Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
LAB QUIM INORG II - Tarea I - Edwin Aquino
Cargado por
Edwin A0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
8 vistas1 páginaDerechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
8 vistas1 páginaLAB QUIM INORG II - Tarea I - Edwin Aquino
Cargado por
Edwin ACopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 1
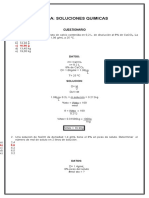
Practica 1 de laboratorio de química inorgánica 2
Título: soluciones molares
Profesor: Félix J. Beltrán, ing. Qui. Ma
Nombre: Edwin Augusto Aquino Payano Matricula: 1-21-5093 Seccion: MED-765-007
Objetivo general: Calcule la molaridad de las soluciones preparadas con:
a) 400 ml de solución con 100 gr de NaCl
Na= 1x23=23 Cl= 1x35=35
P.M. = 58.44 P.M
m=100g
V = 400 mL 400mL = 0.4L
M = m / (P.M) (V) = 100 / 58 x 0.4 = 100/23.376 = M= 4.27789185 M
b) 1000 ml de solución con 80 gr de NaOH
Na= 1x23 = 23 O= 1x16 = 16 H = 1x1 = 1
P.M= 40
m= 80g
V= 100 mL = 0.1 L
M = m / (P.M) (V) = 80 / (40) (0.1) = 80 / 4 = 20.002 M
c) 500 ml de solución con 100 gr de C12H22O11
C= 12 x 12 = 144 H= 22 x 1 = 22 O= 11 x 15.99 = 175.89
P.M= 341.89
m= 100g
V= 500 mL = 0.5 L
M = m / (P.M) (V) = 100 / (341.89) (0.5) = 100/170.945 = 0.584 M
También podría gustarte
- Química Analítica-Ejercicios Resueltos-2019Documento6 páginasQuímica Analítica-Ejercicios Resueltos-2019DarskeidAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios ResueltosDocumento12 páginasEjercicios Resueltosgiancarlo burgos gamarra67% (3)
- Informe #1 Metrologia y CalculosDocumento9 páginasInforme #1 Metrologia y CalculosMaria Elena Mita CallahuancaAún no hay calificaciones
- Quimica Semana 5 Eudardo ArayaDocumento6 páginasQuimica Semana 5 Eudardo ArayaEduardo ArayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Q.a.cualitativa-EjerciciosDocumento19 páginasTrabajo Q.a.cualitativa-EjerciciosGabriela G. Ch0% (1)
- Quimica SEMANA 10 CPU UNSMDocumento5 páginasQuimica SEMANA 10 CPU UNSMSilverTelloFernadez100% (1)
- Tarea 5 QuimicaDocumento6 páginasTarea 5 QuimicaNicole86% (7)
- Seminario 2 de SolucionesDocumento7 páginasSeminario 2 de SolucionesJosé AbantoAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía: Unidades de Concentracion FisicaDocumento3 páginasGuía: Unidades de Concentracion FisicaMACARENA TOROAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de QuimicaDocumento16 páginasEjercicios de QuimicaAndres Camilo Velez Herrera100% (1)
- Quimica en Procesos Productivos Tarea5Documento7 páginasQuimica en Procesos Productivos Tarea5Max Díaz C.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Taller de Ejercicios Sobre Osmolaridad y Presión OsmóticaDocumento1 páginaTaller de Ejercicios Sobre Osmolaridad y Presión OsmóticaJose David Perez NavarroAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica2. AnalisisinstrumentalDocumento10 páginasPractica2. AnalisisinstrumentalJosmar PuigAún no hay calificaciones
- Titulación Redox Vitamina CDocumento6 páginasTitulación Redox Vitamina Clia emiliaAún no hay calificaciones
- Quimica GeneralDocumento25 páginasQuimica Generalvero_328064826Aún no hay calificaciones
- Preparar Una SoluciónDocumento4 páginasPreparar Una SoluciónAlejandro Jesus Escobar JihuañaAún no hay calificaciones
- Nombre de Asignatura: Semana 5: Química en Procesos ProductivosDocumento6 páginasNombre de Asignatura: Semana 5: Química en Procesos ProductivosCinthiaa PailamillaAún no hay calificaciones
- CAHUANA LOPEZ ACTIVIDAD - 20 - MME - RECUPERACION - PREPARACION - DE - SOLUCIONES - NORMALIDAD - AutoguardadoDocumento14 páginasCAHUANA LOPEZ ACTIVIDAD - 20 - MME - RECUPERACION - PREPARACION - DE - SOLUCIONES - NORMALIDAD - AutoguardadoMariela MaldonadoAún no hay calificaciones
