Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Potrait
Cargado por
anushka moreDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Potrait
Cargado por
anushka moreCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
A metal may be defined as a chemical element that possesses ‘Metallic properties’
Metallic properties’ are defined as:
• Luster,
• good thermal and electrical conductivity and the
• Capability of being permanently shaped or deformed at room temperature and which,
in electrolysis, carries a positive charge that is liberated at the cathode.(-) This is use for
plating of metals.
Properties of Metal and Alloys
• Physical properties - relate to color, density, weight and heat conductivity
• Chemical properties - behavior of the metal when placed in contact with the atmosphere, salt water, or
other substances.
• Electrical properties - conductivity, resistance, and magnetic qualities of the metal. • Mechanical
properties – carrying ability, wear resistance, hardness and elasticity.
• Corrosion resistance - ability to withstand attacks from atmospheric, chemical, or electrochemical
conditions.
• Among all above categories of properties of metal and metal alloys , mechanical properties plays major
role in application of metal and their products in building industry.
PROCESSING OF METAL AND ALLOYS
How the gears in your automobile work for years without any breakdown? Or
How a drill is able to make a hole in steel even after numerous holes are made?
These are basically due to the composition of the material and to the structural and
physical alteration of its properties. The art of controlling the metallurgical (structural and
physical) properties of steel or any ferrous material is termed "heat treatment. “ Through
this process the material structure of the metal is altered in order to meet the
requirements of a specific application.
MECHANICAL FORMING PROCESSES
Practically all metals, which are not used in cast form, are reduced to some standard
shapes for subsequent processing. Manufacturing companies producing metals supply
metals in form of ingots which are obtained by casting liquid metal into a square cross
section.
•Slab (500-1800 mm wide and 50 to 300 mm thick)
•Billets (40 to 150 sq mm)
•Blooms (150 to 400 sq mm)
These shapes are further processed through hot rolling, forging or extrusion, to produce
materials in standard form such as plates, sheets, rods, tubes and structural sections. Application –
Shaping process of metal in which ingots or continuously cast materials are converted •used in construction for as compression member - beams, decorative panels (grey Iron),
into shapes and sizes. Another purpose of this process is to alter and modify •Various types of cast irons are widely used for soil, waste and rainwater pipes, valves, pumps, lids
microstructure and properties of products. (manhole lids)
•Foundation for big machines (White Iron),
•Hinges, catches, step iron and similar casting of limited size and decorative panels of fragile design.
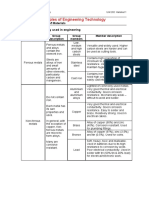
Constituents
Group characteristic Application
Ferritic Principally Fe-Cr-C alloys with Hardened and Automotive
strengthened
stainless 12-14% Cr. contain small by components, valves
additions of Mo, V, Nb, and
steel Ni. cold work and
not heat
METAL ALLOYS treatable.
An alloy is a metal (parent metal) combined with other substances (alloying agents), resulting in superior
properties such as; strength, hardness, durability, ductility, tensile strength and toughness. Alloying agent may magnetic
consist of one or more metals and non-metal. Examples of alloys are: Iron and Carbon forming Steel and great Austenitic contain 18% Cr and 8% Ni plus Hardened and Chemical, food
variety of copper alloys such as brass and bronze. stainless minor alloying elements, strengthened by processing equipment
