Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Understanding Brain Disorders and Aphasia Types
Cargado por
Karen Quing0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
25 vistas21 páginasThe document discusses various types of brain injuries and disorders. It describes how strokes, aneurysms, epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, and different types of amnesia such as anterograde and retrograde amnesia can impact brain function and memory in different ways depending on the location and severity of damage to areas of the brain. Specific language disorders like Broca's and Wernicke's aphasia that result from damage to different language processing areas are also examined in terms of their characteristic speech and comprehension impairments.
Descripción original:
brain disorders
Título original
Brain Disorders
Derechos de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoThe document discusses various types of brain injuries and disorders. It describes how strokes, aneurysms, epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, and different types of amnesia such as anterograde and retrograde amnesia can impact brain function and memory in different ways depending on the location and severity of damage to areas of the brain. Specific language disorders like Broca's and Wernicke's aphasia that result from damage to different language processing areas are also examined in terms of their characteristic speech and comprehension impairments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
0 calificaciones0% encontró este documento útil (0 votos)
25 vistas21 páginasUnderstanding Brain Disorders and Aphasia Types
Cargado por
Karen QuingThe document discusses various types of brain injuries and disorders. It describes how strokes, aneurysms, epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease, and different types of amnesia such as anterograde and retrograde amnesia can impact brain function and memory in different ways depending on the location and severity of damage to areas of the brain. Specific language disorders like Broca's and Wernicke's aphasia that result from damage to different language processing areas are also examined in terms of their characteristic speech and comprehension impairments.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formatos disponibles
Descargue como PPT, PDF, TXT o lea en línea desde Scribd
Está en la página 1de 21
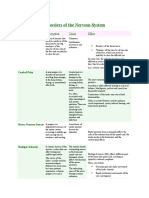
SSC01 GENERAL PSYCHOLOGY
It can have a wide range of causes including
head injury, stroke, bacterial diseases,
complex chemical imbalances, and changes
associated with aging.
Can initiate a cascade of damaging events.
After a blow to the head, a person may be
stunned or may become unconscious for a
moment. This injury, called a concussion,
usually leaves no permanent damage.
If blow is more severe and hemorrhage
(excessive bleeding) and swelling occur,
however, severe headache, dizziness,
paralysis, a convulsion, or temporary
blindness may result, depending on the area
of the brain affected.
Paul Broca was a French neuroanatomist who
discovered the area of the brain referred to as
Brocas area in 1861 based on a series of
consultations with an aphasic gentleman called
Tan. The patient was called Tan because tan
was all the patient could say. After Tan died,
Broca performed an autopsy of his brain and
found that there was an area of damage in the
left hemisphere. This specific location in the left
hemisphere of the brain (towards the back and
bottom of the frontal lobe) became known as
Brocas area.
Aphasia is caused by damage to one or more
of the language areas of the brain. Many
times, the cause of the brain injury is a
stroke. A stroke occurs when blood is unable
to reach a part of the brain. Brain cells die
when they do not receive their normal supply
of blood, which carries oxygen and important
nutrients. Other causes of brain injury are
severe blows to the head, brain tumors, brain
infections, and other conditions of the brain.
Damage to Broca's area results in Broca's
aphasia. Produces both comprehension and
production deficits.
1. Long pauses between words or also called
as dysprosody.
2. Agrammatism is the tendency to omit function
words as well as endings such as -ed in indicating
past tense. Function words are words which tie
sentences together: the, of, is, by, a, etc.
Individuals with Brocas aphasia are able to
understand the speech of others to varying
degrees. Because of this, they are often aware
of their difficulties and can become easily
frustrated by their speaking problems.
Individuals with Brocas aphasia often have
right-sided weakness or paralysis of the arm
and leg because the frontal lobe is also
important for body movement.
3. Some sound changes, simplification of
consonant clusters: It's hard to eat with a
spoon is pronounced as har eat wit poon
4. Frustration. They know there's something
wrong.
In contrast to Brocas aphasia, damage to the
temporal lobe may result in a fluent aphasia
that is called Wernickes aphasia. Individuals
with Wernickes aphasia may speak in long
sentences that have no meaning, add
unnecessary words, and even create new
words.
For example, someone with Wernickes
aphasia may say, You know that smoodle
pinkered and that I want to get him round
and take care of him like you want before,
meaning The dog needs to go out so I will
take him for a walk.
Individuals with Wernickes aphasia usually
have great difficulty understanding speech
and are therefore often unaware of their
mistakes. These individuals usually have no
body weakness because their brain injury is
not near the parts of the brain that control
movement.
