Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Abreviado 2
Cargado por
Leon CarlosDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Abreviado 2
Cargado por
Leon CarlosCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
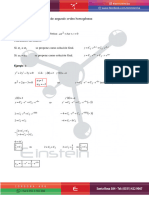
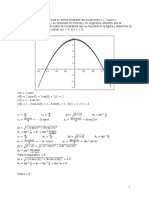
1 ax 1 ax
METODOS ABREVIADOS yp e yp e
FD Fa
y 5y 8y 4y e 2x
1
yp 3 2
e 2x como a 2
D 5D 8D 4
D 3 5D 2 8D 4 0
1
D 1 D 2 D 2 0 yp
23 5 22 8 2 4
e 2x
D1 1, D2 2, D3 2 yp
1
e 2x
8 20 16 4
yh c1e x c2e 2x c3xe 2x yp
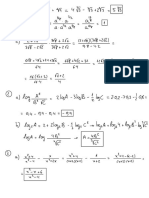
1 2x
e
0
1 1
yp e 2x yp x e 2x
D 3 5D 2 8D 4 3D 2 10D 8
1 2x
yp x e 1
3 22 10 2 8 yp x 2 e 2x
12 10
1 1
yp x e 2x y p x 2 e 2x
12 20 8 2
1
y p x e 2x
yh c1e x c2e 2x c3xe 2x
0
1 1
yp x 2 e 2x y c1e x c2e 2x c3xe 2x x 2e 2x
6D 10 2
1
yp x 2 e 2x
6 2 10
También podría gustarte
- Taller Aplicaciones IntegralDocumento4 páginasTaller Aplicaciones IntegralValentina Alonso MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Prac 2 II EmiDocumento13 páginasPrac 2 II EmiLucio MercadoAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucion Examen Segundo Parcial Ecuaciones Diferenciales 01 06 2021Documento4 páginasSolucion Examen Segundo Parcial Ecuaciones Diferenciales 01 06 2021Jhonatan Ulises Valdez ArellanoAún no hay calificaciones
- 15VariacionParametros PDFDocumento2 páginas15VariacionParametros PDFAlejandro RamirezAún no hay calificaciones
- D R DR: Se SabeDocumento45 páginasD R DR: Se SabeMAYCOL ISAAC QUISPE QUISPEAún no hay calificaciones
- Integrles MúltiplesnDocumento26 páginasIntegrles MúltiplesnLuis Fernando Durán SayguaAún no hay calificaciones
- MúltiplesDocumento1 páginaMúltiplesJosué MuñozAún no hay calificaciones
- EVA4 CICLO I-2022 REPETIDO Y DIFERIDO SoluciónDocumento4 páginasEVA4 CICLO I-2022 REPETIDO Y DIFERIDO Soluciónit21001Aún no hay calificaciones
- Determinación de La Ecuación de Una Circunferencia Bajo Ciertas CondicionesDocumento10 páginasDeterminación de La Ecuación de Una Circunferencia Bajo Ciertas CondicionesJanet Mendoza SAún no hay calificaciones
- Fórmulas Básicasde IntegraciónDocumento2 páginasFórmulas Básicasde Integraciónsantiago gómezAún no hay calificaciones
- EDO Cuasi Homogéneas PDFDocumento2 páginasEDO Cuasi Homogéneas PDFJuan Carlos MalquiAún no hay calificaciones
- 2.1 Ecuaciones Diferenciales de Variables SeparablesDocumento1 página2.1 Ecuaciones Diferenciales de Variables SeparablesCristel Dariel Aguilar AliAún no hay calificaciones
- PDF Guia de Ejercicios Calculo 1 Ing ValenciaDocumento159 páginasPDF Guia de Ejercicios Calculo 1 Ing ValenciaBrian Alanoca BautistaAún no hay calificaciones
- Resolucion Evaluacion #2 2019Documento6 páginasResolucion Evaluacion #2 2019nahirzalazar2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Final Luis Jaime Quintero SanchezDocumento21 páginasTrabajo Final Luis Jaime Quintero SanchezCarlos CabreraAún no hay calificaciones
- 1-3 E.D. 2do Orden HomogeneasDocumento2 páginas1-3 E.D. 2do Orden HomogeneasIgnacio SanguedolceAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemas Semana 9Documento5 páginasProblemas Semana 9Antonio VillaltaAún no hay calificaciones
- Soluciones ComplementariasDocumento18 páginasSoluciones ComplementariasManuel PalaciosAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 1Documento17 páginasTarea 1Froylan De la CruzAún no hay calificaciones
- Primera Practica - SolucionarioDocumento7 páginasPrimera Practica - SolucionarioerickesmeAún no hay calificaciones
- EVA5 CICLO I-2022 mat315-SOLUCIONDocumento7 páginasEVA5 CICLO I-2022 mat315-SOLUCIONHazelAún no hay calificaciones
