Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
DNS Server New
Cargado por
Bandi Bhaskar0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
45 vistas23 páginasEach computer ON Internet has two addresses - a numeric IP address (such as "241.111.4.142") and a host name such as www.bsnl.co.in. DNS is required to translate The Domain name entered by the end user into its IP address to enable the transporting of packets over networks. DNS performs this translation using a database holding the IP address against domain name.
Descripción original:
Derechos de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoEach computer ON Internet has two addresses - a numeric IP address (such as "241.111.4.142") and a host name such as www.bsnl.co.in. DNS is required to translate The Domain name entered by the end user into its IP address to enable the transporting of packets over networks. DNS performs this translation using a database holding the IP address against domain name.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
45 vistas23 páginasDNS Server New
Cargado por
Bandi BhaskarEach computer ON Internet has two addresses - a numeric IP address (such as "241.111.4.142") and a host name such as www.bsnl.co.in. DNS is required to translate The Domain name entered by the end user into its IP address to enable the transporting of packets over networks. DNS performs this translation using a database holding the IP address against domain name.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 23
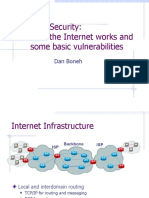
vrm 1
Domain
Name Server
vrm 2
Domain Name Server(DNS)
_
Why DNS
_
History of DNS
_
DNS hierarchy
_
Architecture
_
Domain Name Resolution
vrm 3
Why Domain Name Service?
Each computer ON Internet has two addresses a numeric
IP address (such as 241.111.4.142") and a host name such
as www.bsnl.co.in.
Computer in the Network understands only IP address.
IP address may change whenever hosts are relocated on a
network or from one network to another
It is easy to remember common language names than IP
based name format .
It is required to translate the domain name entered by the
end user into its IP address to enable the transporting of
packets over networks.
DNS performs this translation using a database of host
information
vrm 4
Domain Name Server
It is a database holding the IP address against domain
name.
In the early days the DNS was stored as a simple text
file located on each computer on the internet.
It became impossible to administer this database as
the host on internet grew in fast manner.
Hence DNS become a distributed database.
Portions of DNS database are stored on local name
servers and updated local DNS administrators.
vrm 5
History of DNS
Initially started by ARPANet
Host information collected and organized by
InterNIC.
The information file is called Hosts file or
Phone Book.
In 1980 DARPA shifted its protocol platform to
TCP/IP
This made to grow the network abundantly.
vrm 6
_
Due to the fast growing nature of Internet it become
impossible to have all the host names in a centrally
organized Host file.
_
ARPA adopted new method of maintaining Host
name The Domain Name Service.
vrm 7
~
In this system eight numbers of top level domains
are defined.
~
Sites are categorized and grouped in to the top level
domains.
~
Each domain in the network would maintain a
Domain Name Server.
~
This server would supply information about the
specific hosts with in the domain it served to other
servers.
vrm 8
Advantages of the DNS
Same Domain Name can repeat on different
domains.
The Domain administrator can add new host
without prior intimation to other hosts.
Distributed administration.
vrm 9
Top Level Domains
.com:-Commercial organizations
.edu:-Educational organizations
.gov:-Government organizations
.mil:-Military organizations
.net:-Networking organizations
.org:-Non-Commercial organizations
.int:-International organizations
.arpa:-ARPA Domain*
vrm 10
Control on DNS
IAB
Internet Architecture Board
vrm 11
Geographical domains
In addition to the top level domains IAB decided
to have geographical domains.
Geographical domain name with two alphabet.
Eg: in:- India, uk:- Britain ,fr:-France
vrm 12
Domain Name Hierarchy
.
Domain name can be up to 63 character in length.
.
May contain digits or hyphens.
.
Should start with an alphabet.
.
Not case sensitive.
.
Each domain has a domain server.
.
The collection of hosts which the server can give a name or
IP address is called The Zone of authority
.
Zone of authority defines the boundary of the zone.
.
The entire collection of domains is called domain name
space.
vrm 13
Domain Name Hierarchy
A domain name which can be identified uniquely in a
domain is called fully qualified domain name(FQD)
A domain can have sub domains.
