Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
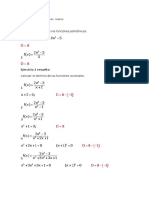
Ejercicios Sobre Funciones
Ejercicios Sobre Funciones
Cargado por
Jose Manuel Sánchez NeiraDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Ejercicios Sobre Funciones
Ejercicios Sobre Funciones
Cargado por
Jose Manuel Sánchez NeiraCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 1 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
Ejercicios Resueltos
Captulo I
Funciones
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 2 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 1:
Considere las funciones f(x) =
x + 2 y g(x) = x
2
1
encontrar los valores de x, para los cuales
(f g)(x) = (g f)(x)
Soluci on:
(f g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(x
2
1) =
x
2
1
(g f)(x) = g(f(x)) = g(
x + 2) = (x + 2) 1 = x + 1
por lo tanto:
x
2
1 = x+1 x
2
+1 = x
2
+2x+1
2x = 0 x = 0
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 3 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 2:
Encontrar la funci on inversa de f(x) =
_
1
1
x
coincide el dominio de f con el de f
1
?
Soluci on:
Sea y =
_
1
1
x
= y
2
= 1
1
x
=
1
x
= 1 y
2
= x =
1
1 y
2
por lo tanto f
1
(x) =
1
1 x
2
El dominio de f es: D
f
= {x IR | 1
1
x
0} =
(, 0) [1, )
El dominio de f
1
es: D
f
1 = {x IR | x
2
= 1} =
IR {1, 1}
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 4 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 3:
Considere la funci on:
f(x) =
_
x
2
si x 0
1
x
2
si x > 0
Hallar su dominio y rango, as como el de su inversa.
Soluci on:
El dominio de f son todos los n umeros reales, y su rango
es [0, ).
En el intervalo (, 0), no tiene inversa, pero la funci on
restringida al intervalo [0, ) tiene como inversa:
f
1
(x) =
_
0 si x = 0
1
x
si x > 0
Tanto el dominio como el rango de f
1
es [0, ).
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 5 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 4:
Una determinada cooperativa ha calculado que su cosecha
anual de manzanas es de 100 000 kg, que piensa vender a raz on
de 7.00 pesos/kg. Cada semana que transcurre se estropean 2 000
kg de manzanas, y para compensar la p erdida, los miembros de
la cooperativa aumentan en 1.40 pesos el precio del kilogramo
por cada semana que pasa. Escribir la funci on que determina el
valor de las manzanas, dependiendo de las semanas transcurridas.
Soluci on:
Si transcurren x semanas, el n umero de manzanas que hay
es 100000-2000x, y el kilo cuesta 7.00 + 1.4x pesos, luego el
precio total de las manzanas es:
f(x)=(100000-2000x)(7.00 + 1.4 x ) pesos.
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 6 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 5:
Hallar el dominio y rango de las siguientes funciones:
a) f(x) =
1
x
2
+ 1
Soluci on:
x
2
+ 1 = 0 para toda x IR, por lo tanto el dominio
de f es todo IR, y como x
2
+ 1 1 el rango es (0, 1].
b) g(x) =
x
2
4
Soluci on:
g tiene sentido si x
2
4 0, x
2
4 =
D
g
= (, 2] [2, ), y su rango es [0, ).
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 7 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 6:
Considerar las funciones f(x) =
x + 1 y g(x) = x
2
1,
encontrar:
a) El dominio de f d) (fg)(x)
b) El dominio de g e) (f g)(x)
c) (f + g)(x) f) (g f)(x)
Soluci on:
Para f: Dominio [1, ), rango: [0, ).
Para g: Dominio (, ), rango: [1, ).
(f + g)(x) =
x + 1 + x
2
1, (f g)(x) = (x
2
+
1)
x + 1.
(f g)(x) =
x
2
1 + 1 = |x|, g f)(x) =
(
x + 1)
2
1 = x.
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 8 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 7:
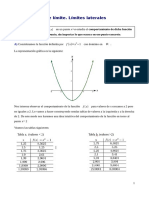
Encontrar el dominio, rango, periodo y ceros y = |senx|.
Soluci on:
El dominio de f es IR, su rango es [0, 1] y su periodo es .
