Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Statistics: By: Reem
Cargado por
Yo DeveraDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Statistics: By: Reem
Cargado por
Yo DeveraCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
STATISTICS
By: Reem
Forms of presentation of data
Grouped data is a statistical term used in data analysis. A raw dataset can be organized by constructing a table showing the frequency distribution of the variable (whose values are given in the raw dataset). Such a frequency table is often referred to as a grouped data.
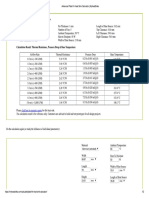
Time taken (in seconds)Frequency 5 and above, below 10 =1 10 and above, below 15 =4 15 and above, below 20 =6 20 and above, below 25 =4 25 and above, below 30 =2 30 and above, below 35 =3
Grouped data is when there is a large number of possible outcomes, we will usually need to group the data. E.g The ages of 200 people entering a park on a Saturday afternoon. The ages have been grouped into the classes 0-9, 10-19, 20-29, etc.
Ungrouped data is the opposite of grouped data with only one possible answer. E.g The ages of 200 people entering a park on a Saturday afternoon. The ages are: 27, 8, 10, 49 etc.
Different kinds of graphs and charts
Graphs are pictures that help us understand amounts. These amounts are called data. There are many kinds of graphs, each having special parts.
A pie chart (or a circle graph) is a circular chart divided into sectors, illustrating proportion. In a pie chart, the arc length of each sector (and consequently its central angle and area), is proportional to the quantity it represents.
In statistics, a histogram is a graphical representation showing a visual impression of the distribution of data. It is an estimate of the probability distribution of a continuous variable and was first introduced by Karl Pearson.
The Frequency Polygon Using the fact that each class interval may be represented, on average, by its class mid-point, we may plot the class mid-points against the class frequencies to obtain a display of single points. By joining up these points with straight line segments and including two extra class midpoints, we obtain a frequency polygon.
The Cumulative Frequency Polygon (or Ogive) The earlier use of the cumulative frequency to estimate the number (or proportion) of values less than a certain amount may be applied graphically by plotting the upper class-boundary against cumulative frequency; then joining up the points plotted with straight line segments. The graph obtained is called the cumulative frequency
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box-andwhisker diagram or plot) is a convenient way of graphically depicting groups of numerical data through their five-number summaries: the smallest observation (sample minimum), lower quartile (Q1),median (Q2), upper quartile (Q3), and largest observation (sample maximum). A boxplot may also indicate which observations, if any, might be considered outliers.
También podría gustarte
- Indian Influences in The PhilippinesDocumento15 páginasIndian Influences in The PhilippinesYo Devera57% (7)
- Buying Solutions' Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) CalculatorDocumento93 páginasBuying Solutions' Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculatorankitch123Aún no hay calificaciones
- Kyabin Studio Pricelist 2021Documento18 páginasKyabin Studio Pricelist 2021BudiAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentation On FacebookDocumento39 páginasPresentation On FacebookShaswat SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Graphical PresentationDocumento6 páginasGraphical PresentationAtiqah RazifAún no hay calificaciones
- BBM AssignmentsDocumento13 páginasBBM AssignmentsSky FallAún no hay calificaciones
- BUSINESS STATISTICS - Unit-2Documento23 páginasBUSINESS STATISTICS - Unit-2Mandeep SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Graphical Representation of DataDocumento6 páginasGraphical Representation of DataJustine Louise Bravo FerrerAún no hay calificaciones
