Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Single Loop Circuits (2.3) Single-Node-Pair Circuits (2.4) : Dr. Holbert January 25, 2006
Cargado por
karlrodDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Single Loop Circuits (2.3) Single-Node-Pair Circuits (2.4) : Dr. Holbert January 25, 2006
Cargado por
karlrodCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
ECE201 Lect-3 1
Single Loop Circuits (2.3);
Single-Node-Pair Circuits (2.4)
Dr. Holbert
January 25, 2006
ECE201 Lect-3 2
Single Loop Circuit
The same current flows through each
element of the circuit---the elements are in
series.
We will consider circuits consisting of
voltage sources and resistors.
ECE201 Lect-3 3
Example: Christmas Lights
+
120V
228O
50 Bulbs
Total
228O
228O
I
ECE201 Lect-3 4
Solve for I
The same current I flows through the source
and each light bulb-how do you know this?
In terms of I, what is the voltage across
each resistor? Make sure you get the
polarity right!
To solve for I, apply KVL around the loop.
ECE201 Lect-3 5
228I + 228I + + 228I -120V = 0
I = 120V/(50 228O) = 10.5mA
+
120V
228O
228O
228O
I +
228I
+
228I
228I
+
ECE201 Lect-3 6
Some Comments
We can solve for the voltage across each
light bulb:
V = IR = (10.5mA)(228O) = 2.4V
This circuit has one source and several
resistors. The current is
Source voltage/Sum of resistances
(Recall that series resistances sum)
ECE201 Lect-3 7
In General: Single Loop
The current i(t) is:
This approach works for any single loop
circuit with voltage sources and resistors.
Resistors in series
s resistance of sum
sources voltage of sum
R
V
t i
j
Si
=
E
E
= ) (
= + + + =
j N series
R R R R R
2 1
ECE201 Lect-3 8
Voltage Division
Consider two resistors in series with a voltage
v(t) across them:
R
1
R
2
v
1
(t)
+
+
v
2
(t)
+
v(t)
2 1
1
1
) ( ) (
R R
R
t v t v
+
=
2 1
2
2
) ( ) (
R R
R
t v t v
+
=
ECE201 Lect-3 9
In General: Voltage Division
Consider N resistors in series:
Source voltage(s) are divided between the
resistors in direct proportion to their
resistances
=
j
i
S R
R
R
t V t V
k i
) ( ) (
ECE201 Lect-3 10
Class Examples
Learning Extension E2.8
Learning Extension E2.9
ECE201 Lect-3 11
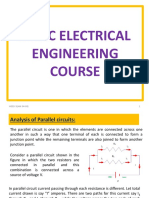
Example: 2 Light Bulbs in
Parallel
How do we find I
1
and I
2
?
I
R
1
R
2
V
+
I
1
I
2
ECE201 Lect-3 12
Apply KCL at the Top Node
I= I
1
+ I
2
Ohms Law:
1
1
R
V
I =
2
2
R
V
I =
I
R
1
R
2
V
+
I
1
I
2
ECE201 Lect-3 13
Solve for V
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ = + = + =
2 1 2 1
2 1
1 1
R R
V
R
V
R
V
I I I
2 1
2 1
2 1
1 1
1
R R
R R
I
R R
I V
+
=
+
=
Rearrange
ECE201 Lect-3 14
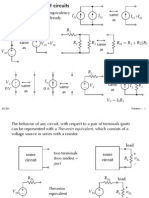
Equivalent Resistance
If we wish to replace the two parallel resistors
with a single resistor whose voltage-current
relationship is the same, the equivalent
resistor has a value of:
Definition: Parallel - the elements share the
same two end nodes
2 1
2 1
R R
R R
R
eq
+
=
ECE201 Lect-3 15
2 1
2
1
2 1
2 1
1
1
R R
R
I
R
R R
R R
I
R
V
I
+
=
+
= =
Now to find I
1
This is the current divider formula.
It tells us how to divide the current through
parallel resistors.
ECE201 Lect-3 16
Example: 3 Light Bulbs in
Parallel
How do we find I
1
, I
2
, and I
3
?
