Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Funciones de Medio Rango PDF
Cargado por
Daniel CastañedaTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Funciones de Medio Rango PDF
Cargado por
Daniel CastañedaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Analogo a funciones de medio rango para funciones en intervalos infinitos.
In[ ]:= f[x_] = Piecewise-k*x , x > 0, {0, x < 0}
-k x x > 0
Out[ ]=
0 True
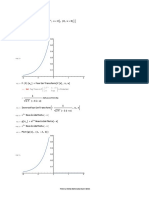
In[ ]:= Plot[f[x], {x, - 5, 5}]
In[ ]:= f[v]
-k v v > 0
Out[ ]=
0 True
extensión par, recordemos que la extension par cumple f p (x) = fp (- x),
por tanto si x < 0 entonces fp (x) = fp (- x) luego para x < 0 tenemos que
fp (x) = -2*(-x) = 2*x
In[ ]:= fp [x_] = Piecewise-2*x , x > 0, 2*x , x < 0
-2 x x > 0
Out[ ]= 2 x x<0
0 True
In[ ]:= Plotfp [x], {x, - 5, 5}
0.4
0.3
Out[ ]=
0.2
0.1
-4 -2 2 4
Extensión impar; recordemos que la extension impar cumple f i (- x) = - fi (x),
por tanto si x < 0 entonces fi (x) = - fi (- x) luego para x < 0 tenemos que
fi (x) = - -2*(-x) = - 2*x
In[ ]:= fi [x_] = Piecewise-2*x , x > 0, - 2*x , x < 0
-2 x x>0
Out[ ]= - 2x
x<0
0 True
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
2 Integral de Fourier de funciones de medio rango.nb
In[ ]:= Plot[fi [x], {x, - 5, 5}]
0.10
0.05
-4 -2
Out[ ]=
2 4
-0.05
-0.10
Integrales de fourier de fp [x] y fi [x],
Para la extension par fp [x] ; en este caso caso B[w] = 0 y
∞
A[w_] =
-k*v
* Cos[v * w] v
2
π 0
, Re[k] > Im[w]
2k
π k2 + w2
Out[ ]= ConditionalExpression
In[ ]:= Clear[A[w]]
Clear: A[w] is not a symbol or a string.
A[w_] =
2k
π k2 + w2
In[ ]:=
2k
π k2 + w2
Out[ ]=
∞
luego IDF fp (x) = Cos[w * x] w
2k
0 π k2 + w2
∞
Si x > 0 entonces e-k*x = Cos[w * x] w
2k
0 π k2 + w2
Calculo de iteraciones para k = 2
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
Integral de Fourier de funciones de medio rango.nb 3
S[a_] = Cos[w * x] w
a 4
π 4 + w2
In[ ]:=
0
Out[ ]= ConditionalExpression
(- Cosh[2 x] CosIntegral[- (- 2 + a) x] + Cosh[2 x] CosIntegral[(2 + a) x] +
1
π
Sinh[2 x] (- SinIntegral[(2 + a) x] + SinIntegral[2 x - a x])),
Im[x] Re[a] + Im[a] Re[x] ≥ 0 && Re[a] Im[x]2 + Re[x]2 ≤ 0 ||
Re[a] Im[x]2 + Re[x]2 ≥ 0 && Im[x] Re[a] + Im[a] Re[x] ≤ 0 &&
(- 2 < Im[a] < 0 || 0 < Im[a] < 2) ||
Re[a] ≠ 0 && Im[x] Re[a] + Im[a] Re[x] ≤ 0 && Re[x] ≥ 0 || Re[a] Im[x]2 + Re[x]2 ≥ 0 ||
≥ ||
Re[x] 1
Im[x] Re[a] + Im[a] Re[x] 2
Im[x] Re[a] + Im[a] Re[x] ≥ 0 && Re[x] ≤ 0 || Re[a] Im[x]2 + Re[x]2 ≤ 0
In[ ]:= Plot-2*x, S[1], S[5], S[10.5], {x, 0, 5}, PlotLegends "Expressions"
0.5
-2 x
0.4
0.3 S(1)
Out[ ]=
0.2 S(5)
S(10.5)
0.1
1 2 3 4 5
Ejercicio calcular la intregral para de fourier para f i (x) y calcular algunas iteraciones
Printed by Wolfram Mathematica Student Edition
También podría gustarte
- Practica III Potencial VectorialDocumento17 páginasPractica III Potencial VectorialDulce MartínezAún no hay calificaciones
- Vectorial WolframDocumento12 páginasVectorial WolframAlejandra Paola Pastrana CaraballoAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentacion IntegralesDocumento4 páginasPresentacion IntegralesRodolfo Ernesto GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Moises 01 20212000982Documento14 páginasMoises 01 20212000982moises sAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea TicksDocumento5 páginasTarea Ticksdanitza ortizAún no hay calificaciones
- Catálogo Parte 2 FuncionesDocumento9 páginasCatálogo Parte 2 FuncionesEstefania MonroyAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe MathematicaDocumento7 páginasInforme MathematicaSarahi SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Guà - A 1 de Repaso Matemãticas Solucià N PDFDocumento6 páginasGuà - A 1 de Repaso Matemãticas Solucià N PDFDenisse AvilezAún no hay calificaciones
- MA5A1S ProyectoDocumento16 páginasMA5A1S ProyectoCindy GaticaAún no hay calificaciones
- Método de HermiteDocumento5 páginasMétodo de HermiteDul MaggotsAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta Control 4Documento5 páginasPauta Control 4losdedAún no hay calificaciones