- Frequency Distribution and Data: Types, Tables, and Graphs: What Is Descriptive Statistics?Documento19 páginasFrequency Distribution and Data: Types, Tables, and Graphs: What Is Descriptive Statistics?Muhammad ZeeshanAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Fields of StatisticsDocumento9 páginas2 Fields of Statisticsthyrany cattelAún no hay calificaciones
- Foundation Notes 2013Documento25 páginasFoundation Notes 2013Anonymous wXV066fAAún no hay calificaciones
- Data InterpretationDocumento3 páginasData InterpretationNavdeep AhlawatAún no hay calificaciones
- 1.1 Constructing and Interpreting Visual Displays of DataDocumento13 páginas1.1 Constructing and Interpreting Visual Displays of Dataelmoelmoelmo2566Aún no hay calificaciones
- L5 - Presentation of DataDocumento35 páginasL5 - Presentation of DataRhen Tomboc Olasiman-MateoAún no hay calificaciones
- Craphing Statistical DataDocumento3 páginasCraphing Statistical Datakevin funtallesAún no hay calificaciones
- DWDM Unit-2Documento20 páginasDWDM Unit-2CS BCAAún no hay calificaciones
- Frequency Distribution ExampleDocumento6 páginasFrequency Distribution ExampleMadison HartfieldAún no hay calificaciones
- Intro of Statistics - OgiveDocumento35 páginasIntro of Statistics - OgiveJeff MaynardAún no hay calificaciones
- Graphical Representation o F DataDocumento13 páginasGraphical Representation o F DataKaran ErAún no hay calificaciones
- Frequency Table: Descriptive StatisticsDocumento27 páginasFrequency Table: Descriptive StatisticsStacy JonesAún no hay calificaciones
- A Pictograph Is A Way of Showing Data Using Images. Each Image Stands For A Certain Number of ThingsDocumento9 páginasA Pictograph Is A Way of Showing Data Using Images. Each Image Stands For A Certain Number of ThingsIj Roxas Cuizon MendozaAún no hay calificaciones
- Picturing Distributions With GraphsDocumento21 páginasPicturing Distributions With GraphsFernan CaboteAún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocumento253 páginasStatistics and Probabilityanirudhsaxena865Aún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics and ProbabilityDocumento196 páginasStatistics and ProbabilitySiddharth GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- ReportDocumento7 páginasReportNecitas Sacnahon SapanghariAún no hay calificaciones
- Frequency (Statistics) - WikipediaDocumento24 páginasFrequency (Statistics) - Wikipediasterling goinAún no hay calificaciones
- PB2MAT - 02Bahan-Presenting Data in Tables and Charts For Categorical and Numerical Data Pert 2Documento23 páginasPB2MAT - 02Bahan-Presenting Data in Tables and Charts For Categorical and Numerical Data Pert 2yeong21Aún no hay calificaciones
- QUALITATIVE DATA Are Measurements For Which There Is No NaturalDocumento9 páginasQUALITATIVE DATA Are Measurements For Which There Is No NaturalMarcelaMorenoAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 14 StatisticsDocumento3 páginasCH 14 StatisticsKarthikeya R SAún no hay calificaciones
- Frequency PolygonsDocumento13 páginasFrequency Polygonsjunaida saripada100% (1)
- MatematikDocumento26 páginasMatematikMuhd Hilmi AkhirAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture 2 NotesDocumento15 páginasLecture 2 NotesSerenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction BS FinalDocumento54 páginasIntroduction BS FinalsathravguptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Visualization & Data Exploration - Unit IIDocumento26 páginasData Visualization & Data Exploration - Unit IIpurusingh23Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aj Ka KaamDocumento21 páginasAj Ka KaamAnonymous fg4ACqAún no hay calificaciones
- MathematicsDocumento9 páginasMathematicsJoseph VijuAún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics Lecture Grouped DataDocumento11 páginasStatistics Lecture Grouped DataMary Roxanne AngelesAún no hay calificaciones
