Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Companies Act 2013 India
Cargado por
Bhagirath AshiyaDerechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Companies Act 2013 India
Cargado por
Bhagirath AshiyaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Companies Act 2013
The Companies Act
Empowers the Central Government to regulate the formation, financing, functioning and winding up of companies It empowers the Government to inspect the books of accounts f the company, direct special audits and other investigations into the affairs of the company if they are in any way violating the act
It is administered by the Central Government and the Offices of Registrar of Companies, Official Liquidators, Public Trustee, Company Law Board, Director of Inspection etc.
Incorporation and the administration of running companies is done by the Registrar of Companies
Objectives of The Companies Act, 1956
Management of companies Control over companies Protection of consumers interest Enforcement of proper performance of duties by management Investors protection Full disclosure of information
Companies Bill 2012
On 18th December, 2012, Lok Sabha passed this bill It has 29 chapters, 7 schedules and 470 clauses as against 658 sections, 13 parts and 15 schedules in the existing Companies Act, 1956 The bill received the Presidents assent on 29th August, 2013 and now is on its way to becoming an act
New introductions
Concept of One Person Company E- governance in all company processes Insider trading of securities is prohibited Punishment for fraud Nomination and remuneration committee
Independent Directors- one-third of board members Corporate Social Responsibility- set aside a certain percentage of profits for CSR Excessive Bureaucracy- Director Identification Number (DIN)
Women Directors- more number of women reaching higher levels of hierarchy Class Action Suits- a large group of people can bring a claim to court in which a group of defendants are sued Company Secretary- Elevates their role to management level
New Definitions Introduced
Associate Company- a company has significant influence over another company, controls 20% of share capital of other company or business decisions Auditing Standard- standards of auditing for companies or class of companies Global Depository Receipt- an instrument created by foreign depository and authorised by company making an issue of such depository receipt
Employee Stock Option- option given to directors, officers or employees of a company to purchase or subscribe for the shares of the company in the future Financial year- a period ending on 31st March of every year in which respect financial statements are made Turnover- aggregate value of realisation of amount made from the sale, supply or distribution of goods by a company in a financial year
One Person Company- a company which has only one person as the member Key Managerial Personnel- it consists the following -the chief executive officer or managing director or manager - Company secretary - Whole time director - Chief Financial Officer
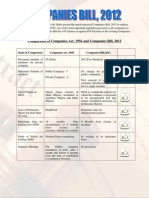
Comparison between the Former and New Act
Basis Maximum no. of members in private company Companies Act, 1956 Companies Act, 2013 50 200
Minimum no. of members
Public- 7 Private- 2
No change but concept of 1 member company introduced 15, more by passing a resolution
Maximum no. of directors
12
Statutory meeting
Public company- mandatory to hold after 1 month but before 6 months from date of entitlement of commencement No specific provisions
No provision
Cross boarder mergers
Mergers of Indian and foreign companies permitted and rules to be notified by Central Government Chairman alone can sign if so authorised by the Board
Certification of financial statements
By manager or secretary, if any, and by not less than 2 directors, one of whom shall be an MD, if there is one 18 months from incorporation or 9 months from closure of accounts, whichever is earlier Written notice mandatory
Maximum time for holding first Annual General Meeting
9 months from closure of accounts