Los ceros de la funci on son 0, , 2
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 9 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 8:
Encontrar la funci on inversa de f(x) =
x + 1
x
Soluci on:
f no existe si x = 0, luego si
x + 1
x
= y = x + 1 =
xy x(y 1) = 1 x =
1
x 1
Por lo tanto f
1
=
1
x 1
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 10 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 9:
Para la siguiente funci on f(x) =
1 x, hallar:
a) Su dominio c) f
1
f
b) f f d) f
1
y su dominio
Soluci on:
Dominio: x IR, tales que 1 x 0 = x 1, por lo
tanto el dominio es (, 1].
(f f)(x) = f(
1 x) =
_
1
1 x
(f
1
f
)(x) = f
_
1
1 x
_
=
1
1
1 x
1 x = y = 1 x = y
2
= x = 1 y
2
, luego, f
1
existe en (, 1] y f
1
(x) = 1 x
2
.
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 11 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 10:
Encontrar el dominio y los ceros de la siguiente funci on ra-
cional:
f(x) =
x
2
+ x 2
x
2
9
Soluci on:
Dominio: {x IR | x
2
9 = 0} = {x IR | x
2
= 9} =
IR {3, 3}
Ceros: {x IR | x
2
+x2 = 0} = {x IR | (x+2)(x
1) = 0} = {2, 1}
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 12 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 11:
Encontrar el dominio de las siguiente funciones:
a) f(x) =
1
1 +
x + 1
b) g(x) =
x + 1 +
x + 2
Soluci on:
a) El dominio de f es:
D
f
= {x IR | 1 +
x + 1 = 0, x + 1 0} = {x
IR|x 1, x = 0} = [1, 0) (0, )
b) El dominio de g es:
D
g
= {x IR | x + 1 0, x + 2 0} = {x IR|x
1, x 2} = [1, )
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 13 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 12:
Sea f(x) =
2x 1
1 + 2x
encontrar: a) f
_
1
x
_
y f
_
1 + x
2 2x
_
Soluci on:
a) f
_
1
x
_
= f
_
2
x
1
1 +
2
x
_
=
2x
x
2+x
x
=
2 x
2 + x
b) f
_
1 + x
2 2x
_
=
2
_
1+x
22x
_
1
1 + 2
_
1+x
22x
_
=
2+2x2+2x
22x
22x+2+2x
22x
=
4x
4
= x
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 14 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 13:
Considerar la funci on:
f(x) =
_
3 si 3 x 2
5 x si 2 < x 6
Encontrar el rango de f y demostrar que no es inyectiva.
Soluci on:
Como 2 < x 6 = 6 x < 2 = 5 6
5 x < 2 + 5 = 1 5 x < 3 y como f(x) = 3 para
3 x 2, el rango de f es [1, 3].
Claramente f no es inyectiva pues f(0) = 3 = f(1) y 0 = 1.
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 15 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 14:
Econtrar el dominio de f g si f(x) =
1
2x 2
y g(x) =
2
x 4
.
Soluci on:
El dominio de f es D
f
= {x IR| 2x 2 = 0} =
{x IR| x = 1} = IR {1}
El dominio de g es D
g
= {x IR| x 4 = 0} = {x
IR| x = 4} = IR {4}
El dominio de f g es D
g
{x IR| g(x) = 1} =
IR {4}
_
x IR|
2
x4
= 1
_
= IR {4, 6}
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 16 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 15:
Hallar la funci on inversa de
f(x) =
_
1 x si x 1
3x
2
si x > 1
Soluci on:
f(x) =
_
1 x si x 1 rango: [2, )
3x
2
si x > 1 rango: , 2)
f
1
(x) =
_
1 x si x 2
3 2x si x < 2
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 17 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 16:
Encontrar el dominio y rango de la funci on f(x) =
x
2
+ 2.
Soluci on:
El dominio de f es {x IR | x
2
+ 2 0} = IR
El rango es el intervalo [
2, )
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 18 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA17:
A partir de las funciones f(x) =
2x 1
2
y g(x) = x
2
+ 2,
calcular:
a) (f + g)(2) c) (f g)(3)
b) (f g)(2) d)
_
f
g
_
(3)
Soluci on:
a) (f +g)(2) = f(2)+g(2) =
2 2 1
2
+(2
2
)+2 =
3
2
+6 =
15
2
b) (f g)(2) = f(2) g(2) =
(2)(2) 1
2
(2)
2
2 =
5
2
6 =
17
2
c) (f g)(3) = f(3) g(3) =
2(3) 1
2
(3
2
+2) =
5
2
11 =
55
2
d)
_
f
g
_
(3) =
f(3)
g(3)
=
2(3)1
2
(3)
2
+ 2
=
7
22
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 19 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA18:
Encontrar el dominio de f + g, f g, f g si f(x) =
1
x2
y
g(x) =
2
3+x
.