- Terms 2Documento11 páginasTerms 2jlayambotAún no hay calificaciones
- 05 Handout 1Documento13 páginas05 Handout 1raulAún no hay calificaciones
- Ogive and BoxplotDocumento3 páginasOgive and BoxplotClarence Tuazon FloresAún no hay calificaciones
- Chap 2 NotesDocumento5 páginasChap 2 NotesKaustubh SaksenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Statistics Ch-02Documento59 páginasStatistics Ch-02seemialvi6Aún no hay calificaciones
- Introductory Statistics (Chapter 2)Documento3 páginasIntroductory Statistics (Chapter 2)Riezel PepitoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2/ Organizing and Visualizing Variables: DcovaDocumento4 páginas2/ Organizing and Visualizing Variables: DcovaThong PhanAún no hay calificaciones
- KKP mATHDocumento6 páginasKKP mATHcegu efaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Idiomatic Programmer - Statistics PrimerDocumento44 páginasThe Idiomatic Programmer - Statistics PrimerssignnAún no hay calificaciones
- Ix. Introduction To Statistical Concepts: Frequency Distribution Measures of Central Tendency Measures of VariabilityDocumento119 páginasIx. Introduction To Statistical Concepts: Frequency Distribution Measures of Central Tendency Measures of VariabilityAppleRoseAgravanteAún no hay calificaciones
- Introductory Statistics (Chapter 2)Documento3 páginasIntroductory Statistics (Chapter 2)Riezel PepitoAún no hay calificaciones
- Stem-and-Leaf Plots Frequencies Tables Frequency ChartsDocumento7 páginasStem-and-Leaf Plots Frequencies Tables Frequency ChartsBabish ShresthaAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment On Paper 6 Topic: Graphical Presentation - HistogramDocumento7 páginasAssignment On Paper 6 Topic: Graphical Presentation - HistogramTluanga HauhnarAún no hay calificaciones
- DataDocumento10 páginasDataAnindita GhoseAún no hay calificaciones
- MT3311D KLLDocumento54 páginasMT3311D KLLChloe LuAún no hay calificaciones
- Quartiles Cumulative FrequencyDocumento7 páginasQuartiles Cumulative FrequencychegeAún no hay calificaciones
- Module in Statistic Data RepresentationDocumento12 páginasModule in Statistic Data RepresentationCarmela UrsuaAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Analytics and R Assignment IDocumento11 páginasData Analytics and R Assignment IVaisistha BalAún no hay calificaciones
- My PPT On Graphical Representation of DataDocumento54 páginasMy PPT On Graphical Representation of DataPedup Dukpa100% (5)
- Engineering Probability and StatisticsDocumento42 páginasEngineering Probability and StatisticsKevin RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- cmp3 GlossaryDocumento66 páginascmp3 Glossaryapi-299469383Aún no hay calificaciones
- Stats Week 1 PDFDocumento6 páginasStats Week 1 PDFAnonymous n0S2m9sR1EAún no hay calificaciones
- BBA Business Statics Course Outline SketchDocumento7 páginasBBA Business Statics Course Outline SketchRabia BhattiAún no hay calificaciones
- 002 Data Presentation (Modified)Documento31 páginas002 Data Presentation (Modified)JM MaguigadAún no hay calificaciones
- GAC - Math Definition - StatisticsDocumento3 páginasGAC - Math Definition - StatisticsTsamara Alifia100% (1)
- Image Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionDe EverandImage Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionAún no hay calificaciones
- Cumulative FrequenciesDocumento4 páginasCumulative FrequenciesYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Rio StatsDocumento4 páginasRio StatsYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Cumulative Frequencies: Third Quarter Examination Scores of 30 Students in Grade IV-Achilles On Their HELE SubjectDocumento4 páginasCumulative Frequencies: Third Quarter Examination Scores of 30 Students in Grade IV-Achilles On Their HELE SubjectYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Cumulative Frequencies: Scores of 20 Students in Grade IV-Aphrodite On Their Third Quarter Examination in HELEDocumento4 páginasCumulative Frequencies: Scores of 20 Students in Grade IV-Aphrodite On Their Third Quarter Examination in HELEYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Folk DanceDocumento3 páginasFolk DanceYo Devera56% (9)
