Documentos de Académico
Documentos de Profesional
Documentos de Cultura
Experiment6 Multiplexer Demultiplexer
Cargado por
Aj DevezaDescripción original:
Título original
Derechos de autor
Formatos disponibles
Compartir este documento
Compartir o incrustar documentos
¿Le pareció útil este documento?
¿Este contenido es inapropiado?
Denunciar este documentoCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
Experiment6 Multiplexer Demultiplexer
Cargado por
Aj DevezaCopyright:
Formatos disponibles
King Saud University
College of Engineering at Alkharj
Electrical Engineering Department
Digital Design Laboratory
CEN206
Term2
1429-1430 h
Experiment 6
MUX. & DEMUX.
1. Objectives :
In this experiment, you will construct and test two multiplexers :
-
The first is 4:1 multiplexer
The second is 8:1 multiplexer
2. Equipment Components needed:
-
Digital Lab trainer
Wires
IC chips (74151)
A- The 8:1 multiplexer (74151):
A-1 Presentation:
The 74151 is a multiplexer that selects binary information from one of 8 input lines and
directs it to a single output line, the circuit has a complemented output. The selection of a
particular input line is controlled by three of selection lines. A strobe control S acts as an
enable signal.
The block diagram of 74151 is shown in figure1
Vcc
GND
8 Data
Inputs
74151
MUX 8:1
2 Outputs
Strobe
3 Select Inputs
Figure 1 : Block diagram of IC type 74150
Experiment 6
MUX. & DEMUX.
A-2 Pin configuration
Figure2 : Connecting diagram (TOP VIEW)
A-3 Theory : Referring to figure 2 and to annex
A-3-1 Compete the following table:
Designation
Data Inputs
Select Inputs
Output
Complemented Output
Strobe
+VCC
Ground
Pin(s) number
. . . . . . . .
. . .
.
.
.
.
.
Table1 : Pins number and their designation for the 74151 IC
A-3-2 Write the Boolean expression of the output by using only data inputs and select inputs.
F1 = xyz + x'yz' + x'y'z' + xyz',
A-3-3 Let
Draw the circuit diagram of F1 (in figure 3) and fill table2.
Step1: Determine the state of each data input and the state of each select input.
Experiment 6
MUX. & DEMUX.
Step2: Draw the circuit and fill the table.
x
0
D0
D1
D2
D3 8:1
D4 MUX
D5
D6
D7
C B A
Figure3
x
0
1
1
0
1
y
1
1
1
0
0
z
0
0
1
1
1
B A D7
D6
Inputs
D5 D4 D3
D2
D1
D0
Output F1
Y
Table2
A-3-4 Let F2 = x'yzt + x'yz't' + x'y'zt + x'y'z't',
Draw the circuit diagram of F2 (in figure 4) and fill table3.
Step1: Determine the state of each data input and the state of each select input.
..
Experiment 6
MUX. & DEMUX.
Step2: Draw the circuit and fill the table.
0
D0
D1
D2
D3 8:1
D4 MUX
D5
D6
D7
C B A
Figure4
x
0
0
0
0
1
y z
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
0 1
t C B A D7
0
0
1
1
1
D6
Inputs
D5 D4 D3
D2
D1
D0
Output F1
Y
Table3
B - Practice Procedures:
Step1: Place the 74151 in the Breadboard.
Step2: Connect Pin8 (GND) to 0V and Pin16 (Vcc) to +5V.
Step3: Implementation of F1 :
According to circuit obtained in figure3, implement the function F1.
Test the circuit and fill table4.
Experiment 6
x
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
y
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
MUX. & DEMUX.
z
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
B A D7
D6
Inputs
D5 D4 D3
D2
D1
D0
Output F1
Y
Table4
Step4: Implementation of F2 :
According to circuit obtained in figure4, implement the function F2.
Test the circuit and fill table5.
x
0
1
1
0
1
1
y z
1 0
1 0
1 1
0 1
0 1
1 1
t C B A D7
0
1
1
0
0
1
D6
Inputs
D5 D4 D3
D2
D1
D0
Output F2
Y
Table5
B- The 1:8 demultiplexer
The logic symbol of a demultiplexer is shown in figure5
Y0
D
DEMUX
Y1
Y2
Y3
S 1 S0
Figure5
B1: Choice the correct answer.
The demultiplexer of figure5 is a :
4 to 1 demultiplexer
1 to 4 demultiplexer
3 to 4 demultiplexer
4:1 demultiplexer
Table6
6
Experiment 6
MUX. & DEMUX.
B2 : Express the Boolean function of each output
Y0=
Y1= Y2= Y3=
B3 : Complete the following truth table
S1
So
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
Y0
Y1
Y2
Y3
Table7
Experiment 6
MUX. & DEMUX.