Soluci on:
El dominio de f es el conjunto D
f
= {x IR| x = 2} y
el dominio de g es el conjunto D
g
= {x IR| x = 3}
Por lo tanto el dominio de f + g, f g, f g es igual a
D
f
D
g
= IR {3, 2}.
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 20 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 19:
Hallar el dominio de f/g si f(x) =
2x 2 y g(x) =
2 x.
Soluci on:
El dominio de f es el conjunto D
f
= {x IR| 2x 2 0} =
[1, ) y el dominio de g es el conjunto D
g
= {x IR| 2
x} = ( , 2]
Por lo tanto el dominio de f/g es el conjunto:
D
f
D
g
{x IR| g(x) = 0} = [1, )(, 2] = [1, )
(, 2]{x IR|
2 x = 0} = [1, )(, 2]{x
IR| x = 2} = [1, ) (, 2] {2} = [1, 2)
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 21 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 2O:
Encontrar f g y g f si f(x) =
x
x2
y g(x) =
2
1x
Soluci on:
(f g)(x) = f(g(x)) =
g(x)
g(x)2
=
2
1x
2
1x
2
=
2
1x
22+2x
1x
=
2
2x
=
1
x
(g f)(x) = g(f(x)) =
2
1f(x)
=
2
1
x
x2
=
2
x2x
x2
=
2
2
x2
=
2(x2)
2
= 2 x
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 22 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 21:
Considerar la funci on f(x) = 2x 4
a). Demostrar que es inyectiva en todo su dominio
b). Encontrar su funci on inversa e indicar su dominio
c). Comprobar que (f f
1
)(x) = (f
1
f)(x) = x
Soluci on:
Claramente el dominio de la funci on es el conjunto de los
n umeros reales, luego a, b IR, tales que f(a) = f(b) =
2a 4 = 2b 4 = 2a = 2b = a = b, por lo tanto f es
inyectiva.
Sea y = f(x) = y = 2x 4 = y + 4 = 2x = x =
y+4
2
por lo tanto la funci on inversa es f
1
(x) =
x+4
2
y su dominio
son todos los n umeros reales.
(f f
1
)(x) = f(f
1
(x)) = f(
x+4
2
) = 2(
x+4
2
) 4 =
x + 4 4 = x, por otro lado
(f
1
f)(x) = (f
1
)(f(x)) =
(2x4)+4
2
=
2x
2
= x
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 23 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 22:
Sean f(x) =
x 1 y g(x) = x
2
, resolver la ecuaci on
(f g)(x) = (g f)(x)
Soluci on:
(f g)(x) = f(g(x)) =
x
2
1 adem as (g f)(x) =
g(f(x)) = (
x 1)
2
= x 1.
igualando las expresiones anteriores tenemos:
x
2
1 = x 1 x
2
1 = (x 1)
2
x
2
1 = x
2
2x + 1 2x = 2 x = 1
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 24 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 23:
Estudiar el tipo de simetra que tiene la siguiente funci on
seccionada:
f(x) =
_
x
2
1 si |x| 3
8 si x (3, 3)
Soluci on:
Se estudia la simetra en cada secci on:
f(x) =
_
(x)
2
1 si |x| 3
8 si x (3, 3)
Luego
f(x) =
_
x
2
1 si |x| 3
8 si x (3, 3)
Por consiguiente f es par pues f(x) = f(x).
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 25 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 24:
Determinar si las siguientes armaciones son verdaderas o
falsas:
a) Una funci on tiene que ser necesariamente par o impar.
b) Si el dominio de f es [0, ), entonces f no puede ser par.
c) Una funci on que tiene un eje de simetra es necesariamente
par.
d) Si f(x) es una funci on par, entonces f(x) es impar.
Soluci on:
a) Falso. La funci on f(x) = x
2
+ x no es ni par ni im-
par.
b) Verdadero. Si el dominio de f es [0, ), entonces f(x) no
tiene sentido para x > 0 y, por lo tanto, no puede cumplirse que
f(x) = f(x), es decir, f no puede ser par.
c) Falso. La funci onn f(x) = x
2
6x + 8 tiene como eje de
simetra el eje de la par abola y no es par.
d) Falso. f(x) = |x| es par y, sin embargo, f(x) no es impar.