A stroke is an event where the whole or
partial functioning of the brain is affected. A
stroke could be ischemic in nature, due to an
obstruction in the vessels or hemorrhagic in
nature, due to bleeding in to the brain cranial
cavity. The obstruction may be due to a clot
formed outside traveling to the vessels of the
brain or a clot formed within the premises of
the brain.
An aneurysm is the abnormal widening of an
artery, anywhere, due to the weakness in the
wall of that vessel. The locations for these
aneurysms are the abdominal aorta, the
cerebral vessels, poplitial arteries, etc. These
dilatations continue to grow and when they
go beyond the 5.5 cm diameter level, there is
a high probability of a rupture leading to
bleeding.
Is a term characterized by seizures, or
convulsions and is usually caused by
abnormal electrical discharges in the brain.
Alzheimer's is a type of dementia that causes
problems with memory, thinking and
behavior.
DEMENTIA - is a general term for a decline in
mental ability severe enough to interfere with daily
life.
Alzheimer's is a progressive disease, where
dementia symptoms gradually worsen over a
number of years. In its early stages, memory
loss is mild, but with late-stage Alzheimer's,
individuals lose the ability to carry on a
conversation and respond to their
environment.
Amnesia is the general term for a condition in
which memory (either stored memories or the
process of committing something to memory) is
disturbed or lost, to a greater extent than simple
everyday forgetting or absent-mindedness.
Amnesia may result either from organic or
neurological causes (damage to the brain
through physical injury, neurological disease or
the use of certain drugs), or
from functional or psychogenic causes
(psychological factors, such as mental disorder,
post-traumatic stress or psychological defence
mechanisms).
Anterograde amnesia (where the ability to
memorize new things is impaired or lost
because data does not transfer successfully
from the conscious short-term memory into
permanent long-term memory.
Here the patient is unable to recollect events,
that occur after the onset of the amnesia, for
more than a few minutes. In other words, in
these patients, recent events are not
transferred to long-term memory.
In this form of amnesia the affected individual
will be unable to recollect events that
occurred before the amnesia set in. The
condition is caused either by disease or a
brain injury especially in areas linked with
episodic memorythe hippocampus and the
median temporal lobes.
También podría gustarte
- Aphasia: NIDCD Fact Sheet - Voice, Speech, and LanguageDocumento4 páginasAphasia: NIDCD Fact Sheet - Voice, Speech, and LanguageNkosivumile Ndlovu ShakespeareAún no hay calificaciones
- Cerebrovascular Accident (Cva)Documento19 páginasCerebrovascular Accident (Cva)Darl DacdacAún no hay calificaciones
- Aphasia: Hana Nabila Ulfia 1102014118Documento14 páginasAphasia: Hana Nabila Ulfia 1102014118hana nabilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aphasia: NIDCD Fact SheetDocumento4 páginasAphasia: NIDCD Fact SheetscorpionmaironAún no hay calificaciones
- What Is DementiaDocumento5 páginasWhat Is DementiaKaren Kenneth BonotanAún no hay calificaciones
- Pathophysiology of Nervous System DisordersDocumento9 páginasPathophysiology of Nervous System DisordersChelito GuarinAún no hay calificaciones
- Neurological Impairment After Stroke....Documento5 páginasNeurological Impairment After Stroke....OGU CourageAún no hay calificaciones
- APHASIADocumento22 páginasAPHASIAMUHAMMAD BILALAún no hay calificaciones
- Amnesia: Amnesia Is The General Term For A Condition in Which Memory (Either StoredDocumento6 páginasAmnesia: Amnesia Is The General Term For A Condition in Which Memory (Either StoredputrianabrsitompulAún no hay calificaciones
- Nervous System DiseasesDocumento3 páginasNervous System DiseasesKenneth Dionysus SantosAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding Traumatic Brain Injury: Causes, Types, Symptoms, Treatment (TBIDocumento50 páginasUnderstanding Traumatic Brain Injury: Causes, Types, Symptoms, Treatment (TBISiesta CatsAún no hay calificaciones
- AmnesiaDocumento9 páginasAmnesiaHafsa KhalidAún no hay calificaciones