Annex
Experiment 6
MUX. & DEMUX.
Experiment 6
MUX. & DEMUX.
10
También podría gustarte
- Design of Multiplexer and Demultiplexer Aim:: Dual 4-Line To 1-Line Multiplexer Dual 1-Line To 4-Line DemultiplexerDocumento11 páginasDesign of Multiplexer and Demultiplexer Aim:: Dual 4-Line To 1-Line Multiplexer Dual 1-Line To 4-Line DemultiplexerPranav Satish0% (1)
- CD4067 Multiplexer Controls LEDs Code CircuitDocumento3 páginasCD4067 Multiplexer Controls LEDs Code CircuitAndreaZannoAún no hay calificaciones
- Microprocessor Question BankDocumento4 páginasMicroprocessor Question BankSubrahmanyam BeharaAún no hay calificaciones
- MatlabGuide - Identification GuideDocumento7 páginasMatlabGuide - Identification GuideCícero G. ReisAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 6 Mux and DecoderDocumento6 páginasLab 6 Mux and DecoderIfthakharul Alam ShuvoAún no hay calificaciones
- Full Adder Experiment 5Documento7 páginasFull Adder Experiment 5jayphil17Aún no hay calificaciones
- Comp ArithDocumento68 páginasComp ArithTun LeAún no hay calificaciones
- EEL 3123 Lab Manual - PDF LABDocumento79 páginasEEL 3123 Lab Manual - PDF LABkamalAún no hay calificaciones
- Arduino 3D Scanner DIY - 1Documento4 páginasArduino 3D Scanner DIY - 1Hilman HazmiAún no hay calificaciones
- 1 1 Eee 1102Documento43 páginas1 1 Eee 1102Siam HasanAún no hay calificaciones
- Engineering Physics Lab ManualDocumento80 páginasEngineering Physics Lab ManualAnuradha ReddyAún no hay calificaciones
- 2 Motor Control JoystickDocumento5 páginas2 Motor Control JoystickMarius DanilaAún no hay calificaciones
- Libraries and Attributes (Logism)Documento7 páginasLibraries and Attributes (Logism)AKooXiiYSmaelAún no hay calificaciones
- Laser Beam Machining (LBM)Documento10 páginasLaser Beam Machining (LBM)RAMAKANT RANAAún no hay calificaciones
- Logic GatesDocumento6 páginasLogic GatesMehar GuptaAún no hay calificaciones
- Auto White Board EraserDocumento7 páginasAuto White Board EraserSaravanan TutyAún no hay calificaciones
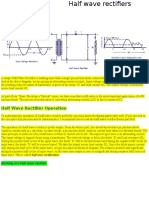
- Half Wave RectifiersDocumento3 páginasHalf Wave RectifiersSaurabhYadav100% (1)
- Logarithm Hydrogen Ion ActivityDocumento4 páginasLogarithm Hydrogen Ion ActivityKashif Ali JalilAún no hay calificaciones
- Testing of HypothesisDocumento3 páginasTesting of HypothesisShankar DashAún no hay calificaciones
- Somprb3 Simple Supported Beam Lab Report: CH Mostert 56000928 Date Due: 4 October 2017Documento16 páginasSomprb3 Simple Supported Beam Lab Report: CH Mostert 56000928 Date Due: 4 October 2017Renae SavannahAún no hay calificaciones
- Practical: - Transmission and AttenuationDocumento4 páginasPractical: - Transmission and AttenuationasithAún no hay calificaciones
- AUTOMATIC BOARD CLEANER SAVES TIMEDocumento3 páginasAUTOMATIC BOARD CLEANER SAVES TIMEIyappan AlagappanAún no hay calificaciones
- Commonly used MATLAB functions and variablesDocumento36 páginasCommonly used MATLAB functions and variablesHadjer zit100% (1)
- MultiplexerDocumento5 páginasMultiplexerhariAún no hay calificaciones
- DSP Lect Note - 6th Sem Etc - PNGDocumento91 páginasDSP Lect Note - 6th Sem Etc - PNGwapota4898Aún no hay calificaciones
- Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Name of The Experiment: Verification of KVL & Voltage Devider RuleDocumento7 páginasBangladesh University of Engineering and Technology: Name of The Experiment: Verification of KVL & Voltage Devider RuleSayeed Mohammed100% (1)
- Half Wave Rectifier - PDFDocumento4 páginasHalf Wave Rectifier - PDFSagnik RoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Spatial Filtering TechniquesDocumento36 páginasSpatial Filtering TechniquesK.R.RaguramAún no hay calificaciones
- Unit 2 Image Compression Multiple ChoiceDocumento7 páginasUnit 2 Image Compression Multiple ChoiceNavaneetha KrishnanAún no hay calificaciones
