Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Análisis Estructural Con Rotula
Cargado por
Smit RodriguezTítulo original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Análisis Estructural Con Rotula
Cargado por
Smit RodriguezCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
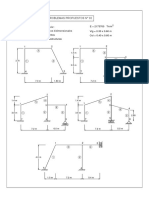
MATRIZ DE RIGIDEZ DE UN ELEMENTO INCLINADO
DEFINICION GENERAL
externas pudiendo ser: por gravedad, viento, sismo, temperatura, asentamientos diferenciales, etc.
La matriz K es la rigidez del elemento o de toda la estructura, dependiendo de lo que se quiere calcular,
MATRIZ DE RIGIDEZ DE UN ELEMENTO INCLINADO (sin considerar factor de forma)
S1 S2 -S4 -S1 -S2 -S4
S2 S3 S 5 -S2 -S3 S5 K11 K12
-S4 S5 S6 S4 -S5 S7
K = -S -S S S S S =
1 2 4 1 2 4
-S2 -S 3 -S5 S2 S 3 -S5 K21 K22
-S4 S5 S7 S4 -S5 S6
2 2 AE 12EI
S1 = K1 cos O + K2 sen O K1 = ; K2 = 3
L L j
S2 = ( K1 - K 2 ) senO.cos O
2 2
S3 = K1 senO + K 2 cos O
to
6EI 4EI
en
K3 = ; K 4=
em
2
S4 = K3 senO L L el
(+)
S5 = K3 cos O O
S6 = K 4 2 EI i
K 5=
L
S7 = K 5
Caso particular siendo:
Para columnas y vigas rectangulares:
A=bxh I = momento de inercia del elemento
3
bxh L = longitud del elemento
I =
12
E = 15000 F'c ( Kg/cm2 )
S1 S2 0 -S1 -S2 -S4
S2 S3 0 -S2 -S3 S5 K11 K12
0 0 0 0 0 0
K = -S -S 0 S1 S 2 S4 =
1 2
-S2 -S 3 0 S2 S 3 -S5 K21 K22
-S4 S5 0 S4 -S5 S6
2 2 AE 3EI
S1 = K1 cos O + K2 sen O K1 = ; K2 = 3
L L
S2 = ( K1 - K 2 ) senO.cos O
2 2
j
S3 = K1 senO + K 2 cos O 3EI 3 EI
K3 = ; K 4=
S4 = K3 senO L
2
L to
en
S5 = K3 cos O em
el (+)
S6 = K4 O
i
Caso particular
Para columnas y vigas rectangulares: siendo:
A=bxh
3 I = momento de inercia del elemento
bxh
I =
12 L = longitud del elemento
E = 15000 F'c ( Kg/cm2 )
elemento
2
1 5
3 4
1 2 6
1
elemento
elemento normal
normal
2 3
4 3
También podría gustarte
- Dosificacion Metodo ACI 211Documento10 páginasDosificacion Metodo ACI 211Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- DG-03 Cerco Perimetrico-De-02Documento1 páginaDG-03 Cerco Perimetrico-De-02Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- DG-04 Detalles de Techos Juntas y Bruñas-Dg-04 Detalles Techo y Juntas PDFDocumento1 páginaDG-04 Detalles de Techos Juntas y Bruñas-Dg-04 Detalles Techo y Juntas PDFSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- DG-08 Detalles de Pisos - Constructivos-D-43Documento1 páginaDG-08 Detalles de Pisos - Constructivos-D-43Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- DG-10 Portadas de Ingreso-P-01Documento1 páginaDG-10 Portadas de Ingreso-P-01Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- DG-5-6 Detalles de SS - HH.-D-52Documento1 páginaDG-5-6 Detalles de SS - HH.-D-52Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- DG-02 Detalles Exteriores-Dg-02Documento1 páginaDG-02 Detalles Exteriores-Dg-02Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- 05 - Principio de ArquimedesDocumento5 páginas05 - Principio de ArquimedesSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- G7-Estrategias para El Desarrollo Del Nivel Crítico y El Análisis de La ArgumentaciónDocumento6 páginasG7-Estrategias para El Desarrollo Del Nivel Crítico y El Análisis de La ArgumentaciónLuis mauricio50% (6)