- Issue A. Definition of AphasiaDocumento8 páginasIssue A. Definition of AphasiaHendryikk BaehaAún no hay calificaciones
- Cerebrovascular AccidentDocumento8 páginasCerebrovascular Accidentplethoraldork100% (10)
- CVA Stroke Guide: Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentDocumento6 páginasCVA Stroke Guide: Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentBrenn Marie RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- SirrrrrDocumento2 páginasSirrrrrLoreth Aurea OjastroAún no hay calificaciones
- Jurnal SOL SerebriDocumento5 páginasJurnal SOL SerebriKomang AyuAún no hay calificaciones
- Ingles - 1° AñoDocumento43 páginasIngles - 1° AñoRox Sof100% (1)
- The Role of in The OF: CAM TreatmentDocumento47 páginasThe Role of in The OF: CAM TreatmenterinahuntAún no hay calificaciones
- Physical Rehabilitation Medicine Terms - THERAPY INSIGHTSDocumento11 páginasPhysical Rehabilitation Medicine Terms - THERAPY INSIGHTSbaji sharifAún no hay calificaciones
- Mention Abnormalities in The Central Nervous System: A.StrokeDocumento3 páginasMention Abnormalities in The Central Nervous System: A.Strokeazizi yemahulAún no hay calificaciones
- CNS Related DiseasesDocumento4 páginasCNS Related DiseasesYzabelle EncoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Cerebral Atrophy: by Tracy Kakish Rebecca Naddaf Atoine HarbDocumento13 páginasCerebral Atrophy: by Tracy Kakish Rebecca Naddaf Atoine HarbRebecca NaddafAún no hay calificaciones
- Visual Perception Physiological Neurological: MuscleDocumento2 páginasVisual Perception Physiological Neurological: MuscleNurul Fahmi Rizka LailyAún no hay calificaciones
- Amnesia With Focus On Post Traumatic AmnesiaDocumento27 páginasAmnesia With Focus On Post Traumatic AmnesiaWilliam ClemmonsAún no hay calificaciones
- AmnesiaDocumento4 páginasAmnesiaapi-351680270Aún no hay calificaciones
- Neurologic Assessment Physiologic Changes With AgingDocumento4 páginasNeurologic Assessment Physiologic Changes With AgingDarl Dacdac100% (1)
- Language Seminar NotesDocumento8 páginasLanguage Seminar NotesCindy Van WykAún no hay calificaciones
- Aphasia, (Difficulty Understanding) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe EverandAphasia, (Difficulty Understanding) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsAún no hay calificaciones
- Cause & Effect ViviDocumento3 páginasCause & Effect ViviFiqhi WulandariAún no hay calificaciones
- Brain: Amnesia Dementia Delirium Anxiety Disorders Mood Disorders Psychotic DisordersDocumento13 páginasBrain: Amnesia Dementia Delirium Anxiety Disorders Mood Disorders Psychotic Disordersmadiha ahmed khanAún no hay calificaciones
- Im Neuro SGDDocumento12 páginasIm Neuro SGDCasey Rae YanoAún no hay calificaciones
- 2019 Ardila Memory DisordersDocumento7 páginas2019 Ardila Memory DisordersLaura Arbelaez ArcilaAún no hay calificaciones
- The SAGE Encyclopedia of Human Communication Sciences and DisordersDocumento7 páginasThe SAGE Encyclopedia of Human Communication Sciences and DisordersLaura Arbelaez ArcilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Dementia and The BrainDocumento20 páginasDementia and The BrainLiviaAún no hay calificaciones
- Focus On StrokeDocumento92 páginasFocus On StrokeDIAH RETNO WULAN100% (2)
- Management of Patients With Cerebrovascular DisordersDocumento115 páginasManagement of Patients With Cerebrovascular DisordersarielleortuosteAún no hay calificaciones
- Broca's Vs WernickesDocumento2 páginasBroca's Vs WernickesDaiana NorinaAún no hay calificaciones
- Aphasia by Akhsaful To Dr. Hakim Arif SirDocumento6 páginasAphasia by Akhsaful To Dr. Hakim Arif SirAkhsaful ImamAún no hay calificaciones
- Psych 212 Aphasia Final NotesDocumento12 páginasPsych 212 Aphasia Final NotesAstra StarlightAún no hay calificaciones
- Subdivisions of ApraxiaDocumento3 páginasSubdivisions of ApraxiaUzra ShujaatAún no hay calificaciones
- Terminology ListDocumento17 páginasTerminology ListNiki SenAún no hay calificaciones
- Seizure DisorderDocumento13 páginasSeizure DisorderAnthony LopezAún no hay calificaciones
- Interventions For AphasiaDocumento22 páginasInterventions For Aphasiakhushi chopra 0050Aún no hay calificaciones