Eg: www.yahoo.com, www.rttctvm.bsnl.co.in
www.ernakulam.sancharnet.in are
fully qualified domain names.
vrm 14
Domain Name Hierarchy
in
sancharnet vsnl satyam
ernakulam chni bgr
www.sancharnet.in
www.satyam.in
www.sancharnet.ernakulam.in
vrm 15
Domain Name-space
.com
.edu
.in
vrm 16
.in -domain name space
sancharnet
satyam
vrm 17
.sancharnet.in -domain name space
ernalulam
chni
vrm 18
How to resolve Domain Name query?
You are requesting www.yahoo.com from a sanchernet client
Query sent to sancharnet nameserver
Query sent to .com rootname server
Response from the root name server
Ask the guy w.x.y.z
Query to name server w.x.y.z
Response from name server w.x.y.z
The address of www.yahoo.com is r.s.t.u
vrm 19
Architecture of DNS
&
There are two type of name servers Primary master and
secondary master.
&
Primary master contains the database for its zone of
authority.
&
Secondary master stores a copy of primary master.
&
Name servers with zone of authority a top level domain is
called root name server.
vrm 20
DNS software
The server application developed for DNS function is
called BIND.
BIND Berkeley Internet Name Domain
BIND is developed in UNIX platform.
A ported version of BIND is developed later for Windows
NT platform.
Microsoft developed its own DNS software for working in
Windows NT platform.
vrm 21
InterNIC
Controls the Domain Name
registration
vrm 22
Controls the Domain Name
Registration in Asia Pacific
APNIC
vrm 23
Controls the Domain Name
registration in in domain
C-DAC(formerly NCST)
Centre for Development of Advanced Computing,
Mumbai (formerly known as National Centre
forSoftware Technology)
También podría gustarte
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (895)
- Math 115 Final Exam Review Exercises Spring 2019Documento11 páginasMath 115 Final Exam Review Exercises Spring 2019Bandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (838)
- AMRUT Guidelines PDFDocumento76 páginasAMRUT Guidelines PDFRanjith ParvathapuramAún no hay calificaciones
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Calificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (98)
- Math 026 Final Exam Review Exercises Fall 2023Documento11 páginasMath 026 Final Exam Review Exercises Fall 2023Bandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (5794)
- Andhra Cem EPABX Proposal PDFDocumento2 páginasAndhra Cem EPABX Proposal PDFBandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (537)
- BroadbandDocumento95 páginasBroadbandBandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (266)
- SOLAR Power For RAVELA Telephone ExchangeDocumento4 páginasSOLAR Power For RAVELA Telephone ExchangeBandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (400)
- Postpaid PlansDocumento6 páginasPostpaid PlansBandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (474)
- Automatic Power Reading System Using GSM NetworkDocumento5 páginasAutomatic Power Reading System Using GSM NetworkAbhi Lash ReddyAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 (1) 1 - OfC CablesDocumento16 páginas2 (1) 1 - OfC CablesBandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (231)
- Unit Cost of Neem Cultivation in One HectareDocumento10 páginasUnit Cost of Neem Cultivation in One HectareBandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (588)
- City Video SurvellianceDocumento28 páginasCity Video SurvellianceBandi BhaskarAún no hay calificaciones
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (271)
- 5 ZXUNENUM&DNSIntroduction PPT+Note - 25Documento25 páginas5 ZXUNENUM&DNSIntroduction PPT+Note - 25Radovan RabrenovicAún no hay calificaciones
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (45)
- Chapter 2 V7 01Documento106 páginasChapter 2 V7 01Anthony YoungAún no hay calificaciones
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (74)
- Cybersecurity Awareness Counter Cyber Threats and Terrorism A Case Study of Cybersecurity in MINICTDocumento15 páginasCybersecurity Awareness Counter Cyber Threats and Terrorism A Case Study of Cybersecurity in MINICTInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAún no hay calificaciones
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (344)