- PRACTICA #4 Analisis Instrumental para Farmaceuticos 2021-IDocumento5 páginasPRACTICA #4 Analisis Instrumental para Farmaceuticos 2021-IIsabel Carpio GüimackAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de Soluciones (Resueltos)Documento10 páginasProblemas de Soluciones (Resueltos)Cesar RAún no hay calificaciones
- Agustin - Solis Tarea 5Documento6 páginasAgustin - Solis Tarea 5Agustin Leonardo Solis MuñozAún no hay calificaciones
- QuimicaDocumento6 páginasQuimicaluis eduardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Parcial Qca Analítica II 2021 2 M1Documento3 páginasParcial Qca Analítica II 2021 2 M1Valee VelasquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Consolidado Trabajo Grupal GR5Documento38 páginasConsolidado Trabajo Grupal GR5Monica JacomeAún no hay calificaciones
- S11 - HOJA TALLER PrácticaDocumento4 páginasS11 - HOJA TALLER PrácticaSTHEFANY JAZMIN AGUILAR RIOSAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de La Práctica N10Documento9 páginasEjercicios de La Práctica N10Stefanny Maza GrauAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemario de Quimica de Soluciones 8 Febrero 2017Documento21 páginasProblemario de Quimica de Soluciones 8 Febrero 2017Laura Jukari Cárdenas HernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de Análisis VolumétricoDocumento4 páginasProblemas de Análisis VolumétricoQuique Báez García100% (1)
- Primer Taller de QuimicaDocumento6 páginasPrimer Taller de QuimicaNicol GambaAún no hay calificaciones
- Química I FACTORES DE CONVERSIÓN-MEGS PDFDocumento7 páginasQuímica I FACTORES DE CONVERSIÓN-MEGS PDFNancy EsquivelAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesión 1. Introduccion A La Química AnaliticaDocumento18 páginasSesión 1. Introduccion A La Química AnaliticaANDERSON JHORDY CARRION PELAEZAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas de Quimica AnaliticaDocumento2 páginasProblemas de Quimica AnaliticaAlondra de DiosAún no hay calificaciones
- Espectrofotometria (Ejercicios)Documento12 páginasEspectrofotometria (Ejercicios)Jhoe RoqueAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Practico Unidad 5Documento5 páginasEjercicios Practico Unidad 5Osmel Elias Suero Terrero0% (1)
- Taller AsincronicoDocumento5 páginasTaller AsincronicoFernando MoreiraAún no hay calificaciones
- SOLUCIONES Guía de Ejercicios PHDocumento7 páginasSOLUCIONES Guía de Ejercicios PHDallit's Sagredo Oyarce100% (1)
- Actividad de Disoluciones Anahuac Ok2Documento3 páginasActividad de Disoluciones Anahuac Ok2pedro lopezAún no hay calificaciones
- SistemasfyqDocumento6 páginasSistemasfyqHugo SánchezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejerccios de Quimica Estequiometria Analitica EtcDocumento74 páginasEjerccios de Quimica Estequiometria Analitica EtcKarolMaricieloAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen RecuperativoDocumento4 páginasExamen RecuperativoEnmanuelAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividades-Unid. Porcentaules 05-05-2023Documento3 páginasActividades-Unid. Porcentaules 05-05-2023Margarita Toledo AcevedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 03 de Quimica ListaDocumento5 páginasPractica 03 de Quimica ListaLorena Izquierdo sabino100% (1)
- Qan U3 A2e1 GoclDocumento7 páginasQan U3 A2e1 Goclgonzalo castro lopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe 2 - Agua y SolucionesDocumento6 páginasInforme 2 - Agua y SolucionesMilena PlazaAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de Apropiación Concentraciónes Tamq 18Documento5 páginasActividad de Apropiación Concentraciónes Tamq 18Valentina PantojaAún no hay calificaciones