- IPE Dept Syllabus 2017-18 Undergraduate and GraduateDocumento28 páginasIPE Dept Syllabus 2017-18 Undergraduate and GraduateMushaer AhmedAún no hay calificaciones
- SST89e51 Programming ManualDocumento9 páginasSST89e51 Programming Manualrudra_150% (2)
- Comparator:: Essential Parts of A ComparatorDocumento5 páginasComparator:: Essential Parts of A ComparatorAnonymous bl0G8KAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics II NotesDocumento41 páginasElectronics II NotesactuatorAún no hay calificaciones
- Title: Encoder Instructional AimsDocumento7 páginasTitle: Encoder Instructional Aimssuv_fame100% (4)
- JNTUK R16 II-I DLD UNIT I NotesDocumento30 páginasJNTUK R16 II-I DLD UNIT I NotesSowmya Koneru100% (1)
- Blood Gas AnalyzerDocumento13 páginasBlood Gas Analyzeranon_708486566Aún no hay calificaciones
- Digital Image Processing - 2 Marks-Questions and AnswersDocumento19 páginasDigital Image Processing - 2 Marks-Questions and AnswersnikitatayaAún no hay calificaciones
- Delay Time Estimation in Digital DesignDocumento12 páginasDelay Time Estimation in Digital DesignSandeep PaulAún no hay calificaciones
- Numerical Analysis Lecture NotesDocumento72 páginasNumerical Analysis Lecture NotesZhenhuan SongAún no hay calificaciones
- Experiment No. 1: Aim: Study of Tanner Tools THEORY: Tanner ToolsDocumento24 páginasExperiment No. 1: Aim: Study of Tanner Tools THEORY: Tanner ToolsVarun GargAún no hay calificaciones
- Design A Full Adder by Using Two Half Adders. (7M, May-19)Documento10 páginasDesign A Full Adder by Using Two Half Adders. (7M, May-19)Sri Silpa PadmanabhuniAún no hay calificaciones
- Fat Papers Vlsi Vellore VitDocumento4 páginasFat Papers Vlsi Vellore VitDebolina RoyAún no hay calificaciones
- Electronics CircuitDocumento0 páginasElectronics Circuitwww.bhawesh.com.npAún no hay calificaciones
- Vlsi Lab Manual 2013Documento64 páginasVlsi Lab Manual 2013harish33330% (1)
- The Cardiovascular System - Physiology Diagnostics and Clinical ImplicationsDocumento492 páginasThe Cardiovascular System - Physiology Diagnostics and Clinical ImplicationsJosé RamírezAún no hay calificaciones
- Verify Ohm's Law ExperimentDocumento3 páginasVerify Ohm's Law ExperimentmohamadalfarAún no hay calificaciones
- DC Characteristics of Opamps ExplainedDocumento23 páginasDC Characteristics of Opamps ExplainedMichael CampbellAún no hay calificaciones
- EC6302 Digital Electronics 2 Marks With AnswersDocumento18 páginasEC6302 Digital Electronics 2 Marks With AnswersBasky40% (5)
- 3 Amplifier Common Mode Rejection Ratio Part I FullDocumento9 páginas3 Amplifier Common Mode Rejection Ratio Part I FullUjjWal MahAjanAún no hay calificaciones
- Chapter 12 (Electronic Devices and Circuits-II) (1) FinalDocumento50 páginasChapter 12 (Electronic Devices and Circuits-II) (1) FinalAhmed HussainAún no hay calificaciones
- Digital Image Processing MCQDocumento5 páginasDigital Image Processing MCQBhawini RajAún no hay calificaciones
- Ec2203-Unit IV Memory Devices Digital ElectronicsDocumento38 páginasEc2203-Unit IV Memory Devices Digital ElectronicsKarthikeyan_Go_952567% (6)
- DC Motor ArduinoDocumento40 páginasDC Motor ArduinoBodo De La BuernoAún no hay calificaciones
- Logic Gate and CircuitDocumento16 páginasLogic Gate and CircuitMd Naimur Rahaman SakibAún no hay calificaciones
- Recording ProblemsDocumento13 páginasRecording ProblemsAleesha100% (1)
- EDC Question BankDocumento13 páginasEDC Question BankvenzkrishAún no hay calificaciones
- Electrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: IT IL IcDocumento4 páginasElectrical, Digital and Industrial Circuits: IT IL IcNGOUNEAún no hay calificaciones
- 372 5Documento5 páginas372 5Phillip TaylorAún no hay calificaciones
- Dual 1-Of-4 Multiplexer: Digital Electronics Dr. Pogo Using The 74153 MUX To Generate A 16 Row Truth TableDocumento1 páginaDual 1-Of-4 Multiplexer: Digital Electronics Dr. Pogo Using The 74153 MUX To Generate A 16 Row Truth TableRolando Choque CahuanaAún no hay calificaciones