- Hoja de Trabajo Sem 6Documento4 páginasHoja de Trabajo Sem 6Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Solucionario T1 10412Documento6 páginasSolucionario T1 10412Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Memoria Descriptiva Valorizacion #01Documento5 páginasMemoria Descriptiva Valorizacion #01Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- T1 - Concreto - Rodriguez Rodriguez Royer SmitDocumento17 páginasT1 - Concreto - Rodriguez Rodriguez Royer SmitSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Iu Agosto 2016Documento1 páginaIu Agosto 2016Angelica Avila VazquesAún no hay calificaciones
- Indices Unificados de Precios para Las Seis Áreas Geográficas - Feb.2018 PDFDocumento1 páginaIndices Unificados de Precios para Las Seis Áreas Geográficas - Feb.2018 PDFSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesión 02 Matriz Rigidez FinalDocumento3 páginasSesión 02 Matriz Rigidez Finalmilier angel diaz muñozAún no hay calificaciones
- Indices Unificados de Precios para Las Seis Áreas Geográficas - Ene.2018Documento1 páginaIndices Unificados de Precios para Las Seis Áreas Geográficas - Ene.2018Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Practica 02 PDFDocumento1 páginaPractica 02 PDFSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Indices Unificados de Precios para Las Seis Áreas Geográficas - Set.2017Documento1 páginaIndices Unificados de Precios para Las Seis Áreas Geográficas - Set.2017Smit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios PropuestosDocumento1 páginaEjercicios PropuestosSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- T2 Etica CiudadaniaDocumento13 páginasT2 Etica CiudadaniaDennis OrtizAún no hay calificaciones
- Link de Video Tutorial 02 PDFDocumento1 páginaLink de Video Tutorial 02 PDFSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Iu Agosto 2016Documento1 páginaIu Agosto 2016Angelica Avila VazquesAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Propuestos 02 PDFDocumento1 páginaEjercicios Propuestos 02 PDFSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Ejercicios Propuestos 02 PDFDocumento1 páginaEjercicios Propuestos 02 PDFSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Iu Agosto 2016Documento1 páginaIu Agosto 2016Angelica Avila VazquesAún no hay calificaciones
- Acta de Entrega de Terreno - ModeloDocumento2 páginasActa de Entrega de Terreno - ModeloSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Valorizacion Pozo TubularDocumento15 páginasValorizacion Pozo TubularSmit Rodriguez100% (1)
- 40-70 Calsificacion de SuelosDocumento106 páginas40-70 Calsificacion de SuelosSmit RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- Resoluci N Examen Intro Ing MecanicaDocumento2 páginasResoluci N Examen Intro Ing MecanicaBenjamin Alvear QuilpatayAún no hay calificaciones
- Opciones Estructurales y Constructivas 2023-1Documento9 páginasOpciones Estructurales y Constructivas 2023-1MANUEL ALFONSO SALAZAR ORTIZAún no hay calificaciones
- EAII 03 Version en LineaDocumento35 páginasEAII 03 Version en LineaIsaac ApaezAún no hay calificaciones
- Mare MotosDocumento6 páginasMare MotosWalter2800Aún no hay calificaciones
- Parcial 2 - Corte II - Análisis Estructural 2021Documento5 páginasParcial 2 - Corte II - Análisis Estructural 2021Juan Pablo GMAún no hay calificaciones