- AlzheimerDocumento2 páginasAlzheimerRjvm Net Ca FeAún no hay calificaciones
- Aphasia and DysphasiaDocumento8 páginasAphasia and Dysphasiamoizghani37Aún no hay calificaciones
- CVADocumento16 páginasCVANithiy TAún no hay calificaciones
- NCM116 Finals CVDDocumento11 páginasNCM116 Finals CVDRachelle DelantarAún no hay calificaciones
- (NCM116) Finals - CVDDocumento10 páginas(NCM116) Finals - CVDKrishelle Kate PannigAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Dyphasia DysarthriaDocumento4 páginas2 Dyphasia DysarthriamuhammadridhwanAún no hay calificaciones
- Amnesia PDFDocumento5 páginasAmnesia PDFElsaAún no hay calificaciones
- StrokeDocumento8 páginasStrokeTease-Me LeicesterAún no hay calificaciones
- Why Understanding Brain Structure and Reflexes Is Important in NursingDocumento10 páginasWhy Understanding Brain Structure and Reflexes Is Important in NursingPaul BarriosAún no hay calificaciones
- Disorders of The Nervous SystemDocumento5 páginasDisorders of The Nervous SystemAgronaSlaughterAún no hay calificaciones
- Anoxic Brain InjuryDocumento9 páginasAnoxic Brain InjuryGymnastK27Aún no hay calificaciones
- Language and The BrainDocumento8 páginasLanguage and The BrainSnow NightAún no hay calificaciones
- Coma, Defined As A Deep Sleeplike State From Which The Patient Cannot Be ArousedDocumento41 páginasComa, Defined As A Deep Sleeplike State From Which The Patient Cannot Be Arousednathan asfahaAún no hay calificaciones
- Parkinsons Disease and Hearing LossDocumento8 páginasParkinsons Disease and Hearing LossJohn OmandacAún no hay calificaciones
- TBI QuizletDocumento4 páginasTBI QuizletLoraine CometaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Women in Jose Rizal's Life (Rizal's Heterosexual Orientation)Documento10 páginasThe Women in Jose Rizal's Life (Rizal's Heterosexual Orientation)Karen QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- FormulasDocumento2 páginasFormulasKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- BullyingDocumento56 páginasBullyingKaren Quing100% (2)
- MemorandumDocumento12 páginasMemorandumKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Early Childhood Development Tasks & MilestonesDocumento5 páginasEarly Childhood Development Tasks & MilestonesKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding Peer Pressure Among Young AdolescentsDocumento35 páginasUnderstanding Peer Pressure Among Young AdolescentsKaren Quing100% (1)
- PsychologyDocumento15 páginasPsychologyKaren Quing0% (1)
- Master of Body Language PDFDocumento10 páginasMaster of Body Language PDFreversoAún no hay calificaciones
- 5S (Practice of Good Housekeepin)Documento64 páginas5S (Practice of Good Housekeepin)Karen QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Filipino Psychology - Concepts and MethodsDocumento116 páginasFilipino Psychology - Concepts and MethodsRoman Sarmiento70% (10)
- 5S (Practice of Good Housekeepin)Documento64 páginas5S (Practice of Good Housekeepin)Karen QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- 33 The Psychoanalytic PerspectiveDocumento20 páginas33 The Psychoanalytic PerspectiveKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- 696Documento6 páginas696Karen QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- How Culture Influences Depth PerceptionDocumento44 páginasHow Culture Influences Depth PerceptionKaren Quing100% (2)
- Frontal Lobe DysfunctionDocumento11 páginasFrontal Lobe DysfunctionKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Emotional Issues at RetirementDocumento3 páginasEmotional Issues at RetirementKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Frontal Lobe DysfunctionDocumento11 páginasFrontal Lobe DysfunctionKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Historical Development of PsychologyDocumento21 páginasHistorical Development of PsychologyKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- 4896 16468 1 PBDocumento11 páginas4896 16468 1 PBKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Sto e PsihologijaDocumento17 páginasSto e Psihologija2001babygirlAún no hay calificaciones
- Youth Participation For Development Daniela Ben AttarDocumento34 páginasYouth Participation For Development Daniela Ben AttarKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Research - Retirement ContextDocumento18 páginasResearch - Retirement ContextKaren QuingAún no hay calificaciones