- Trabajo Autonomo 03 - ProbabilidadesDocumento7 páginasTrabajo Autonomo 03 - ProbabilidadesOberluisAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 04 Sesion 01 - Método de Variación de ParámetroDocumento2 páginasSemana 04 Sesion 01 - Método de Variación de ParámetroJessica Pizarro DávilaAún no hay calificaciones
- G0 IntroducciónDocumento1 páginaG0 Introducciónjverav1108Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Integrales de Linea 8Documento7 páginasEjercicios Integrales de Linea 8Leonor SssAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales 06Documento1 páginaEcuaciones Diferenciales 06Van ArtivillAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea de IntegralesDocumento8 páginasTarea de IntegralesRocisela Isabel Romero BernaolaAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 Int Dobles 3Documento3 páginas7 Int Dobles 3Agos GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- UND3 2 MInerciaMasasDocumento2 páginasUND3 2 MInerciaMasasKEVIN CASTILLO ACUÑAAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 11.90Documento2 páginasEjercicio 11.90Eddie PerezAún no hay calificaciones
- Talleres de Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocumento28 páginasTalleres de Ecuaciones DiferencialesJeison VelásquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Determinación de Longitudes de CurvaDocumento3 páginasEjercicios de Determinación de Longitudes de CurvaMarco Antonio Cervantes YabarAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller1 EDO EcuacionesSinteticoDocumento5 páginasTaller1 EDO EcuacionesSinteticoMayra Alejandra Torres AlfonsoAún no hay calificaciones
- S1eea18 2Documento5 páginasS1eea18 2isaias gueAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones Diferenciales (Ejercicios 3.11)Documento3 páginasEcuaciones Diferenciales (Ejercicios 3.11)Faviola ortizAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Variación de ParametrosDocumento2 páginasEjercicios Variación de Parametrosluis sandovalAún no hay calificaciones
- Corrección Global 4to 1a EvDocumento3 páginasCorrección Global 4to 1a Evgonzamanzano925Aún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario Segundo Examen Parcial 1 - 2022Documento6 páginasSolucionario Segundo Examen Parcial 1 - 2022diego serranoAún no hay calificaciones
- TP 5 - 1er - 2021 - Explicaciones - 27-05Documento4 páginasTP 5 - 1er - 2021 - Explicaciones - 27-05Thomas GiannelliAún no hay calificaciones
- 5 Int DoblesDocumento3 páginas5 Int DoblesAgos GonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Septiembre 2012Documento5 páginasExamen Septiembre 2012rafael hidalgoAún no hay calificaciones
- Guía 6 Ec Dif Lineales Homog Met Coef Indet 2022Documento2 páginasGuía 6 Ec Dif Lineales Homog Met Coef Indet 2022Francisca Isidora Kleisinger LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 02 - Ecuaciones Diferenciales de Variables Separables y HomogeneasDocumento3 páginasTarea 02 - Ecuaciones Diferenciales de Variables Separables y HomogeneasAlex David MuñivargasAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 6 Algebra Q1 2023-1Documento2 páginasTarea 6 Algebra Q1 2023-1Dreybin GrehamAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 3 - Aplicaciones de Las Integrales - John Anderson Martinez SalazarDocumento5 páginasTarea 3 - Aplicaciones de Las Integrales - John Anderson Martinez SalazarJohn Anderson Martínez SalazarAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadernillo Unidad 5 Calculo VectorialDocumento3 páginasCuadernillo Unidad 5 Calculo VectorialJonathan Joseph Torres PérezAún no hay calificaciones
- Práctica Segundo Parcial Mat207 InvDocumento6 páginasPráctica Segundo Parcial Mat207 InvCristiam GutierrezAún no hay calificaciones
- Electromagnetismo 2017. 2 Electrostatica I Clase Martes 171017Documento81 páginasElectromagnetismo 2017. 2 Electrostatica I Clase Martes 171017Paola GongoraAún no hay calificaciones