- Análisis Estructural Ii - Método MatricialDocumento14 páginasAnálisis Estructural Ii - Método MatricialLeonardo Francisco Sanchez Guerrero100% (1)
- Calculo de Rigidez LateralhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhDocumento9 páginasCalculo de Rigidez LateralhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhWladimir Diego CurasmaAún no hay calificaciones
- Semana 5 - EjerciciosDocumento6 páginasSemana 5 - EjerciciosYURI GERMAN VALENCIA OJEDAAún no hay calificaciones
- AE2 Ex2 Pra 2011-11Documento3 páginasAE2 Ex2 Pra 2011-11ropin14Aún no hay calificaciones
- ESTRUCTURALDocumento3 páginasESTRUCTURALBacilo Oviedo quevedoAún no hay calificaciones
- Método de RitterDocumento20 páginasMétodo de RitterSandy BlancasAún no hay calificaciones
- Balo Exm FinalDocumento1 páginaBalo Exm FinalDavichín LCAún no hay calificaciones
- NOMENCLATURADocumento16 páginasNOMENCLATURAJUAN ZARATEAún no hay calificaciones
- 0116 B01 T02 D Diseno SismicoDocumento54 páginas0116 B01 T02 D Diseno Sismico09101972Aún no hay calificaciones
- Capitulo 6.4 Metodo de La Distribucion de Momentos o Metodos de CrossDocumento20 páginasCapitulo 6.4 Metodo de La Distribucion de Momentos o Metodos de CrossFrancisco LuceroAún no hay calificaciones
- CLASE 02 y 03 APLICACION DE EL METODO DE RIGIDEZ PDFDocumento109 páginasCLASE 02 y 03 APLICACION DE EL METODO DE RIGIDEZ PDFWilmer Peña RomeroAún no hay calificaciones
- Rigidez en Vigas 1Documento55 páginasRigidez en Vigas 1Angélica GonzálezAún no hay calificaciones
- Método de Los Desplazamientos (Con Manual de La HP 50g y Excel)Documento68 páginasMétodo de Los Desplazamientos (Con Manual de La HP 50g y Excel)Luis CastilloAún no hay calificaciones
- Antisismica Ejercio1Documento16 páginasAntisismica Ejercio1AntonioFloresGAún no hay calificaciones
- Diseño de Vigas EjemploDocumento6 páginasDiseño de Vigas EjemploDora Anita Mamani ChuraAún no hay calificaciones
- TALLER 1-Richard GuevaraDocumento5 páginasTALLER 1-Richard GuevaraByron GuevaraAún no hay calificaciones
- Informe Columnas LargasDocumento11 páginasInforme Columnas LargasFrancisco AltamiranoAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Ii Unidad - Analisis Estructural IiDocumento44 páginasExamen Ii Unidad - Analisis Estructural IiKevin Ruiz SifuentesAún no hay calificaciones
- Método de Rigidez en Pórticos v2Documento19 páginasMétodo de Rigidez en Pórticos v2Yhan GSAún no hay calificaciones
- EFinitos - Sesion - 02 - 1 - Metodo - DirectoDocumento21 páginasEFinitos - Sesion - 02 - 1 - Metodo - DirectoFernando Vilavila NoriegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Examen Final - 46936249Documento18 páginasExamen Final - 46936249ZELAMIR JAMES ASTO PRUDENCIOAún no hay calificaciones
- MURO DE CONTENCION 6m Junin 2Documento12 páginasMURO DE CONTENCION 6m Junin 2Josmell Kerlin Fabian GuerraAún no hay calificaciones
- Sesion 08 Albañileria 3Documento22 páginasSesion 08 Albañileria 3FRANCO VALENTINO CASTRILLON LAZAROAún no hay calificaciones
- Guia 6 Ejercicios Resueltos de Metodo de Cross Estructuras SimetricasDocumento15 páginasGuia 6 Ejercicios Resueltos de Metodo de Cross Estructuras Simetricascarlos_renovado80% (15)
- Método de Cross - PorticosDocumento18 páginasMétodo de Cross - Porticoscealbruce0% (1)