Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Productos Notables
Cargado por
Sayda MartinezTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Productos Notables
Cargado por
Sayda MartinezCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
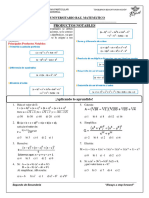
PRODUCTOS NOTABLES 2.
Reducir:
Son los resultados de ciertas R = (a + b)2 – (b - a)2 + (a – 2b)2 – a2 – 4b2
multiplicaciones de polinomios de forma a) 0 b) a c) b
conocida. Estos resultados se pueden d) 2ab e) ab
determinar directamente sin necesidad de
efectuar la propiedad distributiva de la
multiplicación.
3. El valor de:
Ejemplo:
(𝑥 + 3)(𝑥 + 5) = 𝑥 2 + 8𝑥 + 15 N = ( 5 + 24 + 5 − 24 )2
a) 6 b) 8 c) 10
1. Binomio al cuadrado d) 12 e) 14
(𝑎 + 𝑏)2 = 𝑎2 + 2𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2
(𝑎 − 𝑏)2 = 𝑎2 − 2𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2
2. Binomio al cubo 4. Efectuar:
(𝑎 + 𝑏)3 = 𝑎3 + 3𝑎2 𝑏 + 3𝑎𝑏 2 + 𝑏 3 ( 5 + 1)( 5 − 1) + ( 3 + 1)( 3 − 1)
P=
(𝑎 − 𝑏)3 = 𝑎3 − 3𝑎2 𝑏 + 3𝑎𝑏 2 − 𝑏 3 ( 2 + 1)( 2 − 1)
a) 3 b) 4 c) 5
3. Diferencia de cuadrados
d) 6 e) 7
(𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎 − 𝑏) = 𝑎2 − 𝑏 2
ACADEMIA PREPOLICIAL SISTEMA INTEGRAL PERSONALIZADO “SIP”
4. Identidades de Legendre
(𝑎 + 𝑏)2 + (𝑎 − 𝑏)2 = 2(𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 ) 5. Efectuar:
(𝑎 + 𝑏)2 − (𝑎 − 𝑏)2 = 4𝑎𝑏 R = (x + n)(x - n)(x2 + n2)(x4 + n4)(x8 + n8) +
(𝑎 + 𝑏)4 + (𝑎 − 𝑏)4 = 8𝑎𝑏(𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 ) n16
a) x12 b) n16 c) x16
5. Suma y diferencia de cubos d) x + n e) 1
16 16
(𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑎2 − 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 ) = 𝑎3 + 𝑏 3
(𝑎 − 𝑏)(𝑎2 + 𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏 2 ) = 𝑎3 − 𝑏 3
6. Trinomio al cuadrado 6. Luego de efectuar:
(𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐)2 = 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 E = (x + 1)(x + 2) + (x + 3)(x + 4) – 2x(x + 5)
+ 2(𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏𝑐 + 𝑎𝑐) Se obtiene:
a) 15 b) 14 c) 13
7. Trinomio al cubo d) 12 e) 11
(𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐)3 = 𝑎3 + 𝑏 3 + 𝑐 3 + 3(𝑎 + 𝑏)(𝑏
+ 𝑐)(𝑎 + 𝑐)
7. Si: m = 2a + 2b + 2c y 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 = 0
8. Producto de dos binomios con término
Calcular:
en común
(𝑥 + 𝑎)(𝑥 + 𝑏) = 𝑥 2 + (𝑎 + 𝑏)𝑥 + 𝑎𝑏 m2 − (m − a)2 − (m − b)2 − (m − c)2
E=
m2 + a2 + b2 + c2
9. Identidades condicionales a) a + b + c b) 1 c) a2 + b2 +
Si 𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐 = 0, se verifican: c2
• 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 = −2(𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏𝑐 + 𝑎𝑐) d) abc e) -1
• (𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏𝑐 + 𝑎𝑐)2 = (𝑎𝑏)2 + (𝑏𝑐)2 +
(𝑎𝑐)2
• 𝑎3 + 𝑏 3 + 𝑐 3 = 3𝑎𝑏𝑐
8. Hallar el valor numérico de:
EJERCICIOS E = (x + 4)(x + 2) + 1
Para: x = 2 000
1. Efectuar:
a) 2001 b) 2002 c)
E = (x + 2y)2 – (x – 2y)2 – 4xy
2003
a) xy b) 3xy c)
d) 2004 e) 2005
4xy
d) 6xy e) 9xy
9. Efectuar: 19. Reduce:
E = (x + y - 2)2 + (x + y + 3)2 – 2(x + y)2 - 13 (3𝑥 + 4𝑦)2 − (3𝑥 − 4𝑦)2
𝑅=
a) -4(x + y) b) 6(x + y) c) 2(x + y) 𝑥𝑦
d) -4 e) x2 a) 44 b)y c) 46
d) x e)48
10. Si 𝑚 + 𝑛 = 4 y 𝑚𝑛 = 2
calcular el valor numérico de: 20. Si (𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2 ). 𝑥 −1 . 𝑦 −1 = 2. Calcular el valor
𝑚3 + 𝑛3 de:
a) 30 b)1 c)35 𝑥 2 + 𝑥𝑦 + 𝑦 2
𝐸=