Mode of notice for holding and Annual General Meeting
In writing or in electronic form
Object Clause of Consists of main objects, Memorandum of Association incidental or ancillary objects and other objects
Contains the object for which the company is proposed to be incorporated and any matter considered necessary in furtherance thereof
Issue of preference shares for more than 20 years
Prohibited
Permitted only for infrastructure projects
Maximum tenure of auditors
No specific provisions
For listed and other prescribed companies: - individual auditors to be rotated after 5 years - Audit firm after every 10 years
Financial Year and Extension
Not to exceed 15 months but can be extended to 18 months by ROC, financial year can end on a date other than 31st March No specific provision
Financial end on 31st March of every year for all companies and no other provisions for extension are given Within 30 days from date of incorporation Applicable to all companies having share capital
First Board Meeting
Restrictions on commencement of business
Provisions applicable to only public companies
Time gap between two board meetings Quorum of General meeting of private and public companies
At least one meeting every quarter Private- 2 Public- 5
Not more than 120 days of gap between 2 meetings Private- 2 Public- 5 if total members is greater than 1000 -15 if total is greater than 1000 but less than 5000 - 30 if total is greater than 5000
También podría gustarte
- Unit 2 Company LawDocumento34 páginasUnit 2 Company LawPriya SekarAún no hay calificaciones
- Companies Act 2013Documento171 páginasCompanies Act 2013padmanabha14100% (3)
- @clawmcq Indian Contract ActDocumento76 páginas@clawmcq Indian Contract ActRittik PrakashAún no hay calificaciones
- GST Explained: Understanding India's Major Tax ReformDocumento8 páginasGST Explained: Understanding India's Major Tax ReformApoorva Chandra100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of PrivatizationDocumento10 páginasAdvantages and Disadvantages of PrivatizationTalha Sheikh100% (1)
- GST NotesDocumento14 páginasGST NotesPremajohnAún no hay calificaciones
- Trade PolicyDocumento27 páginasTrade PolicyRakesh Valiveti0% (1)
- Income Tax Revision Notes December 2019-Executive-RevisionDocumento114 páginasIncome Tax Revision Notes December 2019-Executive-RevisionMeenaa BalakrishnanAún no hay calificaciones
- Income Tax Quick NotesDocumento75 páginasIncome Tax Quick NotesBasavaraju K RAún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction to GST in IndiaDocumento124 páginasIntroduction to GST in IndiaAruna RajappaAún no hay calificaciones
- GST NotesDocumento22 páginasGST NotesSARATH BABU.YAún no hay calificaciones
- Advance Tax Payment DatesDocumento11 páginasAdvance Tax Payment DatesAdv Aastha MakkarAún no hay calificaciones
- On Residential Status and Scope of Total IncomeDocumento72 páginasOn Residential Status and Scope of Total Incomeaim_naina100% (3)
- Companies Act 2013Documento90 páginasCompanies Act 2013Ankush Kunzru100% (2)
- Short Notes On Companies Act 2013 PDFDocumento52 páginasShort Notes On Companies Act 2013 PDFVeeramani Arumugam0% (1)
- Financial Management by SaumyaDocumento59 páginasFinancial Management by Saumyasaumyaranjanbiswal92Aún no hay calificaciones
- Environmental Laws in IndiaDocumento16 páginasEnvironmental Laws in IndiaRaGa JoThi100% (1)
- The - Arbitration - and - Conciliation - Act - 1996 (1) PPT - Sem III - PGPM - IBS - 2020Documento10 páginasThe - Arbitration - and - Conciliation - Act - 1996 (1) PPT - Sem III - PGPM - IBS - 2020Sanjit SinhaAún no hay calificaciones
- Guide To CGST, SGST and IGST: Inter-State Vs Intra-StateDocumento6 páginasGuide To CGST, SGST and IGST: Inter-State Vs Intra-StateSuman IndiaAún no hay calificaciones
- Non-Fund Bank Facilities GuideDocumento2 páginasNon-Fund Bank Facilities GuideKrupa MochiAún no hay calificaciones
- Corporate Law NotesDocumento71 páginasCorporate Law NotesKeyur Shah100% (1)
- Basis of ChargeDocumento21 páginasBasis of Chargemonirba48Aún no hay calificaciones