I
R
2
V
+
R
1
I
1
I
2
R
3
I
3
ECE201 Lect-3 17
Apply KCL at the Top Node
I= I
1
+ I
2
+ I
3
1
1
R
V
I =
2
2
R
V
I =
3
3
R
V
I =
ECE201 Lect-3 18
Solve for V
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ + = + + =
3 2 1 3 2 1
1 1 1
R R R
V
R
V
R
V
R
V
I
3 2 1
1 1 1
1
R R R
I V
+ +
=
ECE201 Lect-3 19
R
eq
3 2 1
1 1 1
1
R R R
R
eq
+ +
=
= + + + =
i M par
R R R R R
1 1 1 1 1
2 1
Which is the familiar equation for parallel resistors:
ECE201 Lect-3 20
Current Divider
This leads to a current divider equation for
three or more parallel resistors.
For 2 parallel resistors, it reduces to a simple
form.
Note this equations similarity to the voltage
divider equation.
j
par
S R
R
R
I I
j
=
ECE201 Lect-3 21
I
s2
V
R
1
R
2
+
I
1
I
2
Example: More Than One Source
How do we find I
1
or I
2
?
I
s1
ECE201 Lect-3 22
Apply KCL at the Top Node
I
1
+ I
2
= I
s1
- I
s2
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ = + =
2 1 2 1
2 1
1 1
R R
V
R
V
R
V
I I
s s
( )
2 1
2 1
2 1
R R
R R
I I V
s s
+
=
ECE201 Lect-3 23
Multiple Current Sources
We find an equivalent current source by
algebraically summing current sources.
As before, we find an equivalent resistance.
We find V as equivalent I times equivalent
R.
We then find any necessary currents using
Ohms law.
ECE201 Lect-3 24
In General: Current Division
Consider N resistors in parallel:
Special Case (2 resistors in parallel)
= + + + =
=
i N par
j
par
S R
R R R R R
R
R
t i t i
k j
1 1 1 1 1
) ( ) (
2 1
2 1
2
) ( ) (
1
R R
R
t i t i
S R
+
=
ECE201 Lect-3 25
Class Examples
Learning Extension E2.10
Learning Extension E2.11
También podría gustarte
- Loop (Mesh) Analysis (3.2) : Dr. Holbert February 27, 2006Documento26 páginasLoop (Mesh) Analysis (3.2) : Dr. Holbert February 27, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- A. Basic ConceptsDocumento40 páginasA. Basic ConceptsBarkley VelezAún no hay calificaciones
- Time-Domain AnalysisDocumento29 páginasTime-Domain AnalysisdebealAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Electrical Engineering BEE1101Documento101 páginasBasic Electrical Engineering BEE1101DimitriAún no hay calificaciones
- ECE 307 - Lecture 7 Superposition, Maximum Power Transfer, and Dependent SourcesDocumento35 páginasECE 307 - Lecture 7 Superposition, Maximum Power Transfer, and Dependent Sourcesits_crussellAún no hay calificaciones
- Final Review PDFDocumento19 páginasFinal Review PDFurfriend_jjn05Aún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 2 DC Analysis AllDocumento32 páginasChapter 2 DC Analysis Allyibelta abebeAún no hay calificaciones
- Second-Order Circuits (7.3) : Dr. Holbert April 19, 2006Documento31 páginasSecond-Order Circuits (7.3) : Dr. Holbert April 19, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical Circuit Analysis LectureDocumento29 páginasElectrical Circuit Analysis LectureMikeTongAún no hay calificaciones
- 1st Year - Basic Electrical EngineeringDocumento182 páginas1st Year - Basic Electrical EngineeringMurughesh MurughesanAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics Lab 5Documento7 páginasElectronics Lab 5Sano SukiAún no hay calificaciones
- Ece 201 Exam 2 ReviewDocumento12 páginasEce 201 Exam 2 ReviewkarlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Circuit Analysis LawsDocumento50 páginasBasic Circuit Analysis LawsMuhd RzwanAún no hay calificaciones
- Equivalence/Linearity (5.1) Superposition (5.2, 8.8) : Dr. Holbert March 6, 2006Documento29 páginasEquivalence/Linearity (5.1) Superposition (5.2, 8.8) : Dr. Holbert March 6, 2006Satya SharonAún no hay calificaciones
- Ch04 First Order Circuits PDFDocumento96 páginasCh04 First Order Circuits PDFMichelle BatadAún no hay calificaciones
- We Have Seen The Idea of Equivalency Used in Several Instances Already. Same AsDocumento19 páginasWe Have Seen The Idea of Equivalency Used in Several Instances Already. Same Assurag1982Aún no hay calificaciones