d) 40 e)8 (𝑥 + 𝑦)2
1 3
a) b) c)𝑥 2 + 𝑦 2
3 4
11. Reduce 2 3
d) e)
𝐴 = (3𝑥 + 2)(9𝑥 2 − 6𝑥 + 4) 3 2
− (3𝑥 − 2)(9𝑥 2 + 6𝑥 + 4)
a) 8 b) 10 c) 2 21. Si 𝑎 + 𝑏 = 7 𝑦 𝑎𝑏 = 3. 𝐶𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎:
d) 16 e) 1
𝑎2 + 𝑏2
12. Si x+y+z=0, calcula el valor de: a) 40 b) 10 c) 43
𝑥 3 + 𝑦3 + 𝑧3 d) 22 e) 23
𝑀=
9𝑥𝑦𝑧
ACADEMIA PREPOLICIAL SISTEMA INTEGRAL PERSONALIZADO “SIP”
2 1
a) b) c)𝑦 3
3 3
4
d) e)𝑥 3 1
22. Si 𝑥 + = 5, 𝐶𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎:
5 𝑥
1
𝑥2 +
13. Si m+n+p=0, mnp=5. calcula el valor de: 𝑥2
𝑀 = 𝑚3 + 𝑛3 + 𝑝 3 a) 40 b) 10 c) 43
a) 5 b) 10 c) 15 d) 22 e) 23
d) 0 e) 20
23. Calcula:
3 3 3 3 3 3
14. Si 𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐 = 10; 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 = 60. 𝐶𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎: 𝐵 = (√7 + √2)(√49 − √14 + √4) + (√5
𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏𝑐 + 𝑎𝑐 3 3 3
− √3)(√25 + √15 + √9)
3
a) 10 b) 20 c) 60
d) 15 e) 40 a) 20 b) 10 c) 7
d) 22 e) 13
15. Si 𝑎 + 𝑏 + 𝑐 = 8; 𝐶𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎 𝑎2 + 𝑏 2 + 𝑐 2 . 𝑆𝑖:
𝑎𝑏 + 𝑏𝑐 + 𝑎𝑐 = 15
a) 30 b)34 c)44
d) 23 e)40
16. Si 𝑥 + 𝑦 + 𝑧 = 0, 𝐶𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎:
𝑥 3 + 𝑦3 + 𝑧3 𝑥 2 + 𝑦2 + 𝑧2
𝑀= +
𝑥𝑦𝑧 𝑥𝑦 + 𝑥𝑧 + 𝑦𝑧
a) 5 b)3 c)0
d) 2 e)1
17. Efectúa:
(√5 + 1)(√5 − 1) + (√3 + 1)(√3 − 1)
𝑃=
(√2 + 1)(√2 − 1)
a) 4 b)2 c)10
d) 6 e)0
18. Efectúa:
(√6 + 2)(√6 − 2) + (√7 + 1)(√7 − 1)
𝑅=
(√5 + 2)(√5 − 2)
a) 8 b) 4 c) 2
d) 10 e) 6
También podría gustarte
- Arcos Ideales en OrtodonciaDocumento89 páginasArcos Ideales en Ortodonciajuan1pablo1gutierr-6100% (7)
- Productos Notables - Nivel 1 - Parte 1Documento2 páginasProductos Notables - Nivel 1 - Parte 1Matemath100% (6)
- Informe de LaboratorioDocumento22 páginasInforme de LaboratorioGonzalo ValdiviaAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Prodcutos NotablesDocumento4 páginasAlgebra Prodcutos NotablesVictor Ponce GuizabaloAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos Notables IDocumento4 páginasProductos Notables IGuido Mervin Orvezo ZamudioAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra Tema 17 SolucionarioDocumento5 páginasAlgebra Tema 17 SolucionarioAvril Espinoza RomaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Separata - Multiplicación de Un Polinomio Por Un Polinomio - Ua - 2do Sec - SRDocumento1 páginaSeparata - Multiplicación de Un Polinomio Por Un Polinomio - Ua - 2do Sec - SRCarlos HinostrozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminario Álgebra 19-12-2023Documento1 páginaSeminario Álgebra 19-12-2023Maria Arellano JaimeAún no hay calificaciones
- Producto Notable - Ejercicios 4° Sec PDFDocumento4 páginasProducto Notable - Ejercicios 4° Sec PDFJuan Adolfo Nicasio SantillanAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 - Problemas Propuestos de Productos Notables y Division Alg. (CS11)Documento3 páginas2 - Problemas Propuestos de Productos Notables y Division Alg. (CS11)ya2020067078Aún no hay calificaciones
- Practica Cakificada San AgustinDocumento2 páginasPractica Cakificada San AgustinWilfredo ReynosoAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos Notables y FactorizacionDocumento1 páginaProductos Notables y FactorizacionHenry RoyerAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos NotablesDocumento2 páginasProductos NotablesGustavo MaytaAún no hay calificaciones