- R.B.I Function As Banker's BankDocumento28 páginasR.B.I Function As Banker's BankRohit SinhaAún no hay calificaciones
- COMPETITION ACT 2002 KEY PROVISIONS SUMMARYDocumento17 páginasCOMPETITION ACT 2002 KEY PROVISIONS SUMMARYhareshAún no hay calificaciones
- Submitted By: Swati Singh Submitted To: Dr. V. Shunmuga Sundaram SirDocumento17 páginasSubmitted By: Swati Singh Submitted To: Dr. V. Shunmuga Sundaram Sirswatisin93Aún no hay calificaciones
- Balance of PaymentDocumento4 páginasBalance of PaymentAMALA AAún no hay calificaciones
- MRTP Act, 1969Documento13 páginasMRTP Act, 1969Amit Kumar Giri100% (2)
- CA Notes Concept and Accounting of Depreciation PDFDocumento36 páginasCA Notes Concept and Accounting of Depreciation PDFBijay Aryan Dhakal100% (2)
- Contract Act MCQsDocumento11 páginasContract Act MCQsMuhammadIjazAslam0% (1)
- Government Company Act ProvisionsDocumento11 páginasGovernment Company Act Provisions26 Dinesh Kumar PAún no hay calificaciones
- Rights & Duties of AuditorDocumento9 páginasRights & Duties of AuditorShilpa ManoAún no hay calificaciones
- Summary Notes On Company Law by Krishan Commerce ClassesDocumento17 páginasSummary Notes On Company Law by Krishan Commerce Classescommerceclasses80% (10)
- Indian Depository ReceiptsDocumento16 páginasIndian Depository Receipts777priyanka100% (1)
- Redressal Mechanism As Per Consumer Protection ActDocumento23 páginasRedressal Mechanism As Per Consumer Protection ActNandita SadaniAún no hay calificaciones
- Direct and Indirect Taxes ExplainedDocumento42 páginasDirect and Indirect Taxes ExplainedArpit MadaanAún no hay calificaciones
- New Consumer Protection Act 2019 Strengthens RightsDocumento4 páginasNew Consumer Protection Act 2019 Strengthens RightsShivani AntilAún no hay calificaciones
- Non Trading OrganizationDocumento2 páginasNon Trading OrganizationPBGYB60% (5)
- Jkshah Company Law MCQDocumento188 páginasJkshah Company Law MCQIMAM JAVOORAún no hay calificaciones
- AX Educted at Ource - I: KPPM & AssociatesDocumento67 páginasAX Educted at Ource - I: KPPM & AssociatesSaksham JoshiAún no hay calificaciones
- Indicative MCQs-Series 8-Indian Contract Act PDFDocumento18 páginasIndicative MCQs-Series 8-Indian Contract Act PDFBasant RajAún no hay calificaciones
- It - Rebates and ReliefsDocumento5 páginasIt - Rebates and ReliefsJitendra VernekarAún no hay calificaciones
- Companies Act 2013Documento19 páginasCompanies Act 2013Gurpreet Singh100% (1)
- Understanding Supply under GSTDocumento8 páginasUnderstanding Supply under GSTRohit Bajpai100% (1)
- Consumer Protection Act 2019Documento36 páginasConsumer Protection Act 2019Vandana NayakAún no hay calificaciones
- RBI's Central Banking Functions (38Documento52 páginasRBI's Central Banking Functions (38Anonymous im9mMa5100% (1)
- Change in Exim PolicyDocumento50 páginasChange in Exim Policya_aka198986% (7)
- Project On Consumer ProtectionDocumento15 páginasProject On Consumer ProtectionRoopa RajuAún no hay calificaciones
- Measurement and Scale Construction TechniquesDocumento61 páginasMeasurement and Scale Construction TechniquesAbhishek kumarAún no hay calificaciones
- For CS Students-Costing FormulasDocumento85 páginasFor CS Students-Costing FormulasSubhash Sahu100% (12)
- Employee Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provision Act 1952Documento5 páginasEmployee Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provision Act 1952Tanver ShaikhAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 1 MCQs On Income Tax Rates and Basic Concept of Income TaxDocumento25 páginasChapter 1 MCQs On Income Tax Rates and Basic Concept of Income TaxSonu KumarAún no hay calificaciones
- GST in IndiaDocumento12 páginasGST in IndiaRahul ChaturvediAún no hay calificaciones
- Understanding India's Indirect Tax StructureDocumento73 páginasUnderstanding India's Indirect Tax StructureKautilya VithobaAún no hay calificaciones
- Sales of Goods ActDocumento31 páginasSales of Goods Actparidhi123Aún no hay calificaciones
- Presentation On Clubbing of Income Under Income TaxDocumento11 páginasPresentation On Clubbing of Income Under Income TaxCA Arpit Gupta100% (2)