Home Page
Title Page
Contents
Page 26 of 26
Go Back
Full Screen
Close
Quit
First Prev Next Last Go Back Full Screen Close Quit
PROBLEMA 25:
Demostrar que las funciones f(x) = x
3
+1 y g(x) =
3
_
(x1)
son inversas la una de la otra.
Soluci on:
(f g)(x) = f(g(x)) = f(
3
_
(x 1)) = (
3
_
(x 1))
3
+ 1 =
(x 1) + 1 = x = (f g)(x) = x
(g f)(x) = g(f(x)) = g(x
3
+ 1) =
3
x
3
+ 1 1 =
3
x
3
= x = (g f)(x) = x
También podría gustarte
- Aplicación de Las Funciones en El Campo de La EconomíaDocumento26 páginasAplicación de Las Funciones en El Campo de La EconomíaEida Katerine Moreno Niquin100% (1)
- InecuacionesDocumento23 páginasInecuacionesMinerva Bueno100% (20)
- Calculo de Varias Variables Dennis G Zill Warren S Wright 4ta Edicion A29096Documento2 páginasCalculo de Varias Variables Dennis G Zill Warren S Wright 4ta Edicion A29096Jordán López0% (3)
- Soluciones Ejercicios de FuncionesDocumento22 páginasSoluciones Ejercicios de Funcionesadora_las_mates100% (19)
- Relaciones y Funciones RectificadopdfDocumento11 páginasRelaciones y Funciones RectificadopdfRenzo Santamaria AcostaAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones As en La EconomiaDocumento9 páginasFunciones As en La EconomiaHef Varela43% (7)
- Funciones MatematicasDocumento9 páginasFunciones Matematicasandresocampo7100% (2)
- FUNCIÓN EjerciciosDocumento7 páginasFUNCIÓN Ejercicioscvcarlosvilla1100% (4)
- PPT-Semana 6-LÃ-mitesDocumento30 páginasPPT-Semana 6-LÃ-mitesVálery Roxana Bellota ZárateAún no hay calificaciones
- Dominio y Recorrido de FuncionesDocumento71 páginasDominio y Recorrido de FuncionesJ Pomales100% (20)
- Funciones RacionalesDocumento4 páginasFunciones Racionalesprofe mahecha100% (3)
- Dominio y Rango de Una FunciÓn CuadrÁtica (Version Blog)Documento16 páginasDominio y Rango de Una FunciÓn CuadrÁtica (Version Blog)J Pomales95% (19)
- Proyecto Integrales Sobre Superficies - FinalDocumento32 páginasProyecto Integrales Sobre Superficies - FinalYulianaGonzalesEnequeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Funciones RealesDocumento11 páginasEjercicios de Funciones Realesdavid rodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- FuncionesDocumento11 páginasFuncionescvcarlosvilla1100% (6)
- Limites Exponenciales y LogaritmicosDocumento21 páginasLimites Exponenciales y Logaritmicosrosa50% (4)
- Límites Infinitos y Límites Al InfinitoDocumento6 páginasLímites Infinitos y Límites Al Infinitojhongarcia@itm.edu.co89% (37)
- Moisés Villena Muñoz Cap. 2 Optimización de Varias VariablesDocumento26 páginasMoisés Villena Muñoz Cap. 2 Optimización de Varias Variablesb10287366100% (2)
- Repartido 2 - Funciones PolinomicasDocumento5 páginasRepartido 2 - Funciones PolinomicasFederico LarreaAún no hay calificaciones
- FactorizaciónDocumento13 páginasFactorizacióningridinciarte99% (178)
- Funciones RacionalesDocumento9 páginasFunciones RacionalesEdith Llanos ZeballosAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Límites ResueltosDocumento20 páginasEjercicios de Límites Resueltosmiriam2803Aún no hay calificaciones
- Derivadas ParcialesDocumento22 páginasDerivadas ParcialesEdwin SacaAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Resueltos y Propuestos de C Lculo Diferencial de Varias VariablesDocumento102 páginasProblemas Resueltos y Propuestos de C Lculo Diferencial de Varias VariablesPedro JoseAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Dominio y RangoDocumento7 páginasEjercicios de Dominio y RangoEduardo Javier Hernández DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Superficies CuadricasDocumento9 páginasSuperficies CuadricasRicardo Vides100% (3)
- Relaciones y FuncionesDocumento16 páginasRelaciones y FuncionesNelson Jopia100% (1)
- 2da GUÍA FUNCIÓN EXPONENCIAL Y LOGARÍTMICADocumento26 páginas2da GUÍA FUNCIÓN EXPONENCIAL Y LOGARÍTMICAsmallviviAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de DerivadasDocumento20 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de DerivadasDiego Castellón Moyano100% (3)