steel non-magnetic cold work. and welding
non-magnetic construction
SECTIONS
Martensitic alloying elements are: Cr, Mn heat treatable. Cutlery, bearings and
Stainless and Mo. Magnetic. surgical tools
Steels
Precipitation- Ultra high strength due to precipitation hardening. Springs, knives and
Hardening pressure vessel
SS
Production of steel from iron ore
Iron ore: Hermatite Fe2O3, Magnetite Fe3O4
Coke, limestone
Blast furnace Fe2O3 + 3CO 2Fe + 3CO2
4% of carbon along with other
Pig Iron
impurities
Basic Oxygen furnace Cupola Furnace
Steel Cast Iron
up to 1.2% of carbon 2-4% of carbon
Anushka More
Naveen Raikar
Sec B
También podría gustarte
- Lecture 1.3Documento6 páginasLecture 1.3wemata7962Aún no hay calificaciones
- 1.1 Classification of Materials (Tutorial)Documento55 páginas1.1 Classification of Materials (Tutorial)AIZAT ZUL HAIRIE BIN WAHI MoeAún no hay calificaciones
- MODULE 2 Metal 2 PDFDocumento12 páginasMODULE 2 Metal 2 PDFJhun Jhunniee CapiliAún no hay calificaciones
- Welcome To The Wide World of EM!: ALL of Engineering Is Impacted by Materials!Documento47 páginasWelcome To The Wide World of EM!: ALL of Engineering Is Impacted by Materials!shohaimAún no hay calificaciones
- Alloys Handout 1 PDFDocumento61 páginasAlloys Handout 1 PDFcosty6911Aún no hay calificaciones
- EME Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocumento46 páginasEME Mod4@AzDOCUMENTS - inLAKSH RAMASWAMYAún no hay calificaciones
- Engineering MaterialsDocumento24 páginasEngineering MaterialsAngela MayAún no hay calificaciones
- Amirul Afiq Bin Ab Hisham 2017220378 J4Em1102GDocumento3 páginasAmirul Afiq Bin Ab Hisham 2017220378 J4Em1102GFarah RashidAún no hay calificaciones
- Module 1: Fundamentals of Mse 1.: The Materials Selection ProcessDocumento2 páginasModule 1: Fundamentals of Mse 1.: The Materials Selection ProcesstumambingaleahAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Material Science and MetallurgyDocumento28 páginasIntroduction To Material Science and Metallurgytani nAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 01Documento23 páginasCH 01Yahya AbdulsalamAún no hay calificaciones
- Karakterisasi Material PDFDocumento40 páginasKarakterisasi Material PDFmiftakhurAún no hay calificaciones
- Lesson 05Documento12 páginasLesson 05Lia CambangayAún no hay calificaciones
- Engineering Materials NOTES For Academic Year 2012Documento45 páginasEngineering Materials NOTES For Academic Year 2012kundayi shavaAún no hay calificaciones
- Matscie ReviewerDocumento5 páginasMatscie ReviewerClaire Silva PermejoAún no hay calificaciones
- Hernandez - Activity 8Documento3 páginasHernandez - Activity 8Ma Lourdes Diona HernandezAún no hay calificaciones
- 5.1 MetallicDocumento31 páginas5.1 MetallicFARAH AYUNIE BINTI JASNI KM-PensyarahAún no hay calificaciones
- 0323 Sifat MaterialDocumento75 páginas0323 Sifat MaterialOfik Triyadi Musriman D3 Teknik Mesin AAún no hay calificaciones
- Reviewer Chapter 3-4Documento2 páginasReviewer Chapter 3-4Kyle BullandayAún no hay calificaciones
- Amt 611 Prelim Part 2.2Documento43 páginasAmt 611 Prelim Part 2.2Iris GarciaAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 202: Principles of Engineering Technology: Handout 1: Range of Materials Materials Commonly Used in EngineeringDocumento3 páginasUnit 202: Principles of Engineering Technology: Handout 1: Range of Materials Materials Commonly Used in EngineeringyasirAún no hay calificaciones
- Training On Metallography PDFDocumento109 páginasTraining On Metallography PDFWaqas RajaAún no hay calificaciones
- Metal CLGDocumento18 páginasMetal CLGabhishekbanaraseAún no hay calificaciones
- Case Hardening SteelsDocumento52 páginasCase Hardening SteelsGururaja TantryAún no hay calificaciones