- 1-Introducción A Wolfram MathematicaDocumento13 páginas1-Introducción A Wolfram MathematicaEl ClimoskiAún no hay calificaciones
- Aplicaciones de IntegralesDocumento11 páginasAplicaciones de IntegralesADDINSON ANGULO SALAZARAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 3 Extremos Condicionados VVDocumento22 páginas5 3 Extremos Condicionados VVapi-3739458100% (1)
- TALLER FINAL DE DERIVADAS MartesDocumento6 páginasTALLER FINAL DE DERIVADAS MarteskmilitochauxAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 2 Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocumento8 páginasUnidad 2 Ecuaciones Diferencialespablo gutierrez lunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea Métodos Numéricos-ResueltoDocumento8 páginasTarea Métodos Numéricos-ResueltoLulu Gar Honores100% (2)
- Operadores Diferenciales LinealesDocumento7 páginasOperadores Diferenciales LinealesDaniela Carmona RomanAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario - PC2 - A - 2023 - 20Documento8 páginasSolucionario - PC2 - A - 2023 - 20NOELIA ARANA BAUTISTAAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas DireccionalesDocumento11 páginasDerivadas DireccionalesVALERIA LOURDES MADRIDAún no hay calificaciones
- Sebastián Díaz Taller3Documento9 páginasSebastián Díaz Taller3Sebastian DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- PAIEP Sumas de Riemann-II APT 2019Documento8 páginasPAIEP Sumas de Riemann-II APT 2019joaquin herreraAún no hay calificaciones
- Derivación e Integración MatlabDocumento25 páginasDerivación e Integración MatlabJesús Yair Mejía SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 17Documento2 páginasTarea 17Jorge SanchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Bloque II 2Documento6 páginasBloque II 2Daniel BaldeónAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones ComplejasDocumento7 páginasFunciones ComplejasKuroi KarasuAún no hay calificaciones
- Cálculo 1Documento5 páginasCálculo 1Javier Contreras RiosAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucià N Parcial 1 Prácticas 28-11-2022 (P1)Documento3 páginasSolucià N Parcial 1 Prácticas 28-11-2022 (P1)LLados FitnessAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio de La Letra CDocumento11 páginasEjercicio de La Letra CFerney BustamanteAún no hay calificaciones
- Codigo en Wolfram Del Método Diferencias FinitasDocumento23 páginasCodigo en Wolfram Del Método Diferencias FinitasJavier Flores AvalosAún no hay calificaciones
- Determine El Maximo y Mínimo Valor de FDocumento5 páginasDetermine El Maximo y Mínimo Valor de FDenise CondoriAún no hay calificaciones
- S680310290B15F2Documento4 páginasS680310290B15F2Samuel Abreu PradoAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta Prueba Pendiente Versión 1-1002Documento4 páginasPauta Prueba Pendiente Versión 1-1002Matías AvalosAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Con Tecnología Sanabria - OcampoDocumento5 páginasTaller Con Tecnología Sanabria - OcampoCamilo Ocampo.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Taller de DerivadasDocumento4 páginasTaller de DerivadasJuan Diego Graciano PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- 62 Tarea No.3Documento67 páginas62 Tarea No.3bayronAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 - Semana 07032022 - Newton y LagrangeDocumento6 páginas1 - Semana 07032022 - Newton y LagrangemartaAún no hay calificaciones
- Regla TrapezoidalDocumento2 páginasRegla TrapezoidalJan Efrain Duron CamposAún no hay calificaciones
- Certamen 2 Pauta - 1-2009Documento5 páginasCertamen 2 Pauta - 1-2009Gonzalo RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Universidad Nacional de Ingenier Ia Facultad de Ciencias Escuela Profesional de Matem Atica Ciclo 2022-2Documento3 páginasUniversidad Nacional de Ingenier Ia Facultad de Ciencias Escuela Profesional de Matem Atica Ciclo 2022-2christianAún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo V (Integracion)Documento21 páginasCapitulo V (Integracion)Milton HuamanchoqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Punto 7Documento9 páginasPunto 7Ever Rafael MosqueraAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1-Estudiante 3.Documento14 páginasTarea 1-Estudiante 3.Andres SimbaquebaAún no hay calificaciones