- Metodos Abreviados para Ed. Orden Superior PDFDocumento5 páginasMetodos Abreviados para Ed. Orden Superior PDFCamila Carvallo100% (2)
- Tarea 1Documento4 páginasTarea 1Ximena MorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividades Resueltas III Examen (Parte 2 Iiip 2023)Documento9 páginasActividades Resueltas III Examen (Parte 2 Iiip 2023)Faviola ortizAún no hay calificaciones
- VariaparametrosDocumento31 páginasVariaparametrosboyard234000Aún no hay calificaciones
- Sed P2 Ii 2001Documento7 páginasSed P2 Ii 2001SergioAún no hay calificaciones
- Talleres E.D. V (3) 2018-2Documento25 páginasTalleres E.D. V (3) 2018-2Jhon Eddie Ramirez LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Parcial Calculo IIIDocumento6 páginasExamen Parcial Calculo IIICés Avi CelAún no hay calificaciones
- Solución A PC01Documento4 páginasSolución A PC01NELSY YOHANI GUERRERO CANOAún no hay calificaciones
- Sarrus Determinantes 3X3Documento22 páginasSarrus Determinantes 3X3Javier G HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicio 1, Tarea #2Documento4 páginasEjercicio 1, Tarea #2Jhaner Luis Carrera TerronesAún no hay calificaciones
- Caratula InformeDocumento1 páginaCaratula InformeLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Practico Nro 2-Matematicas IIIDocumento2 páginasPractico Nro 2-Matematicas IIILeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Segunda MesaDocumento1 páginaSegunda MesaLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Capítulo 3 Teoría de Errores en Las Mediciones: Topografía I - Civ 231 Capítulo 3 MSC - Ing. Luis Alberto Yurquina FloresDocumento12 páginasCapítulo 3 Teoría de Errores en Las Mediciones: Topografía I - Civ 231 Capítulo 3 MSC - Ing. Luis Alberto Yurquina FloresLeon Carlos100% (1)
- Mesa N°1 Civ112Documento1 páginaMesa N°1 Civ112Leon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos A DesarrollarDocumento4 páginasProductos A DesarrollarLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Practico Nro 3-Matematicas IIIDocumento2 páginasPractico Nro 3-Matematicas IIILeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Certificado 1837908 PDFDocumento1 páginaCertificado 1837908 PDFLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento37 páginasUntitledLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento32 páginasUntitledLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- CINTA Y JALON Virtual LabDocumento67 páginasCINTA Y JALON Virtual LabLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 1 Fisica 2Documento11 páginasGuia 1 Fisica 2Leon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- UntitledDocumento1 páginaUntitledLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 4Documento13 páginasGuia 4Leon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Texto Del Capítulo 4 PDFDocumento26 páginasTexto Del Capítulo 4 PDFLeon Carlos100% (1)
- Guia 5Documento12 páginasGuia 5Leon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 6Documento13 páginasGuia 6Leon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Carimbo Oficila de Diseño Grafico IiDocumento1 páginaCarimbo Oficila de Diseño Grafico IiLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones LinealesDocumento21 páginasEcuaciones LinealesLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia de Laboratorio de TopografíaDocumento57 páginasGuia de Laboratorio de TopografíaLeon Carlos100% (1)
- Baldivieso Alarcon Jessica. Lamina 5 GeoDocumento1 páginaBaldivieso Alarcon Jessica. Lamina 5 GeoLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones
- Baldivieso Alarcon Jessica. Lamina 7 GeoDocumento1 páginaBaldivieso Alarcon Jessica. Lamina 7 GeoLeon CarlosAún no hay calificaciones