calderon CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- EJERCICIOS MATES 1º BACH CCSS (Derivadas)Documento2 páginasEJERCICIOS MATES 1º BACH CCSS (Derivadas)MartaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculo Diferencial: Caratula - Geometría Y Trigonometría - Martin - Indd 5 10/08/15 14:46Documento81 páginasCálculo Diferencial: Caratula - Geometría Y Trigonometría - Martin - Indd 5 10/08/15 14:46Mónica Fabiola Teran EnriquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Parcial 1 ResueltoDocumento4 páginasParcial 1 ResueltoDeraald TasartirAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 2 - Métodos de IntegraciónDocumento6 páginasTarea 2 - Métodos de Integraciónyesica mendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea Semana 8 Ejercicios de Sección 3.9 Y 3.10Documento5 páginasTarea Semana 8 Ejercicios de Sección 3.9 Y 3.10MamamamaAún no hay calificaciones
- Deber 2 Derivada de Funciones CompuestasDocumento2 páginasDeber 2 Derivada de Funciones CompuestasAlex OmarAún no hay calificaciones
- Estudio Del Cambio ETP3Documento8 páginasEstudio Del Cambio ETP3dampro 28Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tabla Derivadas e IntegralesDocumento2 páginasTabla Derivadas e IntegralesAna Laura Garcia WeissiAún no hay calificaciones
- EcuacionesDiferencialesOrdinariasDocumento5 páginasEcuacionesDiferencialesOrdinariasNorbil Sarabia PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Final MatemáticaDocumento9 páginasFinal MatemáticaLeda CamposAún no hay calificaciones
- Tecnologías emergentes y su impactoDocumento3 páginasTecnologías emergentes y su impactoDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad No.3 Video Desarrollo Científico en ColombiaDocumento4 páginasActividad No.3 Video Desarrollo Científico en ColombiaDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Instalación de LinuxDocumento3 páginasInstalación de LinuxDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Importancia de La Comunicación AsertivaDocumento1 páginaImportancia de La Comunicación AsertivaDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Infografia Sobre La Sociedad Del ConocimientoDocumento4 páginasInfografia Sobre La Sociedad Del ConocimientoDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Es Posible Replantear Los Habitos Hacia La LecturaDocumento1 páginaEs Posible Replantear Los Habitos Hacia La LecturaDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Pregunta ForoDocumento1 páginaPregunta ForoDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tecnologías emergentes y su impactoDocumento3 páginasTecnologías emergentes y su impactoDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller de Directorios, Archivos, PermisosDocumento11 páginasTaller de Directorios, Archivos, PermisosDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- So 2021Documento2 páginasSo 2021Daniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Vista de InteracciónDocumento2 páginasVista de InteracciónDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Qué Implicaciones Éticas Tiene El UsoDocumento1 páginaQué Implicaciones Éticas Tiene El UsoDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Modelo de CascadaDocumento4 páginasModelo de CascadaDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Modelo de EspiralDocumento6 páginasModelo de EspiralDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller4 - Calc VectDocumento6 páginasTaller4 - Calc VectDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tecnicas de Levante de IformaciónDocumento2 páginasTecnicas de Levante de IformaciónDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller4 - Calc VectDocumento6 páginasTaller4 - Calc VectDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Caso de UsoDocumento5 páginasCaso de UsoDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cap 03 PDFDocumento35 páginasCap 03 PDFAlejo PrietoAún no hay calificaciones
- Cap 03 PDFDocumento35 páginasCap 03 PDFAlejo PrietoAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller en ClaseDocumento1 páginaTaller en ClaseDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Area de Dos CurvasDocumento1 páginaArea de Dos CurvasDaniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Diagrama Grupo1Documento1 páginaDiagrama Grupo1Daniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 8Documento2 páginasTaller 8Daniel Felipe Quintero JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- 1er Boletin 1 AritmeticaDocumento14 páginas1er Boletin 1 AritmeticaSol TapullimaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía Didáctica 3 Métodos de Factorización DiferentesDocumento15 páginasGuía Didáctica 3 Métodos de Factorización DiferentesKirzy A MoralesAún no hay calificaciones