- ECE 307 MasterDocumento505 páginasECE 307 Mastermmiller276Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ee2001 (Week3 Week6 Wcy)Documento177 páginasEe2001 (Week3 Week6 Wcy)Giang Nguyễn TrườngAún no hay calificaciones
- EE-221-Review of DC CircuitsDocumento51 páginasEE-221-Review of DC CircuitsSean Ng100% (1)
- ECE 307 - Lecture 1 DC Circuit Components, Connections, and KCLDocumento45 páginasECE 307 - Lecture 1 DC Circuit Components, Connections, and KCLCarl FitzpatrickAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Electrical DiscussionDocumento157 páginasBasic Electrical Discussionseul jichuAún no hay calificaciones
- L6 Cap Induc CircuitsDocumento43 páginasL6 Cap Induc CircuitsMukesh Kumar DewraAún no hay calificaciones
- Bee LabDocumento23 páginasBee Labdurgesh choudharyAún no hay calificaciones
- Electric Circuits and Electron DevicesDocumento62 páginasElectric Circuits and Electron DevicesHarshaAún no hay calificaciones
- 18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Documento57 páginas18Ees101J-Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineering: Unit 1Mohammed JavidhAún no hay calificaciones
- Phasor Relationships For Circuit Elements (8.4) Impedance and Admittance (8.5)Documento29 páginasPhasor Relationships For Circuit Elements (8.4) Impedance and Admittance (8.5)karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Magnetically Coupled Circuits: Chapter ObjectivesDocumento25 páginasMagnetically Coupled Circuits: Chapter ObjectivesNitin MarwahAún no hay calificaciones
- FE Exam Review - Circuits - 11182014Documento80 páginasFE Exam Review - Circuits - 11182014Juan Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Final ReportDocumento9 páginasFinal Reportapi-296881750Aún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics Study Material For MSCDocumento23 páginasElectronics Study Material For MSCiswaleha100% (1)
- Magnetically Coupled Circuits: Chapter ObjectivesDocumento25 páginasMagnetically Coupled Circuits: Chapter ObjectivesKarthik Thirumala100% (1)
- TP 1: General TheoremsDocumento4 páginasTP 1: General TheoremsZiad FAwalAún no hay calificaciones
- CHP 1: Circuit TheoryDocumento42 páginasCHP 1: Circuit TheoryjojoAún no hay calificaciones
- Resistive Circuits: Chapter 3 in Dorf and SvobodaDocumento47 páginasResistive Circuits: Chapter 3 in Dorf and Svobodaananzo3biAún no hay calificaciones
- CircuitAnalysis CK Tse PDFDocumento49 páginasCircuitAnalysis CK Tse PDFcivaasAún no hay calificaciones
- 3 Circuit Analysis Using SubcircuitsDocumento21 páginas3 Circuit Analysis Using SubcircuitsAlejandro Salas VásquezAún no hay calificaciones
- Circuits Test 1 ReviewDocumento15 páginasCircuits Test 1 ReviewKelsey KnutsenAún no hay calificaciones
- Ohm's Law: (Essentials of Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Documento5 páginasOhm's Law: (Essentials of Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Josh KingAún no hay calificaciones
- Recall: Functioning Equations For Ideal ElementsDocumento29 páginasRecall: Functioning Equations For Ideal ElementsppAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Electrical Engineering Course: WEEK-5 (JAN 04-08) 1Documento24 páginasBasic Electrical Engineering Course: WEEK-5 (JAN 04-08) 1subhan puram sharadaAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocumento181 páginasBasic Electrical EngineeringPrakash Chandran CAún no hay calificaciones
- Nodal Analysis (3.1) : Dr. Holbert February 22, 2006Documento27 páginasNodal Analysis (3.1) : Dr. Holbert February 22, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- ENEE2304 Circuit Analysis: Welcome ToDocumento16 páginasENEE2304 Circuit Analysis: Welcome ToYoussif AbuziedAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 3Documento8 páginasLab 3TOP 5 GHOSTAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical Energy Generation Electrical Energy GenerationDocumento10 páginasElectrical Energy Generation Electrical Energy GenerationKadhane NavnathAún no hay calificaciones