- Máximos y Mínimos de Una FunciónDocumento4 páginasMáximos y Mínimos de Una Funciónmaria KuyocAún no hay calificaciones
- Unidad 3 - Tarea 3 - Nestor Hernández SustentaciónDocumento4 páginasUnidad 3 - Tarea 3 - Nestor Hernández SustentaciónNestor Camilo Hernandez MorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 3Documento8 páginasTarea 3Leidy VaronAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio Viga Trabajo Virtual 2021-20 - ClaseDocumento9 páginasEjercicio Viga Trabajo Virtual 2021-20 - ClaseAnderson MurilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Primer Parcial Primera Fecha Tema 2Documento4 páginasPrimer Parcial Primera Fecha Tema 2Fede SiriAún no hay calificaciones
- 02 Clase 7 12 2022 EVDocumento42 páginas02 Clase 7 12 2022 EVJosé Antonio FacendaAún no hay calificaciones
- PDF Examen de Aplazados Metodos Numericos Semestre Academico 2018 II TorresDocumento6 páginasPDF Examen de Aplazados Metodos Numericos Semestre Academico 2018 II TorresIndi Huamanvilca HuamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Modelo de Examen 749 Prueba IntegralDocumento4 páginasModelo de Examen 749 Prueba IntegralJavier GutiérrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Jeremiasrichards Invope 5docDocumento6 páginasJeremiasrichards Invope 5docJeremías RichardsAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 - Semana 14032022 - 7 - 2 - HermiteDocumento3 páginas2 - Semana 14032022 - 7 - 2 - HermitemartaAún no hay calificaciones
- Calculo Integral 100411 210Documento29 páginasCalculo Integral 100411 210Johanna HoyosAún no hay calificaciones
- Aplicaciones ER - 4Documento4 páginasAplicaciones ER - 4plantasvssonbis1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Belmont - Barraza - Juan Alberto - Act16Documento9 páginasBelmont - Barraza - Juan Alberto - Act16John O'Belmont Rayel'sAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario PC 2 Modelo BDocumento5 páginasSolucionario PC 2 Modelo BRenzo AlexanderAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 3 Leidy CastiblancoDocumento10 páginasTarea 3 Leidy CastiblancoLeidy Milena Castiblanco LizarazoAún no hay calificaciones
- Carlos Semana 12 Matematica 2Documento7 páginasCarlos Semana 12 Matematica 2CARLOS ANTONIO TORIBIO BOBADILLAAún no hay calificaciones
- Métodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABDe EverandMétodos Matriciales para ingenieros con MATLABCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Manual de Propagacion de Ondas PDFDocumento260 páginasManual de Propagacion de Ondas PDFDaniieliiTa MoRalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Conceptos y Elementos BásicosDocumento57 páginasConceptos y Elementos BásicosDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Titulo - I Manual de Gestión Del EspectroDocumento190 páginasTitulo - I Manual de Gestión Del EspectroDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Resolucion Ane 0181 2019Documento56 páginasResolucion Ane 0181 2019Yimi FerneyAún no hay calificaciones
- Intro Java 1 BASICODocumento50 páginasIntro Java 1 BASICOAdrian RaskovskyAún no hay calificaciones
- Plan de Distribucion de Canales BandaDocumento8 páginasPlan de Distribucion de Canales BandaDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Intro Java 1 BASICODocumento50 páginasIntro Java 1 BASICOAdrian RaskovskyAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones de Medio Rango PDFDocumento3 páginasFunciones de Medio Rango PDFDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- J Introtojava1 PDFDocumento50 páginasJ Introtojava1 PDFDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- J Introtojava1 PDFDocumento50 páginasJ Introtojava1 PDFDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Transfomada Foutier Analisis Completo PDFDocumento2 páginasTransfomada Foutier Analisis Completo PDFDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 2 Receptores ÓpticosDocumento4 páginasTaller 2 Receptores ÓpticosDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Fuentes de Luz ÓpticaDocumento6 páginasTaller Fuentes de Luz ÓpticaDaniel CastañedaAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual Del CompresorDocumento28 páginasManual Del Compresoraeduardo88Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 3 Características de La Producción Científica - Eilen Jemerys SanchezDocumento10 páginasTarea 3 Características de La Producción Científica - Eilen Jemerys Sanchezjairoc2008Aún no hay calificaciones