- Teoria de LimitesDocumento15 páginasTeoria de LimitesfmjrjrcAún no hay calificaciones
- Trazado de CurvasDocumento32 páginasTrazado de CurvasManuela AlfonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- 1-Idea Intuitiva de LímiteDocumento20 páginas1-Idea Intuitiva de Límiteushuaia7745Aún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 4 de Varias (Funciones de Varias Variables)Documento49 páginasCapitulo 4 de Varias (Funciones de Varias Variables)visalex80% (5)
- Método Variables Separables, Reducibles A Separables y HomogéneasDocumento14 páginasMétodo Variables Separables, Reducibles A Separables y HomogéneasPaola Villalobos LópezAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta CertamenGlobalDocumento5 páginasPauta CertamenGlobaldiegoutzcAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta Guia 5Documento10 páginasPauta Guia 5Katherine Martinez DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 1 IP-SolucíonDocumento4 páginasTaller 1 IP-SolucíonFaiber HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Funcion Creciente Decreciente Par e ImparDocumento5 páginasFuncion Creciente Decreciente Par e ImparLuis Alberto Molina JimenezAún no hay calificaciones
- Repaso 2 Invierno 2021Documento2 páginasRepaso 2 Invierno 2021ami306Aún no hay calificaciones
- HojaEjercicios Vectorial08 SolDocumento8 páginasHojaEjercicios Vectorial08 Solbran moralesAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas 1º Parcial-Cálculo 1Documento48 páginasProblemas 1º Parcial-Cálculo 1Fran VegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Serie CDDocumento36 páginasSerie CDKevin HdezAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo de CálculoDocumento5 páginasTrabajo de CálculoFernando Robles100% (1)
- Taller 1-SolucíonDocumento4 páginasTaller 1-SolucíonJuan David HernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Funciones Parte3 UvirtualDocumento14 páginasFunciones Parte3 UvirtualepmelsAún no hay calificaciones
- Dominio TeoríaDocumento4 páginasDominio TeoríaLa profeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ayudantia 4 Matem Ticas I ListaDocumento7 páginasAyudantia 4 Matem Ticas I ListaKAREN MEDRANO CONDORIAún no hay calificaciones
- S9 - 2022-01 - MAT-IND - Composición de FuncionesDocumento11 páginasS9 - 2022-01 - MAT-IND - Composición de FuncionesKelvin Erick Toledo FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- 9 - Practica General - 1PDocumento5 páginas9 - Practica General - 1PJimena Apaza GuachallaAún no hay calificaciones
- Enviar Cálculo IDocumento6 páginasEnviar Cálculo IalexAún no hay calificaciones
- FuncionesDocumento3 páginasFuncionesJoaquin Leonardo Ochoa NuñezAún no hay calificaciones
- AMASesion 6Documento4 páginasAMASesion 6Joan AirbagAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Resueltos de FuncionesDocumento10 páginasEjercicios Resueltos de FuncionesFabián Sánchez Parrines100% (1)
- 2018 19 SeptiembreDocumento6 páginas2018 19 SeptiembreFrancisco PlataAún no hay calificaciones
- D.E. Santiago - Examen Calculo IDocumento2 páginasD.E. Santiago - Examen Calculo Idaniel enrique santiago fontalvoAún no hay calificaciones
- ESTUDIANTE - ABP 1 - Mat Gest II - Tech - AP - 2023Documento8 páginasESTUDIANTE - ABP 1 - Mat Gest II - Tech - AP - 2023gutierrezluengomjAún no hay calificaciones
- Factorizac IC2020 ConResp PDFDocumento31 páginasFactorizac IC2020 ConResp PDFJordy Vinda HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 7 Inversa de Una FunciónDocumento4 páginasTaller 7 Inversa de Una FunciónHugo Leonardo Erazo ReyesAún no hay calificaciones
- Pauta Taller 1 2024-1Documento3 páginasPauta Taller 1 2024-1Josianne De La FuenteAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia de Aprendizaje N°4 - Prismas y Piramides - Grado 9°Documento11 páginasGuia de Aprendizaje N°4 - Prismas y Piramides - Grado 9°spark jiminAún no hay calificaciones