- P02 Productos NotablesDocumento2 páginasP02 Productos NotablesMaycol Janns Quispe ValdezAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra 2 RomaDocumento1 páginaAlgebra 2 RomaEducación EurekaAún no hay calificaciones
- ZAlgebra 2° - N° 7Documento2 páginasZAlgebra 2° - N° 7german dezaAún no hay calificaciones
- Examendealgebra 2007Documento9 páginasExamendealgebra 2007nehuen mapuAún no hay calificaciones
- UI1MA-AL-EJ01-MULTIPLICACIÓN ALGEBRAICA-Prof Ricardo EspinoDocumento2 páginasUI1MA-AL-EJ01-MULTIPLICACIÓN ALGEBRAICA-Prof Ricardo EspinoAlexis Berrocal AllccaAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos Notables - EvaluacionDocumento3 páginasProductos Notables - EvaluacionJeff HerCasas100% (1)
- Algebra Tema 17 Productos Notables IIDocumento5 páginasAlgebra Tema 17 Productos Notables IIAvril Espinoza RomaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminario 1 Algebra - Trigon 2023 IiDocumento3 páginasSeminario 1 Algebra - Trigon 2023 Iimelany medinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Face Cero 2024-1 Ecuaciones OkDocumento2 páginasFace Cero 2024-1 Ecuaciones OkJhoel AnahuaAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebbra QuezadaDocumento2 páginasAlgebbra QuezadaTotti Di Franchesco PelaezAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica de Ecuaciones Cpu 2022 - 2 - Final - ADocumento2 páginasPractica de Ecuaciones Cpu 2022 - 2 - Final - AIsrael CuroAún no hay calificaciones
- Álgebra - Banco de Preguntas EmchDocumento4 páginasÁlgebra - Banco de Preguntas EmchYajhaira Guadalupe Vigo LozadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios de Reforzamiento Productos NotablesDocumento4 páginasEjercicios de Reforzamiento Productos NotablesLos locos de suyoAún no hay calificaciones
- PRODUCTOS NOTABES IiDocumento3 páginasPRODUCTOS NOTABES IiJessus Mamani PampaAún no hay calificaciones
- Problemario Calculo Dif IntDocumento12 páginasProblemario Calculo Dif IntFernanda BffAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra SabadosDocumento2 páginasAlgebra SabadosFrancis W. ArellanoAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra (Libros Praxis)Documento26 páginasAlgebra (Libros Praxis)Gustavo RaulAún no hay calificaciones
- Clase 1Documento1 páginaClase 1Nyll CaldasAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos NotablesDocumento2 páginasProductos NotablesMaria Arellano JaimeAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos Notables.Documento2 páginasProductos Notables.rneyragary25Aún no hay calificaciones
- Agosto - Algebra - 2doDocumento11 páginasAgosto - Algebra - 2doHugo EscobedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica Calificada de AlgebraDocumento3 páginasPractica Calificada de Algebracontador jeremy semestre 2022Aún no hay calificaciones
- Seminario No 1 - Álgebra: X X X X X MDocumento3 páginasSeminario No 1 - Álgebra: X X X X X MEstefano CastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra - MCM y MCDDocumento2 páginasAlgebra - MCM y MCDvictor sAún no hay calificaciones
- Ficha de Trabajo 6Documento2 páginasFicha de Trabajo 6Alessandra MichilotAún no hay calificaciones