- Can't Access H33t.eu - Here's How To Make It Work With A Simple Trick (How ToDocumento22 páginasCan't Access H33t.eu - Here's How To Make It Work With A Simple Trick (How TodhanendrapardhiAún no hay calificaciones
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (234)
- How Does SCAN Listener Works in Oracle RAC 11gR2 PDFDocumento2 páginasHow Does SCAN Listener Works in Oracle RAC 11gR2 PDFangeldn06Aún no hay calificaciones
- TCP/IPDocumento286 páginasTCP/IPbobdxcool100% (12)
- MCSE Sample QuestionsDocumento19 páginasMCSE Sample QuestionsSuchitKAún no hay calificaciones
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (1090)
- PRJ 3Documento14 páginasPRJ 3socializam News networkAún no hay calificaciones
- How To Configure DNS On A Celerra Network ServerDocumento8 páginasHow To Configure DNS On A Celerra Network Servero7bit227Aún no hay calificaciones
- ALFA NETWORK R36 User ManualDocumento58 páginasALFA NETWORK R36 User Manualdeimudda2002Aún no hay calificaciones
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (2259)
- Bind Dns On CentosDocumento4 páginasBind Dns On CentosMd Tanjil Islam BappiAún no hay calificaciones
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDe EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreCalificación: 3.5 de 5 estrellas3.5/5 (137)
- Installing Linux VmwareDocumento16 páginasInstalling Linux VmwareramaAún no hay calificaciones
- Computer Networking Fundamentals Chapter 2Documento133 páginasComputer Networking Fundamentals Chapter 2wfidayuAún no hay calificaciones
- Windows 10 Admin Practice QuestionsDocumento72 páginasWindows 10 Admin Practice QuestionsnagarjunaAún no hay calificaciones
- Embedded Linux Course Slides PDFDocumento571 páginasEmbedded Linux Course Slides PDFranbumailsAún no hay calificaciones
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Calificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (121)
- Troubleshooting Client VPN - Cisco MerakiDocumento15 páginasTroubleshooting Client VPN - Cisco Merakikatherine painiiAún no hay calificaciones
- F5 GTM Specialist Certification Resource Guide: Purpose of This DocumentDocumento15 páginasF5 GTM Specialist Certification Resource Guide: Purpose of This DocumentAlvaro PrietoAún no hay calificaciones
- Application Server AdministrationDocumento440 páginasApplication Server AdministrationStephenson Silva dos Santos OliveiraAún no hay calificaciones
- Domain Names For DummiesDocumento68 páginasDomain Names For Dummiesnevermore1st100% (10)
- 7 Tcp-Ip-DnsDocumento36 páginas7 Tcp-Ip-DnsManaarul HidayatAún no hay calificaciones
- Counteract 6.3.4.0 Quick Install GuideDocumento19 páginasCounteract 6.3.4.0 Quick Install GuidePaul JungAún no hay calificaciones
- DCN Lab Manual PDFDocumento53 páginasDCN Lab Manual PDFmuhammad hassan100% (1)
- Accessing Websites On A Local Network (LAN) Web Server - DeveloperSideDocumento4 páginasAccessing Websites On A Local Network (LAN) Web Server - DeveloperSidebungtekaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Perks of Being a WallflowerDe EverandThe Perks of Being a WallflowerCalificación: 4.5 de 5 estrellas4.5/5 (2104)
- Lab 4Documento7 páginasLab 4HEMANILASHINII A P R THARMALINGAMAún no hay calificaciones
- AWS Route 53: Domain Name System (DNS) ServiceDocumento41 páginasAWS Route 53: Domain Name System (DNS) Serviceexample111222Aún no hay calificaciones
- Linux Fedora Man - K FilesDocumento124 páginasLinux Fedora Man - K Filesgetdownload3525Aún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding How DNS WorksDocumento8 páginasUnderstanding How DNS WorksEduardo Andrés Loaiza MataAún no hay calificaciones
- SnoopyDocumento25 páginasSnoopyM VerbeeckAún no hay calificaciones
- Please Send The Accomplish Form at Dns@asti - Dost.gov - PH For Inquiries, You May Call Us at +63 2 927 3093Documento1 páginaPlease Send The Accomplish Form at Dns@asti - Dost.gov - PH For Inquiries, You May Call Us at +63 2 927 3093Michael EscribaAún no hay calificaciones
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesCalificación: 4 de 5 estrellas4/5 (821)
- Step by Step Procedure For Creating LANDocumento55 páginasStep by Step Procedure For Creating LANHAWLITUAún no hay calificaciones