- Philippine GeographyDocumento23 páginasPhilippine GeographyYo Devera75% (4)
- Pyschology 1st SessionDocumento15 páginasPyschology 1st SessionYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Indianization - HistoryDocumento10 páginasIndianization - HistoryYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Economics LessonsDocumento4 páginasEconomics LessonsYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Superstitious BeliefsDocumento5 páginasSuperstitious BeliefsYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Relations With The Orang DampuansDocumento3 páginasRelations With The Orang DampuansYo Devera100% (1)
- NSTP Written ReportDocumento4 páginasNSTP Written ReportYo DeveraAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual Cmp-Smartrw10 CompDocumento66 páginasManual Cmp-Smartrw10 CompAllegra AmiciAún no hay calificaciones
- Advanced Plate Fin Heat Sink Calculator - MyHeatSinksDocumento2 páginasAdvanced Plate Fin Heat Sink Calculator - MyHeatSinksHarsh BhardwajAún no hay calificaciones
- Sa 449Documento8 páginasSa 449Widya widya100% (1)
- CV Product C-EtdDocumento6 páginasCV Product C-EtdmrmskymanAún no hay calificaciones
- Broadcast Tools Site Sentinel 4 Install Op Manual v2 12-01-2009Documento41 páginasBroadcast Tools Site Sentinel 4 Install Op Manual v2 12-01-2009testeemailAún no hay calificaciones
- Denr Administrative Order (Dao) 2013-22: (Chapters 6 & 8)Documento24 páginasDenr Administrative Order (Dao) 2013-22: (Chapters 6 & 8)Karen Feyt Mallari100% (1)
- Esu Tester WhoDocumento5 páginasEsu Tester WhoquezonAún no hay calificaciones
- SM PC300 350 LC 8Documento1025 páginasSM PC300 350 LC 8dedy imranAún no hay calificaciones
- Karcher Quotation List - 2023Documento12 páginasKarcher Quotation List - 2023veereshmyb28Aún no hay calificaciones
- Pest Control ChennaiDocumento3 páginasPest Control ChennaiControler33Aún no hay calificaciones
- ElinkDocumento36 páginasElinkjosemanuelarangoAún no hay calificaciones
- Em - 1110 1 1005Documento498 páginasEm - 1110 1 1005Sajid arAún no hay calificaciones
- StatementDocumento3 páginasStatementSachinBMetre87 SachinBMetreAún no hay calificaciones
- Sony PMW 200 ManualDocumento141 páginasSony PMW 200 ManualElectra/Off TraxAún no hay calificaciones
- Pads Hyperlynx DDR WizardDocumento3 páginasPads Hyperlynx DDR Wizardkrishna_p_n_44510456Aún no hay calificaciones
- Mapal 2016Documento416 páginasMapal 2016isuntxoAún no hay calificaciones
- TractionBatteries Technical WebDocumento20 páginasTractionBatteries Technical WebnarakribAún no hay calificaciones
- Professional Project ManagementDocumento2 páginasProfessional Project ManagementVirginia Virgie100% (3)
- RSC 406 (English)Documento11 páginasRSC 406 (English)Tuấn DũngAún no hay calificaciones
- YAMAHA Blaster (Parts) PDFDocumento65 páginasYAMAHA Blaster (Parts) PDFAlberto VegaAún no hay calificaciones
- Paul Ryan ResumeDocumento3 páginasPaul Ryan ResumePaul RyanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 8 Designing and Developing Effective HRD ProgramsDocumento37 páginasChapter 8 Designing and Developing Effective HRD ProgramsVincent Raj KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- CR 55 AaaehqqeDocumento7 páginasCR 55 AaaehqqesigithvacAún no hay calificaciones
- DCTN Lsqmdocu63774Documento21 páginasDCTN Lsqmdocu63774Bharani KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- BEAFAd 01Documento124 páginasBEAFAd 01Vina Zavira NizarAún no hay calificaciones
- Oracle® Auto Service Request: Exadata Database Machine Quick Installation Guide Release 5.0Documento12 páginasOracle® Auto Service Request: Exadata Database Machine Quick Installation Guide Release 5.0ManifoldAún no hay calificaciones
- C D C SDocumento4 páginasC D C SandriAún no hay calificaciones