- TP N°6 SolucionesDocumento9 páginasTP N°6 SolucionesMaria Alejandra Leal NigroAún no hay calificaciones
- S08 TALLER GRUPAL FinalizadoDocumento6 páginasS08 TALLER GRUPAL FinalizadoCarlos Roldán ParedesAún no hay calificaciones
- Quimica General Unidad 2 Fase 2 Trabajo Cuantificación y Relación en La Composición de La Materia (Autoguardado)Documento22 páginasQuimica General Unidad 2 Fase 2 Trabajo Cuantificación y Relación en La Composición de La Materia (Autoguardado)vito88% (8)
- COLOQUIO N4 IsotonicidadDocumento12 páginasCOLOQUIO N4 IsotonicidadFer RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- TP 1Documento8 páginasTP 1Facundo Santillan SuarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuestionario 11Documento4 páginasCuestionario 11David Ramírez100% (1)
- Preg Conc SolucionesDocumento4 páginasPreg Conc SolucionesMacarena Jimenez ZapataAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe 5, Soluciones IsotonicasDocumento6 páginasInforme 5, Soluciones IsotonicasNATALIA SARITH HERNÁNDEZ GÓMEZAún no hay calificaciones
- Caraballo - Pamela - Guia #5 - SolucionesDocumento4 páginasCaraballo - Pamela - Guia #5 - SolucionesPamela Maria Caraballo RoaAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Soluciones Sicvi IndividualDocumento11 páginasTaller Soluciones Sicvi IndividualMartín Atehortúa CampoAún no hay calificaciones
- Ponlo en Una Sola ColumanaDocumento7 páginasPonlo en Una Sola Columanafrancis yupanquiAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller 2b - 2022Documento2 páginasTaller 2b - 2022Mariana Eyras CarracoAún no hay calificaciones
- BIO - Ruta Del Plastico - Edwin AquinoDocumento4 páginasBIO - Ruta Del Plastico - Edwin AquinoEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- LAB QUIM INORG II - Tarea II - Edwin AquinoDocumento2 páginasLAB QUIM INORG II - Tarea II - Edwin AquinoEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- BIO - Nutricion - Edwin AquinoDocumento3 páginasBIO - Nutricion - Edwin AquinoEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluación FotosintesisDocumento1 páginaEvaluación FotosintesisÁmbar GuzmánAún no hay calificaciones
- Biología I: Universidad Tecnológica de Santiago (UTESA) Recinto: Santo Domingo de Guzmán Herrera-Facultad de MedicinaDocumento4 páginasBiología I: Universidad Tecnológica de Santiago (UTESA) Recinto: Santo Domingo de Guzmán Herrera-Facultad de MedicinaEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento2 páginasUntitledEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- El ConocimientoDocumento13 páginasEl ConocimientoEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- Parte de Las Células - Biologia I - Edwin AquinoDocumento2 páginasParte de Las Células - Biologia I - Edwin AquinoEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- Organigrama de La Historia de La Biologia - Edwin Aquino BIOLOGIA IDocumento1 páginaOrganigrama de La Historia de La Biologia - Edwin Aquino BIOLOGIA IEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- Organigrama de La Historia de La Biologia - Edwin Aquino BIOLOGIA IDocumento1 páginaOrganigrama de La Historia de La Biologia - Edwin Aquino BIOLOGIA IEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- Mapa Conceptual Biologia I de Edwin UtesaDocumento2 páginasMapa Conceptual Biologia I de Edwin UtesaEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones
- Linea de Tiempo - Biologia I Edwin AquinoDocumento4 páginasLinea de Tiempo - Biologia I Edwin AquinoEdwin AAún no hay calificaciones