- Voltage & Current DividerDocumento4 páginasVoltage & Current DividerSaif Ullah KamranAún no hay calificaciones
- Second-Order Circuits (7.3) : Dr. Holbert April 19, 2006Documento31 páginasSecond-Order Circuits (7.3) : Dr. Holbert April 19, 2006محيي الدين الكميشىAún no hay calificaciones
- Ee 211Documento37 páginasEe 211Muhammad OsamaAún no hay calificaciones
- Booklet Electronics RevisedDocumento24 páginasBooklet Electronics Revisedargantonius6773100% (1)
- Electrical System Building BlocksDocumento71 páginasElectrical System Building BlocksAjay Nath S A100% (1)
- Three Essential Laws For Working With Circuits: What Is Nodal Analysis?Documento3 páginasThree Essential Laws For Working With Circuits: What Is Nodal Analysis?Jaime Ortiz ValentínAún no hay calificaciones
- Nodal and Loop Analysis Cont'd (8.8) : Dr. Holbert March 1, 2006Documento26 páginasNodal and Loop Analysis Cont'd (8.8) : Dr. Holbert March 1, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Kirchoffs LawDocumento22 páginasKirchoffs LawKim OpenaAún no hay calificaciones
- RC CircuitsDocumento23 páginasRC CircuitsmaprofAún no hay calificaciones
- Nodal AnalysisDocumento25 páginasNodal AnalysisFreezing FlamesAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics And Circuit Design Made EasyDe EverandElectronics And Circuit Design Made EasyCalificación: 3 de 5 estrellas3/5 (9)
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesDe EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesCalificación: 5 de 5 estrellas5/5 (1)
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2De EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2Aún no hay calificaciones
- Ece 201 Exam 2 ReviewDocumento12 páginasEce 201 Exam 2 ReviewkarlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Transient Pspice Analysis (7.4) : Dr. Holbert April 26, 2006Documento22 páginasTransient Pspice Analysis (7.4) : Dr. Holbert April 26, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- 400 F 50 MH + - V 10: ECE201-ProblemsDocumento1 página400 F 50 MH + - V 10: ECE201-ProblemskarlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Second-Order Circuits Cont'd: Dr. Holbert April 24, 2006Documento7 páginasSecond-Order Circuits Cont'd: Dr. Holbert April 24, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Second-Order Circuits (7.3) : Dr. Holbert April 19, 2006Documento31 páginasSecond-Order Circuits (7.3) : Dr. Holbert April 19, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Operational Amplifiers (4.1-4.3) : Dr. Holbert April 3, 2006Documento26 páginasOperational Amplifiers (4.1-4.3) : Dr. Holbert April 3, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Capacitors (6.1) Inductors (6.2) LC Combinations (6.3) : Dr. Holbert April 5, 2006Documento21 páginasCapacitors (6.1) Inductors (6.2) LC Combinations (6.3) : Dr. Holbert April 5, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Phasor Relationships For Circuit Elements (8.4) Impedance and Admittance (8.5)Documento29 páginasPhasor Relationships For Circuit Elements (8.4) Impedance and Admittance (8.5)karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- DC and Ac Pspice Analysis (5.5, 8.9) : Dr. Holbert March 22, 2006Documento6 páginasDC and Ac Pspice Analysis (5.5, 8.9) : Dr. Holbert March 22, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Nodal and Loop Analysis Cont'd (8.8) : Dr. Holbert March 1, 2006Documento26 páginasNodal and Loop Analysis Cont'd (8.8) : Dr. Holbert March 1, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Nodal Analysis (3.1) : Dr. Holbert February 22, 2006Documento27 páginasNodal Analysis (3.1) : Dr. Holbert February 22, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Sinusoids (8.1) Phasors (8.3) Complex Numbers (Appendix) : Dr. Holbert January 30, 2006Documento23 páginasSinusoids (8.1) Phasors (8.3) Complex Numbers (Appendix) : Dr. Holbert January 30, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Ohm's Law (2.1) Kirchhoff's Laws (2.2) : Dr. Holbert January 23, 2006Documento15 páginasOhm's Law (2.1) Kirchhoff's Laws (2.2) : Dr. Holbert January 23, 2006karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction Units (1.1) Basic Quantities (1.2) Circuit Elements (1.3)Documento12 páginasIntroduction Units (1.1) Basic Quantities (1.2) Circuit Elements (1.3)karlrodAún no hay calificaciones
