Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
R.Hariharan, Lect / Eee
R.Hariharan, Lect / Eee
Cargado por
Jinto AntonyDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
R.Hariharan, Lect / Eee
R.Hariharan, Lect / Eee
Cargado por
Jinto AntonyCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
R.
HARIHARAN, LECT / EEE
It is an analytical technique to identify foreseeable failures in a product or a process and to eliminate it. It is also defined as a group of activities intended to understand and evaluate the potential failure of a product or process and to eliminate it. FMEA is a Before-the-event action that requires a team effort to easily and inexpensively, improves changes in design and production.
DESIGN FMEA PROCESS FMEA Other types are
Equipment FMEA (modified version of process FMEA) Maintenance FMEA Concept FMEA Service FMEA (modified version of process FMEA) System FMEA ( combination of both design & process) Environmental FMEA (modified version of process FMEA)
It is the design process by identifying the failures. It will rank the failures according to their relative impact on product. It helps to establish priorities based on expected failures and helps to uncover oversights, misjudgments and errors that may have been made. It helps to reduce development time and cost of manufacturing. It also specifies the appropriate tests to check the designed product.
It is to identify potential process failure by ranking the failures. It priorities the failures according to the impact on external and internal customer. It helps to identify manufacturing and assembly failures in order to establish controls for failure reduction.
It is the probability that the product will perform as per the expectations for a certain period of time. The factors to be considered are long life, safety of the product.
DEBUG FAILURE
Failure at initial stages because of inappropriate use or flaws in design.
CHANCE FAILURE
Failure occur in the product due to accidents, poor maintenance or limitations of design.
WEAR OUT FAILURE
It occur in a product after the product has performed as expected for at least the amount of time given by the manufacturer as the product life.
It attempts to find out potential productrelated failures. FMEA is an debugging and preventing problems that may occur in the manufacturing process. FMEA evaluation should be carried out immediately after the design phase of the product certainly before purchasing and setting up any machinery.
Helps in determining the impact of any failure on other items in the product. Helps to calculate the possibilities of failure in assemblies, sub-assemblies, product. Helps to establish test programs to determine failures. Helps to establish test programs to determine failure.
Specifying possibilities Quantifying risk Correcting high risk causes Re-evaluation of risk
Function involved are identified. Possible failure modes are determined. Root causes for the failures are found out. Effects of failures on other components of the system is found out. Steps involved in detection of failures are found out.
Probability of cause is determined. Severity of the failure and its effect is determined. Effectiveness of control system to prevent cause is checked. The risk is prioritized.
The work is prioritized. Action is explained in a detail manner. Now the action is assigned to the necessary people. Go in for check points to check the completion level.
It is the process of determining who is the very best, who sets the standard and what that standard is. It answers to the questions of WHAT can be achieved and HOW can be achieved. The process of identifying, understanding and adapting outstanding practices and processes from organizations anywhere in the world to an organization to improve its performance.
WHAT IS OUR PRESENT PERFORMANCE LEVEL? HOW DO WE DO IT?
WHAT ARE THE OTHERS PERFORMANCE LEVELS? HOW DID THEY GET THERE?
CREATIVE ADAPTION
BREAK THROUGH PERFORMANCE
Reasons to benchmark:
It aims at goal setting process to facilitate comparison with the best. It aims at motivating and stimulating employees towards the goal of continuous quality improvement. It aims at external orientation of the company. It aims at identifying a technological breakthrough. It aims at searching for industry best practices.
Product benchmarking Performance benchmarking Process benchmarking Strategic benchmarking
Planning
What can be benchmarked? To whom or what shall we compare? (partners) Determine data collection method and collect data
Analysis
Determine the current performance gap. Project future performance levels
Integration
Communicate benchmark findings and gain acceptance Establish functional goals
Action
Develop action plans Implement specific actions and monitor the progress Recalibrate benchmarks
Maturity
Attain the leadership position Integrate practices into process
It is the activity to ensure the physical assets to continue to do what their users wanted to do. Types:
Corrective or breakdown maintenance Scheduled or routine maintenance Preventive maintenance Predictive maintenance
TPM is the systematic execution of maintenance by all employees through small group activities. Goals zero breakdown and defects It improves equipment efficiency rate and reduces cost. Implementation of TPM can generate cost saving through increased productivity of the machinery.