- Circulo - Taller 2Documento4 páginasCirculo - Taller 2Gervis Castillo ArceAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos Notables - FactorizaciónDocumento2 páginasProductos Notables - FactorizaciónCristian Omar Gonzales SosaAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos NotablesDocumento4 páginasProductos NotablesRubén Darío Peralta CorreaAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos NotablesDocumento2 páginasProductos NotablesAnthony RomeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos NotablesDocumento2 páginasProductos NotablesbryanmechannunezAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos NotablesDocumento2 páginasProductos NotablesSandoval Cainamari SaritaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ecuaciones FraccionariasDocumento2 páginasEcuaciones FraccionariasMario FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematica Bàsica-EcuacionesDocumento3 páginasMatematica Bàsica-EcuacionesMaría E. Nuñez R.Aún no hay calificaciones
- Lista 3 EdoDocumento2 páginasLista 3 EdoBassai SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos NotablesDocumento3 páginasProductos NotablesJosé Carlos Torres VarillasAún no hay calificaciones
- MateformDocumento2 páginasMateformMirror JeonAún no hay calificaciones
- Mate Basica Examen UniDocumento9 páginasMate Basica Examen UniPatricia ValladolidAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Algebra Basico v1Documento2 páginasExamen Algebra Basico v1Jesus Zurita SilvaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cuadernillo RLM 5to SemestreDocumento23 páginasCuadernillo RLM 5to SemestreCamilo zuñigaAún no hay calificaciones
- ÁlgebraDocumento10 páginasÁlgebraVictoria HernándezAún no hay calificaciones
- LibroDocumento2 páginasLibroJulio Cesar Aponte ArroyoAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Solucionario U3Documento15 páginas3 Solucionario U3Laprimera CopiasAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra - Productos Notables IIDocumento2 páginasAlgebra - Productos Notables IIDiego Cortez PinzónAún no hay calificaciones
- Algebra 2do - Iii - IvbDocumento40 páginasAlgebra 2do - Iii - IvbArquimedes Huamán MenorAún no hay calificaciones
- Taller Aritmética y AlgebraDocumento9 páginasTaller Aritmética y AlgebraCamila PalacioAún no hay calificaciones
- Identidades NotablesDocumento3 páginasIdentidades NotablesWilfredo ReynosoAún no hay calificaciones
- Productos Notables 2ºDocumento2 páginasProductos Notables 2ºKARLA PATRICIAAún no hay calificaciones
- La ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesDe EverandLa ecuación general de segundo grado en dos y tres variablesAún no hay calificaciones
- 6TODocumento2 páginas6TOSayda MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- S18.s1 - Examen FinalDocumento1 páginaS18.s1 - Examen FinalSayda MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- PORTAFOLIODocumento6 páginasPORTAFOLIOSayda MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Física Moderna 2022-II U1Documento1 páginaFísica Moderna 2022-II U1Sayda MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Actividad de AprendizajeDocumento11 páginasActividad de AprendizajeSayda MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Angulos IntermedioDocumento3 páginasAngulos IntermedioSayda MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Angulos BásicoDocumento3 páginasAngulos BásicoSayda MartinezAún no hay calificaciones
- Intruduccion A La Probabilidad para Primero de SecundariaDocumento8 páginasIntruduccion A La Probabilidad para Primero de SecundariaSayda Martinez100% (1)
- Actividad 1 - UII Funciones - Varias Variables - Derivadas Parciales JMDocumento7 páginasActividad 1 - UII Funciones - Varias Variables - Derivadas Parciales JMFernando Solis100% (1)