- Atoll The RF Planning ToolDocumento16 páginasAtoll The RF Planning Toolloc2002Aún no hay calificaciones
- 100G Transport SystemsDocumento12 páginas100G Transport Systemsaltamirandodapaz@msn.comAún no hay calificaciones
- M BusDocumento88 páginasM Busakshay_haridasAún no hay calificaciones
- EMC-Mon GB 04.04.2005Documento62 páginasEMC-Mon GB 04.04.2005mbarete293% (30)
- Behringer PODCAST Quick-Start GuideDocumento6 páginasBehringer PODCAST Quick-Start GuideNidzaAún no hay calificaciones
- Basic Communication Trainer: List of ModulesDocumento4 páginasBasic Communication Trainer: List of ModulesAghaAún no hay calificaciones
- Port City International University: Mid-Term Lab ReportDocumento5 páginasPort City International University: Mid-Term Lab ReportMohammad Azimul HoqueAún no hay calificaciones
- ws10 - en ENCODERDocumento44 páginasws10 - en ENCODERRenato CardosoAún no hay calificaciones
- RP000770 CfamDocumento39 páginasRP000770 CfamprasoonAún no hay calificaciones
- Data Sheet: HEDM-55xx/560x & HEDS-55xx/56xxDocumento13 páginasData Sheet: HEDM-55xx/560x & HEDS-55xx/56xxLuiguiAún no hay calificaciones
- Sarjan: Ssip-Proposal Application Form (Pre Incubation Centre) Govt. Engineering College-Sec-28-GandhinagarDocumento4 páginasSarjan: Ssip-Proposal Application Form (Pre Incubation Centre) Govt. Engineering College-Sec-28-GandhinagarTech4 ManiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Usher X Series, CompassDocumento8 páginasUsher X Series, CompassmilexconsultAún no hay calificaciones
- ProjectDocumento16 páginasProjectKiran TkAún no hay calificaciones
- Fujitsu Amilo Xi 1526Documento3 páginasFujitsu Amilo Xi 1526alelujaAún no hay calificaciones
- Microelectronics Solution Manual by Bahzad RazaviDocumento4 páginasMicroelectronics Solution Manual by Bahzad RazaviBilal Shafique8% (13)
- Triac 2n6073aDocumento7 páginasTriac 2n6073aJorge MoralesAún no hay calificaciones
- Melody Technical Manual - IndexDocumento8 páginasMelody Technical Manual - IndexNassima BELILAún no hay calificaciones
- EMI Class Notes Assignment 1Documento2 páginasEMI Class Notes Assignment 1Praneshvar Praneshvar50% (2)
- Chapter 6 IctDocumento37 páginasChapter 6 IctJood ObeidatAún no hay calificaciones
- Omdb Ils 30 Rwy30lDocumento1 páginaOmdb Ils 30 Rwy30lItsIlaiAún no hay calificaciones
- Arm7tdmi Instruction Set ReferenceDocumento43 páginasArm7tdmi Instruction Set ReferencePrabhu Cpu CAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual de Utilizare UPS Pentru Centrala Termica Njoy Aira 600 UPCSTLP860TAICP01BDocumento13 páginasManual de Utilizare UPS Pentru Centrala Termica Njoy Aira 600 UPCSTLP860TAICP01BEugen BocanAún no hay calificaciones
- GSM Call Processing: Source: InternetDocumento11 páginasGSM Call Processing: Source: InternetAditya RanjanAún no hay calificaciones
- EC Electronic-Devices PDFDocumento37 páginasEC Electronic-Devices PDFscvAún no hay calificaciones
- 377.11 Nvidia Quadro Control Panel Quick Start GuideDocumento67 páginas377.11 Nvidia Quadro Control Panel Quick Start GuideHosam AliAún no hay calificaciones
- Protection Fundamentals - EPR030 Electrical Protection Sept 2010Documento13 páginasProtection Fundamentals - EPR030 Electrical Protection Sept 2010joeblck0Aún no hay calificaciones
- Network ComponentsDocumento52 páginasNetwork ComponentsParthPrajapatiAún no hay calificaciones
- EPAS - Training Plan Common Competency - MTPDocumento12 páginasEPAS - Training Plan Common Competency - MTPnicelyn baisaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sec Engineers ManualDocumento70 páginasSec Engineers ManualPrathap Kumar100% (1)