- Structural MaterialsDocumento24 páginasStructural MaterialsSameer DhruwAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 37 Session 03Documento45 páginasUnit 37 Session 03amdan srlAún no hay calificaciones
- Metal and Metal Alloys NotesDocumento18 páginasMetal and Metal Alloys NotesKshitij SaojiAún no hay calificaciones
- 2-BMCG2323 Manufaturing MaterialsDocumento91 páginas2-BMCG2323 Manufaturing Materialshemarubini96Aún no hay calificaciones
- FittingDocumento16 páginasFittingLALIT 318Aún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Materials: Principles of EngineeringDocumento45 páginasIntroduction To Materials: Principles of EngineeringPrakharAún no hay calificaciones
- Casting 2Documento47 páginasCasting 2Hoza EssamAún no hay calificaciones
- MetallurgyDocumento46 páginasMetallurgyRon KivasuAún no hay calificaciones
- Industrial MaterialsDocumento45 páginasIndustrial MaterialsFarman AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch-07 SteelsDocumento20 páginasCh-07 SteelsKHUSHI JAINAún no hay calificaciones
- Mechanics of Materials - 1 - CDIODocumento43 páginasMechanics of Materials - 1 - CDIOTHÔNG NGUYỄN VÕ MINHAún no hay calificaciones
- Alloys-Module 2-2Documento4 páginasAlloys-Module 2-2MUSKAN 22BCE11024Aún no hay calificaciones
- Karakterisasi Material (S3) ENMT802007Documento19 páginasKarakterisasi Material (S3) ENMT802007fikri wahyu pratamaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ductle Iron Spec2Documento18 páginasDuctle Iron Spec2윤병택Aún no hay calificaciones
- Class Representative: Varun Singh 9733741577Documento36 páginasClass Representative: Varun Singh 9733741577Anshuman TagoreAún no hay calificaciones
- Exercises 6.1, 7.1, 8.1 and 9.1Documento2 páginasExercises 6.1, 7.1, 8.1 and 9.1peter vanderAún no hay calificaciones
- ME 210 Metallurgy and Materials EngineeringDocumento5 páginasME 210 Metallurgy and Materials Engineeringnandan144Aún no hay calificaciones
- Engineering Materials: Sonali Verma 251656009 I&PDocumento20 páginasEngineering Materials: Sonali Verma 251656009 I&Psanjay kajalAún no hay calificaciones
- Polymeric Composite Materials-6Documento16 páginasPolymeric Composite Materials-6HALİM BOZTEPEAún no hay calificaciones
- Experimental Analysis of Aluminium Alloy Reinforced With Rare Earth MetalsDocumento12 páginasExperimental Analysis of Aluminium Alloy Reinforced With Rare Earth MetalsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyAún no hay calificaciones
- Note For Introduction To Materials MST 510Documento147 páginasNote For Introduction To Materials MST 510Khairul BarsriAún no hay calificaciones
- 2-BMCG2312 Manufaturing MaterialsDocumento80 páginas2-BMCG2312 Manufaturing MaterialsMuhd IzzAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 1: Basics of Engineering Materials: Mr. Kashif NaveedDocumento11 páginasCH 1: Basics of Engineering Materials: Mr. Kashif NaveedYour EntertainerAún no hay calificaciones
- Material METALDocumento15 páginasMaterial METALpoAún no hay calificaciones
- Strength and Ductility Characteristics oDocumento9 páginasStrength and Ductility Characteristics otitiAún no hay calificaciones
- PROPERTIESDocumento2 páginasPROPERTIESJezzrel Xandy BalmesAún no hay calificaciones
- Lecture On Metal ReinforcementDocumento3 páginasLecture On Metal ReinforcementJohn Isaac BanaagAún no hay calificaciones
- Advantages and Disadvantages Each MaterialDocumento25 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages Each MaterialPewe WulandariAún no hay calificaciones
- Metals and AlloysDocumento73 páginasMetals and AlloysmahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Elctroslag RemeltingDocumento19 páginasElctroslag Remeltingreza chamanfarAún no hay calificaciones
- MD Mat 2Documento43 páginasMD Mat 2Rounak AgrawalAún no hay calificaciones
- MET ReviewerDocumento56 páginasMET ReviewerJULIAN DOMINIC SOLEDADAún no hay calificaciones