- FACTORIZACIONDocumento15 páginasFACTORIZACIONCarlos HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Simulacion de SotfwareDocumento18 páginasSimulacion de SotfwareCarmen Estupiñán HernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica para Contadores 1Documento36 páginasMatematica para Contadores 1Milagros Cbjl100% (5)
- Planteo de EcuacionesDocumento3 páginasPlanteo de EcuacionesKarl Franco Abt ReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- Oraciones Unimembres y BimembresDocumento25 páginasOraciones Unimembres y BimembresOtoniel Cal QuejAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía de Matemática Fracciones Algebraicas. 2Documento2 páginasGuía de Matemática Fracciones Algebraicas. 2Maria Loreto Gonzalez MercadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones CuadraticasDocumento11 páginasEcuaciones CuadraticasFulliniAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de La Guia - ImparesDocumento14 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de La Guia - ImparesMelisaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bimestre 3 Matematica Comp 2 2023Documento11 páginasBimestre 3 Matematica Comp 2 2023cataAún no hay calificaciones
- Booth Complemento A DosDocumento10 páginasBooth Complemento A DosJesus Eduardo Mutul GongoraAún no hay calificaciones
- sb1 2016 RM 02 PDFDocumento16 páginassb1 2016 RM 02 PDFAlex Robert Tang VenturonAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones_de_primer_gradoDocumento20 páginasEcuaciones_de_primer_gradocafe Sulma InternetAún no hay calificaciones
- EJERCICIOS, Operaciones Basicas de Matematicas, Métodos IDocumento6 páginasEJERCICIOS, Operaciones Basicas de Matematicas, Métodos IMarcialEduardoUrbinaMadridAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica Basica Tarea 1Documento4 páginasMatematica Basica Tarea 1wanderlin acostaAún no hay calificaciones
- Curso Piérdele El Miedo A Las MatesDocumento5 páginasCurso Piérdele El Miedo A Las MatesAldo Mariategui BurroAún no hay calificaciones
- Estructuras Aritméticas Propuesta de Encarnación CastroDocumento82 páginasEstructuras Aritméticas Propuesta de Encarnación CastroSammy Percy Merino RosarioAún no hay calificaciones
- PDF 1 Desigualdades Lineales 1variable m1 l2Documento17 páginasPDF 1 Desigualdades Lineales 1variable m1 l2Fabian Gomez AlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- División de PolinomiosDocumento3 páginasDivisión de PolinomiosLeonard mauricio Demanuel churaAún no hay calificaciones
- CT U1 - Matematica 6Documento83 páginasCT U1 - Matematica 6FELIPE CONTRERASAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Aditivos PDFDocumento76 páginasProblemas Aditivos PDFRosa de AméricaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de Puntos Evaluables - Escenario 6 - Segundo Bloque-Ciencias Basicas - Calculo I - (Grupo c01)Documento6 páginasActividad de Puntos Evaluables - Escenario 6 - Segundo Bloque-Ciencias Basicas - Calculo I - (Grupo c01)JENNY CANO POLOAún no hay calificaciones
- Numeros Decimales Sus Operaciones y PropiedadesDocumento27 páginasNumeros Decimales Sus Operaciones y PropiedadesOsmar Domingo Miguel CortésAún no hay calificaciones
- CLASE 1 - Razones y ProporcionesDocumento17 páginasCLASE 1 - Razones y ProporcionesAdrian HMAún no hay calificaciones
- Sistemas Numéricos y Códigos (Anotaciones)Documento57 páginasSistemas Numéricos y Códigos (Anotaciones)kevin isaiasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tema 4 - Conjuntos Numericos 1Documento15 páginasTema 4 - Conjuntos Numericos 1Sebastian Emiliano MedinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Criterios e Indicadores de Evaluación para Desarrollar Competencias MatemáticasDocumento9 páginasCriterios e Indicadores de Evaluación para Desarrollar Competencias MatemáticasOsman VillanuevaAún no hay calificaciones
- sb1 2016 A 01Documento13 páginassb1 2016 A 01Edinsson R. Javier VillanuevaAún no hay calificaciones
- Factorizacion Productos NotablesDocumento20 páginasFactorizacion Productos Notablesnando1953Aún no hay calificaciones