To improve equipment effectiveness To achieve autonomous maintenance To plan maintenance To train all staff in relevant maintenance skills To achieve early equipment management
Breakdowns long interruption, expensive repairs Setup and changeover- taking much longer than needed Idling and minor stoppages hard to quantify Reduced speed equipment cycle times have gradually deteriorated Defects and rework quality loss Start up losses to get steady state after a change
Preparation stage
Announce top management about the decision to introduce TPM Launch education and campaign to introduce TPM Create organization to promote teams Establish basic TPM policies and goals Formulate basic TPM policies and goals
Preliminary implementation stage
Hold TPM kick-off
TPM implementation stage
Improve effectiveness of each piece of equipment Develop an autonomous maintenance program Develop a scheduled maintenance program for the maintenance department Conduct training to improve operation and maintenance skills. Develop early equipment management program
Stabilization stage
Perfect TPM implementation and raise TPM levels
Increased equipment productivity Improved equipment reliability Reduced equipment downtime Increased plant capacity Extended machine line Improved return on investment improved safety
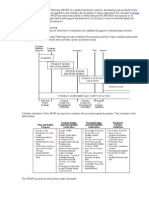
It is a systematic and organized approach of taking customer needs and demands into consideration while designing new products and services. It focus on the voice of the customer or it is called as customer driven engineering.
To identify the true voice of the customer and to use this knowledge to develop products which satisfy customers. To help in the organization and analysis of all the pertinent information associated with the project.
List customer requirements (what) List technical descriptors(how) Develop a relationship matrix Develop an interrelationship matrix Competitive assessments Develop prioritized customer requirements Develop prioritized technical descriptors
Phase I QFD methodology Phase-II- part development
Phase-III- process planning
Deploy QFD process down to sub-components level both in terms of requirements and characteristics. Deploy the component deployment chart. Relate the critical sub-component control characteristics Develop the relationship between the critical characteristics and process used to create the characteristics Develop the control plan relating critical to critical processes.
Phase-IV- Product planning
Tabulate the final product to the market Develop prototype product to the market Launch the final product to the market.
También podría gustarte
- Qgem Management Solution: Welcomes You To Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (Fmea) Training Course 4 EditionDocumento103 páginasQgem Management Solution: Welcomes You To Failure Mode & Effects Analysis (Fmea) Training Course 4 EditionVINOTH100% (2)
- Failure Mode Effect AnalysisDocumento36 páginasFailure Mode Effect AnalysisCharanjeet SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Artificial Intelligence GlossaryDocumento2 páginasArtificial Intelligence GlossaryJohnAún no hay calificaciones
- PMP Exam PREP - CONDENSED NOTES - Prepared by Cindy J, Bell, PMPDocumento9 páginasPMP Exam PREP - CONDENSED NOTES - Prepared by Cindy J, Bell, PMPBeth SaadAún no hay calificaciones
- Fmea TrainingDocumento54 páginasFmea Trainingazadsingh10% (1)
- FMEA AnalysisDocumento53 páginasFMEA AnalysisDhilip KannanAún no hay calificaciones
- Manufacturing System: Prepared byDocumento33 páginasManufacturing System: Prepared bynorizayusofAún no hay calificaciones
- The 5 Core ToolDocumento17 páginasThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshAún no hay calificaciones
- Istqb NotesDocumento11 páginasIstqb Notesmadhumohan100% (2)
- Unit 1 Fundamentals of Software TestingDocumento50 páginasUnit 1 Fundamentals of Software TestingrajehshsjAún no hay calificaciones
- FMEADocumento29 páginasFMEAKarthik Kr100% (1)
- Learn Software Testing For BeginnersDocumento168 páginasLearn Software Testing For Beginnersamar_123inAún no hay calificaciones
- Learn Software Testing For BeginnersDocumento168 páginasLearn Software Testing For BeginnersMima VasiljevićAún no hay calificaciones
- CH 12& Ch13quality and Control of QualityDocumento15 páginasCH 12& Ch13quality and Control of QualityRebecca RodriguezAún no hay calificaciones
- A Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryDocumento8 páginasA Case Study: A Process FMEA Tool To Enhance Quality and Efficiency of Manufacturing IndustryBONFRINGAún no hay calificaciones
- Total Productive MaintenanceDocumento46 páginasTotal Productive MaintenanceMKPashaPasha100% (3)
- FMEADocumento42 páginasFMEAibal_machine100% (1)