- MODULE 5 Typical Engineering MaterialsDocumento39 páginasMODULE 5 Typical Engineering Materialssrinidhi kulkarniAún no hay calificaciones
- Difference Between Austenitic, Ferritic, and MartensiticDocumento3 páginasDifference Between Austenitic, Ferritic, and Martensitickihal zohirAún no hay calificaciones
- The Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersDe EverandThe Essentials of Material Science and Technology for EngineersCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- r05322003 Metal FormingDocumento8 páginasr05322003 Metal FormingSRINIVASA RAO GANTAAún no hay calificaciones
- Layout StrategyDocumento78 páginasLayout StrategyUsman ShahidAún no hay calificaciones
- Copy ofDocumento80 páginasCopy ofdoniAún no hay calificaciones
- Human Powered ForkliftDocumento3 páginasHuman Powered ForkliftVinay MuleyAún no hay calificaciones
- Aqueduct@Km 31.925 Final - 2Documento1 páginaAqueduct@Km 31.925 Final - 2Rama KrishnaAún no hay calificaciones
- Material Rate Tamil NaduDocumento6 páginasMaterial Rate Tamil NaduManoj KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment 6.2Documento3 páginasExperiment 6.2jueliiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Pipe CoatingDocumento2 páginasPipe CoatingDeepak MoreAún no hay calificaciones
- 04 Essex WiresDocumento39 páginas04 Essex WiresRenzo Rios Roque0% (1)
- Rigid and Speciality PackagingDocumento44 páginasRigid and Speciality PackagingBhupendra Singh100% (2)
- Aci 207 Restraint EffectDocumento1 páginaAci 207 Restraint EffectChhour CEAún no hay calificaciones
- MSE 280: Introduction To Engineering MaterialsDocumento44 páginasMSE 280: Introduction To Engineering Materialsjains.boyAún no hay calificaciones
- Fusing TechnologyDocumento59 páginasFusing TechnologyShreyasiSaxena100% (2)
- Design of Material Handling System For SpecificDocumento14 páginasDesign of Material Handling System For SpecificKaran Virbhadre100% (3)
- Bosch Multi Functional CatalogDocumento2 páginasBosch Multi Functional CatalogjacquesmayolAún no hay calificaciones
- Proposed Duplex Structural DetailsDocumento16 páginasProposed Duplex Structural DetailsDamsha Ndahi0% (1)
- 42crmo6 : Steel GradeDocumento2 páginas42crmo6 : Steel GradeYonas Dwiananta YuwonoAún no hay calificaciones
- Rel Luting 2 SellDocumento2 páginasRel Luting 2 Selldrg. Rifqie Al HarisAún no hay calificaciones
- Defect and LimitationDocumento4 páginasDefect and LimitationFirdaus IliasAún no hay calificaciones
- Use of E-Plastic Waste in Bituminous PavementsDocumento9 páginasUse of E-Plastic Waste in Bituminous PavementsmalesevacAún no hay calificaciones
- 3A Sifat Fisik Mekanik Batuan Utuh KuliahDocumento70 páginas3A Sifat Fisik Mekanik Batuan Utuh KuliahJeffrey Leonardi Nurkamal100% (1)
- Design and Analysis of Heavily Loaded Reinforced Concrete Link Beams For Burj DubaiDocumento10 páginasDesign and Analysis of Heavily Loaded Reinforced Concrete Link Beams For Burj DubaiJoão Rocha de Lima100% (1)
- Floor Leveling in TilingDocumento6 páginasFloor Leveling in TilingHarsa VardhanAún no hay calificaciones
- AK9ch - АК9ч Aluminium Casting Alloys gost standardDocumento2 páginasAK9ch - АК9ч Aluminium Casting Alloys gost standardVivek GoudAún no hay calificaciones
- B-1003 HDPE GDB50 PE4710 Natural Gas Distribution PipeDocumento2 páginasB-1003 HDPE GDB50 PE4710 Natural Gas Distribution PipeZulfikar NoerAún no hay calificaciones
- Carbon and Alloy Steel PDFDocumento52 páginasCarbon and Alloy Steel PDFmaz234100% (3)
- 002-PDS-CON-008 Method Statement For Material Handling ManualDocumento11 páginas002-PDS-CON-008 Method Statement For Material Handling ManualMalik ZamanAún no hay calificaciones
- VDADocumento9 páginasVDAAnonymous ugAY1fsF0aAún no hay calificaciones
- Assessment For Fitness For Purpose of Cracked Piping Components-IDocumento27 páginasAssessment For Fitness For Purpose of Cracked Piping Components-Iapi-3855165100% (2)