- Separata Numero 01 Mayo Agosto 2021 IiDocumento19 páginasSeparata Numero 01 Mayo Agosto 2021 IiFrancoFernadezNoruegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Apuntadores C++Documento3 páginasApuntadores C++Kevin Salmeron VicenteAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 7 PDFDocumento1 páginaGuia 7 PDFkatherine valderramaAún no hay calificaciones
- Geometria - 2do Año - Guia Nº7 - RepasoDocumento5 páginasGeometria - 2do Año - Guia Nº7 - RepasoCarolina Izquierdo Sandoval100% (1)
- TensoresDocumento3 páginasTensoresRoberto Carlos Gironda yujraAún no hay calificaciones
- R-Reporte Práctica 8 Resistencia y Ley de OhmDocumento8 páginasR-Reporte Práctica 8 Resistencia y Ley de OhmRosario Valenzuela BarrazaAún no hay calificaciones
- Orientacion y Convivencia IVDocumento4 páginasOrientacion y Convivencia IVCarlos Daniel CapechiAún no hay calificaciones
- Evaluacion Matemáticas 1° BásicoDocumento4 páginasEvaluacion Matemáticas 1° BásicoADRIANAAún no hay calificaciones
- 2019-1 DMAE E003 06 Medidas de PosicionDocumento11 páginas2019-1 DMAE E003 06 Medidas de PosicionJoaquin Ignacio Milla FuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño Factorial Complet DOEDocumento6 páginasDiseño Factorial Complet DOEPaolo ValdiviaAún no hay calificaciones
- Matematicas FinancierasDocumento43 páginasMatematicas FinancierasRoman FrancoAún no hay calificaciones
- Razonamiento Matemático 1 Minuto/ejercicioDocumento16 páginasRazonamiento Matemático 1 Minuto/ejerciciojotahcqAún no hay calificaciones
- Arturo Saravia CVDocumento3 páginasArturo Saravia CVRuben Samanamud NatividadAún no hay calificaciones
- Tareas Primer Parcial Fundamentos de ProgramaciónDocumento13 páginasTareas Primer Parcial Fundamentos de ProgramaciónJhonn ChaucaAún no hay calificaciones
- Patrones de Succión en El Recién NacidoDocumento15 páginasPatrones de Succión en El Recién NacidoestebannicolasignaciAún no hay calificaciones
- Expresiones y OperadoresDocumento16 páginasExpresiones y Operadores007skyline001Aún no hay calificaciones
- Portafolio 1 - Lógica Matemática y Teoría de ConjuntosDocumento5 páginasPortafolio 1 - Lógica Matemática y Teoría de ConjuntosMorales P Kilsia100% (1)
- Guia de Laboratorio 4 Medidas de PosicionDocumento19 páginasGuia de Laboratorio 4 Medidas de PosicionProfe JamesAún no hay calificaciones
- Operadores Aritméticos en CDocumento4 páginasOperadores Aritméticos en CJesús ReañoAún no hay calificaciones
- Laura Redondo FlorezDocumento20 páginasLaura Redondo FlorezJORGE IRAM BARRAZA ROMEROAún no hay calificaciones
- Lógica JurídicaDocumento15 páginasLógica Jurídicaamilexa gonzalezAún no hay calificaciones
- Línea de Tiempo de La Probabilidad y LaDocumento16 páginasLínea de Tiempo de La Probabilidad y LaBrayan JulianAún no hay calificaciones
- Laboratorio #1 Mar - 2016v00Documento3 páginasLaboratorio #1 Mar - 2016v00Nayla Chuquimia MamaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Números Pseudo AleatoriosDocumento6 páginasNúmeros Pseudo AleatoriosVictor Enrique Toro AlvarezAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesión 01Documento20 páginasSesión 01Anonymous faRVVGNAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica Dirigida Unidad 4 - Prueba Kruskal WallisDocumento3 páginasPractica Dirigida Unidad 4 - Prueba Kruskal WallisAngel Inconfundible Povis OreAún no hay calificaciones
- Tarea 7 de EstadisticaDocumento8 páginasTarea 7 de EstadisticaXavier HilarioAún no hay calificaciones