- Parámetros EstadísticosDocumento44 páginasParámetros EstadísticosJesus SevillaAún no hay calificaciones
- Clases de OctavoDocumento33 páginasClases de OctavoJavier LeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Conceptos Basicos de AlgebraDocumento1 páginaConceptos Basicos de AlgebraMiriam López Sánchez50% (2)
- Mat 4°p Iv Bim 2020Documento107 páginasMat 4°p Iv Bim 2020Stephano Cartagena VasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Proyecto de MatemáticasDocumento16 páginasProyecto de MatemáticasJafer Giler ParedesAún no hay calificaciones
- Trigonometría - RT 2023Documento4 páginasTrigonometría - RT 2023Luis GarnicaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lineas Notables TeoriaDocumento2 páginasLineas Notables TeoriaReynaldo Mamani mamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 11 - Teorema Del Seno y CosenoDocumento4 páginasGuia 11 - Teorema Del Seno y Cosenoderly delgadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sistemas de NumeraciónDocumento10 páginasSistemas de NumeraciónjonasfranciscocmAún no hay calificaciones
- Razonamiento Matematico Jorge Enrique More GómezDocumento5 páginasRazonamiento Matematico Jorge Enrique More GómezJhony renzo Samame coronelAún no hay calificaciones
- XVI Olimpiada Nacional Escolar de Matem Atica (ONEM 2019)Documento2 páginasXVI Olimpiada Nacional Escolar de Matem Atica (ONEM 2019)JoseLuis MalagaAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 Segmentos-AngulosDocumento5 páginas1 Segmentos-AngulosKevinEqAún no hay calificaciones
- Temario Admisión Umch PDFDocumento2 páginasTemario Admisión Umch PDFJesus Paiva LaymeAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de GeometriaDocumento5 páginasEjercicios de GeometriaFABIAN VERAAún no hay calificaciones
- DibisibilidadDocumento2 páginasDibisibilidadLuis Armando Cuzco TrigozoAún no hay calificaciones
- Clasificacion de TriangulosDocumento1 páginaClasificacion de TriangulosELVA HUAYHUA CCOYORIAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de Triangulos 1Documento4 páginasProblemas de Triangulos 1Zoila Maria Alvino HuancaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Movimiento Circular McuDocumento2 páginasEjercicios Movimiento Circular McuPedro Araya FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodode Volumenes FinitosDocumento4 páginasMetodode Volumenes FinitosMichael EinstenAún no hay calificaciones
- Interpretación Géometrica de Las Derivadas Parciales de Una Funcion de Dos VariablesDocumento2 páginasInterpretación Géometrica de Las Derivadas Parciales de Una Funcion de Dos VariablesMiguelito Pa Q MasAún no hay calificaciones
- Carl Jung PsicoanalisisDocumento18 páginasCarl Jung PsicoanalisisLuis Enrique Tenorio AguadoAún no hay calificaciones
- (247611234) Números Enteros 708Documento10 páginas(247611234) Números Enteros 708KaRi PedrEroAún no hay calificaciones
- Apunte Longitud de ArcoDocumento9 páginasApunte Longitud de ArcoAndres Montecinos LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha 4 PDFDocumento24 páginasFicha 4 PDFKevin B. Sulca GonzalesAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de Ecuaciones de Segundo GradoDocumento2 páginasProblemas de Ecuaciones de Segundo GradoClases particulares en la LagunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de Puntos Evaluables - Escenario 2 - PRIMER BLOQUE-CIENCIAS BASICAS - VIRTUAL - CÁLCULO 2 - (GRUPO B05)Documento5 páginasActividad de Puntos Evaluables - Escenario 2 - PRIMER BLOQUE-CIENCIAS BASICAS - VIRTUAL - CÁLCULO 2 - (GRUPO B05)Jeyson Neyder LozanotarazonaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia Volumen II MedioDocumento2 páginasGuia Volumen II MedioFrancisca SanhuezaAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen de Matemáticas I, Primer BimestreDocumento4 páginasExamen de Matemáticas I, Primer BimestremequixcoAún no hay calificaciones
- Tangentes y Empalmes DocumentoDocumento8 páginasTangentes y Empalmes DocumentoAlvaro HenriquezAún no hay calificaciones