- Double Entry Accounting ExplainedDocumento6 páginasDouble Entry Accounting ExplainedKarthikacauraAún no hay calificaciones
- The Negotiable Instruments ActDocumento14 páginasThe Negotiable Instruments ActPrasanna Subramanian100% (1)
- Companies Act 2013 IndiaDocumento15 páginasCompanies Act 2013 IndiaAadil KakarAún no hay calificaciones
- Study Material-Overview of The Companies Act, 2013-AM-IX-CL-IDocumento6 páginasStudy Material-Overview of The Companies Act, 2013-AM-IX-CL-IannnooonnyyyymmousssAún no hay calificaciones
- Companies Bill 2012 2Documento5 páginasCompanies Bill 2012 2KunwarAjaySinghAún no hay calificaciones
- E Journal On Environmental LawDocumento2 páginasE Journal On Environmental LawBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Academic Writing and Referencing Guide (Final)Documento53 páginasAcademic Writing and Referencing Guide (Final)Bhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Report On Taxation of ECommerce TransactionsDocumento124 páginasReport On Taxation of ECommerce TransactionsManish NamaAún no hay calificaciones
- Framing a NationDocumento28 páginasFraming a NationBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Insurance FraudDocumento14 páginasInsurance FraudBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- HRJ India's Transgender Rights Bill: The Way ForwardDocumento1 páginaHRJ India's Transgender Rights Bill: The Way ForwardBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- International Commercial Arbitration GuideDocumento24 páginasInternational Commercial Arbitration GuideBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Prevention of Terrorism ActDocumento10 páginasPrevention of Terrorism ActBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Jurisdiction in International Commercial ArbitrationDocumento43 páginasJurisdiction in International Commercial ArbitrationBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- International Commercial Arbitration GuideDocumento24 páginasInternational Commercial Arbitration GuideBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Constitution of IndianDocumento291 páginasConstitution of IndianRajendra PrasadAún no hay calificaciones
- RTI Guidelines PDFDocumento11 páginasRTI Guidelines PDFBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ancient IsraelDocumento10 páginasAncient IsraelBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Systems ApproachDocumento1 páginaSystems ApproachBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Consideration - Indian Contract ActDocumento13 páginasConsideration - Indian Contract ActBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Communalism 1Documento36 páginasCommunalism 1Bhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Indian Economy - Fiscal PolicyDocumento26 páginasIndian Economy - Fiscal PolicyBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- The World BankDocumento30 páginasThe World BankBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Time Value of Money: Family Economics & Financial EducationDocumento32 páginasTime Value of Money: Family Economics & Financial EducationBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Consumer Protection Act 1986Documento22 páginasConsumer Protection Act 1986Bhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Israel Poll Feb 2012Documento11 páginasIsrael Poll Feb 2012Bhagirath Ashiya100% (1)
- Autism DisorderDocumento30 páginasAutism DisorderBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Forms of Business EnterprisesDocumento32 páginasForms of Business EnterprisesBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Supreme Court of IndiaDocumento30 páginasSupreme Court of IndiaBhagirath Ashiya100% (4)
- Monopolistic Competition Eco.Documento25 páginasMonopolistic Competition Eco.Bhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Foreign TradeDocumento44 páginasForeign TradeBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Police StateDocumento26 páginasPolice StateBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- The Population of IndiaDocumento29 páginasThe Population of IndiaBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Rising Poverty TrendsDocumento8 páginasRising Poverty TrendsBhagirath AshiyaAún no hay calificaciones