- Integ Equ Phys571 T131Documento19 páginasInteg Equ Phys571 T131raoni_jampaAún no hay calificaciones
- Destined To ReignDocumento7 páginasDestined To ReignMichael B. BolotaoloAún no hay calificaciones
- Qimen Grup2Documento64 páginasQimen Grup2lazuli29100% (3)
- Human Resource Management and The Banking SectorDocumento5 páginasHuman Resource Management and The Banking SectorAkshay DagurAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 17. Bothriocephalus Acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934: December 2012Documento16 páginasChapter 17. Bothriocephalus Acheilognathi Yamaguti, 1934: December 2012Igor YuskivAún no hay calificaciones
- Multiple Leiomyomas After Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Report of Two CasesDocumento5 páginasMultiple Leiomyomas After Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Report of Two CasesYosef Dwi Cahyadi SalanAún no hay calificaciones
- Stories of Narada Pancaratra and Lord Krishna's protection of devoteesDocumento9 páginasStories of Narada Pancaratra and Lord Krishna's protection of devoteesPedro RamosAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Rs910Documento36 páginasData Rs910Cusco PardoAún no hay calificaciones
- Cooking Taoshobuddha Way Volume 2Documento259 páginasCooking Taoshobuddha Way Volume 2Taoshobuddha100% (3)
- Eunoia Fit 'n Slim - Slimming Coffee (Meal Plan)Documento2 páginasEunoia Fit 'n Slim - Slimming Coffee (Meal Plan)jbkmw4hmvmAún no hay calificaciones
- Mab, Boy, Son), Used in Patronymics See AlsoDocumento46 páginasMab, Boy, Son), Used in Patronymics See AlsoEilise IrelandAún no hay calificaciones
- RFQ for cat and dog food from Arbab TradersDocumento2 páginasRFQ for cat and dog food from Arbab TradersAnas AltafAún no hay calificaciones
- 7 Hemolytic Anemias PDFDocumento44 páginas7 Hemolytic Anemias PDFWin Ni del PîlarAún no hay calificaciones
- RIZALDocumento36 páginasRIZALRichard GonowonAún no hay calificaciones
- Bio1227 Microbiology and Parasitology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocumento16 páginasBio1227 Microbiology and Parasitology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDannielle EvangelistaAún no hay calificaciones
- Week 5 AssignmentDocumento2 páginasWeek 5 AssignmentNGUYEN HAIAún no hay calificaciones
- Marketing NUTH fashion brand through influencers and offline storesDocumento18 páginasMarketing NUTH fashion brand through influencers and offline storescandyAún no hay calificaciones
- KnowThem PPT FDocumento18 páginasKnowThem PPT FAANANDHINI SAún no hay calificaciones
- Mayo ClinicDocumento2 páginasMayo Clinicapi-3695725Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fear of Allah-HW Assignment by TahiyaDocumento10 páginasFear of Allah-HW Assignment by TahiyashafaqkaziAún no hay calificaciones
- Poster: Cloud API Testing: Junyi Wang, Xiaoying Bai, Haoran Ma, Linyi Li, Zhicheng JiDocumento2 páginasPoster: Cloud API Testing: Junyi Wang, Xiaoying Bai, Haoran Ma, Linyi Li, Zhicheng JiHa NhAún no hay calificaciones
- SOAL US Adaptif Bhs InggrisDocumento15 páginasSOAL US Adaptif Bhs InggrisNur RochiemAún no hay calificaciones
- Sa Tally Education BrochureDocumento6 páginasSa Tally Education BrochurePoojaMittalAún no hay calificaciones
- Word Wall Frys ListDocumento10 páginasWord Wall Frys Listapi-348815804Aún no hay calificaciones
- Information Technology (Code No. 402) CLASS IX (SESSION 2019-2020)Documento1 páginaInformation Technology (Code No. 402) CLASS IX (SESSION 2019-2020)Debi Prasad SinhaAún no hay calificaciones
- MKT Cat ELT 2022 YoungAdultDocumento36 páginasMKT Cat ELT 2022 YoungAdultnoah_mxAún no hay calificaciones
- PROACTIVITYDocumento8 páginasPROACTIVITYShikhaDabralAún no hay calificaciones
- Crisostomo Et Al. v. Atty. Nazareno, A.C. No. 6677, June 10, 2014Documento6 páginasCrisostomo Et Al. v. Atty. Nazareno, A.C. No. 6677, June 10, 2014Pamela TambaloAún no hay calificaciones
- 2014 JC2 H2 Econs Prelim Paper 2Documento3 páginas2014 JC2 H2 Econs Prelim Paper 2Ezra Notsosure WongAún no hay calificaciones
- Amdocs FSDocumento4 páginasAmdocs FSlionrudrams81Aún no hay calificaciones