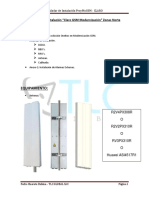
Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
ALCPlus2 and ALCPlus2e QoS - 2
Cargado por
Marcos BermudezTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
ALCPlus2 and ALCPlus2e QoS - 2
Cargado por
Marcos BermudezCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
ALCPlus2 – Descripción QoS
Calidad de servicio (QoS) es una característica esencial cuando la red Ethernet debe llevar, con excepción de
los paquetes de datos, también aplicaciones de tiempo interactiva y real.
Aplicaciones en tiempo real (por ejemplo, VoIP) tienen requisitos estrictos en términos de ancho de banda,
latencia y jitter. Por lo tanto, cuando el rendimiento de la red se vuelve insuficiente para garantizar el transporte
de todo el tráfico de Ethernet, los mecanismos de QoS se utilizan para distinguir entre los diferentes tipos de
tráfico, dando alta prioridad a los paquetes críticos (tiempo real) y la reducción del ancho de banda dedicado a
paquetes de datos.
QoS Mecanismo:
QoS en los equipos ALC Plus2 se pueden activar en el Capa 2, en el Capa 3, o ambos, dependiendo de los
requerimientos del usuario:
IEEE 802.1p QoS (Capa 2 Calidad de Servicio), donde el tráfico se prioriza de acuerdo con los tres bits del
TAG 802.1Q.
IPv4 ToS (Capa 3 Tipo de Servicio de la cabecera IP v4), donde el tráfico se prioriza de acuerdo con los seis
bits del ToS (DSCP).
IPv6 ToS (Capa 3 Tipo de Servicio de la cabecera IP v6) donde el tráfico se prioriza de acuerdo con los seis
bits del ToS (DSCP).
Cuando se activan los dos mecanismos de QoS (802.1p y IPToS), el diseñador puede elegir la prioridad de
cada mecanismo de QoS (es decir 802.1p - IPToS o IPToS - 802.1p).
All rights reserved © SIAE microelettronica 1
ALCPlus2 - QoS Description
Scheduling:
The integrated switch has four queues where the packets are stored in case of traffic congestions. The
priority management is done by sending the packets on these output queues. The traffic is sent to each
queue on the basis of its 802.1p or ToS values. The correspondence between the 802.1p or ToS values
and each output queue can be set via software.
Output Queues of ALCplus2:
The packets on the queue can be sent on the basis of two different policies (selectable via software):
• Strict Priority (SP): First all the packets from the highest priority queue are transmitted, then all the
packets from the second queue, and so on (CASE 1 of the figure reported below).
• Weighted Round Robin (W.R.R.): The packets are sent following the 8-4-2-1 rule. I.e., first are
transmitted 8 packets from the highest priority queue, then 4 packets from the second queue, then 2
packets from the third queue and finally 1 packet from the lowest priority queue (CASE 2).
• It is also possible to use hybrid priority policies, defining Queue 3 (or Queue 3 and Queue 2) as SP and
the rest of the queues as WRR (CASE 3 and 4).
High Low
Queue 3 Queue 2 Queue 1 Queue 0
CASE 1 Strict Priority
CASE 2 8 4 2 1 WRR
CASE 3 4 2 1
CASE 4 2 1
All rights reserved © SIAE microelettronica 2
ALCPlus2e - Queues and Scheduling
Scheduling:
The FPGA has 8 queues where the packets are stored in case of traffic congestions. The priority
management is done by sending the packets on these output queues. The traffic is sent to each queue on the
basis of its 802.1p or ToS values. The correspondence between the 802.1p or ToS values and each output
queue can be set via software.
Output Queues:
The packets can be sent to the Servant (radio) based on different policies (selectable via software):
• Strict Priority (SP): First all the packets from the highest priority queue are transmitted, then all the packets
from the second queue and so on
All rights reserved © SIAE microelettronica 3
ALCPlus2e - Queues and Scheduling
Weighted Fair Queueing (WFQ): The packets are sent on the radio following a rule based on the weight
assigned to each Queue.