- Uco Deposit ManualDocumento314 páginasUco Deposit ManualS.s.SubramanianAún no hay calificaciones
- Last Resort 2Documento2 páginasLast Resort 2Francis TutorAún no hay calificaciones
- ProrepDocumento24 páginasProrepKrishna RaoAún no hay calificaciones
- California Contract LawDocumento32 páginasCalifornia Contract LawShelley YeamanAún no hay calificaciones
- Assign 1 Engagement LetterDocumento4 páginasAssign 1 Engagement LetterValentin MozheevAún no hay calificaciones
- Summer Training Project Report SbimfDocumento41 páginasSummer Training Project Report SbimfPrateek PanchalAún no hay calificaciones
- Assess Control Risk and Design Substantive TestsDocumento16 páginasAssess Control Risk and Design Substantive TestsVương Trần LưuAún no hay calificaciones
- OperationDocumento6 páginasOperationKenncy50% (2)
- IndiDocumento8 páginasIndileochunheiAún no hay calificaciones
- The Audit Market: Principles of Auditing: An Introduction To International Standards On Auditing - Ch. 2Documento29 páginasThe Audit Market: Principles of Auditing: An Introduction To International Standards On Auditing - Ch. 2Cherry BlasoomAún no hay calificaciones
- ICICI Bank FE West India Online AuctionDocumento15 páginasICICI Bank FE West India Online AuctionAnonymous rtDlncdAún no hay calificaciones
- FA SBD Goods NCB - November-FinalDocumento114 páginasFA SBD Goods NCB - November-FinalMezid MuhajAún no hay calificaciones
- Sales Ops Best PracticesDocumento31 páginasSales Ops Best PracticesSamuel Saavedra100% (3)
- Written Report in Applied EconomicsDocumento11 páginasWritten Report in Applied EconomicsSharina ElricAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 01 Review Questions and Cases for Governmental and Not-for-Profit AccountingDocumento3 páginasChapter 01 Review Questions and Cases for Governmental and Not-for-Profit Accountingfernbern0131Aún no hay calificaciones
- Marketing Plan of Emirates Airline - Marketing MixxDocumento4 páginasMarketing Plan of Emirates Airline - Marketing Mixxbrojas35Aún no hay calificaciones
- Facilitator's GuideDocumento39 páginasFacilitator's GuideAldwin UnisanAún no hay calificaciones
- Directory GIAMM 2019Documento241 páginasDirectory GIAMM 2019andri100% (1)
- Top 500 Fortune Company 2019Documento13 páginasTop 500 Fortune Company 2019BALRAJAún no hay calificaciones
- Christine's Creative Business StartupDocumento7 páginasChristine's Creative Business StartupSrinivasa VelupulaAún no hay calificaciones
- IGCSE Business ActivityDocumento1 páginaIGCSE Business ActivityemonimtiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Hyundai Motors CompanyDocumento44 páginasHyundai Motors CompanyVirendra Singh ThakurAún no hay calificaciones
- Account Opening Form for Non-IndividualsDocumento21 páginasAccount Opening Form for Non-IndividualsSifyIway Shivaji ParkAún no hay calificaciones
- Philips Electronic India LTD.: Account Statement and Open ItemsDocumento1 páginaPhilips Electronic India LTD.: Account Statement and Open ItemsNidhin VtyAún no hay calificaciones
- Produk BatalDocumento30 páginasProduk BatalNurul AtikAún no hay calificaciones
- Piercing Corporate Veil CaseDocumento6 páginasPiercing Corporate Veil CaseBetson CajayonAún no hay calificaciones
- Silvio Napoli at Schindler IndiaDocumento2 páginasSilvio Napoli at Schindler IndiaEmilia ElenaAún no hay calificaciones
- RVA Trading branch reporting and past due account updatesDocumento16 páginasRVA Trading branch reporting and past due account updatesDenzel Edward CariagaAún no hay calificaciones
- S.No Item of Works Targeted Maximum Response Time (In No. of Working Days)Documento21 páginasS.No Item of Works Targeted Maximum Response Time (In No. of Working Days)shafeeqm3086Aún no hay calificaciones
- Aditya Birla Nuvo Columbian ChemicalsDocumento21 páginasAditya Birla Nuvo Columbian ChemicalssearchingnobodyAún no hay calificaciones