- Secuenciado de La ProducciónDocumento22 páginasSecuenciado de La ProducciónDayana ParadaAún no hay calificaciones
- 11 Dinámica LinealDocumento6 páginas11 Dinámica LinealVale Angulo ButronAún no hay calificaciones
- Rúbricas Aulas MultigradoDocumento6 páginasRúbricas Aulas Multigradoanaceci7120% (1)
- El Derecho Ruso Hasta 1900Documento5 páginasEl Derecho Ruso Hasta 1900Agustín DávilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad 6 Corriente ElctricaDocumento1 páginaActividad 6 Corriente ElctricaJAIR CRUZ CASTILLOAún no hay calificaciones
- Dinamicas GrupalesDocumento44 páginasDinamicas GrupalesSaMy Perez ChavezAún no hay calificaciones
- Enfermeria GeriatricaDocumento5 páginasEnfermeria GeriatricaBáthory de Ecsed100% (1)
- Aedes Legum de Juan Luis VivesDocumento8 páginasAedes Legum de Juan Luis VivesSilvana Graciela BrizuelaAún no hay calificaciones
- Fase 4 - YinethBalanta - 83Documento11 páginasFase 4 - YinethBalanta - 83yineth balanta minaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ensayo de Placa de CargaDocumento15 páginasEnsayo de Placa de CargaAnonymous 7LTu7jrAún no hay calificaciones
- Conducta I DefinitivaDocumento147 páginasConducta I DefinitivaMiguel LizardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Aplicaciones de Las Rocas en La Ingeniería Civil..Documento26 páginasAplicaciones de Las Rocas en La Ingeniería Civil..Iris MitchelAún no hay calificaciones
- Resolución 4272 de 2021 - ALTURASDocumento20 páginasResolución 4272 de 2021 - ALTURASJane BerrioAún no hay calificaciones
- Qué Es El Método CuantitativoDocumento10 páginasQué Es El Método Cuantitativoluis perezAún no hay calificaciones
- El Loco PeligrosoDocumento14 páginasEl Loco PeligrosoMatius De la MadridAún no hay calificaciones
- Desarrollo y Sustentabilidad en La GerenciaDocumento5 páginasDesarrollo y Sustentabilidad en La GerenciaDouglas PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- 16S 1650 IVECO O.D.-nº 0091 008 006-Fev-2005 - 1297095070-071 - 092 PDFDocumento43 páginas16S 1650 IVECO O.D.-nº 0091 008 006-Fev-2005 - 1297095070-071 - 092 PDFÁlvaro Ricardo Lopatiuk100% (1)
- Informe 3 Laboratorio de CorrosionDocumento11 páginasInforme 3 Laboratorio de CorrosionMario A. Sánchez Pabón0% (1)
- Enunciado Caso Práctico - M1T4 - Diseño de Tuberías de Plantas Industriales IIDocumento3 páginasEnunciado Caso Práctico - M1T4 - Diseño de Tuberías de Plantas Industriales IIAnny Carolina Correa RamírezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos Sobre Estadística DescriptivaDocumento11 páginasEjercicios Resueltos Sobre Estadística DescriptivaMario Orlando Suárez IbujésAún no hay calificaciones
- T Uce 0011 80Documento295 páginasT Uce 0011 80El Libertador EmperadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Implementacion Programa de FarmacovigilanciaDocumento76 páginasImplementacion Programa de FarmacovigilanciaCarolina CeballosAún no hay calificaciones
- MontessoriDocumento2 páginasMontessoriMEDINA GARCIA Abigail MedinaAún no hay calificaciones
- BPZ - Lote Z-1Documento19 páginasBPZ - Lote Z-1Walter Eloy Ramirez CarranzaAún no hay calificaciones
- TP 1 Conciliacion BancariaDocumento2 páginasTP 1 Conciliacion BancariaLucas LiendoAún no hay calificaciones
- El Clima Del GenioDocumento2 páginasEl Clima Del GenioSandro F. Acosta OchoaAún no hay calificaciones
- INFO2020 - Taller de Illustrator PDFDocumento3 páginasINFO2020 - Taller de Illustrator PDFleidy seguraAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía No. 3 EmprendimientoDocumento10 páginasGuía No. 3 EmprendimientoJonathan alejandro Castaño leeAún no hay calificaciones