Each queue “i" with WFQ is given a weight (importance) Wi.
WFQ guarantees a minimum service rate to queue “i"
Ri = R * Wi / (W1 + W2 + ... + Wn) [Rate of the queue i]
Where:
R = rate of the servant ( Capacity available on the MW link)
Wi = weight of the Queue taken in consideration
Wn = weight of the last Queue with WFQ enabled
• It is also possible to use Hybrid Priority Policies, defining queue by queue either Strict Priority or WFQ.
Queue Type Weight Sum of the Weights 35
7 WFQ 8
6 WFQ 8 Serving Priority:
Higher Priority
5 WFQ 6 1.The packets present in the Queue 7 will be transmitted
4 WFQ 4 with a Rate 8/35
3 WFQ 4 2.The packets present in the Queue 6 will be transmitted
2 WFQ 2 with a Rate 8/35
1 WFQ 2
3.…..
Lower Priority
0 WFQ 1
4.…..
5.The packets present in the Queue 0 will be transmitted
with a Rate 1/35
All rights reserved © SIAE microelettronica 4
ALCplus2e IDU – Queue Architecture Review
Queue 7
Queue 6
Queue 5
LAN2 LAN4 Toward
Queue 4 Servant
Queue 3 Radio
LAN1 LAN3
Queue 2
Ethernet
L2 switch Queue 1
Queue 0
FPGA
The Output scheduling policy
is software selectable:
Strict Priority
Weighed Fair Queue
Mixed All rights reserved © SIAE microelettronica 5
ALCPlus2e Queues and Scheduling
Policy Type: WFQ Weight
Buffer Size: • Strict Priority
(for SP this field
128 – 256 – 512 – 1024 – 2048 •Weighted Fair Queueing does not apply)
– 4096 – 8192 Kbit
Drop Type:
• Tail
•Queue
•Red
•Wred
Drop Types:
When the queue is full, we are in a congestion situation. This means that the resources are not enough to
serve all the packets and there is not enough room in the queue for more storage. In this case some packet
must be dropped. There are different policy of dropping that can be adopted:
• Tail: In this case the last packets that come to the full queue are dropped (default configuration)
• Queue: In this case all the queue is emptied, i.e. all the packets present in the Queue are dropped
• Red: Random Early Discard: with this policy, before the Queue is full some packet belonging to the queue
are dropped randomly regardless if they are high priority traffic or low priority traffic
• Wred: Weighted Random early Discard: with this policy, before the Queue is full some packet belonging to
the queue are dropped randomly. First are dropped the packets with low priority and then are dropped the
packet of high priority
All rights reserved © SIAE microelettronica 6
También podría gustarte
- Tilt ElectricoDocumento13 páginasTilt ElectricoMarcos BermudezAún no hay calificaciones
- ALC Plus2e - Caracteristicas-Instalación-ComisionamientoDocumento34 páginasALC Plus2e - Caracteristicas-Instalación-ComisionamientoMarcos BermudezAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual Configuracion IP Estatica en BTS 3900 (RAN 13)Documento5 páginasManual Configuracion IP Estatica en BTS 3900 (RAN 13)Marcos BermudezAún no hay calificaciones
- Estándar de Instalación Proy MoGSMDocumento26 páginasEstándar de Instalación Proy MoGSMMarcos BermudezAún no hay calificaciones
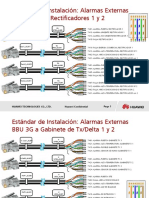
- Estándar de Instalación Alarmas Externas v4 - Claro GSM ModernizationDocumento12 páginasEstándar de Instalación Alarmas Externas v4 - Claro GSM ModernizationMarcos BermudezAún no hay calificaciones