- Lab 09Documento10 páginasLab 09Aafaq khanAún no hay calificaciones
- Paging Ravi PPT 130527123536 Phpapp01Documento10 páginasPaging Ravi PPT 130527123536 Phpapp01Vivek KesharwaniAún no hay calificaciones
- WWW - Goair.In: Go Airlines (India) LTDDocumento2 páginasWWW - Goair.In: Go Airlines (India) LTDdhavalesh1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Diophantine Equations in Three VariablesDocumento8 páginasDiophantine Equations in Three VariablesJacmAún no hay calificaciones
- Sap ABAP Mock Test 1Documento4 páginasSap ABAP Mock Test 1Siddhant ShekharAún no hay calificaciones
- User Manual Touch Lux 4 EN PDFDocumento88 páginasUser Manual Touch Lux 4 EN PDFRebird555Aún no hay calificaciones
- Financials in Purchase to Pay Process - Guide to Integrating Procurement and Accounting in SAPDocumento41 páginasFinancials in Purchase to Pay Process - Guide to Integrating Procurement and Accounting in SAPelixi67% (3)
- MIT6 0002F16 ProblemSet5Documento13 páginasMIT6 0002F16 ProblemSet5DevendraReddyPoreddyAún no hay calificaciones
- Salesforce Syllabus For Job Ready ProgramDocumento41 páginasSalesforce Syllabus For Job Ready ProgramsurajAún no hay calificaciones
- Webnew 24QDocumento2021 páginasWebnew 24QSean WilsonAún no hay calificaciones
- Linear Programming Graphical and Simplex MethodsDocumento11 páginasLinear Programming Graphical and Simplex MethodsKristienalyn De AsisAún no hay calificaciones
- Examine 3DDocumento217 páginasExamine 3DWilson Suaña DiazAún no hay calificaciones
- Analisa Rasio Keuangan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Kinerja Bank Perkreditan Rakyat Di Wilayah Kabupaten TegalDocumento6 páginasAnalisa Rasio Keuangan Pengaruhnya Terhadap Kinerja Bank Perkreditan Rakyat Di Wilayah Kabupaten TegalAnissaAún no hay calificaciones
- HTML markup guideDocumento2 páginasHTML markup guidefcmitcAún no hay calificaciones
- The Second Machine AgeDocumento6 páginasThe Second Machine AgeShivangi ZalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Adaptive QuadratureDocumento35 páginasAdaptive QuadratureMarsetiayuNingsih100% (1)
- GUI Payroll SystemDocumento4 páginasGUI Payroll Systemfeezy1Aún no hay calificaciones
- Introduction To Information Technology: Lecture #6Documento22 páginasIntroduction To Information Technology: Lecture #6Yesu Babu AAún no hay calificaciones
- Agile Test Strategy: Paul GerrardDocumento40 páginasAgile Test Strategy: Paul Gerrardketantank09Aún no hay calificaciones
- 20773A ENU TrainerHandbook PDFDocumento340 páginas20773A ENU TrainerHandbook PDFRicardo AraujoAún no hay calificaciones
- Quality Assurance Specialist in NJ NY Resume Fred PuchalaDocumento2 páginasQuality Assurance Specialist in NJ NY Resume Fred PuchalaFredPuchalaAún no hay calificaciones
- Ajax CheatSheetDocumento7 páginasAjax CheatSheetdrypzAún no hay calificaciones
- VLSM Subnetting Worksheet ExampleDocumento1 páginaVLSM Subnetting Worksheet ExampleJose Manuel Iglesias ArreguiAún no hay calificaciones
- First Article Inspection InstructionDocumento21 páginasFirst Article Inspection Instructiongranburyjohnstevens100% (1)
- Lit RevDocumento9 páginasLit RevBattuDedSec AC418Aún no hay calificaciones
- APO Master DataDocumento120 páginasAPO Master DataNeeraj Kumar100% (1)
- Actual Stored Procedure CodeDocumento7 páginasActual Stored Procedure CodeJason HallAún no hay calificaciones
- Arcgis For Desktop: Powerful ApplicationsDocumento3 páginasArcgis For Desktop: Powerful Applicationskarthikp207Aún no hay calificaciones
- Fundamental Principle of CountingDocumento16 páginasFundamental Principle of CountingEcho AlbertoAún no hay calificaciones
- Sathyabama: (Deemed To Be University)Documento3 páginasSathyabama: (Deemed To Be University)viktahjmAún no hay calificaciones
- Manual LCD DaewooDocumento48 páginasManual LCD DaewooPedro MoraAún no hay calificaciones