- SAP TestingDocumento7 páginasSAP Testingpvpreddy67Aún no hay calificaciones
- The 5 Core ToolDocumento17 páginasThe 5 Core ToolRajesh GhoshAún no hay calificaciones
- Software Testing An Overview: Srihari TechsoftDocumento158 páginasSoftware Testing An Overview: Srihari TechsoftbawyakAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 5 Queueing TheoryDocumento32 páginasChapter 5 Queueing TheoryIzzati AtirahAún no hay calificaciones
- Process Approach-Tqm StudyDocumento9 páginasProcess Approach-Tqm StudyShekinah Faith RequintelAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Lean Manufacturing TPM1Documento42 páginasIntroduction To Lean Manufacturing TPM1Lakshmanan VenkatesanAún no hay calificaciones
- Quality Core ToolsDocumento14 páginasQuality Core Toolsالعاب الاطفال- jeux enfantsAún no hay calificaciones
- Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993Documento5 páginasFailure Modes and Effects Analysis (Fmea) : Mechanical Engineering, September 1993JeevanAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Advanced Product Quality PlanningDocumento14 páginasIntroduction To Advanced Product Quality PlanningAbraham GuerraAún no hay calificaciones
- Development of Quality System For Engine AssemblyDocumento55 páginasDevelopment of Quality System For Engine AssemblysvrbchaudhariAún no hay calificaciones
- STN HiAv V2.0Documento88 páginasSTN HiAv V2.0Sagar JadhavAún no hay calificaciones
- Optimising Productivity in Foundry Optimising Productivity in FoundryDocumento57 páginasOptimising Productivity in Foundry Optimising Productivity in FoundrykarthikkandaAún no hay calificaciones
- Software Testing An OverviewDocumento158 páginasSoftware Testing An OverviewYashodhan BhattAún no hay calificaciones
- All Tools in OneDocumento38 páginasAll Tools in Oneom_3334Aún no hay calificaciones
- Real-Estate Project ReportDocumento111 páginasReal-Estate Project ReportTushar Jaiswal100% (3)
- Process FmeaDocumento8 páginasProcess Fmeaanirudha samalAún no hay calificaciones
- FMEADocumento64 páginasFMEAbipin.chouguleAún no hay calificaciones
- TPMDocumento28 páginasTPMVinay Simha SAún no hay calificaciones
- FMEA A Complete Guide To Identifying and Preventing Risks in Your CompanyDocumento42 páginasFMEA A Complete Guide To Identifying and Preventing Risks in Your CompanyGabriel Domé100% (1)
- Ebook 9 Steps Reliability ProcessDocumento33 páginasEbook 9 Steps Reliability ProcesstohemaAún no hay calificaciones
- Bench Marking & FMEADocumento38 páginasBench Marking & FMEASantosh SandyAún no hay calificaciones
- Business Communication Chapter 01Documento26 páginasBusiness Communication Chapter 01javedaa444Aún no hay calificaciones
- Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisDocumento5 páginasFailure Modes and Effects AnalysisBoBo KyawAún no hay calificaciones
- BY Kiran S Shinde Kishor L RasalDocumento10 páginasBY Kiran S Shinde Kishor L RasalKiran ShindeAún no hay calificaciones
- Seminar Report - Atharva - Sanglikar - 19121236Documento22 páginasSeminar Report - Atharva - Sanglikar - 19121236Atharva SanglikarAún no hay calificaciones
- FMECADocumento5 páginasFMECAGayathri Ragunathan0% (1)
- Modern Trends in ManufacturingDocumento34 páginasModern Trends in Manufacturingalan ShajuAún no hay calificaciones
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocumento6 páginasNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentZaman Parvez100% (1)
- Operations Management: Lecture NotesDocumento49 páginasOperations Management: Lecture NotesKajal NainAún no hay calificaciones
- Learn Software Testing For BeginnersDocumento168 páginasLearn Software Testing For Beginnersramesh26Aún no hay calificaciones
- Tcs InterviewDocumento10 páginasTcs InterviewYogi GowdaAún no hay calificaciones
- Function:: Yield Fatigue Material Instability Creep Wear Corrosion Cracked Deformed LeakingDocumento16 páginasFunction:: Yield Fatigue Material Instability Creep Wear Corrosion Cracked Deformed LeakingAnita SinghAún no hay calificaciones
- Presentation For Viva: Omkar SakpalDocumento19 páginasPresentation For Viva: Omkar Sakpalomkar sakpalAún no hay calificaciones
- Senior Warranty Engineer Generic JDDocumento4 páginasSenior Warranty Engineer Generic JDAmr MohsenAún no hay calificaciones
- tqm4 PDFDocumento37 páginastqm4 PDFmaria69Aún no hay calificaciones
- Are The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapDocumento4 páginasAre The Tools That Help Us Greatly Reduce Quality Problems in The Launch of New Products Apqp & CP, Amef, Control Plan, SPC, R & R and PpapSergio Cristobal Bonilla CegadorAún no hay calificaciones
- Process Focus: By: Dr. Jestita F. GurreaDocumento23 páginasProcess Focus: By: Dr. Jestita F. GurreaNorjanah MacabatoAún no hay calificaciones
- Cause-And-Effect Diagram Check Sheet: Control Charts: Histogram: Pareto Chart: Scatter Diagram StratificationDocumento3 páginasCause-And-Effect Diagram Check Sheet: Control Charts: Histogram: Pareto Chart: Scatter Diagram StratificationAlain DoniAún no hay calificaciones
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento7 páginasTotal Quality Managementkaavya satsangiAún no hay calificaciones
- Software Quality ManagementDocumento22 páginasSoftware Quality ManagementAbdul WahabAún no hay calificaciones
- WP Effectiveness of UatDocumento6 páginasWP Effectiveness of UatboomsmcaAún no hay calificaciones
- FMEA ArticleDocumento4 páginasFMEA Articlekiran2381Aún no hay calificaciones
- Presentation1 TQMDocumento70 páginasPresentation1 TQMrochelle regenciaAún no hay calificaciones
- QM 0013Documento9 páginasQM 0013Mrinal KalitaAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 4Documento13 páginasAssignment 4api-265324689Aún no hay calificaciones
- Failure Mode and Effect AnalysisDocumento9 páginasFailure Mode and Effect AnalysisameliaAún no hay calificaciones
- Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-TrainingDocumento12 páginasImproving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-TrainingMichael GotamaAún no hay calificaciones
- Process Control Fundamentals Related To Distributed Control System PDFDocumento15 páginasProcess Control Fundamentals Related To Distributed Control System PDFRamesh NklAún no hay calificaciones
- Design For Reliability PDFDocumento44 páginasDesign For Reliability PDFMohamed ZafatiAún no hay calificaciones
- Hybrid Control For Global Stabilization of The Cart) Pendulum SystemDocumento11 páginasHybrid Control For Global Stabilization of The Cart) Pendulum SystemirqoviAún no hay calificaciones
- Sad Mini Project ProposalDocumento15 páginasSad Mini Project ProposalTHANYASRI DEVANATHANAún no hay calificaciones
- Group Assignment Technology Park Malaysia CT046-3-2 System Development Methodology NP2F1909ITDocumento48 páginasGroup Assignment Technology Park Malaysia CT046-3-2 System Development Methodology NP2F1909ITAaditya JhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Icompass PFE BookDocumento15 páginasIcompass PFE Bookguizeni ahmedAún no hay calificaciones
- Assignment 2 - Project Management PlanDocumento2 páginasAssignment 2 - Project Management PlanRahul Pandey100% (1)
- C11SL - 1 Systems Thinking and Analysis Intro 2017Documento34 páginasC11SL - 1 Systems Thinking and Analysis Intro 2017Karl AbiKaramAún no hay calificaciones
- Exam Test Questions and AnswersDocumento36 páginasExam Test Questions and Answersmanu saxenaAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Modeling and SimulationDocumento8 páginasIntroduction To Modeling and Simulationmagno magroAún no hay calificaciones
- Neural Network Tutorial 1Documento3 páginasNeural Network Tutorial 1Omer ElsirAún no hay calificaciones
- IT-34 KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION AND Management PapersDocumento4 páginasIT-34 KNOWLEDGE REPRESENTATION AND Management Paperscokog41585Aún no hay calificaciones
- Complex Networks (CS60078) : Instructor: Bivas MitraDocumento16 páginasComplex Networks (CS60078) : Instructor: Bivas MitraE JagadeeshAún no hay calificaciones
- Requirement Analysis ProcessDocumento10 páginasRequirement Analysis ProcessgeethabvAún no hay calificaciones
- Artificial IntelligenceDocumento2 páginasArtificial IntelligenceAbhi AndhariyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Simplilearn Deep LearningDocumento6 páginasSimplilearn Deep LearningramubaluAún no hay calificaciones
- OTESDC Activity Plan of 2021: Task Responsible Start Date End DateDocumento16 páginasOTESDC Activity Plan of 2021: Task Responsible Start Date End DateJames RecañaAún no hay calificaciones
- Training Deep Spiking Neural Networks Using Backpropagation: Jun Haeng Lee, Tobi Delbruck and Michael PfeifferDocumento13 páginasTraining Deep Spiking Neural Networks Using Backpropagation: Jun Haeng Lee, Tobi Delbruck and Michael Pfeifferzhili zouAún no hay calificaciones
- Ijest11 03 07 142Documento5 páginasIjest11 03 07 142hoangductuanAún no hay calificaciones
- Control System Engineering 3Documento3 páginasControl System Engineering 3Mohamed RiyaazAún no hay calificaciones
- Dalhousie Academic Calendars 2 - View CalendarDocumento4 páginasDalhousie Academic Calendars 2 - View CalendarBrandin RoveloAún no hay calificaciones
- Software Testing - R.S. Pressman & Associates, Inc.Documento63 páginasSoftware Testing - R.S. Pressman & Associates, Inc.Karthik Tantri100% (2)
- World Class Manufacturing, 16Documento14 páginasWorld Class Manufacturing, 16Santhilal S Pillai100% (1)
- Think Like A Usability EngineerDocumento8 páginasThink Like A Usability EngineerLucas Neubert100% (1)